Abstract
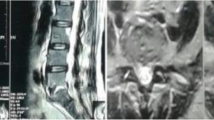
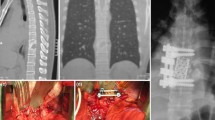
The role of antibiotic prophylaxis in preventing postoperative lumbar spondylodiscitis is still controversial in medical, ethical, economic, and legal terms. The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the efficacy of two intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis protocols in a large series of lumbar microdiscectomies performed in two different neurosurgical centres. We reviewed the outcome of 1167 patients operated on for a lumbar disc herniation with microsurgical technique, in order to detect the incidence of postoperative spondylodiscitis. Group A included 450 patients operated on in a 3-year period in the Neurosurgical Division of the University Hospital of Ancona; group P consisted of 717 patients operated on in a 4-year period in the Neurosurgical Division of the Sandro Pertini Hospital of Rome. In both groups intraoperative antibiotics for prophylaxis were administered, whereas postoperative prophylaxis was not performed. Protocol of group A: single intravenous dose of cefazoline 1 g at induction of general anesthesia and generous washing with saline solution and irrigation with a solution containing rifamicin at the end of microsurgical procedure. Protocol of group P: single-dose of intravenous ampicillin 1000 mg and sulbactam 500 mg at induction of anesthesia and generous irrigation with saline solution at the end of microsurgical procedure. A diagnosis of postoperative spondylodiscitis was made in three out of 450 patients in group A (0.67%) and in 5 out of 717 patients in group P (0.69%). In all cases, treatment consisted of rigid thoraco-lumbar orthesis and 4- to 6-week administration of amoxicillin/clavulanate compound (500/125 mg). The low incidence of postoperative spondylodiscitis obtained with both our protocols seems to confirm that intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis is associated with the same rate of discitis of prolonged prophylaxis usually still adopted in many centres, but is more advantageous both in terms of welfare and comfort for patients and in economic terms. However, at the moment it is not possible identify the ideal antibiotic for this purpose. It seems to be reasonable to search for the solution through large multicenter prospective studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrington JA, Murtagh FR, Rechtine GR, Nokes SR (1986) Magnetic resonance imaging of post-discogram discitis and osteomyelitis in the lumbar spine. Case report. J Fla Med Assoc 73:192–194
Cusmano F, Calabrese G, Bassi S, Branislav S, Bassi P (2000) Radiologic diagnosis of spondylodiscitis: role of magnetic resonance. Radiol Med (Torino) 100:112–119
Dall BE, Rowe DE, Odette WG, Batts DH (1987) Postoperative discitis. Diagnosis and management. Clin Orthop 224:138–146
Davis RA (1994) A long-term outcome analysis of 984 surgically treated herniated lumbar discs. J Neurosurg 80:415–421
Dempsey R, Rapp RP, Young B, Johnston S, Tibbs P (1988) Prophylactic parenteral antibiotics in clean neurosurgical procedures. A review. J Neurosurg 69:52–57
Dimick JB, Lipsett PA, Kostuik JP (2000) Spine update: antimicrobial prophylaxis in spine surgery. Basic principles and recent advances. Spine 25:2544–2548
Ford LT, Key JA (1955) Postoperative infection of intervertebral disc space. South Med J 48:1295–1303
Fouquet B, Goupille P, Jattiot F, Cotty P, Lapierre F, Valat JP, Amouroux J, Benatre A (1992) Discitis after lumbar disc surgery: features of aseptic and septic forms. Spine 17:356–358
Frank U, Schmidt-Eisenlohr E, Joos-Wurttemberger A, Hasse J, Daschner F (1990) Concentrations of sulbactam/ampicillin in serum and lung tissue. Infection 18:307–309
Fraser RD, Osti OL, Vernon-Roberts B (1987) Discitis after discography. J Bone Jt Surg [Br] 14:1025–1032
Grane P, Josephsson A, Seferlis A, Tullberg T (1998) Septic and aseptic post-operative discitis in the lumbar spine-evaluation by MR imaging. Acta Radiol 39:108–115
Guiboux JP, Cantor JB, Small SD, Zervos M, Herkowitz HN (1995) The effect of prophylactic antibiotics on iatrogenic intervertebral disc infections. A rabbit model. Spine 20:685–688
Guyer RD, Collier R, Stith WJ, Ohnmeiss DD, Hochschuler SH, Rashbaum RF, Regan JJ (1988) Discitis after discography. Spine 13:1352–1354
Imae S, Igarashi S, Koyama T (1996) Spondylodiscitis after operation for lumbar disc herniation. No Shinkei Geka 24:149–155
Kylanpaa-Back ML, Suominen RA, Salo SA, Soiva M, Korkala OL, Mokka RE (1999) Postoperative discitis: outcome and late magnetic resonance image evaluation of ten patients. Ann Chir Gynaecol 88:61–64
Luer MS, Hatton J (1993) Appropriateness of antibiotic selection and use in laminectomy and microdiscectomy. Am J Hosp Pharm 50:667–670
Maiuri F, Iaconetta G, Gallicchio B, Manto A (1997) Spondylodiscitis. Clinical and magnetic resonance diagnosis. Spine 22:1741–1746
Martin C (2000) Guidelines for antibiotic prophylaxis in surgery patients: application to neurosurgery. 1999 update. Working Group of Experts of the Societé Francaise of Anesthesie et de Rianimation (SFAR). Neurochirurgie 46:402–405
McDonald LC, Yu HT, Yin HC, Hsiung AC, Ho M (2001) Antibiotic use working group. Use and abuse of surgical prophylaxis in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc 100:5–13
Meinig G, Kretzschmar K, Samii M (1977) Spondylodiscitis: lumbar disc removal. Adv Neurosurg 4:55–57
Oishi CS, Carrion VW, Hoaglund FT (1992) Use of parenteral prophylactic antibiotics in clean orthopedic surgery. A review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res 296:249–255
Pilgaard S (1969) Discitis (closed space infection) following removal of lumbar intervertebral disc. J Bone Jt Surg [Am] 51:713–716
Piotrowski WP, Krombholz MA, Muhl B (1994) Spondylodiscitis after lumbar disk surgery. Neurosurg Rev 17:189–193
Puranen J, Mäkelä J, Lähde S (1984) Postoperative intervertebral discitis. Acta Orthop Scand 55:461–465
Quartey GRC, Polyzoides K (1981) Intra-operative antibiotic prophylaxis in neurosurgery: a clinical study. Neurosurgery 8:669–671
Rawlings CE III, Wilkins RH (1996) Postoperative intervertebral disc space infection. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery, vol 3. Macgraw Hill, New York, pp 3825–3830
Riley LH III, Banovac K, Martinez OV, Eismonts FJ (1994) Tissue distribution of antibiotics in the intervertebral disc. Spine 19:2619–2625
Rohde V, Meyer B, Schaller C, Hassler WE (1998) Spondylodiscitis after lumbar discectomy. Incidence and a proposal for prophylaxis. Spine 23:615–620
Savitz M, Savitz S, Malis L (1999) Ethical issues in the history of prophylactic antibiotics use in neurosurgery. Br J Neurosurg 13:306–311
Schulitz KP, Assheuer J (1994) Discitis after procedures on the intervertebral disc. Spine 19:1172–1177
Schurman DJ, Hirschman HP, Katijama BA, Moser K, Burton D (1978) Cefazolin concentration in bone and synovial fluid. J Bone Jt Surg 65A:359–362
Seifert V, Stolke D, Vogelsang H (1983) Die postoperative discitis intervertebralis lumbalis. Akt Neurol 10:161–166
Steller G, Dalicho R, Moldenhauer H (1991) Die MR-tomographie der spondylodiszitis. Röntgenpraxis 44:180–184
Szypryt EP, Hardy JG, Hinton CE, Worthington BS, Mulholland RC (1988) A comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and scintigraphic bone imaging in the diagnosis of disc space infection in an animal model. Spine 13:1042–1048
Trappe AE, Frank AM (1994) Postoperative spondylodiscitis as the cause of failed-back syndrome-clinical aspects, diagnosis, therapy. Zentralbl Neurochir 55:158–161
Tronnier V, Schneider R, Kunz U, Albert F, Oldenkott P (1992) Postoperative spondylodiscitis: results of a prospective study about the aetiology of spondylodiscitis after operation for lumbar disc herniation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 117:149–152
Van Goethem JW, Parizel PM, van den Hauwe L, Van de Kelft E, Verlooy J, De Schepper AM (2000) The value of MRI in the diagnosis of postoperative spondylodiscitis. Neuroradiology 42:580–585
Zink PM, Frank AM, Trappe AE (1989) Prophylaxis of postoperative lumbar spondylodiscitis. Neurosurg Rev 12:297–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mastronardi, L., Rychlicki, F., Tatta, C. et al. Spondylodiscitis after lumbar microdiscectomy: effectiveness of two protocols of intraoperative antibiotic prophylaxis in 1167 cases. Neurosurg Rev 28, 303–307 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-005-0404-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-005-0404-7