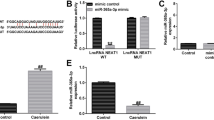
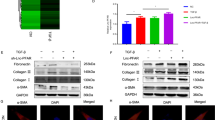
Abstract
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a dysfunctional pancreas disease marked by severe inflammation. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) involving in the regulation of inflammatory responses have been frequently mentioned. The purpose of this study was to ensure the function and action mode of lncRNA maternally expressed gene 3 (MEG3) in caerulein-induced AP cell model. HPDE cells were treated with caerulein to establish an AP model in vitro. The expression of MEG3, miR-195-5p, and fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) was measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell proliferation and apoptosis were detected by 3-(4, 5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and flow cytometry assay, respectively. The expression of CyclinD1, B cell lymphoma/leukemia-2 (Bcl-2), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), FGFR2, P65, phosphorylated P65 (p-P65), alpha inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa beta (NF-κB) (IκB-α), and phosphorylated IκB-α (p-IκB-α) at the protein level was quantified by western blot. The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were monitored by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The targeted relationship between miR-195-5p and MEG3 or FGFR2 was forecasted by the online software starBase v2.0 and verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. As a result, the expression of MEG3 and FGFR2 was decreased in caerulein-induced HPDE cells, while the expression of miR-195-5p was increased. MEG3 overexpression inhibited cell apoptosis and inflammatory responses that were induced by caerulein. Mechanically, miR-195-5p was targeted by MEG3 and abolished the effects of MEG3 overexpression. FGFR2 was a target of miR-195-5p, and MEG3 regulated the expression of FGFR2 by sponging miR-195-5p. FGFR2 overexpression abolished miR-195-5p enrichment-aggravated inflammatory injuries. Moreover, the NF-κB signaling pathway was involved in the MEG3/miR-195-5p/FGFR2 axis. Collectively, MEG3 participates in caerulein-induced inflammatory injuries by targeting the miR-195-5p/FGFR2 regulatory axis via mediating the NF-κB pathway in HPDE cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leppaniemi, A., M. Tolonen, A. Tarasconi, H. Segovia-Lohse, E. Gamberini, A.W. Kirkpatrick, C.G. Ball, N. Parry, M. Sartelli, D. Wolbrink, H. van Goor, G. Baiocchi, L. Ansaloni, W. Biffl, F. Coccolini, S. Di Saverio, Y. Kluger, E. Moore, and F. Catena. 2019. WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis. World Journal of Emergency Surgery : WJES 14: 27.
Yadav, D., and A.B. Lowenfels. 2013. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 144 (6): 1252–1261.
Afghani, E., S.J. Pandol, T. Shimosegawa, R. Sutton, B.U. Wu, S.S. Vege, F. Gorelick, M. Hirota, J. Windsor, S.K. Lo, M.L. Freeman, M.M. Lerch, Y. Tsuji, G.Y. Melmed, W. Wassef, and J. Mayerle. 2015. Acute pancreatitis-progress and challenges: A report on an international symposium. Pancreas 44 (8): 1195–1210.
Banks, P.A., T.L. Bollen, C. Dervenis, H.G. Gooszen, C.D. Johnson, M.G. Sarr, G.G. Tsiotos, S.S. Vege, and Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working, G. 2012. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62 (1): 102–111.
Dellinger, E.P., C.E. Forsmark, P. Layer, P. Levy, E. Maravi-Poma, M.S. Petrov, T. Shimosegawa, A.K. Siriwardena, G. Uomo, D.C. Whitcomb, J.A. Windsor, and Pancreatitis Across Nations Clinical, R., and Education. 2012. A. Determinant-based classification of acute pancreatitis severity: An international multidisciplinary consultation. Annals of Surgery 256 (6): 875–880.
Greenberg, J.A., J. Hsu, M. Bawazeer, J. Marshall, J.O. Friedrich, A. Nathens, N. Coburn, G.R. May, E. Pearsall, and R.S. McLeod. 2016. Clinical practice guideline: Management of acute pancreatitis. Canadian Journal of Surgery 59 (2): 128–140.
Padua, D., S. Mahurkar-Joshi, I.K. Law, C. Polytarchou, J.P. Vu, J.R. Pisegna, D. Shih, D. Iliopoulos, and C. Pothoulakis. 2016. A long noncoding RNA signature for ulcerative colitis identifies IFNG-AS1 as an enhancer of inflammation. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 311 (3): G446–G457.
Schmitz, S.U., P. Grote, and B.G. Herrmann. 2016. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 73 (13): 2491–2509.
Wang, L., X. Zhao, and Y. Wang. 2019. The pivotal role and mechanism of long non-coding RNA B3GALT5-AS1 in the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 47 (1): 2307–2315.
Liu, H., K. Yu, P. Ma, L. Xiong, M. Wang, and W. Wang. 2018. Long noncoding RNA myocardial infarction-associated transcript regulated the pancreatic stellate cell activation to promote the fibrosis process of chronic pancreatitis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 120 (6): 9547–9555.
Zhao, D., H. Ge, B. Ma, D. Xue, W. Zhang, Z. Li, and H. Sun. 2018. The interaction between ANXA2 and lncRNA Fendrr promotes cell apoptosis in caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 120 (5): 8160–8168.
Ghaedi, H., A. Zare, M.D. Omrani, A.H. Doustimotlagh, R. Meshkani, S. Alipoor, and B. Alipoor. 2018. Genetic variants in long noncoding RNA H19 and MEG3 confer risk of type 2 diabetes in an Iranian population. Gene 675: 265–271.
Qiu, Y.Y., Y. Wu, M.J. Lin, T. Bian, Y.L. Xiao, and C. Qin. 2019. LncRNA-MEG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate Treg/Th17 balance in patients with asthma by targeting microRNA-17/RORgammat. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 111: 386–394.
Li, J., Y. Zi, W. Wang, and Y. Li. 2018. Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in chronic myeloid leukemia via targeting miR-184. Oncology Research 26 (2): 297–305.
Chou, C.H., F.M. Lin, M.T. Chou, S.D. Hsu, T.H. Chang, S.L. Weng, S. Shrestha, C.C. Hsiao, J.H. Hung, and H.D. Huang. 2013. A computational approach for identifying microRNA-target interactions using high-throughput CLIP and PAR-CLIP sequencing. BMC Genomics 14 (1): S2.
Dixit, A.K., A.E. Sarver, Z. Yuan, J. George, U. Barlass, H. Cheema, A. Sareen, S. Banerjee, V. Dudeja, R. Dawra, S. Subramanian, and A.K. Saluja. 2016. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA signature of mouse pancreatic acini: overexpression of miR-21-3p in acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 311 (5): G974–G980.
Tian, R., R.L. Wang, H. Xie, W. Jin, and K.L. Yu. 2013. Overexpressed miRNA-155 dysregulates intestinal epithelial apical junctional complex in severe acute pancreatitis. World Journal of Gastroenterology 19 (45): 8282–8291.
Fu, Q., T. Qin, L. Chen, C.J. Liu, X. Zhang, Y.Z. Wang, M.X. Hu, H.Y. Chu, and H.W. Zhang. 2016. miR-29a up-regulation in AR42J cells contributes to apoptosis via targeting TNFRSF1A gene. World Journal of Gastroenterology 22 (20): 4881–4890.
Bloomston, M., W.L. Frankel, F. Petrocca, S. Volinia, H. Alder, J.P. Hagan, C.G. Liu, D. Bhatt, C. Taccioli, and C.M. Croce. 2007. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 297 (17): 1901–1908.
Zhang, J., D. Upadhya, L. Lu, and L.W. Reneker. 2015. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) is required for corneal epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation during embryonic development. PLoS One 10 (1): e0117089.
Chen, X., H. Ouyang, Z. Wang, B. Chen, and Q. Nie. 2018. A novel circular RNA generated by FGFR2 gene promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation by sponging miR-133a-5p and miR-29b-1-5p. Cells 7 (11): 199.
Chen, J., Z. Wang, Z. Zheng, Y. Chen, S. Khor, K. Shi, Z. He, Q. Wang, Y. Zhao, H. Zhang, X. Li, J. Li, J. Yin, X. Wang, and J. Xiao. 2017. Neuron and microglia/macrophage-derived FGF10 activate neuronal FGFR2/PI3K/Akt signaling and inhibit microglia/macrophages TLR4/NF-kappaB-dependent neuroinflammation to improve functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Cell Death & Disease 8 (10): e3090.
Huang, T., D. Liu, Y. Wang, P. Li, L. Sun, H. Xiong, Y. Dai, M. Zou, X. Yuan, and H. Qiu. 2018. FGFR2 Promotes gastric cancer progression by inhibiting the expression of Thrombospondin4 via PI3K-Akt-Mtor pathway. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 50 (4): 1332–1345.
Nakada, S., K. Tsuneyama, I. Kato, Y. Tabuchi, I. Takasaki, Y. Furusawa, H. Kawaguchi, M. Fujimoto, H. Goto, H. Hikiami, T. Kondo, Y. Takano, and Y. Shimada. 2010. Identification of candidate genes involved in endogenous protection mechanisms against acute pancreatitis in mice. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 391 (3): 1342–1347.
Liu, P., L. Xia, W.L. Zhang, H.J. Ke, T. Su, L.B. Deng, Y.X. Chen, and N.H. Lv. 2014. Identification of serum microRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 14 (3): 159–166.
Zhou, Y., X. Zhang, and A. Klibanski. 2012. MEG3 noncoding RNA: a tumor suppressor. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology 48 (3): R45–R53.
Zhu, Y., P. Chen, Y. Gao, N. Ta, Y. Zhang, J. Cai, Y. Zhao, S. Liu, and J. Zheng. 2018. MEG3 activated by vitamin D inhibits colorectal cancer cells proliferation and migration via regulating clusterin. EBioMedicine 30: 148–157.
Wang, P., D. Chen, H. Ma, and Y. Li. 2017. LncRNA MEG3 enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-21-5p/SOX7 axis. Oncotargets and Therapy 10: 5137–5149.
Ma, L., F. Wang, C. Du, Z. Zhang, H. Guo, X. Xie, H. Gao, Y. Zhuang, M. Kornmann, H. Gao, X. Tian, and Y. Yang. 2018. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a tumour suppressor and has prognostic predictive value in human pancreatic cancer. Oncology Reports 39 (3): 1132–1140.
Li, X., C. Tang, J. Wang, P. Guo, C. Wang, Y. Wang, Z. Zhang, and H. Wu. 2018. Methylene blue relieves the development of osteoarthritis by upregulating lncRNA MEG3. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 15 (4): 3856–3864.
Li, G., Y. Liu, F. Meng, Z. Xia, X. Wu, Y. Fang, C. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and D. Liu. 2019. LncRNA MEG3 inhibits rheumatoid arthritis through miR-141 and inactivation of AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 23 (10): 7116–7120.
Ballantyne, M.D., R.A. McDonald, and A.H. Baker. 2016. lncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 99 (5): 494–501.
Shi, G., J. Shi, K. Liu, N. Liu, Y. Wang, Z. Fu, J. Ding, L. Jia, and W. Yuan. 2013. Increased miR-195 aggravates neuropathic pain by inhibiting autophagy following peripheral nerve injury. Glia 61 (4): 504–512.
Cheng, H.Y., Y.S. Wang, P.Y. Hsu, C.Y. Chen, Y.C. Liao, and S.H. Juo. 2019. miR-195 has a potential to treat ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke through neurovascular protection and neurogenesis. Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development 13: 121–132.
Bjersing, J.L., C. Lundborg, M.I. Bokarewa, and K. Mannerkorpi. 2013. Profile of cerebrospinal microRNAs in fibromyalgia. PLoS One 8 (10): e78762.
Muratore, C.S., F.I. Luks, Y. Zhou, M. Harty, J. Reichner, and T.F. Tracy. 2009. Endotoxin alters early fetal lung morphogenesis. The Journal of Surgical Research 155 (2): 225–230.
Liu, Y., V. Tergaonkar, S. Krishna, and E.J. Androphy. 1999. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6-enhanced susceptibility of L929 cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha correlates with increased accumulation of reactive oxygen species. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (35): 24819–24827.
Li, F., J. Zhang, F. Arfuso, A. Chinnathambi, M.E. Zayed, S.A. Alharbi, A.P. Kumar, K.S. Ahn, and G. Sethi. 2015. NF-kappaB in cancer therapy. Archives of Toxicology 89 (5): 711–731.
Tong, L., and V. Tergaonkar. 2014. Rho protein GTPases and their interactions with NFkappaB: Crossroads of inflammation and matrix biology. Bioscience Reports 34 (3): 183–295.
Hoesel, B., and J.A. Schmid. 2013. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Molecular Cancer 12: 86.
Vermeulen, L., G. De Wilde, S. Notebaert, W. Vanden Berghe, and G. Haegeman. 2002. Regulation of the transcriptional activity of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Biochemical Pharmacology 64 (5-6): 963–970.
Baldwin, A.S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annual Review of Immunology 14: 649–683.
Barnes, P.J., and M. Karin. 1997. Nuclear factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. The New England Journal of Medicine 336 (15): 1066–1071.
Baumann, B., M. Wagner, T. Aleksic, G. von Wichert, C.K. Weber, G. Adler, and T. Wirth. 2007. Constitutive IKK2 activation in acinar cells is sufficient to induce pancreatitis in vivo. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 117 (6): 1502–1513.
Vaquero, E., I. Gukovsky, V. Zaninovic, A.S. Gukovskaya, and S.J. Pandol. 2001. Localized pancreatic NF-kappaB activation and inflammatory response in taurocholate-induced pancreatitis. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 280 (6): G1197–G1208.
Altavilla, D., C. Famulari, M. Passaniti, M. Galeano, A. Macri, P. Seminara, L. Minutoli, H. Marini, M. Calo, F.S. Venuti, M. Esposito, and F. Squadrito. 2003. Attenuated cerulein-induced pancreatitis in nuclear factor-kappaB-deficient mice. Laboratory Investigation 83 (12): 1723–1732.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Figure S1.
Cell viability was decreased in caerulein-treated HPDE cells in a dose/time-dependent manner. (A) Cell viability in HPDE cells exposed to different doses of caerulein (5, 10 and 15 nmol/L) was assessed by MTT assay. (B) Cell viability in HPDE cells exposed to 10 nmol/L caerulein for different time (4, 8 and 12 h) was assessed by MTT assay. *P < 0.05. (PNG 674 kb)
Figure S2.
LncRNA MEG3 was mainly distributed in the cytoplasm. The distribution of MEG3 in the cytoplasm and nucleus was examined using qRT-PCR, and GAPDH or U6 acted as the control in cytoplasm or nucleus, respectively. *P < 0.05. (PNG 365 kb)
Figure S3.
MEG3 repressed caerulein-induced apoptosis of HPDE cells by targeting miR-195-5p, and miR-195-5p promoted caerulein-induced apoptosis of HPDE cells by binding to FGFR2. (A) Cell apoptosis was monitored in caerulein-treated HPDE cells transfected with MEG3, pcDNA, MEG3+miR-195-5p or MEG3+miR-NC using flow cytometry assay. (B) Cell apoptosis was determined in caerulein-treated HPDE cells transfected with miR-195-5p, miR-NC, miR-195-5p+FGFR2 or miR-195-5p+pcDNA by flow cytometry analysis. *P < 0.05. (PNG 2892 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Song, D. LncRNA MEG3 Participates in Caerulein-Induced Inflammatory Injury in Human Pancreatic Cells via Regulating miR-195-5p/FGFR2 Axis and Inactivating NF-κB Pathway. Inflammation 44, 160–173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01318-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01318-6