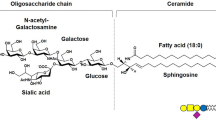
Abstract
It has been recently reported by our group that GM1-oligosaccharide added to neuroblastoma cells or administered to mouse experimental model mimics the neurotrophic and neuroprotective properties of GM1 ganglioside. In addition to this, differently from GM1, GM1-oligosaccharide is not taken up by the cells, remaining solubilized into the extracellular environment interacting with cell surface proteins. Those characteristics make GM1-oligosaccharide a good tool to study the properties of the endogenous GM1, avoiding to interfere with the ganglioside natural metabolic pathway. In this study, we show that GM1-oligosaccharide administered to mice cerebellar granule neurons by interacting with cell surface induces TrkA-MAP kinase pathway activation enhancing neuron clustering, arborization and networking. Accordingly, in the presence of GM1-oligosaccharide, neurons show a higher phosphorylation rate of FAK and Src proteins, the intracellular key regulators of neuronal motility. Moreover, treated cells express increased level of specific neuronal markers, suggesting an advanced stage of maturation compared to controls. In parallel, we found that in the presence of GM1-oligosaccharide, neurons accelerate the expression of complex gangliosides and reduce the level of the simplest ones, displaying the typical ganglioside pattern of mature neurons. Our data confirms the specific role of GM1 in neuronal differentiation and maturation, determined by its oligosaccharide portion. GM1-oligosacchairide interaction with cell surface receptors triggers the activation of intracellular biochemical pathways responsible for neuronal migration, dendrites emission and axon growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGN:
-
cerebellar granule neurons
- Ctx-B:
-
cholera toxin-subunit B
- CTRL:
-
control
- ERK1/2:
-
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- GM1:
-
II3Neu5Ac-Gg4Cer, β-Gal-(1–3)-β-GalNAc-(1–4)-[α-Neu5Ac-(2–3)]-β-Gal-(1–4)-β-Glc-Cer
- HPTLC:
-
high-performance silica gel thin-layer chromatography
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NGF:
-
nerve growth factor
- OligoGM1:
-
GM1-oligosaccharide, II3Neu5Ac-Gg4.
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- P-ERK1/2:
-
phosphorylated ERK1/2
- P-TrkA:
-
phosphorylated TrkA
- PM:
-
plasma membrane
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene difluoride
- RRID:
-
Research Resource Identifiers
- Trk:
-
neurotrophin tyrosin kinase receptor
- Tyr490:
-
tyrosine 490
References
IUPAC-IUMB JCoBN: Nomenclature of glycolipids. Carbohydr. Res. 312, 167–175 (1998)
Ledeen, R., Wu, G.: Gangliosides of the nervous system. In: Sonnino, S., Prinetti, A. (eds.) Gangliosides. Methods in Molecular Biology, pp. 19–55. Humana Press, New York (2018)
Aureli, M., Mauri, L., Ciampa, M.G., Prinetti, A., Toffano, G., Secchieri, C., Sonnino, S.: GM1 ganglioside: past studies and future potential. Mol. Neurobiol. 53, 1824–1842 (2016)
Dreyfus, H., Louis, J.C., Harth, S., Mandel, P.: Gangliosides in cultured neurons. Neuroscience. 5, 1647–1655 (1980)
Ngamukote, S., Yanagisawa, M., Ariga, T., Ando, S., Yu, R.K.: Developmental changes of glycosphingolipids and expression of glycogenes in mouse brains. J. Neurochem. 103, 2327–2341 (2007)
Svennerholm, L., Boström, K., Fredman, P., Månsson, J.E., Rosengren, B., Rynmark, B.M.: Human brain gangliosides: developmental changes from early fetal stage to advanced age. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1005, 109–117 (1989)
Sonnino, S., Mauri, L., Chigorno, V., Prinetti, A.: Gangliosides as components of lipid membrane domains. Glycobiology. 17, 1R–13R (2007)
Furukawa, K., Ohmi, Y., Ohkawa, Y., Tokuda, N., Kondo, Y., Tajima, O., Furukawa, K.: Regulatory mechanisms of nervous systems with glycosphingolipids. Neurochem. Res. 36, 1578–1586 (2011)
Sandhoff, R., Schulze, H., Sandhoff, K.: Ganglioside metabolism in health and disease. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 156, 1–62 (2018)
Ledeen, R.W., Wu, G.: The multi-tasked life of GM1 ganglioside, a true factotum of nature. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40, 407–418 (2015)
Schengrund, C.L.: Gangliosides: glycosphingolipids essential for normal neural development and function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40, 397–406 (2015)
Mocchetti, I.: Exogenous gangliosides, neuronal plasticity and repair, and the neurotrophins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 2283–2294 (2005)
Rabin, S.J., Mocchetti, I.: GM1 ganglioside activates the high-affinity nerve growth factor receptor TrkA. J. Neurochem. 65, 347–354 (1995)
Mutoh, T., Tokuda, A., Miyadai, T., Hamaguchi, M., Fujiki, N.: Ganglioside GM1 binds to the Trk proteins and regulates receptor function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 92, 5087–5091 (1995)
Schengrund, C.L., Prouty, C.: Oligosaccharide portion of GM1 enhances process formation by S20Y neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 51, 277–282 (1988)
Fantini, J., Yahi, N.: Lipid regulation of receptor function. In: Fantini, J., Yahi, N. (eds.) Brain Lipids in Synaptic Function and Neurological Disease, pp. 163–181. Elsevier, San Diego (2015)
Chiricozzi, E., Pomè, Y.D., Maggioni, M., Di Biase, E., Parravicini, C., Palazzolo, L., Loberto, N., Eberini, I., Sonnino, S.: Role of GM1 ganglioside oligosaccharide portion in the TrkA-dependent neurite sprouting in neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 143, 645–659 (2017)
Chiricozzi, E., Di Biase, E., Maggioni, M., Lunghi, G., Fazzari, M., Pomè, Y.D., Casellato, R., Loberto, N., Mauri, L., Sonnino, S.: GM1 promotes TrkA-mediated neuroblastoma cell differentiation by occupying a plasma membrane domain different from TrkA. J. Neurochem. 149, 231–241 (2019)
Chiricozzi, E., Mauri, L., Lunghi, G., Di Biase, E., Fazzari, M., Maggioni, M., Valsecchi, M., Prioni, S., Loberto, N., Pomè, D.Y., Ciampa, M.G., Fato, P., Verlengia, G., Cattaneo, S., Assini, R., Wu, G., Alselehdar, S., Ledeen, R.W., Sonnino, S.: Parkinson's disease recovery by GM1 oligosaccharide treatment in the B4galnt1+/− mouse model. Sci. Rep. 9, 19330 (2019)
Tettamanti, G., Bonali, F., Marchesini, S., Zambotti, V.: A new procedure for the extraction, purification and fractionation of brain gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 296, 160–170 (1973)
Acquotti, D., Cantu, L., Ragg, E., Sonnino, S.: Geometrical and conformational properties of ganglioside GalNAc-GD1a, IV4GalNAcIV3Neu5AcII3Neu5AcGgOse4Cer. Eur. J. Biochem. 225, 271–288 (1994)
Koul, O., Prada-Maluf, M., McCluer, R.H., Ullman, M.D.: Rapid isolation of monosialogangliosides from bovine brain gangliosides by selective-overload chromatography. J. Lipid Res. 32, 1712–1715 (1991)
Sonnino, S., Nicolini, M., Chigorno, V.: Preparation of radiolabeled gangliosides. Glycobiology. 6, 479–487 (1996)
Wiegandt, H., Bucking, H.W.: Carbohydrate components of extraneuronal gangliosides from bovine and human spleen, and bovine kidney. Eur. J. Biochem. 15, 287–292 (1970)
Chiricozzi, E., Maggioni, M., Di Biase, E., Lunghi, G., Fazzari, M., Loberto, N., Maffioli, E., Grassi Scalvini, F., Tedeschi, G., Sonnino, S.: The Neuroprotective role of the GM1 oligosaccharide, II3Neu5Ac-Gg4, in Neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 6673–6702 (2019)
Bilimoria, P. M., Bonni, A.: Cultures of cerebellar granule neurons. CSH Protoc. 2008:pdb.prot5107
Chigorno, V., Pitto, M., Cardace, G., Acquotti, D., Kirschner, G., Sonnino, S., Ghidoni, R., Tettamanti, G.: (1985) Association of gangliosides to fibroblasts in culture: a study performed with GM1 [14C]-labelled at the sialic acid acetyl group. Glycoco. J. 2, 279–291 (2008)
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-[Delta][Delta] CT method. Methods. 25, 402–408 (2001)
Cardani, S., Di Lascio, S., Belperio, D., Di Biase, E., Ceccherini, I., Benfante, R., Fornasari, D.: Desogestrel down-regulates PHOX2B and its target genes in progesterone responsive neuroblastoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 370, 671–679 (2018)
Fazzari, M., Frasca, A., Bifari, F., Landsberger, N.: Aminoglycoside drugs induce efficient read-through of CDKL5 nonsense mutations, slightly restoring its kinase activity. RNA Biol. 16, 1414–1423 (2019)
Prinetti, A., Prioni, S., Chiricozzi, E., Schuchman, E.H., Chigorno, V., Sonnino, S.: Secondary alterations of sphingolipid metabolism in lysosomal storage diseases. Neurochem. Res. 36, 1654–1668 (2011)
Chiricozzi, E., Niemer, N., Aureli, M., Magini, A., Loberto, N., Prinetti, A., Bassi, R., Polchi, A., Emiliani, C., Caillaud, C., Sonnino, S.: Chaperone therapy for GM2 gangliosidosis: effects of pyrimethamine on bhexosaminidase activity in Sandhoff fibroblasts. Mol. Neurobiol. 50, 159–167 (2014)
Samarani, M., Loberto, N., Soldà, G., Straniero, L., Asselta, R., Duga, S., Lunghi, G., Zucca, F.A., Mauri, L., Ciampa, M.G., Schiumarini, D., Bassi, R., Giussani, P., Chiricozzi, E., Prinetti, A., Aureli, M., Sonnino, S.: A lysosome-plasma membrane-sphingolipid axis linking lysosomal storage to cell growth arrest. FASEB J. 32, 5685–5702 (2018)
Malekkou, A., Samarani, M., Drousiotou, A., Votsi, C., Sonnino, S., Pantzaris, M., Chiricozzi, E., Zamba-Papanicolaou, E., Aureli, M., Loberto, N., Christodoulou, K.: Biochemical Characterization of the GBA2 c.1780G>C Missense Mutation in Lymphoblastoid Cells from Patients with Spastic Ataxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 3099 (2018)
Loberto, N., Lunghi, G., Schiumarini, D., Samarani, M., Chiricozzi, E., Aureli, M.: Methods for assay of Ganglioside catabolic enzymes. In: Sonnino, S., Prinetti, A. (eds.) Gangliosides. Methods in Molecular Biology Pp. 383–400. Humana Press, New York (2018)
Folch, J., Lees, M., Sloane Stanley, G.H.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957)
Scandroglio, F., Loberto, N., Valsecchi, M., Chigorno, V., Prinetti, A., Sonnino, S.: Thin layer chromatography of gangliosides. Glycoconj. J. 26, 961–973 (2008)
Wu, G., Ledeen, W.R.: Quantification of gangliotetraose gangliosides with cholera toxin. Anal. Biochem. 173, 368–375 (1988)
Valaperta, R., Valsecchi, M., Rocchetta, F., Aureli, M., Prioni, S., Prinetti, A., Chigorno, V., Sonnino, S.: Induction of axonal differentiation by silencing plasma membrane-associated sialidase Neu3 in neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 100, 708–719 (2007)
Chiricozzi, E., Mauri, L., Ciampa, M.G., Prinetti, A., Sonnino, S.: On the use of cholera toxin. Glycoconj. J. 35, 161–163 (2018)
Facci, L., Leon, A., Toffano, G., Sonnino, S., Ghidoni, R., Tettamanti, G.: Promotion of neuritogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells by exogenous gangliosides. Relationship between the effect and the cell association of ganglioside GM1. J Neurochem. 42, 299–305 (1984)
Kappagantula, S., Andrews, M.R., Cheah, M., Abad-Rodriguez, J., Dotti, C.G., Fawcett, J.W.: Neu3 sialidase-mediated ganglioside conversion is necessary for axon regeneration and is blocked in CNS axons. J. Neurosci. 34, 2477–2492 (2014)
Tucker, B.A., Rahimtula, M., Mearow, K.M.: Src and FAK are key early signalling intermediates required for neurite growth in NGF-responsive adult DRG neurons. Cell. Signal. 20, 241–257 (2008)
Carragher, N.O., Frame, M.C.: Focal adhesion and actin dynamics: a place where kinases and proteases meet to promote invasion. Trends Cell Biol. 14, 241–249 (2004)
Stevens, G.R., Zhang, C., Berg, M.M., Lambert, M.P., Barber, K., Cantallops, I., Routtenberg, A., Klein, W.L.: CNS neuronal focal adhesion kinase forms clusters that co-localize with vinculin. J. Neurosci. Res. 46, 445–455 (1996)
Albertinazzi, C., Gilardelli, D., Paris, S., Longhi, R., de Curtis, I.: Overexpression of a neural-specific rho family GTPase, cRac1B, selectively induces enhanced neuritogenesis and neurite branching in primary neurons. J. Cell Biol. 142, 815–825 (1998)
Corbetta, S., Gualdoni, S., Ciceri, G., Monari, M., Zuccaro, E., Tybulewicz, V.L., de Curtis, I.: Essential role of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in neuronal development. FASEB J. 23, 1347–1357 (2009)
Prinetti, A., Chigorno, V., Prioni, S., Loberto, N., Marano, N., Tettamanti, G., Sonnino, S.: Changes in the lipid turnover, composition, and organization, as sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains, in rat cerebellar granule cells developing in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 21136–21145 (2001)
Aureli, M., Samarani, M., Murdica, V., Mauri, L., Loberto, N., Bassi, R., Prinetti, A., Sonnino, S.: Gangliosides and cell surface ganglioside glycohydrolases in the nervous system. Adv Neurobiol. 9, 223–244 (2014)
Aureli, M., Loberto, N., Lanteri, P., Chigorno, V., Prinetti, A., Sonnino, S.: Cell surface sphingolipid glycohydrolases in neuronal differentiation and aging in culture. J. Neurochem. 116, 891–899 (2011)
Van Echten-Deckert, G., Herget, T.: Sphingolipid metabolism in neural cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1758, 1978–1994 (2006)
Yu, R., Ariga, T., Yanagisawa, M., Zeng, G.: Gangliosides in the nervous system: biosynthesis and degradation. In: Fraser-Reid, B.O., Tatsuta, K., Thiem, J. (eds.) Glycoscience, Pp. 1671–1695 Springer. Heidelberg, Berlin (2008)
Manev, H., Favaron, M., Vicini, S., Guidotti, A., Costa, E.: Glutamate-induced neuronal death in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells: protection by synthetic derivatives of endogenous sphingolipids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 252, 419–427 (1990)
Costa, E., Armstrong, D., Guidotti, A., Kharlamov, A., Kiedrowski, L., Wroblewski, J.T.: Ganglioside GM1 and its semisynthetic lysogangliosides reduce glutamate neurotoxicity by a novel mechanism. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 341, 129–141 (1993)
Kharlamov, A., Guidotti, A., Costa, E., Hayes, R., Armstrong, D.: Semisynthetic sphingolipids prevent protein kinase C translocation and neuronal damage in the perifocal area following a photochemically induced thrombotic brain cortical lesion. SJ Neurosci. 13, 2483–2494 (1993)
Saito, M., Saito, M., Berg, M.J., Guidotti, A., Marks, N.: Gangliosides attenuate ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Neurochem. Res. 24, 1107–1115 (1999)
Rabin, S.J., Bachis, A., Mocchetti, I.: Gangliosides activate Trk receptors by inducing the release of neurotrophins. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49466–49472 (2002)
Wu, G., Lu, Z.H., Xie, X., Ledeen, R.W.: Susceptibility of cerebellar granule neurons from GM2/GD2 synthase-null mice to apoptosis induced by glutamate excitotoxicity and elevated KCl: rescue by GM1 and LIGA20. Glycoconj. J. 21, 305–313 (2004)
Wu, G., Lu, Z.H., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Xie, X., Meyenhofer, M.F., Ledeen, R.W.: Enhanced susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures, neuronal apoptosis, and death in mice lacking gangliotetraose gangliosides: protection with LIGA 20, a membrane-permeant analog of GM1. J. Neurosci. 25, 11014–11022 (2005)
Hadaczek, P., Wu, G., Sharma, N., Ciesielska, A., Bankiewicz, K., Davidow, A.L., Lu, Z.H., Forsayeth, J., Ledeen, R.W.: GDNF signaling implemented by GM1 ganglioside; failure in Parkinson's disease and GM1-deficient murine model. Exp. Neurol. 263, 177–189 (2015)
Farooqui, T., Franklin, T., Pearl, D.K., Yates, A.J.: Ganglioside GM1 enhances induction by nerve growth factor of a putative dimer of TrkA. J. Neurochem. 68, 2348–2355 (1997)
Singleton, D.W., Lu, C.L., Colella, R., Roisen, F.J.: Promotion of neurite outgrowth by protein kinase inhibitors and ganglioside GM1 in neuroblastoma cells involves MAP kinase ERK1/2. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 18, 797–805 (2000)
Duchemin, A.M., Ren, Q., Mo, L., Neff, N.H., Hadjiconstantinou, M.: GM1 ganglioside induces phosphorylation and activation of Trk and Erk in brain. J. Neurochem. 81, 696–707 (2002)
Da Silva, J.S., Hasegawa, T., Miyagi, T., Dotti, C.G., Abad-Rodriguez, J.: Asymmetric membrane ganglioside sialidase activity specifies axonal fate. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 606–615 (2005)
Zakharova, I.O., Sokolova, T.V., Vlasova, Y.A., Furaev, V.V., Rychkova, M.P., Avrova, N.F.: GM1 ganglioside activates ERK1/2 and Akt downstream of Trk tyrosine kinase and protects PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide toxicity. Neurochem. Res. 39, 2262–2275 (2014)
Limpert, A.S., Karlo, J.C., Landreth, G.E.: Nerve growth factor stimulates the concentration of TrkA within lipid rafts and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation through c-Cbl-associated protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27, 5686–5589 (2007)
Navarro, A.I., Rico, B.: Focal adhesion kinase function in neuronal development. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 27, 89–95 (2014)
Armendáriz, B.G., Masdeu Mdel, M., Soriano, E., Ureña, J.M., Burgaya, F.: The diverse roles and multiple forms of focal adhesion kinase in brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 40, 3573–3590 (2014)
Bolis, A., Corbetta, S., Cioce, A., de Curtis, I.: Differential distribution of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases in the developing mouse brain: implications for a role of Rac3 in Purkinje cell differentiation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 18, 2417–2424 (2003)
De Curtis, I.: Roles of Rac1 and Rac3 GTPases during the development of cortical and hippocampal GABAergic interneurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 8, 307 (2014)
Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Aebi, M., Packer, N.H., Seeberger, P.H., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G., Darvill, A., Kinoshita, T., Prestegard, J.J., Schnaar, R.L., Freeze, H.H., Marth, J.D., Bertozzi, C.R., Etzler, M.E., Frank, M., Vliegenthart, J.F., Lütteke, T., Perez, S., Bolton, E., Rudd, P., Paulson, J., Kanehisa, M., Toukach, P., Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., Dell, A., Narimatsu, H., York, W., Taniguchi, N., Kornfeld, S.: Symbol nomenclature for graphical representations of Glycans. Glycobiology. 25, 1323–1324 (2015)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 2015-2016 contract from FIDIA s.p.a in favor to S.S. and by University of Milan departmental funds Fond PSR2017_RONDELLI-CHIRICOZZI to E.C.
The authors acknowledge Euro-BioImaging (www.eurobioimaging.eu) for providing access to imaging technologies and services via the Italian Node (ALEMBIC, Milano, Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
This figure shows the contrast phase images of one week of OligoGM1 treated or not CGN. This figure shows the frame images of the time laps acquisition of OligoGM1 treated or not CGN. (PDF 1185 kb)
ESM 2
Video clip shows the entire video of 24 h time laps analysis of untreated CGN (CTRL). (MP4 8965 kb)
ESM 3
Video clip shows the entire video of 24 h time laps analysis of OligoGM1 treated CGN. (MP4 9257 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Biase, E., Lunghi, G., Fazzari, M. et al. Gangliosides in the differentiation process of primary neurons: the specific role of GM1-oligosaccharide. Glycoconj J 37, 329–343 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09919-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09919-x