Abstract—
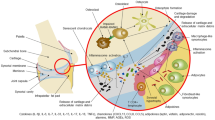
Hypoxia and increased levels of inflammatory cytokines in the joints are characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effects of hypoxia and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) on interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 production on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) remain to be clarified. This study aimed to explore how hypoxia and TNF-α affect the expression of IL-6 and IL-8 in human FLSs isolated from RA patients. Hypoxia or TNF-α treatment alone significantly increased the expression and promoter activity of IL-6, IL-8, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Treatment of hypoxic FLSs with TNF-α further significantly elevated the expression of these cytokines and enhanced promoter activity of HIF-1α, which was abrogated by treatment with the HIF-1α inhibitor YC-1. Similarly, TNF-α alone elevated the phosphorylation and promoter activity of nuclear factor-κBp65 (NF-κBp65) in the FLSs. These effects were further enhanced by the combined treatment of hypoxia and TNFα but were attenuated by the NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7082. NF-κB-p65 inhibition decreased the effect of TNF-α on HIF-1α upregulation in the FLSs in response to hypoxia. The combination of hypoxia and TNF-α also significantly upregulated transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) expression, and silencing TAK1 dramatically decreased NF-κB-p65, HIF-1α, IL-6, and IL-8 expression under the same conditions. Our results indicate that hypoxia and TNF-α synergistically increase IL-6 and IL-8 expression in human FLSs via enhancing TAK1/NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Materials Availability
Not applicable.
References
Korb-Pap, A., J. Bertrand, J. Sherwood, and T. Pap. 2016. Stable activation of fibroblasts in rheumatic arthritis - causes and consequences. Rheumatology 55: 64–67.
Huber, L.C., O. Distler, I. Tarner, R.E. Gay, S. Gay, and T. Pap. 2006. Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45: 669–675.
Yokota, K., T. Miyazaki, M. Hirano, Y. Akiyama, and T. Mimura. 2006. Simvastatin inhibits production of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-8 and cell proliferation induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 33: 463–471.
Luo, X.J., X.R. Mo, and L.L. Zhou. 2012. The effect of Hsp72 on IL-6, IL-8 expression and activation of NF-kappaB in synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 28: 336–339.
Li, Y., and W. Zhang. 2017. IL-6: The next key target for rheumatoid arthritis after TNF-alpha. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 33: 36–43.
Quinonez-Flores, C.M., S.A. Gonzalez-Chavez, and C. Pacheco-Tena. 2016. Hypoxia and its implications in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Biomedical Science 23: 62.
Fearon, U., M. Canavan, M. Biniecka, and D.J. Veale. 2016. Hypoxia, mitochondrial dysfunction and synovial invasiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 12: 385–397.
Muz, B., M.N. Khan, S. Kiriakidis, and E.M. Paleolog. 2009. Hypoxia The role of hypoxia and HIF-dependent signalling events in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 11: 201.
Niu, X., Y. Chen, L. Qi, G. Liang, Y. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Qu, and W. Wang. 2019. Hypoxia regulates angeogenic-osteogenic coupling process via up-regulating IL-6 and IL-8 in human osteoblastic cells through hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha pathway. Cytokine 113: 117–127.
D’Ignazio, L., and S. Rocha. 2016. Hypoxia induced NF-kappaB. Cells 5: 10.
Deng, W., X. Feng, X. Li, D. Wang, and L. Sun. 2016. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in autoimmune diseases. Cellular Immunology 303: 7–15.
Guan, S.Y., R.X. Leng, J.H. Tao, X.P. Li, D.Q. Ye, N. Olsen, S.G. Zheng, and H.F. Pan. 2017. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha: A promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets 21: 715–723.
Guo, X., and G. Chen. 2020. Hypoxia-inducible factor is critical for pathogenesis and regulation of immune cell functions in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers in Immunology 11: 1668.
Ryu, J.H., C.S. Chae, J.S. Kwak, H. Oh, Y. Shin, Y.H. Huh, C.G. Lee, Y.W. Park, C.H. Chun, Y.M. Kim, S.H. Im, and J.S. Chun. 2014. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is an essential catabolic regulator of inflammatory rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Biology 12: e1001881.
Nonomura, Y., F. Mizoguchi, A. Suzuki, T. Nanki, H. Kato, N. Miyasaka, and H. Kohsaka. 2009. Hypoxia-induced abrogation of contact-dependent inhibition of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast proliferation. Journal of Rheumatology 36: 698–705.
Sabi, E.M., A. Singh, Z.M. Althafar, T. Behl, A. Sehgal, S. Singh, N. Sharma, S. Bhatia, A. Al-Harrasi, H.M. Alqahtani, and S. Bungau. 2022. Elucidating the role of hypoxia-inducible factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacology 30: 737–748.
Malkov, M.I., C.T. Lee, and C.T. Taylor. 2021. Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Cells 10: 2340.
Thornton, R.D., P. Lane, R.C. Borghaei, E.A. Pease, J. Caro, and E. Mochan. 2000. Interleukin 1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human gingival and synovial fibroblasts. The Biochemical Journal 350 (Pt 1): 307–312.
Hellwig-Burgel, T., K. Rutkowski, E. Metzen, J. Fandrey, and W. Jelkmann. 1999. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate DNA binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Blood 94: 1561–1567.
Westra, J., E. Brouwer, R. Bos, M.D. Posthumus, B. Doornbos-van der Meer, C.G. Kallenberg, and P.C. Limburg. 2007. Regulation of cytokine-induced HIF-1alpha expression in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1108: 340–348.
Georganas, C., H. Liu, H. Perlman, A. Hoffmann, B. Thimmapaya, and R.M. Pope. 2000. Regulation of IL-6 and IL-8 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts: The dominant role for NF-kappa B but not C/EBP beta or c-Jun. The Journal of Immunology 165: 7199–7206.
Luo, X., X. Zuo, Y. Zhou, B. Zhang, Y. Shi, M. Liu, K. Wang, D.R. McMillian, and X. Xiao. 2008. Extracellular heat shock protein 70 inhibits tumour necrosis factor-alpha induced proinflammatory mediator production in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Research & Therapy 10: R41.
Mo, X.R., J.W. Xie, G.J. Lv, Y.P. Ke, and X.J. Luo. 2017. Effects of TAK gene silencing on the expressions of IL-6 and IL-8 induced by TNF-alpha in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 33: 471–475.
Zhang, J., F.F. Gao, and J. Xie. 2021. LncRNA linc00152/NF-kappaB feedback loop promotes fibroblast-like synovial cells inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis via regulating miR-103a/TAK1 axis and YY1 expression. Immun Inflamm Dis 9: 681–693.
Li, G., Y. Zhang, Y. Qian, H. Zhang, S. Guo, M. Sunagawa, T. Hisamitsu, and Y. Liu. 2013. Interleukin-17A promotes rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes migration and invasion under hypoxia by increasing MMP2 and MMP9 expression through NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha pathway. Molecular Immunology 53: 227–236.
Hui, W., C. Zhao, and S.G. Bourgoin. 2017. Differential effects of inhibitor combinations on lysophosphatidic acid-mediated chemokine secretion in unprimed and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed synovial fibroblasts. Frontiers in Pharmacology 8: 848.
Fabre, C., G. Carvalho, E. Tasdemir, T. Braun, L. Ades, J. Grosjean, S. Boehrer, D. Metivier, S. Souquere, G. Pierron, P. Fenaux, and G. Kroemer. 2007. NF-kappaB inhibition sensitizes to starvation-induced cell death in high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 26: 4071–4083.
Taylor, C.T., and E.P. Cummins. 2009. The role of NF-kappaB in hypoxia-induced gene expression. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1177: 178–184.
Maxwell, P.J., R. Gallagher, A. Seaton, C. Wilson, P. Scullin, J. Pettigrew, I.J. Stratford, K.J. Williams, P.G. Johnston, and D.J. Waugh. 2007. HIF-1 and NF-kappaB-mediated upregulation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 expression promotes cell survival in hypoxic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 26: 7333–7345.
Akimoto, R., T. Tanaka, T. Nakano, Y. Hozumi, K. Kawamae, and K. Goto. 2020. DGKzeta depletion attenuates HIF-1alpha induction and SIRT1 expression, but enhances TAK1-mediated AMPKalpha phosphorylation under hypoxia. Cellular Signalling 71: 109618.
Lee, Y.A., H.M. Choi, S.H. Lee, S.J. Hong, H.I. Yang, M.C. Yoo, and K.S. Kim. 2012. Hypoxia differentially affects IL-1beta-stimulated MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in an HIF-1alpha-dependent manner. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51: 443–450.
Ahn, J.K., E.M. Koh, H.S. Cha, Y.S. Lee, J. Kim, E.K. Bae, and K.S. Ahn. 2008. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hypoxia-induced expressions of IL-8, MMP-1 and MMP-3 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 834–839.
Charbonneau, M., K. Harper, F. Grondin, M. Pelmus, P.P. McDonald, and C.M. Dubois. 2007. Hypoxia-inducible factor mediates hypoxic and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced increases in tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM17 expression by synovial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry 282: 33714–33724.
Islam, S.M.T., J. Won, M. Khan, M.D. Mannie, and I. Singh. 2021. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 drives divergent immunomodulatory functions in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Immunology 164: 31–42.
Taylor, C.T., G. Doherty, P.G. Fallon, and E.P. Cummins. 2016. Hypoxia-dependent regulation of inflammatory pathways in immune cells. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 126: 3716–3724.
Li, X., H. Kimura, K. Hirota, K. Kasuno, K. Torii, T. Okada, H. Kurooka, Y. Yokota, and H. Yoshida. 2005. Synergistic effect of hypoxia and TNF-alpha on production of PAI-1 in human proximal renal tubular cells. Kidney International 68: 569–583.
Lee, S.H., Y.J. Lee, and H.J. Han. 2010. Effect of arachidonic acid on hypoxia-induced IL-6 production in mouse ES cells: Involvement of MAPKs, NF-kappaB, and HIF-1alpha. Journal of Cellular Physiology 222: 574–585.
Cetin, A., T. Kaya, N. Demirkoprulu, B. Karadas, B. Duran, and M. Cetin. 2004. YC-1, a nitric oxide-independent activator of soluble guanylate cyclase, inhibits the spontaneous contractions of isolated pregnant rat myometrium. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 94: 19–24.
Flores-Costa, R., J. Alcaraz-Quiles, E. Titos, C. Lopez-Vicario, M. Casulleras, M. Duran-Guell, B. Rius, A. Diaz, K. Hall, C. Shea, R. Sarno, M. Currie, J.L. Masferrer, and J. Claria. 2018. The soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator IW-1973 prevents inflammation and fibrosis in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. British Journal of Pharmacology 175: 953–967.
Rius, J., M. Guma, C. Schachtrup, K. Akassoglou, A.S. Zinkernagel, V. Nizet, R.S. Johnson, G.G. Haddad, and M. Karin. 2008. NF-kappaB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1alpha. Nature 453: 807–811.
Culver, C., A. Sundqvist, S. Mudie, A. Melvin, D. Xirodimas, and S. Rocha. 2010. Mechanism of hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB. Molecular and Cellular Biology 30: 4901–4921.
Lian, L.H., Q. Jin, S.Z. Song, Y.L. Wu, T. Bai, S. Jiang, Q. Li, N. Yang, and J.X. Nan. 2013. Ginsenoside Rh2 downregulates LPS-induced NF- kappa B activation through inhibition of TAK1 phosphorylation in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013: 646728.
Zhou, Y., T. Tao, G. Liu, X. Gao, Y. Gao, Z. Zhuang, Y. Lu, H. Wang, W. Li, L. Wu, D. Zhang, and C. Hang. 2021. TRAF3 mediates neuronal apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via targeting TAK1-dependent MAPKs and NF-kappaB pathways. Cell Death & Disease 12: 10.
Hammaker, D.R., D.L. Boyle, M. Chabaud-Riou, and G.S. Firestein. 2004. Regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase by MEKK-2 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Immunology 172: 1612–1618.
Luo, X., Y. Chen, G. Lv, Z. Zhou, J. Chen, X. Mo, and J. Xie. 2017. Adenovirus-mediated small interfering RNA targeting TAK1 ameliorates joint inflammation with collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Inflammation 40: 894–903.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number LTY21H100001) and the College Students’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project of China (Grant number 202110350052,202210350058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W.G. designed the experiments and edited the final manuscript. W. J. and L. X. collected synovial tissue samples and analyzed the data. W. Q. and Y. R. performed the experiments and data analysis. L. X. conceived and designed the study and drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The experiments were performed according to the protocols approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Taizhou University (2020-sc-032).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Wang, J., Li, X. et al. Hypoxia and TNF-α Synergistically Induce Expression of IL-6 and IL-8 in Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via Enhancing TAK1/NF-κB/HIF-1α Signaling. Inflammation 46, 912–924 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01779-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01779-x