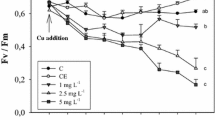
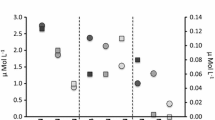
Abstract
Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) is an important organism in coastal marine waters and is highly likely to encounter exposure to multiple stressors, both anthropogenic contaminants and natural stressors. Here, we exposed eelgrass to a range of Cu concentrations and salinities, and also varied exposure route between sediment and water. Measured endpoints were Cu accumulation in root and leaves, relative growth rate, leaf mortality, chlorophyll concentration, and maximum photosynthetic quantum yield. Cu accumulation from the sediment was translocated to all parts of the plant, while Cu taken up from the water showed a tendency to remain in leaves. Effects on relative growth rate and leaf mortality were found only following uptake of Cu from the sediment. We tested effects of different salinities, acting as multiple stressors, together with Cu, but found only weak effects with little interaction with Cu. Experiments with anthropogenic contaminants that marine plants are mainly exposed to through the sediment should be done using sediment exposure, as the common practice of using only water exposure will lead to underestimation of harmful effects. Future studies should take all relevant factors into consideration, as anthropogenic inputs and natural factors are prone to fluctuations due to e.g., climate change.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert, P., 1991. Nitrogen sharing among ramets increases clonal growth in Fragaria chiloensis. Ecology 72: 69–80.
Alpert, P., 1996. Nutrient sharing in natural clonal fragments of Fragaria chiloensis. Journal of Ecology 84: 395–406.
Ambo-Rappe, R., D. L. Lajus & M. J. Schreider, 2011. Heavy metal impact on growth and leaf asymmetry of seagrass, Halophila ovalis. Journal of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology 3: 149–159.
Anonymous, 1999. Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Copper Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg.
Apel, K. & H. Hirt, 2004. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annual Review of Plant Biology 55: 373–399.
Ashraf, U., A. S. Kanu, Z. W. Mo, S. Hussain, S. A. Anjum, I. Khan, R. N. Abbas & X. R. Tang, 2015. Lead toxicity in rice: effects, mechanisms, and mitigation strategies-a mini review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22: 18318–18332.
Bloom, H. & G. M. Ayling, 1977. Heavy-metals in Derwent Estuary. Environmental Geology 2: 3–22.
Burkholder, J. M., D. A. Tomasko & B. W. Touchette, 2007. Seagrasses and eutrophication. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 46–72.
Canal-Verges, P., M. Vedel, T. Valdemarsen, E. Kristensen & M. R. Flindt, 2010. Resuspension created by bedload transport of macroalgae: implications for ecosystem functioning. Hydrobiologia 649(1): 69–76.
Corellou, F., S. R. Bisgrove, D. L. Kropf, L. Meijer, B. Kloareg & F. Y. Bouget, 2000. A S/M DNA replication checkpoint prevents nuclear and cytoplasmic events of cell division including centrosomal axis alignment and inhibits activation of cyclin-dependent kinase-like proteins in fucoid zygotes. Development 127: 1651–1660.
Denny, P., 1972. Sites of nutrient absorption in aquatic macrophytes. Journal of Ecology 60: 819–829.
Epstein, E. & A. J. Bloom, 2005. Mineral Nutrition of Plants. Principles and Perspectives. Sinauer, Sunderland.
Frederiksen, M. S., D. Krause-Jensen, M. Holmer & J. S. Laursen, 2004. Long-term changes in area distribution of eelgrass (Zostera marina) in Danish coastal waters. Aquatic Botany 78: 167–181.
Heck, K. L., G. Hays & R. J. Orth, 2003. Critical evaluation of the nursery role hypothesis for seagrass meadows. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 253: 123–136.
HELCOM, 2010. Hazardous substances in the Baltic Sea – An integrated thematic assessment of harzardous substances in the Baltic Sea Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings no 120B. Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission – Helsinki Commission, Helsinki.
Jespersen, A.-M. & K. Christoffersen, 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 109(3): 445–454.
Kupper, H., I. Setlik, M. Spiller, F. C. Kupper & O. Prasil, 2002. Heavy metal-induced inhibition of photosynthesis: targets of in vivo heavy metal chlorophyll formation. Journal of Phycology 38: 429–441.
Macinnis-Ng, C. M. O. & P. J. Ralph, 2002. Towards a more ecologically relevant assessment of the impact of heavy metals on the photosynthesis of the seagrass, Zostera capricorni. Marine Pollution Bulletin 45: 100–106.
Macinnis-Ng, C. M. O. & P. J. Ralph, 2003. In situ impact of petrochemicals on the photosynthesis of the seagrass Zostera capricorni. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46: 1395–1407.
Macinnis-Ng, C. M. O. & P. J. Ralph, 2004a. In situ impact of multiple pulses of metal and herbicide on the seagrass, Zostera capricorni. Aquatic Toxicology 67: 227–237.
Macinnis-Ng, C. M. O. & P. J. Ralph, 2004b. Variations in sensitivity to copper and zinc among three isolated populations of the seagrass, Zostera capricorni. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 302: 63–83.
Madsen, T., L. Samsøe-Petersen, K. Gustavson & D. Rasmussen, 1999. Økotoksikologisk vurdering af antibegroninghindrende biocider og biocidfrie bundmalinger. Miljøprojekt. vol nr. 507. Danish Environmental Protection Agency, Copenhagen.
Marbà, N., M. A. Hemminga, M. A. Mateo, C. M. Duarte, Y. E. M. Mass, J. Terrados & E. Gacia, 2002. Carbon and nitrogen translocations between seagrass ramets. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 226: 287–300.
Mascaró, O., T. Valdemarsen, M. Holmer, M. Pérez & J. Romero, 2009. Experimental manipulation of sediment organic content and water column aeration reduces Zostera marina (eelgrass) growth and survival. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373: 26–34.
Maxwell, K. & G. N. Johnson, 2000. Chlorophyll fluorescence – a practical guide. Journal of Experimental Botany 51: 659–668.
Meharg, A. A. & M. R. MacNair, 1992. Genetic correlation between arsenate tolerance and the rate of influx of arsenate and phosphate in Holcus lanatus L. Heredity 69: 336–341.
Monferran, M. V., J. A. S. Agudo, M. L. Pignata & D. A. Wunderlin, 2009. Copper-induced response of physiological parameters and antioxidant enzymes in the aquatic macrophyte Potamogeton pusillus. Environmental Pollution 157: 2570–2576.
Namiesnik, J. & A. Rabajczyk, 2010. The speciation and physico-chemical forms of metals in surface waters and sediments. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability 22: 1–24.
Nejrup, L. B. & M. F. Pedersen, 2008. Effects of salinity and water temperature on the ecological performance of Zostera marina. Aquatic Botany 88: 239–246.
Nielsen, H. D. & S. L. Nielsen, 2005. Photosynthetic responses to Cu2+ exposure are independent of light acclimation and uncoupled from growth inhibition in Fucus serratus (Phaeophyceae). Marine Pollution Bulletin 51: 715–721.
Nielsen, H. D. & S. L. Nielsen, 2008. Evaluation of imaging and conventional PAM as a measure of photosynthesis in thin- and thick-leaved marine macroalgae. Aquatic Biology 3: 121–131.
Nielsen, S. L., K. Sand-Jensen, J. Borum & O. Geertz-Hansen, 2002a. Depth colonization of eelgrass (Zostera marina) and macroalgae as determined by water transparency in Danish coastal waters. Estuaries 25: 1025–1032.
Nielsen, S. L., K. Sand-Jensen, J. Borum & O. Geertz-Hansen, 2002b. Phytoplankton, nutrients, and transparency in Danish coastal waters. Estuaries 25: 930–937.
Nielsen, H. D., M. T. Brown & C. Brownlee, 2003. Cellular responses of developing Fucus serratus embryos exposed to elevated concentrations of Cu2+. Plant, Cell and Environment 26: 1737–1747.
Orth, R. J., T. J. B. Carruthers, W. C. Dennison, C. M. Duarte, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F. T. Short, M. Waycott & S. L. Williams, 2006. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56: 987–996.
Pedersen, M. F. & J. Borum, 1993. An annual nitrogen budget for a seagrass Zostera marina population. Marine Ecology Progress Series 101: 169–177.
Riemann, B., J. Carstensen, K. Dahl, H. Fossing, J. Hansen, H. Jakobsen, A. Josefson, D. Krause-Jensen, S. Markager, P. Stæhr, K. Timmermann, J. Windolf & J. Andersen, 2016. Recovery of Danish coastal ecosystems after reductions in nutrient loading: a holistic ecosystem approach. Estuaries and Coasts 39: 82–97.
Rigollet, V., T. Laugier, M. L. de Casabianca, A. Sfriso & A. Marcomini, 1998. Seasonal biomass and nutrient dynamics of Zostera marina L. in two Mediterranean lagoons: Thau (France) and Venice (Italy). Botanica Marina 41(2):167–179.
Salo, T. & M. F. Pedersen, 2014. Synergistic effects of altered salinity and temperature on estuarine eelgrass (Zostera marina) seedlings and clonal shoots. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 457: 143–150.
Salo, T., M. F. Pedersen & C. Bostrom, 2014. Population specific salinity tolerance in eelgrass (Zostera marina). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 461: 425–429.
Sand-Jensen, K., 1975. Biomass, net production and growth dynamics in an eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) population in Vellerup Vig, Denmark. Ophelia 14: 185–201.
Sanz-Lazaro, C., P. Malea, E. T. Apostolaki, I. Kalantzi, A. Marin & I. Karakassis, 2012. The role of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica in the cycling of trace elements. Biogeosciences 9: 2497–2507.
Schroder, W. P., J. B. Arellano, T. Bittner, M. Baron, H. J. Eckert & G. Renger, 1994. Flash-induced absorption-spectroscopy studies of copper interaction with photosystem-II in higher-plants. Journal of Biological Chemistry 269: 32865–32870.
Thomas, G., H. J. Stark, G. Wellenreuther, B. C. Dickinson & H. Kupper, 2013. Effects of nanomolar copper on water plants-Comparison of biochemical and biophysical mechanisms of deficiency and sublethal toxicity under environmentally relevant conditions. Aquatic Toxicology 140: 27–36.
Turley, P. A., R. J. Fenn & J. C. Ritter, 2000. Pyrithiones as antifoulants: environmental chemistry and preliminary risk assessment. Biofouling 15: 175–182.
Valdemarsen, T., P. Canal-Vergés, E. Kristensen, M. Holmer, M. D. Kristiansen & M. R. Flindt, 2010. Vulnerability of Zostera marina seedlings to physical stress. Marine Ecology Progress Series 418: 119–130.
Valdemarsen, T., C. O. Quintana, E. Kristensen & M. R. Flindt, 2014. Recovery of organic-enriched sediments through microbial degradation: implications for eutrophic estuaries. Marine Ecology Progress Series 503: 41–58.
van der Heide, T., E. H. van Nes, M. M. van Katwijk, H. Olff & A. J. P. Smolders, 2011. Positive feedbacks in seagrass ecosystems – evidence from large-scale empirical data. PLoS One 6(1): e16504.
Vanderkooij, L. A., D. Vandemeent, C. J. Vanleeuwen & W. A. Bruggeman, 1991. Deriving quality criteria for water and sediment from the results of aquatic toxicity tests and product standards – application of the equilibrium partitioning method. Water Research 25: 697–705.
Villazan, B., T. Salo, F. G. Brun, J. J. Vergara & M. F. Pedersen, 2015. High ammonium availability amplifies the adverse effect of low salinity on eelgrass Zostera marina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 536: 149–162.
Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short & S. L. Williams, 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106: 12377–12381.
Yang, Q., L. H. Wang, Q. Zhou & X. H. Huang, 2015. Toxic effects of heavy metal terbium ion on the composition and functions of cell membrane in horseradish roots. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 111: 48–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: André Padial
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nielsen, S.L., Banta, G.T., Khan, F.R. et al. Copper in the sediment: a major stressor for eelgrass, Zostera marina L.. Hydrobiologia 788, 143–155 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2994-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2994-1