Abstract
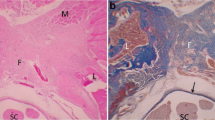
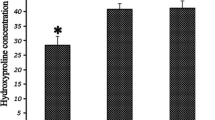
The aim of the study was to determine the effect of direct application of rifampin, povidone-iodine, and hydrogen peroxide on the formation of epidural fibrosis in rats. Forty-eight adult male Wistar albino rats were equally and randomly divided into four groups (laminectomy, topical rifampin, topical povidone-iodine, and topical hydrogen peroxide). Laminectomy was performed at the T12 level in all rats. Four weeks later, the extent of epidural fibrosis was assessed both macroscopically and histopathologically. ANOVA test was used for the evaluation of dural thickness. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for the pathology and macroscopic evaluation. Chi-square test was used for evaluation of the arachnoid involvement. p value <0.05 was accepted as statistically significant. Our data revealed that topical application of both povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide were effective in reducing epidural fibrosis formation. The results of our study provide the experimental evidence of the preventive effects of topical application of povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide over epidural fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeinalizadeh, M., S.M. Miri, F.A. Ardalan, F. Maleki, M. Zakeri, E. Aqhajanzadeh, and Z. Habibi. 2014. Reduction of epidural fibrosis and dural adhesions after lamina reconstruction by absorbable cement: an experimental study. The Spine Journal 14(1): 113–118.
Tao, H., and H. Fan. 2009. Implantation of amniotic membrane to reduce postlaminectomy epidural adhesions. European Spine Journal 18(8): 1202–1212.
Alkalay, R.N., D.H. Kim, D.W. Urry, J. Xu, T.M. Parker, and P.A. Glazer. 2003. Prevention of postlaminectomy epidural fibrosis using bioelastic materials. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28(15): 1659–1665.
Watts, C.C., A. Bremer, and T. Nguyen. 1983. Autogenic fat transplants in the epidural space in routine spine surgery. Neurosurgery 13(4): 367–370.
Liu, J., B. Ni, L. Zhu, J. Yang, X. Cao, and W. Zhou. 2010. Mitomycin C-polyethylene glycol controlled-release film inhibits collagen secretion and induces apoptosis of the fibroblasts in the early wound of a postlaminectomy rat model. The Spine Journal 10(5): 441–447.
Fischgrund, J.S. 2000. Perspectives on modern orthopaedics: use of Adcon-L for epidural scar prevention. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 8(6): 339–343.
Chang, F.Y., M.C. Chang, S.T. Wang, W.K. Yu, C.L. Liu, and T.H. Chen. 2006. Can povidone-iodine solution be used safely in spinal surgery. European Spine Journal 15(6): 1005–1014.
Ulivieri, S., S. Toninelli, C. Petrini, A. Giorgio, and G. Oliveri. 2011. Prevention of post-operative infection in spine surgery by wound irrigation with a solution of povidone-iodine and hydrogen peroxide. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery 131(9): 1203–1206.
Mastronardi, L., F. Rychlicki, C. Tatta, L. Morabito, U. Agrillo, and A. Ducati. 2005. Spondylodiscitis after lumbar microdiscectomy: effectiveness of two protocols f intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis in 1167 cases. Neurosurgical Review 28(4): 303–307.
Samancıoğlu, H., S. Yaycıoğlu, H. Ak, C. Tataroğlu, and I. Gülşen. 2014. The effect of povidone-iodine on peridural fibrosis in spinal surgery. Journal of Neurological Science (Turkish) 31(4): 687–692.
Gutierrez-Venegas, G., A. Guadarrama-Solis, C. Munoz-Seca, and J.A. Arrequin-Cano. 2015. Hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human gingival fibroblasts. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology 8(12): 15563–15572.
Thomas, G.W., L.T. Real, R. Bar-Or, R. Shimonkevitz, C.W. Mains, D.S. Slone, et al. 2009. Mechanisms of delayed wound healing by commonly used antiseptics. The Journal of Trauma 66(1): 82–90.
Gurel, M.S., S. Naycı, A.V. Turgut, and E.R. Bozkurt. 2015. Comparison of the effect of topical fusidic acid and rifamycin on wound healing in rats. International Wound Journal 12(1): 106–110.
Caruso, I. 1997. Twenty years of experience with intra-articular rifamycin for chronic arthritides. Journal of International Medical Research 25(6): 307–317.
Sartor RB. 2016. Review article: the potential mechanisms of action of rifaximin in the management of the bowel disease. 43 suppl 1:27–36.
Gionchetti, P., F. Rizello, A. Venturi, F. Ugolini, M. Rossi, P. Brigidi, et al. 1999. Review: antibiotic treatment in inflammatory bowel disease: rifaximin, a new possible approach. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 3(1): 27–30.
Rosette, C., F. Buendia-Laysa Jr., S. Patkar, L. Moro, G. Celasco, R. Bozzella, et al. 2013. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of rifamycin SV. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 42(2): 182–186.
Rydell, N. 1970. Decreased granulation tissue reaction after installment of hyaluronic acid. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 41: 307–311.
Cemil, B., K. Tun, E. Kaptanoglu, F. Kaymaz, B. Cevirgen, A. Comert, and I. Tekdemir. 2011. Use of pimecrolimus to prevent epidural fibrosis in a postlaminectomy rat model. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine 11(6): 758–763.
He, Y., M. Revel, and B. Loty. 1995. A quantitative model of post-laminectomy scar formation. Effects of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Spine (PhilaPa 1976) 20(5): 557–563.
Gürer, B., R. Kahveci, E.C. Gökçe, H. Özevren, E. Turkoglu, and A. Gökçe. 2015. Evaluation of topical application and systemic administration of rosuvastatin in preventing epidural fibrosis in rats. The Spine Journal 15(3): 522–529.
Masopust, V., M. Hackel, D. Netuka, O. Bradac, R. Rokyta, and M. Vrabec. 2009. Postoperative epidural fibrosis. The Clinical Journal of Pain 25(7): 600–606.
Mohi Eldin, M.M., and N.M. Abdel Razek. 2015. Epidural fibrosis after lumbar disc surgery: prevention and outcome evaluation. Asian Spine Journal 9(3): 370–378.
Kalakoti, P., S. Missios, T. Maiti, S. Konar, S. Bir, P. Bollam, and A. Nanda. 2016. Inpatient outcomes and postoperative complications after primary versus revision lumbar spinal fusion surgeries for degenerative lumbar disc disease: a national (nationwide) inpatient sample analysis, 2002–2011. World Neurosurgery 85: 114–124.
Shah, J.M., E. Omar, D.R. Pai, and S. Sood. 2012. Cellular events and biomarkers of wound healing. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery 45(2): 220–228.
Kozma, E.M., G. Wisowski, D. Kusz, and K. Olczyk. 2011. The role of decorin and biglycan dermatan sulfate chain(s) in fibrosis-affected fascia. Glycobiology 21(10): 1301–1316.
Mohan, R.R., R. Gupta, M.K. Mehan, J.W. Cowden, and S. Sinha. 2010. Decorin transfection suppresses profibrogenic genes and myofibroblast formation in human corneal fibroblast. Experimental Eye Research 91(2): 238–245.
Sun, Y., L. Wang, S. Sun, B. Liu, N. Wu, and X. Cao. 2008. The effect of 10-hydroxycamptothecinein preventing fibroblast proliferation and epidural scar adhesion after laminectomy in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology 593(1–3): 44–48.
Zhu, J., Y. Li, W. Shen, C. Qiao, F. Ambrosio, M. Lavasani, et al. 2007. Relationships between transforming growth factor-beta1, myostatin, and decorin: implications for skeletal muscle fibrosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 282(35): 25852–25863.
Baqual, N., A. Ganjre, S.N. Goryawala, R. Kathariya, and S. Dusane. 2015. Dynamic role of myofibroblast in oral lesion. World Journal of Clinical Oncology 6(6): 264–271.
Tracy, L.E., R.A. Minasian, and E.J. Caterson. 2016. Extracellular matrix and dermal fibroblast function in the healing wound. Advances in Wound Care (New Rochelle) 5(3): 119–136.
Sandoval, M.A., and D. Hernandez-Vaquero. 2008. Preventing epidural fibrosis with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. European Spine Journal 17(3): 451–455.
He, Y., M. Revel, and B. Loty. 1995. A quantitative model of post-laminectomy scar formation. Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Spine (Phila Pa) 20(5): 557–563.
Yildiz, K.H., F. Gezen, M. Is, S. Cukur, and M. Dosoglu. 2007. Mitomycin C, 5-fluorouracil, and cyclosporin a prevent epidural fibrosis in experimental laminectomy model. European Spine Journal 16(9): 1525–1530.
Parchi, P.D., G. Evangelisti, L. Adreani, F. Girardi, L. Darren, A. Sama, et al. 2015. Postoperative spine infections. Orthopedic Reviews (Pavia) 7(3): 5900.
Oksuz E, Deniz FE, Gunal O, Demir O, Barut S, Markoc F, et al. 2015. Which method is the most effective for preventing postoperative infection in spinal surgery? European Spine Journal 19.
Cheng, M.T., M.C. Chang, S.T. Wang, W.K. Yu, C.L. Liu, and T.H. Chen. 2005. Efficacy of dilute betadine solution irrigation in the prevention of postoperative infection of spinal surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30(15): 1689–1693.
Bennett, L., S. Richard, C. Davidson, M. Jeffrey, R. Barton, and L. Nanney. 2001. An in vivo comparison of topical agents on wound repair. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 108(3): 675–687.
Khan, M.N., and A.H. Naqvi. 2006. Antiseptic, iodine, povidone iodine and traumatic wound cleansing. Journal of Tissue Viability 16(4): 6–10.
Viljanto, J. 1980. Disinfection of surgical wounds without inhibition of normal wound healing. Archives of Surgery (Chicago,III.1960:) 115(3): 253–256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kizilay, Z., Cetin, N.K., İsmailoglu, Ö. et al. The Effects of Rifampin, Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide on the Formation of Epidural Fibrosis in the Experimental Epidural Fibrosis Model. Inflammation 39, 1495–1502 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0383-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0383-6