Abstract
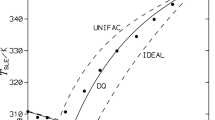
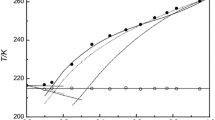
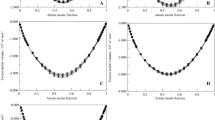
Group contribution models can be used to predict the thermodynamic properties. The basic data used to determine the interaction parameters are VLE, HE and infinite dilution activity coefficient data. However in the absence of the required data, SLE measurements of eutectic systems are of great interest for fitting interaction parameters of group contribution methods. The knowledge of solid–liquid equilibria (SLE) of binary mixtures is essential for the design and development of separation process involving crystallization. In the present study, experimental SLE of binary mixtures containing N,N-dimethylaniline, diethylamine, cyclohexylamine, n-alkanes, and cyclohexane were measured by a static method of direct thermal analysis, using an apparatus derived from that of Smit. The experimental data obtained with this technique are compared with those predicted by Group contribution models: Mod. UNIFAC (Do) and DISQUAC models. The liquid-phase activity coefficients were also calculated. The experimental results illustrated that these systems showed a eutectic behavior, and a good agreement is obtained between experimental and predicted SLE. The use of the new c-CHNH2 group instead of the CHNH2 group in the modified UNIFAC Dortmund model showed excellent results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Gryc, M. Strouhalová, B. Smetana, L. Socha, K. Michalek, Arch. Metall. Mater. 60, 2867 (2015)
M.M. Lencka, J.J. Kosinski, P.M. Wang, A. Anderko, Fluid Phase Equilib. 418, 160 (2016)
C. Gobble, N. Rath, J. Chickos, J. Chem. Eng. Data. 58, 2600 (2013)
J.A. González, I. Alonso, C. Alonso, I.G. la Fuente, J.C. Cobos, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 56, 89 (2013)
J.A. González, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 50, 9810 (2011)
A. Grenner, M. Klauck, J. Schmelzer, Fluid Phase Equilib. 233, 170 (2005)
M. Klauck, T. Hahnel, S. Richter, J. Schmelzer, G. Kalies, J. Chem. Eng. Data. 63, 119 (2018)
J. Lohmann, T. Röpke, J. Gmehling, J. Chem. Eng. Data. 43, 856 (1998)
I. Velasco, J. Fernandez, S. Otín, H. Kehiaian, Fluid Phase Equilib. 69, 15 (1991)
J.A. Gonzalez, I. Mozo, I. García de la Fuente, J.C. Cobos, Can. J. Chem. 83, 1812 (2005)
M.R. Tine, H.V. Kehiaian, Fluid Phase Equilib. 32, 211 (1987)
U. Domanska, M. Zawadzki, J.A. González, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 42, 545 (2010)
J.A. González, U. Domanska, M. Zawadzki, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 40, 1261 (2008)
U. Domańska, M. Głoskowska, J. Chem. Eng. Data. 49, 101 (2004)
U. Domańska, M. Głoskowska, Fluid Phase Equilib. 216, 135 (2004)
J.A. Gonzalez, I. GarcíadelaFuente, J.C. Cobos, Fluid Phase Equilib. 168, 31 (2000)
F. Allal, A. Dahmani, J. Them. Anal. Cal. 73, 961 (2003)
A. Dahmani, J. Jose, Fluid Phase Equilib. 134, 255 (1997)
F. Allal, A. Dahmani, Fluid Phase Equilib. 190, 33 (2001)
K. Khimeche, A. Dahmani, J. Chem. Thermodyn. 38, 1192 (2006)
K. Khimeche, A. Dahmani, J. Therm. Anal. Cal. 84, 47 (2006)
K. Khimeche, A. Dahmani, J. Chem. Eng. Data 51, 382 (2006)
H.V. Kehiaian, Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 15 (1985)
J. Gmehling, J. Li, M. Schiller, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 32, 178–193 (1993)
J. Gmehling, J. Lohmann, A. Jakob, J. Li, R. Joh, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 37, 4876 (1998)
A. Jakob, H. Grensemann, J. Lohmann, J. Gmehling, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 7924 (2006)
J.A. Riddick, W.B. Bunger, T.K. Sakano, Organic solvents, in Techniques of chemistry, vol. II, ed. by A. Weissberger (Wiley, New York, 1986)
A.M.I. Ahmed, R.G. Eades, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 2, 2017 (1972)
F. Hamann, A. Wurflinger, Phys. Chemie. 211, 85 (1999)
A. Van de Vloed, Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 48, 229–268 (1939)
J. Timmermans, J.F. Mattaar, Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 30, 213 (1921)
M.J. Rotrekl, P. Vrbka, Appl. Chem. 87, 453 (2015)
W.M. Smit, Rec Trav Chim Pays-Bas (1956). https://doi.org/10.1002/recl.19560751112
M.A. Michou-Saucet, J. Jose, L.M. Riollot, Thermochim. Acta. 68, 207 (1983)
A. Dahmani, A. Ait Kaci, Int. DATA Ser., Sel. Data Mixtures, Ser. A. 141, 147 (1988)
A. Dahmani, I. Mokbel, G. Ghanem, J. Jose, J. Chim. Phys. (1995). https://doi.org/10.1051/jcp/1995921093
A. Dahmani, J. Jose, A. Kaci, J. Chim. Phys. (1996). https://doi.org/10.1051/jcp/1996932001
M. Klauck, R. Silbermann, R. Metasch, S. Unger, J. Schmelzer, Fluid Phase Equilib. 314, 169 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Djellouli, F., Dahmani, A. & Hassani, A. Solid–Liquid Equilibria of Binary Systems Containing Amines: Experimental Data and Prediction with DISQUAC and UNIFAC Models. Int J Thermophys 42, 39 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02789-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02789-3