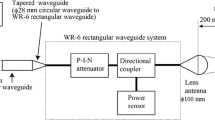
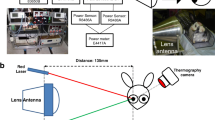
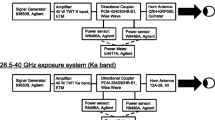
Abstract
Millimeter waves (MMW) absorbed by skin or cornea may induce damage by heat. We have developed a 60 GHz MMW exposure-induced eye injury model that reproducibly presents the extent of such ocular injury, including its clinical process and healing process. Findings by the model suggested an ocular damage threshold for an exposure dose of about 60 GHz 200–300 mW/cm2 for 6 min. Using the probit model, DD50, defined as the dose to cause ocular damage with 50% probability, was estimated to be 233 mW/cm2. A novel finding was that exposure of 60 GHz 400 mW/cm2 to a closed eyelid for 6 min not only damaged the eyelid (including the palpebral conjunctiva), but the eyeball surface beneath (the bulbar conjunctiva and cornea) it.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Hof, A. Sanderovich, E. Hemo, “Gesture recognition with 60GHz 802.11 waveforms”, arXiv:2002.10836v1 [eess.SP] 25 Feb 2020.
S. W. Rosenthal, L. Birenbaum, I. T. Kaplan, W. Metlay, W. Z. Snyder, and M. M. Zaret, “Effects of 35 and 107 GHz CW microwaves on the rabbit eye”, Biological effects of electromagnetic waves. Selected Papers of the USNC/URSI Annual Meeting, Boulder, Colorado, October 1975 Rockville, Maryland, US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, HEW Publication (FDA) 77–8010, vol. 1, pp. 110–128, 1976.
S. Chalfin, J. A. D’Andrea, P. D. Comeau, M. E. Belt, and D. J. Hatcher, “Millimeter wave absorption in the nonhuman primate eye at 35 GHz and 94 GHz”, Health Phys, vol. 83, pp. 83-90, 2002.
H. A. Kues, S. A. D’Anna, R. Osiander, W. R. Green, and J. C. Monahan, “Absence of ocular effects after either single or repeated exposure to 10 mW/cm2 from a 60 GHz CW source”, Bioelectromagnetics, vol. 20, pp. 463-473, 1999.
M. Kojima, M. Hanazawa, Y. Yamashiro, H. Sasaki, S. Watanabe, M. Taki, Y. Suzuki, A. Hirata, Y. Kamimura, and K. Sasaki, “Acute ocular injuries caused by 60-Ghz millimeter-wave exposure”, Health Phys, vol. 97, pp. 212-218, 2009.
M. Kojima, Y. Suzuki, K. Sasaki, M. Taki, K. Wake, S. Watanabe, M. Mizuno, T. Tasaki, and H. Sasaki, “Ocular effects of exposure to 40, 75, and 95 GHz millimeter waves,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 39, pp. 912-925, 2018.
M. Kojima, Y. Suzuki, T. Tasaki, Y. Tatematsu, M. Mizuno, M. Fukunari and H. Sasaki, “Clinical course of high-frequency millimeter-wave (162 GHz) induced ocular injuris and investigation of damage thresholds” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 41, pp. 834-845, 2020.
ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research https://www.arvo.org/About/policies/statement-for-the-use-of-animals-in-ophthalmic-and-vision-research/ Accessed 12 August 2021.
M. Kojima, C.-Y. Tsai, Y. Suzuki, K. Sasaki, T. Tasaki, M. Taki, S. Watanabe and H. Sasaki, Ocular response to millimeter wave exposure under different levels of humidity, J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, 40, 574-584 (2019)
C. I. Bliss, The Method of Probits, Science, 79, 38-39 (1934)
R Core Team (2021). R, A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/. Assessed 9 January, 2022
Science Council of Japan, “Guidelines for Proper Conduct of Animal Experiments”, https://www.scj.go.jp/ja/info/kohyo/pdf/kohyo-20-k16-2e.pdf, Accessed 21 January 2022.
D. R. Korb, J. V. Greiner, T. Glonek, A. Whalen, S. L. Hearn, J. E. Esway, and C. D. Leahy, " Human and rabbit lipid layer and interference pattern observations." Adv Exp Med Biol., vol. 438, pp. 305-308, 1998.
B. Schwartz, "The effect of lid closure upon the ocular temperature gradient", Investigative Ophthalmology, vol. 3, pp. 100-106, 1964.
B. Schendowich, "The science and art of blinking", National Keratoconus Foundation Website, http://www.nkcf.org/science-and-art-of-blinking/. Accessed 26 November 2021.
Ludwig and H. Reimann, "Eye", In: Practical pharmaceutics: An international guideline for the preparation, care and use of medicinal products. ed. by Y. Bouwman-Boer, V. Fenton-May, and P. Le Brun (Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, 2015), p. 163-188.
H. Hachisu, “The standards of the rearing environment for laboratory animals in Japan. Proc 6th World Congress on Alternatives & Animal Use in the Life Sciences, Tokyo, Japan, 21–25 August 2007. http://asas.or.jp/jsaae/jsaae/zasshi/WC6_PC/paper57.pdf Accessed 16 February 2022.
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Japan, “Radio-radiation protection guideline” in Japanese. https://www.tele.soumu.go.jp/j/sys/ele/medical/protect/index.htm. Accessed 15 February, 2022.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Japan, Grant Number JPMI10001. Japan. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors are indebted to Ms. Mari Seto for their technical assistance, and to Mr. David Price for English proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, M., Tasaki, T., Suzuki, Y. et al. Threshold for Millimeter-Wave (60 GHz)-Induced Ocular Injury. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 43, 260–271 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-022-00850-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-022-00850-w