Abstract
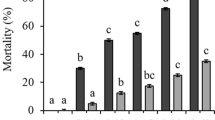
During a cyanobacterial bloom in a eutrophic environment, particularly at the end when decomposition occurs, toxic compounds such as the cyanotoxins and the lipopolysaccharides can be released in high concentrations into the water column damaging aquatic organisms. In this work, the effects of this release of toxic compounds during a cyanobacterial bloom were investigated. The acute and chronic toxicity of cyanobacterial crude extracts from two natural blooms in the Barra Bonita and Ibitinga reservoirs (Middle Tietê River, São Paulo State, Brazil) and of a toxic strain cultured in the laboratory were tested. The cladocerans Daphnia similis, Ceriodaphnia dubia and Ceriodaphnia silvestrii were used as test organisms. In the chronic toxicity tests, only a native cladoceran found in Brazilian freshwaters, Ceriodaphnia silvestrii, was used. Microcystins were detected in all cyanobacterial samples. The acute toxicity tests showed that the crude bloom material extract from the Ibitinga Reservoir (48-h EC50 values between 32.6 and 35.8 μg microcystin g−1 of freeze-dried material) exhibited higher toxicity to cladoceran than did the crude bloom material extract from Barra Bonita Reservoir (48-h EC50 values between 46.0 and 80.2 μg microcystin g−1 of freeze-dried material). The chronic toxicity test data showed that the three extracts reduced the fecundity of C. silvestrii, and the crude extract of Barra Bonita Reservoir bloom material also affected the survival of this cladoceran. Both acute and chronic tests effectively prognosticated possible changes in the cladoceran population, and probably other components of the biota due to cyanobacterial blooms in natural aquatic ecosystems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (ABNT) (2003) NBR 13373: Ecotoxicologia aquática—Toxicidade crônica—Método de ensaio com Ceriodaphnia spp (Cladocera, Crustacea). Rio de Janeiro, 12 p
Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (ABNT) (2004) NBR 12713: Ecotoxicologia aquática—Toxicidade aguda—Método de ensaio com Daphnia spp (Cladocera, Crustacea). Rio de Janeiro, 21 p
Aboal M, Puig MA (2005) Intracellular and dissolved microcystin in reservoirs of the river Segura basin, Murcia, SE Spain. Toxicon 45:509–518
Araújo R, Botta-Paschoal CMR, Silvério PF, Almeida FV, Rodrigues PF, Umbuzeiro GA, Jardim WF, Mozeto AA (2006) Application of toxicity identification evaluation to sediment in a highly contaminated water reservoir in southeastern Brazil. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:581–588
Bartram J, Carmichael WW, Chorus I, Jones G, Skulberg OM (1999) Introduction. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in water—A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. E & FN Spon, London, pp 1–13
Calijuri MC, Dos-Santos ACA, Jati S (2002) Temporal changes in the phytoplankton community structure in a tropical and eutrophic reservoir (Barra Bonita, SP—Brazil). J Plankton Res 4:617–634
Codd GA, Bell SG (1985) Eutrophication and toxic cyanobacteria in freshwaters. J Water Pollut Control 34:225–232
Chu FS, Huang X, Wei RD (1990) Enzyme-linked immunosorbentd assay for microcystins in the blue–green algal blooms. J Assoc Offic Anal Chem 73:451–456
DeMott WR, Zhang Q, Carmichael WW (1991) Effects of toxic cyanobacteria and purified toxins on survival and feeding of a copepod and three species of Daphnia. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1346–1357
Dietrich D, Hoeger S (2005) Guidance values for microcystins in water and cyanobacterial supplement products (blue–green algal supplements): a reasonable or misguided approach? Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:273–289
Domingos P, Rubim TK, Molica RJR, Azevedo SMFO, Carmichael WW (1998) First report of Microcystin production by picoplanktonic cyanobacteria isolalated from a northeasth brasilian drinking water supply. Environ Toxicol 14:31–35
Environment Canada (1990a). Biological test methods: acute lethality test using the Daphnia spp. Report EPS 1/RM/11 Environmental Canada Conservation and Protection, Ottawa, Ontario
Environment Canada (1990b). Biological test methods: reference method for determining acute lethality test of effluents to Daphnia magna Report EPS 1/RM/14 Environmental Canada, Conservation and Protection, Ottawa, Ontario
Fracácio R, Verani NF, Espíndola ELG, Rocha O, Rigolin-Sá O, Andrade CA (2003) Alterations on growth and gill morphology of Danio rerio (Pisces, Ciprinidae) exposed to the toxic sediments. Braz Arch Biol Techn 46:685–695
Gilbert JJ (1990) Differential effects of Anabaena affinis on cladocerans and rotifers: mechanisms and implications for zooplankton community structure. Ecology 71:1727–1740
Gorham PR, McLachlan J, Hammer UT, Dim WK (1964) Isolation and culture of toxic strain of Anabaena flos-aquae (Lyngb.) de Bréb. Verh Int Ver Limnol 15:796–804
Gulley DD, Boetter AM and Bergman HL (1991). TOXSTAT 3.3, Computer Program
Guo N, Xie P (2006) Development of tolerance against toxic Microcystis aeruginosa in three cladocerans and the ecological implications. Environ Pollut 143:513–518
Gustafsson S, Hansson LA (2004) Development of tolerance against toxic cyanobacteria in Daphnia. Aquat Ecology 38:37–44
Hamilton MA, Russo RC, Thurfton RB (1977) Trimmed Spearman-Karber methods for estimating median lethal concentration in toxicity bioassay. Environ Sci Technol 11:714–719
Hanazato T (2000) Toxic cyanobacteria and the zooplankton community. In: Watanabe MF, Harada K, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (eds) Toxic Microcystis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 79–98
Hitzfeld B, Lampert C, Spaeth N, Mountfort D, Kaspar H, Dietrich D (2000) Toxin production in cyanobacterial mats from ponds on the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Toxicon 38:1731–1748
Komárek J, Komárková-Legnerová J, Sant’anna CL, Azevedo MTP, Senna PAC (2002) Two common Microcystis species (Chroococcales, Cyanobacteria) from tropical America, including M. panniformis sp. nov. Crytogamie Algol 23:159–177
Lampert W (1981) Inhibitory and toxic effects of blue–green algae on Daphnia. Int Rev der ges Hydrobiol 66:285–298
Oberemm A, Becker J, Codd GA, Steinberg C (1999) Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and aqueous crude extracts of cyanobacteria on the development of fish and amphibians. Environ Toxicol 14:77–88
Oliveira ACP, Magalhães VF, Soares RM, Azevedo SMFO (2005) Influence of drinking water composition on quantitation and biological activity of dissolved microcystin (cyanotoxin). Environ Toxicol 20:126–130
Pietsch C, Wiegand C, Amé MV, Nicklisch A, Wunderlin D, Pflugmacher S (2001) The effects of a cyanobacterial crude extract on different aquatic organisms: evidence for cyanobacterial toxin modulating factors. Environ Toxicol 16:535–542
Pouria S, de Andrade A, Barbosa J, Cavalcanti R, Barreto V, Ward C, Preiser W, Poon G, Neild G, Codd G (1998) Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 352:21–26
Reinikainen M, Ketola M, Jantunen M, Walls M (1995) Effects of Microcystis aeruginosa exposure and nutritional status on reproduction of Daphnia pulex. J Plankton Res 17:431–436
Rocha O, Matsumura-Tundisi T, Sampaio EV (1997) Phytoplankton and zooplankton community structure and production as related to trophic state in some Brazilian lakes and reservoirs. Vehr Int Verein Limnol Stuttgart 26:599–604
Rohrlack T, Christoffersen K, Hansen PE, Zhang W, Zarnecki O, Henning M, Fastner J, Erhard M, Neilan BA, Kaebernick M (2003) Isolation, characterization, and quantitative analysis of Microviridin J, a new Microcystis metabolite toxic to Daphnia. J Chem Ecol 29:1757–1770
Soares RM, Magalhães VF, Azevedo SMFO (2004) Accumulation and depuration of microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) in Tilapia rendalli (Cichlidae) under laboratory conditions. Aquat Toxicol 70:1–10
Silvério PF, Fonseca AL, Botta-Paschoal CMR, Mozeto AA (2005) Release, bioavailability and toxicity of metals in lacustrine sediments: A case study of reservoirs and lakes in Southeast Brazil. Aquat Ecosyst Health Manage 8:313–122
Sivonen K, Jones G (1999) Cyanobacterial toxins. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in water–A guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. E & FN Spon, London, pp 41–91
Sotero-Santos RB, Souza e Silva CR, Verani NF, Nonaka KO, Rocha O (2006) Toxicity of a cyanobacteria bloom in Barra Bonita Reservoir (Middle Tietê River, São Paulo, Brazil). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 64:163–170
Thostrup L, Christoffersen K (1999) Accumulation of microcystin in Daphnia magna feeding on toxic Microcystis. Arch Hydrobiol 145:447–467
Törökne AK, Laszlo E, Chorus I, Sivonen K, Barbosa FAR (2000) Cyanobacterial toxins detected by Thamnotoxkit: a double blind experiment. Environ Toxicol 15:549–553
Tundisi TM, Tundisi JG, Rocha O (2002) Zooplankton diversity in eutrophic systems and its relation to the occurrence of cyanophycean blooms. Verh Internat Verein Limnol Stuttgart 26:671–674
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1993). Methods for estimating the chronic toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater organisms. EPA 600/4—91/002
Wynn-Williams DD (2000) Cyanobacteria in the Deserts–Life at the Limit? In: Whitton BA, Potts M (eds) The Ecology of Cyanobacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 341–366
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (Processos 03/00352-2, 01/13213-5 and 02/08341-7) for financial support and fellowships during the course of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okumura, D.T., Sotero-Santos, R.B., Takenaka, R.A. et al. Evaluation of cyanobacteria toxicity in tropical reservoirs using crude extracts bioassay with cladocerans. Ecotoxicology 16, 263–270 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0126-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0126-9