Abstract
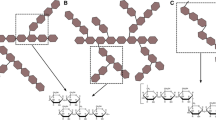
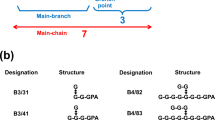
Glycogen debranching enzyme (GDE) is bifunctional in that it exhibits both 4-α-glucanotransferase and amylo-α-1,6-glucosidase activity at two distinct catalytic sites. GDE converts the phosphorylase-limit biantennary branch [G-G-G-G-(G-G-G-G↔)G-G- residue, where G = d-glucose, hyphens represent α-1,4-glycosidic bonds, and the double-headed arrow represents an α-1,6-glycosidic bond] into a linear maltooligosyl residue, which is then subjected to phosphorylase, and glycogen degradation continues. The prevailing hypothesis regarding the glycogen debranching pathway was that 4-α-glucanotransferase converts the phosphorylase-limit biantennary branch into the G-G-G-G-G-G-G-(G↔)G-G- residue and amylo-α-1,6-glucosidase cleaves the remaining α-1,6-linked G residue. In the present study, we analyzed the substrate specificities of 4-α-glucanotransferase and amylo-α-1,6-glucosidase using fluorogenic biantennary dextrins such as G-G-G-G-(G-G-G-G↔)G-G-GPA (F4/4/2; where GPA = 1-deoxy-1-[(2-pyridyl)amino]-d-glucitol), G-(G-G-G-G↔)G-G-GPA (F1/4/2), and G-G-G-G-G-G-G-(G↔)G-G-GPA (F7/1/2). Contrary to the prevailing hypothesis, the main branch of F4/4/2 was an important donor substrate component of 4-α-glucanotransferase and did not serve as an acceptor substrate. However, when G-G-G-G-G-GPA was added to the mixture, it successfully accepted a maltotriosyl (G3-) residue from F4/4/2. In addition, amylo-α-1,6-glucosidase exhibited strong activity towards G-G-G-G-(G↔)G-G-GPA but weak activity towards F7/1/2. Furthermore, the debranching activity of GDE towards phosphorylase-limit glycogen substantially increased when methyl α-maltooligosides with lengths equal to or greater than that of methyl α-maltopentaoside (G5-OCH3) were added to the enzyme reaction mixture. Based on these results, we propose the following macroscopic debranching pathway: Via 4-α-glucanotransferase, the G3- residue of the donor branch is transferred to a long (n ≥ 5) linear Gn- residue linked to a different branching G residue.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting the findings of the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Roach, P.J., Depaoli-Roach, A.A., Hurley, T.D., Tagliabracci, V.S.: Glycogen and its metabolism: some new developments and old themes. Biochem. J. 441, 763–787 (2012)
Prats, C., Graham, T.E., Shearer, J.: The dynamic life of the glycogen granule. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 7089–7098 (2018)
Berg, J.M., Tymoczko, J.L., Gatto Jr., G.J., Stryer, L.: Biochemistry (9th edition) pp. 679–707. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York (2019).
Vollhardt, K.P.C., Schore, N.E.: Organic Chemistry; Structure and Function (7th edition) pp. 1103–1110. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York (2014)
Nelson, D.L., Cox, M.M.: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (7th international edition) pp. 601–608. Macmillan Higher Education, Basingstoke (2017)
Voet, D., Voet, J.D.: Biochemistry (3rd edition) pp. 626–656. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Hoboken (2004)
Conn, E.E., Stumpf, P.K.: Outlines of Biochemistry (4th edition) pp. 279–316. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Hoboken (1976)
Papachristodoulou, D., Snape, A., Elliott, W.H., Elliott, D.C.: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (5th edition) pp. 173–190. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2014)
Melendez-Hevia, E., Waddell, T.G., Shelton, E.D.: Optimization of molecular design in the evolution of metabolism: the glycogen molecule. Biochem. J. 295, 477–483 (1993)
Sentner, C.P., Hoogeveen, I.J., Weinstein, D.A., Santer, R., Murphy, E., McKiernan, P.J., Steuerwald, U., Beauchamp, N.J., Taybert, J., Laforêt, P., Petit, F.M., Hubert, A., Labrune, P., Smit, G.P.A., Derks, T.G.J.: Glycogen storage disease type III: diagnosis, genotype, management, clinical course and outcome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 39, 697–704 (2016)
Nakayama, A., Yamamoto, K., Tabata, S.: Identification of the catalytic residues of bifunctional glycogen debranching enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 28824–28828 (2001)
Zhai, L., Feng, L., Xia, L., Yin, H., Xiang, S.: Crystal structure of glycogen debranching enzyme and insights into its catalysis and disease-causing mutations. Nat. Commun. 7, 11229 (2016)
Makino, Y., Omichi, K.: Acceptor specificity of 4-α-glucanotransferases of mammalian glycogen debranching enzymes. J. Biochem. 139, 535–541 (2006)
Yamamoto, E., Makino, Y., Omichi, K.: Active site mapping of amylo-α-1,6-glucosidase in porcine liver glycogen debranching enzyme using fluorogenic 6-O-α-glucosyl-maltooligosaccharides. J. Biochem. 141, 627–634 (2007)
Sakaguchi, M., Makino, Y., Matsubara, H.: New approach to prepare fluorogenic branched dextrins for assaying glycogen debranching enzyme. Glycoconj. J. 37, 667–679 (2020)
Fujii, Y., Makino, Y., Sato, M.: A new interpretation of sulfate activation of rabbit muscle glycogen phosphorylase. Glycoconj. J. 35, 299–309 (2018)
Hii, S.L., Tan, J.S., Ling, C.L., Ariff, A.B.: Pullulanase: role in starch hydrolysis and potential industrial applications. Enzyme Res. 921362 (2012)
Fromm, H.J.: Initial rate enzyme kinetics. pp. 1–82. Springer, Berlin (1975)
Watanabe, Y., Makino, Y., Omichi, K.: Activation of 4-α-glucanotransferase activity of porcine liver glycogen debranching enzyme with cyclodextrins. J. Biochem. 140, 135–140 (2006)
Yamamoto, E., Watanabe, Y., Makino, Y., Omichi, K.: Inspection of the activator binding site for 4-α-glucanotransferase in porcine liver glycogen debranching enzyme with fluorogenic dextrins. J. Biochem. 145, 585–590 (2009)
Taylor, C., Cox, A.J., Kernohan, J.C., Cohen, P.: Debranching enzyme from rabbit skeletal muscle: purification, properties and physiological role. Eur. J. Biochem. 51, 105–115 (1975)
Gordon, R.B., Brown, D.H., Brown, B.I.: Preparation and properties of the glycogen-debranching enzyme from rabbit liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 289, 97–107 (1972)
Gutman, A., Ben-Bassat, Y., Schramm, H., Lilling, S.: 64 assay of amylo-1,6-glucosidase-transferase activity by release of glucose from phosphorylase limit dextrin - a reassessment. Pediatr. Res. 20, 1044 (1986)
Syson, K., Stevenson, C.E.M., Miah, F., Barclay, J.E., Tang, M., Gorelik, A., Rashid, A.M., Lawson, D.M., Bornemann, S.: Ligand-bound structures and site-directed mutagenesis identify the acceptor and secondary binding sites of Streptomyces coelicolor maltosyltransferase GlgE. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 21531–21540 (2016)
Hu, X., Legler, P.M., Khavrutskii, I., Scorpio, A., Compton, J.R., Robertson, K.L., Friedlander, A.M., Wallqvist, A.: Probing the donor and acceptor substrate specificity of the γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochemistry 51, 1199–1212 (2012)
Light, S.H., Cahoon, L.A., Mahasenan, K.V., Lee, M., Boggess, B., Halavaty, A.S., Mobashery, S., Freitag, N.E., Anderson, W.F.: Transferase versus hydrolase: the role of conformational flexibility in reaction specificity. Structure. 25, 295–304 (2017)
Mili, A., Ben Charfeddine, I., Mamaï, O., Cherif, W., Adala, L., Amara, A., Pagliarani, S., Lucchiari, S., Ayadi, A., Tebib, N., Harbi, A., Bouguila, J., H’Mida, D., Saad, A., Limem, K., Comi, G.P., Gribaa, M.: Molecular and biochemical characterization of Tunisian patients with glycogen storage disease type III. J. Hum. Genet. 57, 170–175 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Takaaki Miyaji and Ms. Asako Kawakami at the Department of Genomics & Proteomics of the Advanced Science Research Center of Okayama University for performing MALDI-TOF MS on the fluorogenic biantennary dextrins.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This work does not include any studies involving humans or animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, A., Makino, Y. & Matsubara, H. Glycogen debranching pathway deduced from substrate specificity of glycogen debranching enzyme. Glycoconj J 39, 345–355 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10046-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10046-y