Abstract
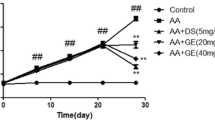
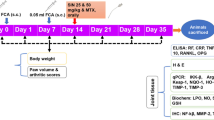
Previous studies demonstrated that penta-acetyl geniposide ((Ac)5GP, an acetylated derivative of geniposide) exhibited better pharmacological functions than geniposide. This study was aimed to observe the potential effect of (Ac)5GP on adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) in rat and explore the involved mechanisms. Rat AIA was induced by complete Freund’s adjuvant. (Ac)5GP (30, 60, 120 mg/kg) was given to AIA rats by intragastric administration. Paw swelling, polyarthritis index, serum pro-inflammatory cytokines levels, histological assessments of ankle joint, and proteoglycan expression were respectively measured to evaluate the therapeutic effect of (Ac)5GP on rat AIA. Immunohistochemistry for Ki67 and TUNEL assay were performed to reveal the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of (Ac)5GP on AIA synoviocytes in vivo. Protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase 3, IκBα, p-IκBα, and NF-κB p65 in synovial tissues were detected by Western blot. We found that (Ac)5GP treatment could suppress secondary hind paw swelling, reduce polyarthritis index, decrease TNF-α and IL-1β serum levels, attenuate pathological damage of ankle joint, and promote proteoglycans expression. (Ac)5GP treatment also could reduce Ki67 positive expression rate and raise the synovial apoptosis index in synovial tissues. Additionally, (Ac)5GP (120 mg/kg) could significantly decrease Bcl-2 protein level, increase Bax and cleaved caspase 3 protein levels, and normalize the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax. Moreover, (Ac)5GP (120 mg/kg) could inhibit the degradation and phosphorylation of IκBα and reduce NF-κB p65 protein level in nuclear extracts. In conclusion, (Ac)5GP showed a potent anti-arthritic effect on AIA rats via inducing synovial apoptosis and inhibiting NF-κB activation in synovial tissues.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott, D.L., F. Wolfe, and T.W. Huizinga. 2010. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376: 1094–1108.
Bartok, B., and G.S. Firestein. 2010. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunological Reviews 233: 233–255.
Pope, R.M. 2002. Apoptosis as a therapeutic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Immunology 2: 527–535.
Miagkov, A.V., D.V. Kovalenko, C.E. Brown, J.R. Didsbury, J.P. Cogswell, S.A. Stimpson, A.S. Baldwin, and S.S. Makarov. 1998. NF-kappaB activation provides the potential link between inflammation and hyperplasia in the arthritic joint. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95: 13859–13864.
Xu, S., Y. Xiao, S. Zeng, Y. Zou, Q. Qiu, M. Huang, Z. Zhan, L. Liang, X. Yang, and H. Xu. 2018. Piperlongumine inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation Research 67: 233–243.
Makarov, S.S. 2001. NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Research 3: 200–206.
Roman-Blas, J.A., and S.A. Jimenez. 2008. Targeting NF-kappaB: a promising molecular therapy in inflammatory arthritis. International Reviews of Immunology 27: 351–374.
Lampropoulos, C.E., P. Orfanos, V.K. Bournia, T. Karatsourakis, C. Mavragani, D. Pikazis, M.N. Manoussakis, A.G. Tzioufas, H.M. Moutsopoulos, and P.G. Vlachoyiannopoulos. 2015. Adverse events and infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with conventional drugs or biologic agents: a real world study. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 33: 216–224.
Ren, D.Y., T. Xu, R. Li, C. Huang, Y. Huang, R.Q. Li, H.Y. Li, and J. Li. 2013. 5,7,3′-Triacetyl hesperetin suppresses adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats through modulating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 41: 601–614.
Zhu, L., J. Wang, T. Wei, J. Gao, H. He, X. Chang, and T. Yan. 2015. Effects of Naringenin on inflammation in complete freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis by regulating Bax/Bcl-2 balance. Inflammation 38: 245–251.
Shan, M., S. Yu, H. Yan, S. Guo, W. Xiao, Z. Wang, L. Zhang, A. Ding, Q. Wu, and S.F.Y. Li. 2017. A review on the phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of geniposide, a natural product. Molecules 22.
Dai, M.M., H. Wu, H. Li, J. Chen, J.Y. Chen, S.L. Hu, and C. Shen. 2014. Effects and mechanisms of geniposide on rats with adjuvant arthritis. International Immunopharmacology 20: 46–53.
Wang, F., J. Cao, J. Hao, and K. Liu. 2014. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and tissue distribution of geniposide following intravenous and peroral administration to rats. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 35: 97–103.
Peng, C.H., C.N. Huang, and C.J. Wang. 2005. The anti-tumor effect and mechanisms of action of penta-acetyl geniposide. Current Cancer Drug Targets 5: 299–305.
Zhang, H., T. Shi, J. Wang, R. Li, and W. Tang. 2013. Protective effect of penta-acetyl geniposide on acute liver injury induced by D-galactosamine in mice. British Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 4: 256–261.
Huang, H.P., Y.W. Shih, C.H. Wu, P.J. Lai, C.N. Hung, and C.J. Wang. 2009. Inhibitory effect of penta-acetyl geniposide on C6 glioma cells metastasis by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression involved in both the PI3K and ERK signaling pathways. Chemico-Biological Interactions 181: 8–14.
Peng, C.H., C.N. Huang, S.P. Hsu, and C.J. Wang. 2007. Penta-acetyl geniposide-induced apoptosis involving transcription of NGF/p75 via MAPK-mediated AP-1 activation in C6 glioma cells. Toxicology 238: 130–139.
Zhao, X., L. Cai, R. Li, and W.W. Gao. 2017. The effect of penta-acetyl geniposide on CUMS-induced depressive behaviors and HPA axis in rats. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui 52: 1164–1168.
Yuan, F.L., F.H. Chen, W.G. Lu, X. Li, J.P. Li, C.W. Li, R.S. Xu, F.R. Wu, W. Hu, and T.Y. Zhang. 2010. Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels in articular chondrocytes by amiloride attenuates articular cartilage destruction in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Inflammation Research 59: 939–947.
Huang, L., G. Mackenzie, N. Ouyang, Y. Sun, G. Xie, F. Johnson, D. Komninou, and B. Rigas. 2011. The novel phospho-non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, OXT-328, MDC-22 and MDC-917, inhibit adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. British Journal of Pharmacology 162: 1521–1533.
Barbosa, C.P., A.M. Ritter, L.G. da Silva, R. Grespan, R.K. Cuman, L. Hernandes, and C.A. Bersani-Amado. 2014. Effects of simvastatin, ezetimibe, and their combination on histopathologic alterations caused by adjuvant-induced arthritis. Inflammation 37: 1035–1043.
Matsuno, H., K. Yudoh, R. Katayama, F. Nakazawa, M. Uzuki, T. Sawai, T. Yonezawa, Y. Saeki, G.S. Panayi, C. Pitzalis, and T. Kimura. 2002. The role of TNF-alpha in the pathogenesis of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a study using a human RA/SCID mouse chimera. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41: 329–337.
Kay, J., and L. Calabrese. 2004. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43 (Suppl 3): iii2–iii9.
Otero, M., and M.B. Goldring. 2007. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Chondrocytes. Arthritis Research & Therapy 9: 220.
Pattacini, L., L. Boiardi, B. Casali, and C. Salvarani. 2010. Differential effects of anti-TNF-alpha drugs on fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49: 480–489.
Ospelt, C., M. Neidhart, R.E. Gay, and S. Gay. 2004. Synovial activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Frontiers in Bioscience 9: 2323–2334.
Gerdes, J., H. Lemke, H. Baisch, H.H. Wacker, U. Schwab, and H. Stein. 1984. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Journal of Immunology 133: 1710–1715.
Lam, M., G. Dubyak, L. Chen, G. Nunez, R.L. Miesfeld, and C.W. Distelhorst. 1994. Evidence that BCL-2 represses apoptosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum-associated Ca2+ fluxes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91: 6569–6573.
Crompton, M. 2000. Bax, Bid and the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane in apoptosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 12: 414–419.
Nagata, S. 1997. Apoptosis by death factor. Cell 88: 355–365.
Busteed, S., M.W. Bennett, C. Molloy, A. Houston, M.A. Stone, F. Shanahan, M.G. Molloy, and J. O'Connell. 2006. Bcl-x(L) expression in vivo in rheumatoid synovium. Clinical Rheumatology 25: 789–793.
Song, S., K.N. Jacobson, K.M. McDermott, S.P. Reddy, A.E. Cress, H. Tang, S.M. Dudek, S.M. Black, J.G. Garcia, A. Makino, and J.X. Yuan. 2016. ATP promotes cell survival via regulation of cytosolic [Ca2+] and Bcl-2/Bax ratio in lung cancer cells. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 310: C99–C114.
Jiang, L., W. Li, Y. Wang, X. Zhang, D. Yu, Y. Yin, Z. Xie, and Y. Yuan. 2014. Effects of cichoric acid extract from Echinacea purpurea on collagen-induced arthritis in rats. American Journal of Chinese Medicine 42: 679–692.
Li, Y., L.M. Wang, J.Z. Xu, K. Tian, C.X. Gu, and Z.F. Li. 2017. Gastrodia elata attenuates inflammatory response by inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 85: 177–181.
Simmonds, R.E., and B.M. Foxwell. 2008. Signalling, inflammation and arthritis: NF-kappaB and its relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 584–590.
Okamoto, H., T. Yoshio, H. Kaneko, and H. Yamanaka. 2010. Inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling by fasudil as a potential therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 62: 82–92.
van Loo, G., and R. Beyaert. 2011. Negative regulation of NF-kappaB and its involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 13: 221.
Chiu, C.C., J.Y. Chen, K.L. Lin, C.J. Huang, J.C. Lee, B.H. Chen, W.Y. Chen, Y.H. Lo, Y.L. Chen, C.H. Tseng, Y.L. Chen, and S.R. Lin. 2010. p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways are involved in naphtho[1,2-b] furan-4,5-dione induced anti-proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatoma cells. Cancer Letters 295: 92–99.
Schett, G., M. Tohidast-Akrad, J.S. Smolen, B.J. Schmid, C.W. Steiner, P. Bitzan, P. Zenz, K. Redlich, Q. Xu, and G. Steiner. 2000. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 2501–2512.
Thiel, M.J., C.J. Schaefer, M.E. Lesch, J.L. Mobley, D.T. Dudley, H. Tecle, S.D. Barrett, D.J. Schrier, and C.M. Flory. 2007. Central role of the MEK/ERK MAP kinase pathway in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis: potential proinflammatory mechanisms. Arthritis and Rheumatism 56: 3347–3357.
Thalhamer, T., M.A. McGrath, and M.M. Harnett. 2008. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 409–414.
Zuo, J., Y. Xia, X. Li, Z. Ou-Yang, and J.W. Chen. 2015. Selective modulation of MAPKs contribute to the anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities of 1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone in rheumatoid arthritis-derived fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 168: 248–254.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81102273, 81201052), the Program for Outstanding Young Talents of Higher Education Institution of Anhui Province (gxyqZD2016045), and the Program for the Young and Middle-aged Academic Technology Leaders of Anhui Medical University (201309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Li, Cm., Tang, Wj. et al. Therapeutic Effect of Penta-acetyl Geniposide on Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats: Involvement of Inducing Synovial Apoptosis and Inhibiting NF-κB Signal Pathway. Inflammation 41, 2184–2195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0861-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0861-0