Abstract
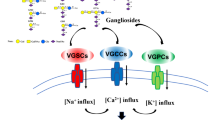
In the brain interneuronal communications occur at synapses. Synapses are specialized junctions between the presynaptic terminals of the afferent neurons and the receiving part of the postsynaptic neurons: the pre- and postsynaptic components are separated by a space termed a synaptic gap. Nerve impulses reaching the presynaptic terminal release a transmitter which is stored in synaptic vesicles preferentially located in the nerve terminal. The transmitter is released into the synaptic gap and diffuses in this space thereby reaching specific sites that bind the transmitter with high affinity. These transmitter recognition sites are part of a more complex supramolecular structure termed transmitter receptor(s) which are located on the post and presynaptic component of the synaptic junction. There are two structurally and functionally distinct types of transmitter receptors (ionotropic and metabotropic) which differ by the mechanism attending the transduction of the transmitter signals into specific receptor responses. Both transduction mechanisms generate a metabolic event of high functional significance for the receiving neuron. When metabotropic receptors (Fig. 1) are activated by the transmitter, the catalytic activity of specific enzymes which are coupled to the receptor increases. Upon binding of the transmitter, greater amounts of the products of the receptor-linked enzyme (second messenger) are produced inside the receiving neuron. This messenger diffuses into accessible intraneuronal metabolic compartments of the receiving neuron thereby activating a specific key enzyme (often a protein kinase) which triggers a cascade of metabolic events.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakmann, B., 1992, Elementary steps in synaptic transmission revealed by currents through single ion channels, Neurons. 8:613–629.
Sommer, B., Keinanen, K., Verdon, T. A., Wisden, W., Burnashev, N.,Herb, A., Kohler, M., Tagaki, T., Sakmann, B., and Seeburg, P. H., 1990, Flip and Flop: A cell specific functional switch in glutamate operated channels of CNS. Science. 249:1580–1585.
Sommer, B., Kohler, M., Sprengle, R., and Seeburg, P. H., 1991, RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate gated channel, Cell. 67:11–20.
Sommer, B., and Seeburg, P. H., 1992, Glutamate receptor channels: novel properties and new clones, TIPS 13:291–296.
Hollman, M., O’Shea-Greenfield, A., Rogers, W., and Heineman, S., 1991, Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA-gated glutamate receptor channels depend on subunit composition, Science. 252:851–853.
Connor, J. A., 1991, In pursuit of neuronal calcium: confessions of a bio-optician, Fidia Research Foundation Neuroscience Award Lectures, New York: Raven Press 6:111–139.
Vaccarino, F., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., 1988, Gangliosid inhibition of glutamate mediated protein kinase C translocation in primary cultures of cerebellar neurons, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:8707–8710.
Berridge, M. J., 1991, Phosphoinosities and cell signaling. Fidia Research Foundation Neuroscience Award Lectures. New York: Raven Press 6:5–45.
Curran, T., Fos and Jun: inducible oncogenic transcription factors that function in neuronal signal transduction. (in press) Fidia Research Foundation Neuroscience Award Lectures. New York: Raven Press.
Szekely, A.M., Costa, E., and Grayson, D. R., 1990, Transcriptional program coordination by NMDA-sensitive glutamate receptor stimulation in primary cultures of cerebellar neurons, Mol. Pharmacol. 38:624–633.
Conn, P. J., and Desai, M. A., 1991, Pharmacology and physiology of metabotropic glutamate receptorsin mammalian central nervous system, Drug Dev. Res. 24:207–229.
Memo, M., Bovolin, P., Costa, E., Grayson, D. R., 1991, Regulation of γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor subunit expression by activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-selective glutamate receptors, Mol. Pharmacol. 39:599–603.
Seeburg, P. M., Wisden, W., Werden, T. A., Pritchet, D. B., Werner, P., Herb, A., Luddens, H., Sprengel, R., and Sanman, B., 1990, The GABA receptor family: Molecular and functional diversity. In: Cold Spring Harbor Symposium On Quantitative Biology. vol. LV: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press pp. 29–40.
Nicolletti, F., Iadarola, M. J., Wroblewski, J. T., and Costa, E., 1986, Excitatory amino acid recognition sites coupled and with inosital phospholipid metabolism: Developmental changes and interaction with α1 adreneceptors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:1931–1935.
Nicoletti, F., Wroblewksi, J. T., Novelli, A., Alho, H., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., 1986, The activation of isonitol phospholipid metabolism as a signal-transducing system for excitatory amino acids in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells, J. Neurosci. 6:1905–1911.
Sladeczek, F., Recasens, M., and Bockaert, J., 1988, A new mechanism for glutamate reception action: Phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Trends in Neurosci. 11:545–549.
Masu, M., Tanabe, Y., Tsuchida, K, Shigemoto, R., and Nakanishi, S., 1991, Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, Nature 349:760–765.
Tanabe, Y., Masu, M., Ishis, T., Shigemoto, R., and Nakanishi, S., 1992, A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors, Neuron 8:169–179.
Siliprandi, R., Lipartiti, M., Fadda, E., Santter, J., and Manev, H., 1992, Activation of the glutamate metabotropic receptor protects retina against N-methyl-D-aspartate-toxicity, Europ. J. Pharmacol. 19:173–179.
Comelli, M. C., Seren, M. S., Gudolin, D., Manev, R. M., Favaron, M., Rimland, J. M., Canella, R., Negro, A., and Manev, H., 1992, Photochemical stroke and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA expression, Neuroreport 3:437–476.
Choi, D. W., 1988, Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity, J. Neurosci. 7:369–379.
Choi, D. W., 1991, Excitatory amino acid neurotransmitters: Anatomical systems. In B.S. Meldrum (Ed.), Excitatory Amino Acid Antagonists, Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, pp. 14–38.
Favaron, M., Manev, H., Siman, R., Bertolino, M., Szekely, A. M., de Erausquin, G., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., 1990, Down regulation of protein kinase C protects cerebellar granule neurons in primary culture from glutamate induced neuronal death, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:1983–1987.
Connor, J. A., Wadman, W. J., and Hockberger, P. E., 1988, Sustained dendritic gradients of Ca2+ induced by excitatory amino acid in CAI hippocampal neurons, Science 240:649–653.
Favaron, M., Manev, H., Alho, H., Bertolino, M., Ferret, B., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., 1988, Gangliosides prevent glutamate and kainate neurotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures of neonatal rat cerebellum and cortex, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:7351–7355.
Manev, H., Costa, E., Wroblewski, J. T., and Gudiotti, A., 1990b, Abusive stimulation of excitatory amino acid receptors: A strategy to limit neurotoxicity, J. Faseb. 4:2789–2797.
De Erausquin, G., Manev, H., Guidotti, A., Costa, E., and Brooker, G., 1990, Gangliosides normalize distorted single cell intracellular free Ca2+ dynamics after toxic doses of glutamate in cerebellar granule cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:8017–8021.
Candeo, P., Favaron, M., Lengyel, I., Manev, R. M., Rimland, J. M., and Manev, H., (in press) Pathological phosphorylation causes neuronal death: Effect of okadaic acid in primary culture of cerebellar granule cells, J. Neurochem.
Baumann, N., Harpin, M. L., Jacque, C., 1980, Brain gangliosides in shiverer mouse: Comparison with other dysmyelinated mutants, quaking and jumpy. In: Neurological Mutations Affecting Myelination, N. Baumann (Ed.), INSERM Symposium 14, Elsevier North Holland: Amsterdam, pp. 257–262.
Purpura, D., 1978, Ectopic dendritic growth in mature pyramidal neruons in human ganglioside storage disease, Nature 276:520–521.
Qi, Y., and Xue, Q. M., 1991, Ganglioside levels in hypoic brains from neonatal and premature infants, Mol. and Chem. Neuropathology 16:87–95.
Ghidoni, R., Riboni, L., and Tettamanti, G., 1989, Metabolisms of exogenous gangliosides in cerebellar granular cells differentiated in culture. J. Neurochem. 53:1567–1574.
Sonnino, S., Cantu, L., Corti, M., Acquotti, D., Kirschner, G., and Tettamanti, G., 1990, Aggregation properties of semisynthetic GM1 ganglioside (113 Neu 5-Ac Gg Ose4 Cer) containing an acetyl group as acylmoiety, Chem. Phys. Lipids 56:49–57.
Manev, H., Favaron, M., Vicini, S., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., 1990, Glutamate induced neuronal death in primary cultures of cerebellar granule cells: Protection by synthetic derivatives of endogenous sphingolipids, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap. 252:419–427.
Higashi, H., Omozi, A., Yamagoto, T., 1992, Calmodulin, a ganglioside binding pr otein, J. Biol. Chem. 267:9831–9838.
Watson, D. B., Dietrich, W. D., Busto, R., Wachtel, M. S., Ginstery, M. D., 1985, Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis, Amer. Neurol. 17:497–504.
Dietrich, W. D., Watson, B. D., Busto, R., Ginsberg, M. D., Bethea, J. R., 1987, Photochemically induced cerebral infartion I early microvascular alternations, Acta Neurol. 72:315–334.
Costa, E., Kharlamov, A., Guidotti, A., Hayes, R., Armstrong, D., in press, Sequelae of biochemical events following photochemical injury of rat sensory-motor cortex: Mechanism of ganglioside protection, Physiopath. Exp. Therp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1993 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Costa, E., Armstrong, D., Guidotti, A., Kharlamov, A., Kiedrowski, L., Wroblewski, J.T. (1993). Ganglioside GM1 and its Semisynthetic Lysogangliosides Reduce Glutamate Neurotoxicity by a Novel Mechanism. In: Grisolía, S., Felipo, V. (eds) Cirrhosis, Hyperammonemia, and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 341. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2484-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2484-7_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6058-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-2484-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive