Abstract
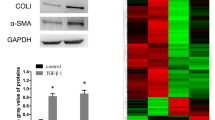
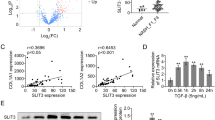
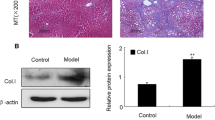
Activation of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) is the central event in liver fibrosis. NS5ATP9 is related to many malignant tumors, but little is known about its function in HSC activation. The aim of this study is to investigate the role of NS5ATP9 in HSC activation in vitro. Genes related to liver fibrosis were detected after NS5ATP9 overexpression or silencing with or without transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 stimulation in the human HSCs by real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. Cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis were tested, and the mechanisms underlying the effect of NS5ATP9 on HSC activation were studied. We showed that NS5ATP9 suppressed HSC activation and collagen production, with or without TGF-β1 induction. Also, NS5ATP9 inhibited cell proliferation and migration and promoted apoptosis. Furthermore, NS5ATP9 reduced basal and TGF-β1-mediated Smad3/phosphorylated-Smad3 expression. The existence of a physical complex between NS5ATP9 and Smad3 was illustrated. NS5ATP9 suppresses HSC activation, extracellular matrix production, and promotes apoptosis, in part through reducing Smad3/phosphorylated-Smad3 expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bataller, R., and D.A. Brenner. 2005. Liver fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115: 209–218.
Mahato, R.I., K. Cheng, and R.V. Guntaka. 2005. Modulation of gene expression by antisense and antigene oligodeoxynucleotides and small interfering RNA. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2: 3–28.
Friedman, S.L. 2008. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 134: 1655–1669.
Inagaki, Y., and I. Okazaki. 2007. Emerging insights into transforming growth factor beta Smad signal in hepatic fibrogenesis. Gut 56: 284–292.
Piek, E., C.H. Heldin, and D.P. Ten. 1999. Specificity, diversity, and regulation in TGF-beta superfamily signaling. FASEB Journal 13: 2105–2124.
Massague, J. 2000. How cells read TGF-beta signals. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 1: 169–178.
Yu, P., B. Huang, M. Shen, et al. 2001. p15(PAF), a novel PCNA associated factor with increased expression in tumor tissues. Oncogene 20: 484–489.
Shi, L., S.L. Zhang, K. Li, et al. 2008. NS5ATP9, a gene up-regulated by HCV NS5A protein. Cancer Letters 259: 192–197.
Kato, T., Y. Daigo, M. Aragaki, K. Ishikawa, M. Sato, and M. Kaji. 2012. Overexpression of KIAA0101 predicts poor prognosis in primary lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 75: 110–118.
Liu, L., X. Chen, S. Xie, C. Zhang, Z. Qiu, and F. Zhu. 2012. Variant 1 of KIAA0101, overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma, prevents doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting p53 activation. Hepatology 56: 1760–1769.
Li, K., Q. Ma, L. Shi, et al. 2008. NS5ATP9 gene regulated by NF-kappaB signal pathway. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 479: 15–9.
Mizutani, K., M. Onda, S. Asaka, et al. 2005. Overexpressed in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma-1 (OEATC-1) as a novel gene responsible for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 103: 1785–1790.
Yuan, R.H., Y.M. Jeng, H.W. Pan, et al. 2007. Overexpression of KIAA0101 predicts high stage, early tumor recurrence, and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research 13: 5368–5376.
Emanuele, M.J., A. Ciccia, A.E. Elia, and S.J. Elledge. 2011. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-associated KIAA0101/PAF15 protein is a cell cycle-regulated anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome substrate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108: 9845–9850.
Turchi, L., M. Fareh, E. Aberdam, et al. 2009. ATF3 and p15PAF are novel gatekeepers of genomic integrity upon UV stress. Cell Death and Differentiation 16: 728–737.
Quan M, Liu S, Li G, et al. 2013. A functional role for NS5ATP9 in the induction of HCV NS5A-mediated autophagy. J Viral Hepat, accepted.
Xu, L., A.Y. Hui, E. Albanis, et al. 2005. Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: new tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut 54: 142–151.
Chen, Y.L., J. Lv, X.L. Ye, et al. 2011. Sorafenib inhibits transforming growth factor beta1-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology 53: 1708–1718.
Xiao, X., Y. Gang, Y. Gu, et al. 2012. Osteopontin contributes to TGF-beta1 mediated hepatic stellate cell activation. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 57: 2883–2891.
Shimada, H., N.R. Staten, and L.E. Rajagopalan. 2011. TGF-beta1 mediated activation of Rho kinase induces TGF-beta2 and endothelin-1 expression in human hepatic stellate cells. Journal of Hepatology 54: 521–528.
Lim, J.Y., M.A. Oh, W.H. Kim, H.Y. Sohn, and S.I. Park. 2012. AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TGF-beta-induced fibrogenic responses of hepatic stellate cells by targeting transcriptional coactivator p300. Journal of Cellular Physiology 227: 1081–1089.
Krizhanovsky, V., M. Yon, R.A. Dickins, et al. 2008. Senescence of activated stellate cells limits liver fibrosis. Cell 134: 657–667.
Shi, Y., and J. Massague. 2003. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 113: 685–700.
Massague, J., and Y.G. Chen. 2000. Controlling TGF-beta signaling. Genes and Development 14: 627–644.
Jiao, J., S.L. Friedman, and C. Aloman. 2009. Hepatic fibrosis. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology 25: 223–229.
Lotersztajn, S., B. Julien, F. Teixeira-Clerc, P. Grenard, and A. Mallat. 2005. Hepatic fibrosis: molecular mechanisms and drug targets. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 45: 605–628.
Friedman, S.L. 2008. Hepatic fibrosis—overview. Toxicology 254: 120–129.
Jain, M., L. Zhang, E.E. Patterson, and E. Kebebew. 2011. KIAA0101 is overexpressed, and promotes growth and invasion in adrenal cancer. PLoS ONE 6: e26866.
Hosokawa, M., A. Takehara, K. Matsuda, et al. 2007. Oncogenic role of KIAA0101 interacting with proliferating cell nuclear antigen in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Research 67: 2568–2576.
Guo, M., J. Li, D. Wan, and J. Gu. 2006. KIAA0101 (OEACT-1), an expressionally down-regulated and growth-inhibitory gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 6: 109.
Wang, Q., Y. Wang, Y. Li, X. Gao, S. Liu, and J. Cheng. 2013. NS5ATP9 contributes to inhibition of cell proliferation by hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) via MEK/extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14: 10539–10551.
Simpson, F., K.L. Lammerts van Bueren, N. Butterfield, et al. 2006. The PCNA-associated factor KIAA0101/p15(PAF) binds the potential tumor suppressor product p33ING1b. Experimental Cell Research 312: 73–85.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Hongshan Wei and Guoli Li, Beijing Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases; Dkewr Peng Wang, Liang Zhang, Lei Sun, and Xingang Zhou, Department of Pathology, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University; and Dr. Min Li, Department of Infectious Disease, the First Affiliated Hospital of Lanzhou University, for the supportive discussions and technical assistance.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Financial Support
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81470863), the Healthy Talent Leadership Programs of Beijing (nos. 2009-1-09), and the National Key Subjects Foundation of Infectious Diseases during the Five-Year Plan Period of China (nos. 2012ZX10002003, 2013ZX10002005, and 2012ZX10004904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mengran Zhang and Jinqian Zhang contributed equally to this work
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Zhang, J., Liu, S. et al. NS5ATP9 Suppresses Activation of Human Hepatic Stellate Cells, Possibly via Inhibition of Smad3/Phosphorylated-Smad3 Expression. Inflammation 38, 278–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0031-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0031-y