Abstract
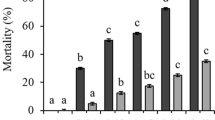
Cyanobacteria often have a deleterious effect on zooplankton. We hypothesized that the presence of either M. aeruginosa cells or microcystin extracts from M. aeruginosa would have a significant impact on the population growth rate, survivorship, and fecundity of Moina cf. micrura isolated from L’Albufera, Valencia, Spain. The cladocerans were exposed to different concentrations of Microcystis extracts on a diet of Nannochloris oculata (Chlorococcales) as well as different proportions of Microcystis single cells and N. oculata. Cyanotoxins were extracted from a Microcystis bloom by its repeated freezing, thawing, and sonication. Total microcystin concentration was 138.2 µg l−1. M. aeruginosa single cells were obtained by sonication. We used five microcystin concentrations (from 4.3 to 69.1 µg l−1 and controls without microcystins) with non-toxic Nannochloris oculata at 0.5 × 106 cells ml−1 as diet or on different proportions of M. aeruginosa single cells and N. oculata. Microcystin reduced generation time and longevity of M. cf. micrura but increased daily production of offspring. Single-celled Microcystis (100%) diet for Moina cf. micrura decreased growth rates compared with treatments using cyanotoxin extracts. We suggest routine testing of cyanobacterial crude extracts using plankton to estimate harmful impacts of blooms especially for drinking water reservoirs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, M. K., A. Zitt, D. Bagchi, J. Weckesser, S. N. Bagchi & E. von Elert, 2005a. Characterization of proteases in guts of Daphnia magna and their inhibition by Microcystis aeruginosa. Environmental Toxicology 20: 314–322.
Agrawal, M. K., D. Bagchi & S. N. Bagchi, 2005b. Acute inhibition of protease and suppression of growth in zooplankter, Moina macrocopa, by Microcystis blooms collected in Central India. Hydrobiologia 464: 37–44.
Alillo-Sanchez, J. L., M. Gaytan-Herrera, V. Martínez-Almeida & P. Ramírez-García, 2014. Microcystin-LR equivalents and their correlation with Anabaena spp. in the main reservoir of a hydraulic system of Central Mexico. Inland Waters 4: 327–336.
Baird, D. J., I. B. M. Bradley, A. M. V. M. Soares & P. Calow, 1991. A comparative study of genotype sensitivity to acute toxic stress using clones of Daphnia magna Straus. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 21: 257–265.
Bednarska, A., B. Pietrzak & J. Pijanowska, 2014. Effect of poor manageability and low nutritional value of cyanobacteria on Daphnia magna life history performance. Journal of Plankton Research 36: 838–847.
Benider, A., A. Tifnouti & R. Pourriot, 2002. Growth of Moina macrocopa (Straus 1820) (Crustacea, Cladocera): influence of trophic conditions, population density and temperature. Hydrobiologia 468: 1–11.
Berry, J. P. & O. Lind, 2010. First evidence of “paralytic shellfish toxins” and cylindrospermopsin in a Mexican freshwater system, Lago Catemaco, and apparent bioaccumulation of the toxins in “tegogolo” snails (Pomacea patula catemacensis). Toxicon 55: 930–938.
Berry, J. P., E. Lee, K. Walton, A. E. Wilson & F. Bernal-Brooks, 2011. Bioaccumulation of microcystins by fish associated with a persistent cyanobacterial bloom in Lago de Patzcuaro (Michoacán, Mexico). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 30: 1621–1628.
Bigham, D. L., M. V. Hoyer & D. E. Canfield Jr, 2009. Survey of toxic algal (microcystin) distribution in Florida lakes. Lake and Reservoir Management 25: 264–275.
Boersma, M., P. Spaak & L. De Meester, 1998. Predator-mediated plasticity in morphology, life-history and behavior of Daphnia: the uncoupling of responses. The American Naturalist 152: 237–248.
Borowitzka, M. A. & L. J. Borowitzka, 1988. Micro-algal Biotechnology. Cambridge University Press, London.
Bossuyt, B. & C. R. Janssen, 2005. Copper toxicity to different field-collected cladoceran species: intra- and inter-species sensitivity. Environmental Pollution 136: 145–154.
Carmichael, W. W., 1997. The cyanotoxins. Advances in Botanical Research 27: 211–256.
Chen, F., X. Dai, T. Shu, R. D. Gulati & Z. Liu, 2013. Microcystins derived from lysing Microcystis cells do not cause negative effects on crustacean zooplankton in Lake Taihu, China. Aquatic Ecology 47: 379–387.
Chorus, I., 2005. Current approaches to cyanotoxin risk assessment, risk management and regulations in different countries. Federal Environmental Agency. http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/current-approaches-to-cyanotoxin-risk-assessment-0
Davis, T. W., D. L. Berry, G. L. Boyer & C. J. Gobler, 2009. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 8: 715–725.
Dodson, S. I. & D. G. Frey, 2001. Cladocera and other Branchiopoda. In Thorp, J. H. & A. P. Covich (eds), Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates. Academic Press, New York: 849–913.
Dow, C. S. & U. K. Swoboda, 2002. Cyanotoxins. In Whitton, B. A. & M. Potts (eds), The Ecology of Cyanobacteria. Springer, Dordrecht: 613–632.
Duy, T. N., P. K. S. Lam, G. R. Shaw & D. W. Connell, 2000. Toxicology and risk assessment of freshwater cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in water. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 163: 113–185.
Ebert, D. & J. Jacobs, 1991. Differences in life-history and aging in two clonal groups of Daphnia cucullata Sars (Crustacea:Cladocera). Hydrobiologia 225: 245–253.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S. & S. M. F. O. Azevedo, 2003. Effects of unicellular and colonial forms of toxic Microcystis aeruginosa from laboratory cultures and natural populations on tropical cladocerans. Aquatic Ecology 37: 23–35.
Ferrão-Filho, A. S. & B. Kozlowsky-Suzuki, 2011. Cyanotoxins: bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Marine Drugs 9: 2729–2772.
Freitas, E. C., L. B. Printes & O. Rocha, 2014a. Acute effects of Anabaena spiroides extract and paraoxon-methyl on freshwater cladocerans from tropical and temperate regions: links between the ChE activity and survival and its implications for tropical ecotoxicological studies. Aquatic Toxicology 146: 105–114.
Freitas, E. C., C. Pinheiro, O. Rocha & S. Loureiro, 2014b. Can mixtures of cyanotoxins represent a risk to the zooplankton? The case study of Daphnia magna Straus exposed to hepatotoxic and neurotoxic cyanobacterial extracts. Harmful Algae 31: 143–152.
Gilbert, J. J., 1996. Effect of temperature on the response of planktonic rotifers to a toxic cyanobacterium. Ecology 77: 1174–1180.
Hairston Jr, N. G., W. Lampert, C. E. Cáceres, C. L. Holtmeier, L. J. Weider, U. Gaedke, J. M. Fischer, J. A. Fox & D. M. Post, 1999. Rapid evolution revealed by dormant eggs. Nature 446(401): 231.
Haney, J. F., J. J. Sasner & M. Ikawa, 1995. Effects of products released by Aphanizomenon flos-aquae and purified saxitoxin on the movements of Daphnia carinata feeding appendages. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 263–272.
Hardy, E. R. & A. Duncan, 1994. Food concentration and temperature effects on life cycle characteristics of tropical cladocera (Daphnia gessneri Herbst, Diaphanosoma sarsii Richard, Moina reticulata (Daday)): I Development time. Acta Amazonica 24: 119–134.
Harper, D., 1992. Eutrophication of Freshwaters: Principles. Problems and Restoration. Chapman & Hall, London.
Herrera, N. A., L. A. Echeverri & A. S. Ferrao-Filho, 2015. Effects of phytoplankton extracts containing the toxin microcystin-LR on the survival and reproduction of cladocerans. Toxicon 95: 38–45.
Hietala, J., C. Lauron-Maatta & M. Walls, 1997. Life history responses of Daphnia clones to toxic Microcystis at different food levels. Journal of Plankton Research 19: 917–926.
Jacoby, J. M., D. C. Collier, E. B. Welch, F. J. Hardy & M. Crayton, 2000. Environmental factors associated with a toxic bloom of Microcystis aeruginosa. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 57: 231–240.
Krebs, C. J., 2009. Ecology. The Experimental Analysis of Distribution and Abundance, 6th ed. Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco.
Lahti, K., J. Rapala, M. Fardig, M. Niemelx & K. Sivonen, 1997. Persistence of cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, microcystin-lr in particulate material and dissolved in lake water. Water Research 3: 1005–1012.
Lampert, W., 1987. Laboratory studies on zooplankton-cyanobacteria interactions. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 483–490.
Li, M., P. N. Nkrumah & M. Xiao, 2014. Biochemical composition of Microcystis aeruginosa related to specific growth rate: insight into the effects of abiotic factors. Inland Waters 4: 357–362.
Lopes, I., M. Moreira-Santos, J. Rendón-von Osten, D. J. Baird, A. M. V. M. Soares & R. Ribeiro, 2011. Suitability of five cladoceran species from Mexico for in situ experimentation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 74: 111–116.
Miracle, M. R. & M. Serra, 1989. Salinity and temperature influence in rotifer life history characteristics. Hydrobiologia 186(187): 81–102.
Müller, J. P., D. Laloi, C. Yepremian, C. Bernard & F. D. Hulot, 2013. To flee or not to flee: detection, avoidance of and attraction to food resources by Daphnia magna studied with an olfactometer. Journal of Limnology 72: 464–472.
Nandini, S. & S. S. S. Sarma, 2003. Population growth of some genera of cladocerans (Cladocera) in relation to algal food (Chlorella vulgaris) levels. Hydrobiologia 491: 211–219.
Nogueira, I. C. G., M. L. Saker, S. Pflugmacher, C. Wiegand & V. M. Vasconcelos, 2004. Toxicity of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii to Daphnia magna. Environmental Toxicology 19: 453–459.
Okumura, D., R. Sotero-Santos, R. Takenaka-Akemi & O. Rocha, 2007. Evaluation of cyanobacteria toxicity in tropical reservoirs using crude extracts bioassay with cladocerans. Ecotoxicology 16: 263–270.
Olvera-Ramírez, R., C. Centeno-Ramos & F. Martínez-Jerónimo, 2010. Toxic effects of Pseudanabaena tenuis (Cyanobacteria) on the cladocerans Daphnia magna and Ceriodaphnia dubia. Hidrobiológica 20: 203–212.
Paerl, H. W. & T. G. Otten, 2013. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microbial Ecology 65: 995–1010.
Pagano, M., L. Saint-Jean, R. Arfi, M. Bouvy & H. Shep, 2000. Population growth capacities and regulatory factors in monospecific cultures of the cladocerans Moina micrura and Diaphanosoma excisum and the copepod Thermocyclops decipiens from Côte d’Ivoire (West Africa). Aquatic Living Resources 13: 163–172.
Pal, D., I. Khozin-Goldberg, Z. Cohen & S. Boussiba, 2011. The effect of light, salinity, and nitrogen availability on lipid production by Nannochloropsis sp. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 90: 1429–1441.
Paul, V. J., 2008. Global warming and cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 619: 239–257.
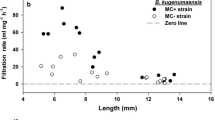
Pérez-Morales, A., S. S. S. Sarma & S. Nandini, 2014. Feeding and filtration rates of zooplankton (rotifers and cladocerans) fed toxic cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa). Journal of Environmental Biology 35: 1013–1020.
Petrusek, A., M. Černý & E. Audenaert, 2004. Large intercontinental differentiation of Moina micrura (Crustacea: Anomopoda): one less cosmopolitan cladoceran? Hydrobiologia 526: 73–81.
Pietsch, C., C. Wiegand, M. V. Ame, A. Nicklisch, D. Wunderlin & S. Pflugmacher, 2001. The effects of a cyanobacterial crude extract on different aquatic organisms: Evidence for cyanobacterial toxin modulating factors. Environmental Toxicology 16: 535–542.
Pineda-Mendoza, R. M., R. Olvera-Ramírez & F. Martínez-Jerónimo, 2012. Microcystins produced by filamentous cyanobacteria in urban lakes. A case study in Mexico City. Hidrobiológica 22: 290–298.
Rohrlack, T., M. Henning & J. G. Kohl, 1999. Mechanisms of the inhibitory effect of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on Daphnia galeata’s ingestion rate. Journal of Plankton Research 41: 1489–1500.
Romo, S., F. Fernández, Y. Ouahid & A. Barón-Sola, 2012. Assessment of microcystins in lake water and fish (Mugilidae, Liza sp.) in the largest Spanish coastal lake. Environmental Monitoring Assessment 184: 939–949.
Romo, S., J. Soria, F. Fernández & A. Barón-Solá, 2013. Water residence time and the dynamics of toxic cyanobacteria. Freshwater Biology 58: 513–522.
Romo, S., M. J. Villena, M. Sahuquillo, J. M. Soria, M. Gimenez, T. Alfonso, E. Vicente & M. R. Miracle, 2005. Response of a shallow Mediterranean lake to nutrient diversion: does it follow similar patterns as in northern shallow lakes? Freshwater Biology 50: 1706–1717.
Rouhiainen, L., T. Vakkilainen, B. L. Siemer, W. Buikema, R. Haselkorn & K. Sivonen, 2004. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70: 686–692.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Sipaúba-Tavares, L. H. & M. A. Bachion, 2002. Population growth and development of two species of Cladocera, Moina micrura and Diaphanosoma birgei, in laboratory. Brazilian Journal of Biology 62: 701–711.
Sotero-Santos, R. B., E. G. Carvalho, M. J. Dellamano-Oliveira & O. Rocha, 2008. Occurrence and toxicity an Anabaena bloom in a tropical reservoir (Southeast Brazil). Harmful Algae 7: 590–598.
Vicente, E. & M. R. Miracle, 1992. The coastal lagoon Albufera de Valencia: an ecosystem under stress. Limnetica 8: 87–100.
Weber, C. I., 1993. Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms. 4th ed. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Cincinnati, Ohio, EPA/600/4-90/027F.
Wilson, A. E., O. Sarnelle & A. R. Tillmanns, 2006. Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: Meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 1915–1924.
Work, K. A. & K. E. Havens, 2003. Zooplankton grazing on bacteria and cyanobacteria in a eutrophic lake. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 1301–1306.
Zadereev, Y. S., 2003. Maternal effects, conspecific chemical cues, and switching from parthenogenesis to gametogenesis in the cladoceran Moina macrocopa. Aquatic Ecology 37: 251–255.
Zamora Barrios, C. A., S. Nandini & S. S. S. Sarma, 2015. Effect of crude extracts of Dolichospermum planctonicum on the demography of Plationus patulus (Rotifera) and Ceriodaphnia cornuta (Cladocera). Ecotoxicology 24: 85–93.
Zhang, Y., X. Gu, G. Zhu & J. He, 2007. Experimental biological approach to the effects of Microcystis on some cladoceran population in Lake Taihu. Hupo Kexue (Journal of Lake Science) 19: 566–571.
Acknowledgments
We thank Adam Petrusek and two anonymous reviewers for their detailed suggestions which helped improve the manuscript. This study was supported by a short stay grant from University of Valencia and PASPA, UNAM, Mexico support to SN and SSSS as well as by the Spanish I + D project DGICT CGL2009-12229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Adam Petrusek & Piet Spaak / Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Cladocera
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nandini, S., Miracle, M.R., Vicente, E. et al. Microcystis extracts and single cells have differential impacts on the demography of cladocerans: a case study on Moina cf. micrura isolated from the Mediterranean coastal shallow lake (L’Albufera, Spain). Hydrobiologia 798, 127–139 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2665-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2665-2