Abstract
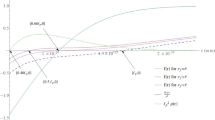
The notion of black hole singularity and the proof of the singularity theorem were considered great successes in classical general relativity whereas they meanwhile brought with deep puzzles. Conceptual challenges were set up by the intractability of the singularity. The existence of black hole horizons which cover up the black hole interior including the singularity from outside observers, builds an information curtain, further hindering physicists from understanding the nature of the singularity and the interior structure of black holes. The regular black hole is a concept produced out of multiple attempts of establishing a tractable and understandable interior structure for black holes as well as avoiding the singularity behind the black hole horizon. The practicality of the new constructions of black holes would be considered more reliable if there can be found some connection between the interior of regular black holes and some far-reaching signals released from the black hole. After studying the Hawking radiation by fermion tunnelling from one type of regular black hole, structure dependent results were obtained. The result being structure dependent hints the prospects of employing the Hawking radiation as a method to probe into the structure of black holes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Penrose, R.: Gravitational collapse and space-time singularities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 14, 57–59 (1965)
Hawking, S.W.: Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 300, 1870 (1967)
Hawking, S.W., Penrose, R.: Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 314, 529–548 (1970)
Hawking, S.W., Ellis, G.F: The Large Scale Structure of Spacetime. Cambridge University Press (1973)
Frolov, V.P., Vilkovisky, G.A.: Spherically symmetric collapse in quantum gravity. Phys. Lett. B 106(4), 307–313 (1981)
Frolov, V.P., Markov, M.A., Mukhanov, V.F.: Black holes as possible sources of closed and semiclosed worlds. Phys. Rev. D 41(2), 383 (1990)
Kawai, H., Yokokura, Y.: Interior of black holes and information recovery. Phys. Rev. D 93, 044011 (2016)
Bardeen, J.M.: Non-singular general relativistic gravitational collapse. In: Proceedings of GR5 (1968)
Mars, M., Martin-Prats, M. M., Senovilla, J. M. M.: Class. Quant. Grav. 13, L51 (1996)
Cabo, A., Ayn-Beato, E.: About black holes without trapping interior. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A14, 2013–2022 (1999)
Borde, A.: Phys. Rev. D 50, 3392 (1994)
Borde, A.: Phys. Rev. D 55, 7615 (1997)
Barrabés, C., Frolov, V.P.: Phys. Rev. D 53, 3215 (1996)
Ayn-Beato, E., Garcia, A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 23, 5056 (1998)
Hayward, S. A.: Formation and evaporation of regular black holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 031103 (2006)
Lin, K., Li, J., Yang, S., Zu, X.: A new regular black hole. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 1013–1019 (2013)
Dymnikova, I.: Vacuum nonsingular black hole. Gen. Rel. Grav. 24, 235–242 (1992)
Dymnikova, I. G.: The algebraic structure of a cosmological term in spherically symmetric solutions. Phys. Lett. B 472, 33–38 (2000)
Dymnikova, I.: Cosmological term as a source of mass. Class Quant. Grav. 19, 725–740 (2002)
Dymnikova, I., Soltysek, B.: Spherically symmetric space-time with two cosmological constants. Gen. Rel. Grav. 30, 1775–1793 (1998)
Dymnikova, I., Korpusik, M.: Regular black hole remnants in de Sitter space. Phys. Lett. B685, 12–18 (2010)
Li, J., Lin, K., Yang, N.: Nonlinear electromagnetic quasinormal modes and Hawking radiation of a regular black hole with magnetic charge. Eur. Phys. J. C 75(3), 131 (2015)
Lin, K., Li, J., Yang, S.: Quasinormal modes of Hayward regular black hole. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 3771–3778 (2013)
Li, J., Hong, M., Lin, K.: Dirac quasinormal modes in spherically symmetric regular black holes. Phys. Rev. D 88, 064001 (2013)
Flachi, A., Lemos, J. P. S.: Quasinormal modes of regular black holes. Phys. Rev. D 87(2), 024034 (2013)
Hawking, S.W.: Commun. Math. Phys. 43, 199 (1975)
Kraus, P., Wilczek, F.: Nucl. Phys. B 433, 403 (1995). [grqc/9408003]
Parikh, M.K., Wilczek, F.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(5042), 2000
Srinivasan, K., Padmanabhan, T.: Phys. Rev. D 60, 24007 (1999)
Kerner, R., Mann, R.B.: Class. Quantum. Grav. 25, 095014 (2008)
Kerner, R., Mann, R.B.: Phys. Lett. B 665(277), 2008
Lin, K., Yang, S.Z.: Phys. Rev. D 79, 064035 (2009)
Lin, K., Yang, S.Z.: Phys. Lett. B 674(127), 2009
Chen, G.R., Huang, Y.C.: Fermions tunneling from a general static Riemann black hole. Gen. Rel. Grav. 47(5), 57 (2015)
Chen, G.R., Huang, Y.C.: Corrected Hawking radiation of dirac particles from a general static Riemann black hole. Adv. High Energy Phys., 982146 (2013)
Nicolini, P., Smailagic, A., Spallucci, E.: Noncommutative geometry inspired Schwarzschild black hole. Phys. Lett. B 632, 547–551 (2006)
Nicolini, P.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 24, 1229 (2009)
Larranaga, A., Cardenas-Avendano, A., Torres, D.A.: On a general class of regular rotating black holes based on a smeared mass distribution. Phys. Lett. B 743, 492–502 (2015)
Nicolini, P.: The final stage of gravitationally collapsed thick matter layers. Adv. High Energy Phys. 812084 (2013)
Zhang, B., Cai, Q., Zhan, M., You, L.: Noncommutative information is revealed from Hawking radiation as tunneling. Europhys. Lett. 94, 20002 (2011)
Smailagic, A., Spallucci, E.: Kerrr black hole: The Lord of the string. Phys. Lett. B 688, 82–87 (2010)
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Prof. Anzhong Wang and Drs. V.H. Satheeshkumar, Xinwen Wang, Tao Zhu, Miao Tian and Chikun Ding for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y., Cleaver, G. Hawking Radiation as a Possible Probe for the Interior Structure of Regular Black Holes. Int J Theor Phys 56, 741–750 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-016-3215-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-016-3215-4