Abstract
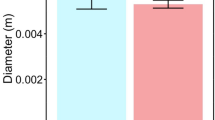
Two salt-sensitive (Yongliang-15, GS-6058) and two salt-tolerant (JS-7, Xinchun-31) wheat cultivars were used to investigate the extension, extensibility (viscoelastic parameters), and chemical composition of the cell walls in their root elongation regions (apical 10 mm-long root segments), under salinity stress. The elasticity of the root cell wall, indicated by E0, significantly decreased in the salt-sensitive cultivars, whereas the E0 in the salt-tolerant cultivars was maintained at the same level as that in the non-saline condition. Root extension and the differences among cultivars were largely dependent on elastic extension, which accounts for one-half to two-thirds of the total extension. Viscosity, indicated by η0, and the plastic extension of the root cell walls did not change across the treatments and cultivars. The significant decrease in cell wall elasticity in the root elongation region was one of the factors that depressed root growth in salt-sensitive cultivars under the saline condition. The well-maintained elasticity of salt-tolerant cultivars alleviated the depression of root growth by NaCl. Cell wall elasticity was positively correlated with the relative pectin and hemicellulose I contents and negatively correlated with the relative cellulose content. Under saline conditions, the relative hemicellulose II content did not change in the salt-sensitive cultivars; however, it decreased in the salt-tolerant ones. Thus, changes in chemical composition of the cell wall were correspond with the cell wall extensibility and root growth in wheat cultivars with different degrees of salt tolerance.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Al-Yasi H, Attia H, Alamer K et al (2020) Impact of drought on growth, photosynthesis, osmotic adjustment, and cell wall elasticity in Damask rose. Plant Physiol Biochem 150:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.038
An P, Li X, Zheng Y et al (2014a) Effects of NaCl on root growth and cell wall composition of two soya bean cultivars with contrasting salt tolerance. J Agron Crop Sci 200:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12060
An P, Li X, Zheng Y et al (2014b) Calcium effects on root cell wall composition and ion contents in two soybean cultivars under salinity stress. Can J Plant Sci 94:733–740. https://doi.org/10.4141/CJPS2013-291
Aslan D, Zencırcı N, Etöz M et al (2016) Bread wheat responds salt stress better than einkorn wheat does during germination. Turkish J Agric For 40:783–794. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1604-59
Barbez E, Dünser K, Gaidora A et al (2017) Auxin steers root cell expansion via apoplastic pH regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E4884–E4893. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1613499114
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54:484–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1
Boudaoud A (2010) An introduction to the mechanics of morphogenesis for plant biologists. Trends Plant Sci 15:353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.04.002
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y et al (2020) TBtools - an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Colzi I, Arnetoli M, Gallo A et al (2012) Copper tolerance strategies involving the root cell wall pectins in Silene paradoxa L. Environ Exp Bot 78:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.12.028
Corrêa-Ferreira ML, Viudes EB, de Magalhães PM et al (2019) Changes in the composition and structure of cell wall polysaccharides from Artemisia annua in response to salt stress. Carbohydr Res 483:107753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2019.107753
Cosgrove DJ (2018) Diffuse growth of plant cell walls. Plant Physiol 176:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01541
Dubois M, Gilles K, Hamilton JK et al (1951) A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature 168:167–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/168167a0
Dugasa MT, Feng X, Wang NH et al (2021) Comparative transcriptome and tolerance mechanism analysis in the two contrasting wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars in response to drought and salinity stresses. Plant Growth Regul. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-021-00699-4
Fan L, Linker R, Gepstein S et al (2006) Progressive inhibition by water deficit of cell wall extensibility and growth along the elongation zone of maize roots is related to increased lignin metabolism and progressive stelar accumulation of wall phenolics. Plant Physiol 140:603–612. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.073130
Feng W, Kita D, Peaucelle A et al (2018) The FERONIA receptor kinase maintains cell-wall integrity during salt stress through Ca2+ Signaling. Curr Biol 28:666-675.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.023
Flowers TJ, Hajibagheri MA (2001) Salinity tolerance in Hordeum vulgare: Ion concentrations in root cells of cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Plant Soil 231:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010372213938
Hattori T, Inanaga S, Tanimoto E et al (2003) Silicon-induced changes in viscoelastic properties of sorghum root cell walls. Plant Cell Physiol 44:743–749. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcg090
Hongo S, Sato K, Yokoyama R, Nishitani K (2012) Demethylesterification of the primary wall by PECTIN METHYLESTERASE35 provides mechanical support to the Arabidopsis stem. Plant Cell 24:2624–2634. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099325
Hossain MT, Mori R, Soga K et al (2002) Growth promotion and an increase in cell wall extensibility by silicon in rice and some other Poaceae seedlings. J Plant Res 115:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s102650200004
Hossain MT, Soga K, Wakabayashi K, Hoson T (2015) Effects of lead toxicity on growth and cell wall extensibility in rice seedlings. Bangladesh J Bot 44:333–336. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjb.v44i2.38526
Inukai Y, Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y et al (2012) Root growth inhibiting, a rice endo-1, 4-β-D-glucanase, regulates cell wall loosening and is essential for root elongation. J Plant Growth Regul 31:373–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-011-9247-3
Iraki NM, Singh N, Bressan RA, Carpita NC (1989) Cell walls of tobacco cells and changes in composition associated with reduced growth upon adaptation to water and saline stress. Plant Physiol 91:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.91.1.48
Kaku T, Tabuchi A, Wakabayashi K et al (2002) Action of xyloglucan hydrolase within the native cell wall architecture and its effect on cell wall extensibility in azuki bean epicotyls. Plant Cell Physiol 43:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcf004
Koyro H-W (1997) Ultrastructural and physiological changes in root cells of sorghum plants (Sorghum bicolor x S sudanensis cv Sweet Sioux) induced by NaCl. In: J. Exp. Bot. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/48.3.693.
Ma JF, Shen R, Nagao S, Tanimoto E (2004) Aluminum targets elongating cells by reducing cell wall extensibility in wheat roots. Plant Cell Physiol 45:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pch060
Mahajan MM, Goyal E, Singh AK et al (2020) Shedding light on response of Triticum aestivum cv. Kharchia Local roots to long-term salinity stress through transcriptome profiling. Plant Growth Regul 90:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00565-4
Majda M, Robert S (2018) The role of auxin in cell wall expansion. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040951
Miedes E, Zarra I, Hoson T et al (2011) Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase and cell wall extensibility. J Plant Physiol 168:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.06.029
Mujeeb-Kazi A, Munns R, Rasheed A, et al (2019) Breeding strategies for structuring salinity tolerance in wheat. In: Advances in Agronomy. Academic Press Inc., pp 121–187
Naeem M, Iqbal M, Shakeel A et al (2020) Genetic basis of ion exclusion in salinity stressed wheat: implications in improving crop yield. Plant Growth Regul 92:479–496
Ogawa A, Yamauchi A (2006) Root osmotic adjustment under osmotic stress in maize seedlings 1. Transient change of growth and water relations in roots in response to osmotic stress. Plant Prod Sci 9:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.9.27
Podgórska A, Burian M, Gieczewska K et al (2017) Altered cell wall plasticity can restrict plant growth under ammonium nutrition. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01344
Renault S, Zwiazek JJ (1997) Cell wall composition and elasticity of dormant and growing white spruce (Picea glauca) seedlings. Physiol Plant 101:323–327. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb01003.x
Sadat Noori SA, McNeilly T (2000) Assessment of variability in salt tolerance based on seedling growth in Triticum durum Desf. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008749312148
Safari M, Ghanati F, Safarnejad MR, Chashmi NA (2018) The contribution of cell wall composition in the expansion of Camellia sinensis seedlings roots in response to aluminum. Planta 247:381–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2792-7
Sakurai N (1991) Cell wall functions in growth and development -a physical and chemical point of view. Bot Mag Tokyo 104:235–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02489456
Sakurai N, Tanaka S, Kuraishi S (1987) Changes in wall polysaccharides of squash (Cucurbita maxima Duch.) hypocotyls under water stress condition: I. Wall sugar composition and growth as affected by water stress. Plant Cell Physiol 28:1051–1058. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a077385
Shigeyama T, Watanabe A, Tokuchi K et al (2016) α-Xylosidase plays essential roles in xyloglucan remodelling, maintenance of cell wall integrity, and seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 67:5615–5629. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw321
Siedlecka A, Wiklund S, Péronne MA et al (2008) Pectin methyl esterase inhibits intrusive and symplastic cell growth in developing wood cells of Populus. Plant Physiol 146:554–565. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.111963
Tabuchi A, Matsumoto H (2001) Changes in cell-wall properties of wheat (Triticum aestivum) roots during aluminum-induced growth inhibition. Physiol Plant 112:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1120308.x
Tan L, Eberhard S, Pattathil S et al (2013) An Arabidopsis cell wall proteoglycan consists of pectin and arabinoxylan covalently linked to an arabinogalactan protein. Plant Cell 25:270–287. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.107334
Tanimoto E, Fujii S, Yamamoto R, Inanaga S (2000) Measurement of viscoelastic properties of root cell walls affected by low pH in lateral roots of Pisum sativum L. Plant Soil 226:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026460308158
Veselov DS, Sharipova GV, Akhiyarova GR, Kudoyarova GR (2009) Fast growth responses of barley and durum wheat plants to NaCl- and PEG-treatment: Resolving the relative contributions of water deficiency and ion toxicity. Plant Growth Regul 58:125–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-009-9359-y
Wang B, Sun Z, Yu Z (2020) Pectin degradation is an important determinant for alfalfa silage fermentation through the rescheduling of the bacterial community. Microorganisms 8(488). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040488
Wang T, Park YB, Cosgrove DJ, Hong M (2015) Cellulose-pectin spatial contacts are inherent to never-dried Arabidopsis primary cell walls: evidence from solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance. Plant Physiol 168:871–884. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00665
Wu Y, Jeong BR, Fry SC, Boyer JS (2005) Change in XET activities, cell wall extensibility and hypocotyl elongation of soybean seedlings at low water potential. Planta 220:593–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1369-4
Xiao C, Zhang T, Zheng Y et al (2016) Xyloglucan deficiency disrupts microtubule stability and cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis, altering cell growth and morphogenesis. Plant Physiol 170:234–249. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01395
Zhong H, Lauchli A (1993) Changes of cell wall composition and polymer size in primary roots of cotton seedlings under high salinity. J Exp Bot 44:773–778. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/44.4.773
Acknowledgements
This study is partially funded by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, No. 26450020.
Funding
This study is partially funded by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, No. 26450020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yang Shao designed and carried out the experiments, analyzed the results. Yang Shao and Ping An wrote the manuscript. Xiaohui Feng, Irshad Muhammad, Victoria Otie, Weiqiang Li and Yuanrun Zheng provided scientific advice, and revised the manuscript. Ping An conceived the research area and supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by wenying zhang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Y., An, P., Feng, X. et al. Differential responses of roots for varying tolerance to salinity stress in wheat with special reference to elasticity. Plant Growth Regul 94, 183–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-021-00707-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-021-00707-7