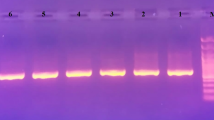
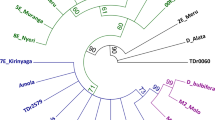
Abstract
In this study, DNA barcoding and phylogenetic analysis of five Prunus armeniaca L. genotypes (Cataloglu, Hacihaliloglu, Hasanbey, Hudayi, and Kabaasi) grown in Malatya/Türkiye were conducted using chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) matK and rbcL regions. The cpDNA matK region was amplified using matK472F and matK1248R primers, while the rbcL region was amplified with rbcLaF and rbcLaR primers. The matK and rbcL sequences were utilized to assess nucleotide ratios, genetic distance, and nucleotide diversity (π). The neighbor- joining (NJ) tree including other Prunus species from NCBI was created. In addition, physiochemical and 3-D analysis of matK and rbcL proteins were performed. As a result, π = 0.000549 for matK sequence and π = 0.002657 for rbcL sequence were determined. NJ (neighbor joining) phylogenetic trees formed with both matK and rbcL sequences were found to be compatible with each other. The matK and rbcL gene regions were found to be suitable for phylogenetic analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam NR, Hasan ME, Javed T, Rabie SM, El-Wakeel HEDM et al (2022) Endorsement and phylogenetic analysis of some Fabaceae plants based on DNA barcoding. Mol Biol Rep 49(6):5645–5657
Akbulut GB (2023) Structural modeling and functional evaluation of pectate lyase protein from Prunus armeniaca. Erwerbs-Obstbau 65(3):469–477
Asma BM, Kan T, Birhanlı O (2007) Characterization of promising apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) genetic resources in Malatya, Turkey. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:205–212
Bailey CH, Hough LF (1975) Apricots. In: Janick J, Moore JN (eds) Advances in fruit breeding. Purdue University Press, West Lafayette, pp 367–383
Beğen HA, Eminağaoğlu Ö (2022) Türkiye Rosaceae familyasına yeni cinsler (Aria, Hedlundia, Torminalis) ile taksonomik katkılar. Turk J Biodivers 5(1):36–49
CBOL Plant Working Group (2009) A DNA barcode for land plants. PNAS 31:12794–12797
Chinnkar M, Jadhav P (2023) Evaluating DNA barcoding using five loci (matK, ITS, trnH-psbA, rpoB, and rbcL) for species identification and phylogenetic analysis of Capsicum frutescens. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 11(3):97–103
Depypere L, Chaerle P, Breyne P, Mijnsbrugge KV, Goetghebeur P (2009) A combined morphometric and AFLP based diversity study challenges the taxonomy of the European members of the complex Prunus L. section Prunus. Plant Syst and Evol 279:219–231
Ehliz F, Karakurt Y, Çelik C (2021) Kayısı (Prunus armeniaca L.) Çeşitlerinin Ssr Belirteçleriyle Moleküler Karakterizasyonu. Isparta Uygulamalı Bilimler Üniv Ziraat Fak Derg 16(1):79–85
Felsenstein J (1985) Confdence limits on the phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Filiz E, Koç İ (2012) Bitkilerde DNA Barkotları (011007). Afyon Kocatepe Üniv Fen ve Mühendislik Bilimleri Derg 12(1):53–57
Filiz E, Koç İ (2014) In silico sequence analysis and homology modeling of predicted beta-amylase 7-like protein in Brachypodium distachyon L. J Bio Sci Biotech 3(1):61–67
Furan MA (2023) Species identification and germplasm conservation of origanum based on chloroplast genes. Genet Resour Crop Evolut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-023-01679-5
Gamache J, Sun G (2015) Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Pseudoroegneria and the Triticeae tribe using the rbcL gene. Biochem Syst Ecol 62:73–81
Gao Y, Yin S, Yang H, Wu L, Yan Y (2018) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of seven Amorphophallus species in southwestern China revealed by chloroplast DNA sequences. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 29(5):679–686
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud SE, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. Humana press, New Jerssy, pp 571–607
Gilani SA, Qureshi RA, Khan AM, Potter D (2010) A molecular phylogeny of selected species of genus Prunus L. (Rosaceae) from Pakistan using the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) spacer DNA. Afr J Biotechnol 9(31):4867–4872
Gilani SA, Qureshi RA, Khan M, Ullah F, Nawaz Z, Ahmad I, Potter D (2011) A molecular phylogeny of selected species of Genus Prunus L. (Rosaceae) from Pakistan using the TRN-L and TRN-F spacer DNA. Afr J Biotechnol 10(22):4550–4554
Golshani F, Fakheri BA, Solouki M, Mahdinezhad N, Feriz MRK (2020) Evolutionary and phylogenic relationships of wild and crop species of iranian saffron by DNA barcoding. Bangladesh J Bot 49(2):287–296
Gostel MR, Carlsen MM, Devine A, Barker KB, Coddington JA, Steier J (2022) Data Release: DNA barcodes of plant species collected for the global genome initiative for gardens (GGI-gardens) II. Diversity 14:234
Hall TA (1999) Bioedit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analyses program for windows 95/98/ NT. Nucleic Acids Symp 41:95–98
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, Waard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 270:313–321
Hürkan K (2020) Analysis of various DNA barcodes on the turkish protected designation of origin apricot Iğdır Kayısısı (Prunus armeniaca cv. Şalak). TURJAF 8(9):1982–1987
Inal B, Karaca M (2019) MatK ve trnh-psba barkot genleri kullanılarak bazı bitki taksonlarının moleküler olarak sınıflandırılması. Türkiye Tarımsal Araştırmalar Dergisi 6(1):87–93
Ince AG, Karaca M, Onus AN, Bilgen M (2005) Chloroplast matK gene phylogeny of some important species of plants. Akdeniz Universites Ziraat Fakultesi Dergisi 18:157–162
Jiang F, Zhang J, Wang S, Yang L, Luo Y, Gao S, Zhang M, Wu S, Hu S, Sun H, Wang Y (2019) The apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) genome elucidates Rosaceae evolution and beta-carotenoid synthesis. Hortic Res 6:1–12
Kress WJ, Erickson DL, Jones FA, Swenson NG, Perez R, Sanjur O, Bermingham E (2009) Plant DNA barcodes and a community phylogeny of a tropical forest dynamic plot in Panama. PNAS 106:18621–18626
Levin RA, Wagner WL, Hoch PC, Nepokroeff M, Pires JC, Zimmer EA et al (2003) Family-level relationships of Onagraceae based on chloroplast rbcL and ndhF data. Am J Bot 90:107–115
Li M, Zhao Z, Miao XJ (2013) Genetic variability of wild apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) populations in the Ili Valley as revealed by ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60:2293–2302
Moradi Ashour B, Rabiei M, Shiran B (2023) Intraspecific identification of some pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) genotypes based on DNA barcoding and morpho-biochemical characteristics. Trees 37:1435–1442
Nigro D, Giove SL, Colasuonno P, de Pinto R, Marcotuli I, Gadaleta A (2022) Characterization of Ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activase (Rca) genes in durum wheat. Genet Resour Crop Evol 69(6):2191–2202
Paksoy MY, Sevindik E, Başköse İ (2022) DNA barcoding and phylogenetic analysis of endemic Astragalus nezaketiae and Vicia alpestris subsp. hypoleuca (Fabaceae): evidence from nrDNA ITS and cpDNA matK and rbcL sequences. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj Napoca 50(3):12900–12900
Pang X, Song J, Zhu Y, Xu H, Huang L, Chen S (2011) Applying plant DNA barcodes for Rosaceae species identification. Cladistics 27:165–170
Penjor T, Yamamoto M, Uehara M, Ide M, Matsumoto N, Matsumoto R, Nagano Y (2013) Phylogenetic relationships of Citrus and its relatives based on matK gene sequences. PLoS ONE 8(4):e62574
Qiu Z, Zhao Y, Qian Y, Tan C, Tang C, Chen X (2023) Seed and pollen morphology in nine native Chinese species of Sorbus (Rosaceae). Int J Fruit Sci 23(1):87–101
Said EM, Hassan ME (2023) DNA barcodes in Egyptian olive cultivars (Olea europaea L.) using the rbcL and matK coding sequences. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 26:1–10
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Phylogenet Evol 4(4):406–425
Sayed HA, Mostafa S, Haggag IM, Hassan NA (2023) DNA barcoding of Prunus species collection conserved in the National Gene Bank of Egypt. Mol Biotechnol 65:410–418
Sevindik E, Murathan ZT, Sevindik M (2020) Molecular genetic diversity of Prunus armeniaca L. (Rosaceae) genotypes by RAPD, ISSR-PCR, and chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) trnL-F sequences. Int J Fruit Sci 20(sup3):S1652–S1661
Shi S, Li J, Sun J, Yu J, Zhou S (2013) Phylogeny and classification of Prunus sensu lato (Rosaceae). J Integr Plant Biol 55(11):1069–1079
Spreitzer RJ, Salvucci ME (2002) Rubisco: structure, regulatory interactions, and possibilities for a better enzyme. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53(1):449–475
Stucky BJ (2012) SeqTrace: a graphical tool for rapidly processing DNA sequencing chromatograms. J Biomol Tech: JPT 23(3):90–93
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Ulaszewski B, Jankowska-Wróblewska S, Świło K, Burczyk J (2021) Phylogeny of Maleae (Rosaceae) based on complete chloroplast genomes supports the distinction of aria, Chamaemespilus and Torminalis as separate genera, different from Sorbus sp. Plants 10:2534
Waheed A, Rehman S, Parveen B et al (2023) Assessment of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship among brinjal genotypes based on chloroplast rps 11 gene. Genet Resour Crop Evol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-023-01632-6
Wang M, Zhao HX, Wang L, Wang T, Yang RW, Wang XL, Zhang L (2013) Potential use of DNA barcoding for the identification of Salvia based on cpDNA and nrDNA sequences. Gene 528(2):206–215
Yu J, Xue JH, Zhou SL (2011) New universal matK primers for DNA barcoding angiosperms. J Syst Evol 49:176–181
Zhang D, Ren J, Jiang H, Wanga VO, Dong X, Hu G (2023) Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of six Polygonatum species (Asparagaceae). Sci Rep 13(1):7237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZTM collected plant specimens. Molecular and data analyses were done by ES and YK. The manuscript was drafted by ES, YK, ZTM and reviewed by all of the authors before submission. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sevindik, E., Korkom, Y. & Murathan, Z.T. Evaluating DNA barcoding using cpDNA matK and rbcL for species identification and phylogenetic analysis of Prunus armeniaca L. (Rosaceae) genotypes. Genet Resour Crop Evol 71, 1825–1835 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-023-01748-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-023-01748-9