Abstract
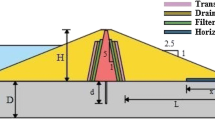
Seepage and water flow into soil are of the critical factors in the design of earth dams. There are various methods to control seepage in the dam foundation. One solution is the use of plastic concrete cutoff wall. Due to a higher hydraulic gradient in the union area and pressure increase of embankment above the wall by time, a considerable consolidation occurs in the wall. Therefore, crack in the wall, water seepage and erosion in the union area may occur. Hence, one of the items considered in earth the dams sealing system of design especially for plastic concrete cutoff walls is union area. This paper focuses on the effects of penetration depth of cutoff walls into the core of earth dams. To this aim, Anbaran dam located in the north-west of Iran was selected as a case study. Various penetration depths of cutoff walls including 0, 1, 2 and 3 m were considered. A two-dimensional model was defined and the results were compared together. For the numerical modeling and analysis of stresses and displacements in the mode of statics, including the construction stage and the first impoundment stage, GeoStudio-2007 and FLAC2D softwares were used, and for the dynamic stage FLAC2D was used. The results show that the penetration depth of wall plays an effective role in the flow rate of water, hydraulic gradient, stress and displacement of wall and union area. The results of numerical model revealed that, as the penetration depth increases, stresses and displacements of union area increase while the hydraulic gradient and seepage at the union area decrease. Finally, by analyzing the dam behaviorial parameters such as stress, displacement, seepage and hydraulic gradient, and also considering the economic and implementation aspects, the penetration depth of 2 m is chosen as an optimum penetration depth of this case. In this state, the maximum magnitudes of vertical and horizontal stresses are 2371 kPa and 728 kPa, respectively and the maximum magnitudes of vertical and horizontal displacements are 19.36 cm and 7.42 cm, respectively. The amount of seepage under the dam body is 3.330 × 10−6 m3/s/m and the maximum hydraulic gradient in the wall is 39.222. However, to find an optimum penetration depth of cutoff wall into the clay core, numerical analysis with corresponding specifications are strictly needed, indeed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajani HF, Anzabi MM, Sheikhi Z, Shokri R (2018) Selecting optimum cutoff wall position for rehabilitation of an inclined core earthfill dam. In: Hu L, Gu X, Tao J, Zhou A (eds) Proceedings of GeoShanghai 2018 international conference: multi-physics processes in soil mechanics and advances in geotechnical testing. GSIC 2018. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0095-0_29
Bagheri AR, Alibabaie M, Babaie M (2008) Reduction in the permeability of plastic concrete for cut-off walls through utilization of silica fume. Constr Build Mater 22(6):1247–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.01.024
Cundall PA (1976) Explicit finite difference method in geomechanics. In: Second international conference on numerical methods in geomechanics, Blacksburg, 1976, vol 1, pp 132–150
Duncan JM (1970) Nonlinear analysis of stresses and strains in soils. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE 96(5):117–141
GEOSLOPE (2004) GeoStudio tutorials, 1st ed. GEOSLOPE International, Ltd., Calgary. http://www.geo-slope.com/
Ghazavi M, Safarzadeh Z, Hashemolhoseini H (2004) Response of plastic concrete cut-off walls in earth dams to seismic loading using finite element methods. In: 13th World conference on earthquake engineering, Vancouver, BC, Canada, Paper (No. 2961). www.iitk.ac.in/nicee/wcee/article/13_2961.pdf
Harr ME (1962) Groundwater and seepage. McGraw-Hill, New York
Hassan WH (2019) Application of a genetic algorithm for the optimization of a location and inclination angle of a cut-off wall for anisotropic foundations under hydraulic structures. Geotech Geol Eng 37(2):883–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0658-9
Hekmatzadeh AA, Zarei F, Johari A, Haghighi AT (2018) Reliability analysis of stability against piping and sliding in diversion dams, considering four cutoff wall configurations. Comput Geotech 98:217–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.02.019
ICOLD, International Commission on Large Dams (1985) Filling materials for watertight cut-off walls, Bulletin 51
Itasca (2005) FLAC Version 5.0, User’s Manuals
Jafari MK, Davoodi M (2006) Dynamic characteristics evaluation of Masjed Soleiman Dam using in situ dynamic tests. Can Geotech J 43(10):997–1014. https://doi.org/10.1139/t06-059
Javanmard M, Mottaghi R, Hosseini SMM (2018) Investigating the influence of penetration length of cut-off wall on its dynamic interaction with core and foundation of earth dam. Civ Eng J 4(12):3019–3026. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-03091217
Karimnia M, Shahkarami A (2000) Study on the behaviour of cut-off-walls in homogeneous and heterogeneous dam foundations. http://iransaze.com/files-for-download/maghale/haftomin%20konferanse%20sarasari%20mohandsi%20omran/latin/E1069.pdf
Kazemian S, Ghareh S (2016) Effects of cement, different bentonite, and aggregates on plastic concrete in Besh–Ghardash dam, Iran. J Testing Eval 45(1):242–248. https://doi.org/10.1520/JTE20160161
Kazemian S, Ghareh S, Torkanloo L (2016) To investigation of plastic concrete bentonite changes on it’s physical properties. Procedia Eng 145:1080–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.04.140
Khalili Shayan H, Amiri-Tokaldany E (2015) Effects of blanket, drains, and cutoff wall on reducing uplift pressure, seepage, and exit gradient under hydraulic structures. Int J Civ Eng 13(4):486–500. https://doi.org/10.22068/IJCE.13.4.486
Krahn J (2004) Seepage modeling with SEEP/W: an engineering methodology. GEO-SLOPE International Ltd., Calgary
Liu SH, Wang LJ, Wang ZJ, Bauer E (2016) Numerical stress–deformation analysis of cut-off wall in clay-core rockfill dam on thick overburden. Water Sci Eng 9(3):219–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2016.11.002
Lobbestael AJ (2014) An investigation of the seismic response of earthen levees with cutoff walls with a focus on the development of a high performance cutoff wall material. https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/handle/2027.42/110458/ajimlobb_1.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Mahboubi A, Ajorloo A (2005) Experimental study of the mechanical behavior of plastic concrete in triaxial compression. Cem Concr Res 35(2):412–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.09.011
Mahinroosta R, Shoaei M, Pishgar F (2012) Evaluation of the penetration depth of sealing plastic concrete walls in the clay core of earth dams. J Am Sci 8(8):465–473. http://www.jofamericanscience.org/journals/am-sci/am0808/071_9905am0808_465_473.pdf
Mansuri B, Salmasi F (2013) Effect of horizontal drain length and cutoff wall on seepage and uplift pressure in heterogeneous earth dam with numerical simulation. J Civ Eng Urbanism 3(3):114–121
Mansuri B, Salmasi F, Oghati B (2014) Effect of location and angle of cutoff wall on uplift pressure in diversion dam. Geotech Geol Eng 32(5):1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9774-3
Mirghasemi AA, Moshashai H (2001) Plastic concrete specification a case study—Karkheh dam project. In: International conference on civil engineering, Bangalore. https://www.tib.eu/en/search/id/BLCP%3ACN045637335/Plastic-Concrete-Specification-A-Case-Study-Karkheh/
Mirghasemi AA, Pakzad M, Shadravan B (2005) The world’s largest cutoff wall at Karkheh dam. Int J Hydropower Dams 12(2):90–94
Moharrami A, Moradi G, Bonab MH, Katebi J, Moharrami G (2015) Performance of cutoff walls under hydraulic structures against uplift pressure and piping phenomenon. Geotech Geol Eng 33(1):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9827-7
Nayebzadeh R, Mohammadi M (2011) The effect of impervious clay core shape on the stability of embankment dams. Geotech Geol Eng 29(4):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-011-9395-z
Peter P (1982) Canal and river levees. In: Developments of civil engineering, vol. 29. Elsevier/North-Holland, Inc., New York. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Canal+and+river+levees.+In%3A+Developments+of+civil+engineering&btnG=
Raja MA, Maheshwari BK (2016) Behaviour of earth dam under seismic load considering nonlinearity of the soil. Open J Civ Eng 6(02):75. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojce.2016.62007
Sherard JL, Gizienski SF, Clevenger WA (1963) Earth and earth-rock dams. Wiley, New York
Technical reports of Anabaran storage dam’s study (2012) Pazhoohesh Omran Rahvar Consulting Engineers Company, Tehran, Iran (In Farsi)
Vahdati P (2014) Identification of soil parameters in an embankment dam by mathematical optimization (Doctoral dissertation, Luleå tekniska universitet). https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:976631/FULLTEXT01.pdf
Vahdati P, Levasseur S, Mattsson H, Knutsson S (2013) Inverse Mohr-Coulomb soil parameter identification of an earth and rockfill dam by genetic algorithm optimization. Electron J Geotech Eng 18(X):5419–5440
Yu X, Kong X, Zou D, Zhou Y, Hu Z (2015) Linear elastic and plastic-damage analyses of a concrete cut-off wall constructed in deep overburden. Comput Geotech 69:462–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.05.015
Zienkiewicz OC (1977) The finite element method. McGraw Hill, New York
Zoorasna Z, Hamidi A, Ghanbari A (2008) Mechanical and hydraulic behavior of cut off-core connecting systems in earth dams. Electron J Geotech Eng 13(K):1–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakouri, B., Mohammadi, M. Evaluation of Penetration Depth for Cutoff Walls in the Core of Earth Dams. Geotech Geol Eng 38, 151–167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01004-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01004-x