Abstract
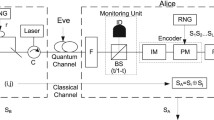
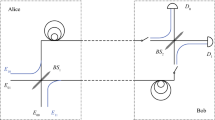
Quantum key distribution (QKD) can achieve information security theoretically. However, it should be based on the reliable identity of both parties in the communication. Compared with classical identity authentication protocols, quantum identity authentication (QIA) protocols have higher security level in theory, and they are easier to be combined with quantum cryptography protocols, so more and more scholars take part in the research of QIA. In the past 3 decades, various of QKD protocols have been proposed. One of them is Round Robin Differencial Phase Shift Quantum Key Distribution (RRDPS QKD) proposed by T. Sasaki et al. RRDPS QKD uses laser pulse sequences to modulate photons, and it has great bit error tolerance and finite length key effect. This paper proposes a QIA protocol which can be implemented in modified RRDPS QKD communication line. And we also analyze the security of the proposed protocol.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014)
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283, 2050–2056 (1999)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 441–444 (2000)
Schneier, B.: Applied Cryptography, Protocols, Algorithms, and Source Code in C. Wiley (1994)
Wegman, M.N., Carter, J.L.: New hash functions and their use in authentication and set equality. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 22, 265 (1981)
Ljunggren, D., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A.: Authority-based user authentication in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A. 62, 022305 (2000)
Shi, B -S, Li, J., Liu, J.-M., Fan, X.-F., Guo, G.-C.: Quantum key distribution and quantum authentication based on entangled state. Phys. Lett. A. 281, 83–87 (2001)
Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Tang, C.-J.: Multiparty simultaneous quantum identity authentication based on entanglement swapping. Chinese Phys. Lett. 23, 2360–2363 (2006)
Zhang, Z.-S., Zeng, G.-H., Zhou, N.-R., Xiong, J.: Quantum identity authentication based on ping-pong technique for photons. Phys. Lett. A. 356, 199–205 (2006)
Yuan, H., Liu, Y.-M., Pan, G.-Z., Zhang, G, et al: Quantum identity authentication based onm ping-pong technique without entanglements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2535–2549 (2014)
Hong, C.-H., Heo, J., Jang, J.-G.: Quantum identity authentication with single photon. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, UNSP 236 (2017)
Zeng, G.-H, Zhang, W.-P.: Identity verification in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61, 022303 (2000)
Li, X.-Y, Barnum, H.: Quantum authentication using entangled states. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 15, 609–617 (2004)
Jensen, J.G., Schack, R.: Quantum authentication and key distribution using catalysis. Quant-ph 0003104 (2000)
Mihara, T.: Quantum identification schemes with entanglements. Phys. Rev. A. 65, 052326 (2002)
Zeng, G.-H, Guo, G.-C.: Quantum authentication protocol. Quant-ph 0001046 (2000)
Hillery, M., Buzek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A. 59, 1829–1824 (1999)
Qin, S.-J, Gao, F., Wen, Q.-Y, Zhu, F.-C.: Security of quantum secret sharing with two-particle entanglement against individual attacks. Quant. Inf. Comput. 9, 0765–0772 (2009)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.-Y, Qin, S.-J, Zhu, F.-C.: Multiparty quantum secret sharing with collective eavesdropping-check. Opt. Commun. 282, 4455–4459 (2009)
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L.: Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 230502 (2008)
Jakobi, M., Simon, C., Gisin, N., et al: Practical private database queries based on a quantum-key-distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. A. 83, 022301 (2011)
Gao, F., Liu, B., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Postprocessing of the oblivious key in quantum private query. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 21(3), 6600111 (2015)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W, et al.: QKD-based quantum private query without a failure probability. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 58, 100301 (2015)
Wei, C.-Y, Cai, X.-Q, Liu, B., Wang, T.-Y, Gao, F.: A generic construction of quantum-oblivious-transfer-based private query with ideal database security and zero failure. IEEE T. Comput. 67(1), 2–8 (2018)
Gao, F., Qin, S.-J, Huang, W, et al.: Quantum private query: A new kind of practical quantum cryptographic protocol. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 62, 070301 (2019)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.-Y., Liu, B, et al.: Deterministic secure quantum communication with collective detection using single photons. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 51, 2787–2797 (2012)
Long, G.-L, Liu, X.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum key distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Bostrom, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 187902 (2002)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.-Y, Zhu, F. -C.: Quantum secure direct communication with x-type entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 78, 064304 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos 61702061, U19A2076), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant Nos cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0719), National Science Key Lab Fund project (Grant Nos 6142103200105), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2020CDJQY-A018, 2020CDJ-LHZZ-056), Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant 019JDJQ0060)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Y., Gui, C., Liu, B. et al. Quantum Identity Authentication Based on Round Robin Differencial Phase Shift Communication Line. Int J Theor Phys 61, 44 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-04988-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-04988-0