Abstract
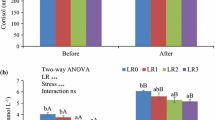
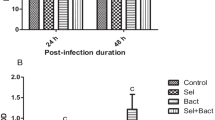
Dietary supplementation of selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) at different levels (0, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg kg−1 diet) was evaluated to find out the effects on serum and skin immune responses as well as stress resistance in the red sea bream (Pagrus major). After 45 days of experimental trial, serum and mucosal immune responses were significantly high in fish fed 1 mg Se-NPs kg−1 diet (P < 0.05). In this group, alternative complement pathway, total serum protein, antioxidant activity of catalase enzyme, serum bactericidal activity, serum lysozyme activity, and amounts of skin mucus secretions as well as stress resistance against low salinity stress increased significantly, when compared to fish fed Se-NP-free diet (P < 0.05). Furthermore, fish fed Se-NPs at 2 mg kg−1 diet exhibited higher alternative complement pathway, total serum protein, mucus lysozyme activity, serum and mucus peroxidases, amount of mucus secreted, and tolerance against low salinity stress than the fish fed Se-NP-free diet (P < 0.05). Interestingly, the nitro blue tetrazolium activity in all groups fed with diets supplemented with Se-NPs are significantly higher than Se-NP-free diet (P < 0.05). The present results demonstrate that the dietary supplementation with Se-NPs (mainly from 1 to 2 mg kg−1 level) could be useful for maintaining the overall health status of red sea bream.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkhalek NK, Eissa IA, Ahmed E, Kilany OE, El-Adl M, Dawood MAO, Hassan AM, Abdel-Daim MM (2017) Protective role of dietary Spirulina platensis against diazinon-induced oxidative damage in Nile tilapia; Oreochromis niloticus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 54:99–104
Adel M, Caipang CMA, Dawood MAO (2017) Immunological responses and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) juveniles following dietary administration of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica). Fish Shellfish Immunol 71:230–238
Adel M, Yeganeh S, Dadar M, Sakai M, Dawood MAO (2016) Effects of dietary Spirulina platensis on growth performance, humoral and mucosal immune responses and disease resistance in juvenile great sturgeon (Huso huso Linnaeus, 1754). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 56:436–444
Anderson DP, Siwicki AK (1995) Basic haematology and serology for fish health programs, Shariff M, Arthur JR, R.P. Subasinghe (Eds.), Diseases in Asian aquaculture II. Manila: Philippines fish health section, Asian Fisheries Soc, p. 185
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) (2000) Pages 46 in P. Cunniff, editor. Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 17th edition, Chapter 4. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Inc., Arlington, VA
Ashouri S, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Johari SA, Pasha-Zanoosi H (2015) Effects of different levels of dietary selenium nanoparticles on growth performance, muscle composition, blood biochemical profiles and antioxidant status of common carp (C. carpio). Aquaculture 446:25–29
Atencio L, Moreno I, Jos Á, Prieto AI, Moyano R, Blanco A, Cameán AM (2009) Effects of dietary selenium on the oxidative stress and pathological changes in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to a microcystin-producing cyanobacterial water bloom. Toxicon 53(2):269–282
Balasubramanian S, Baby Rani P, Arul Prakash A, Prakash M, 743 PS, Gunasekaran G (2012) Antimicrobial properties of skin mucus from four freshwater cultivable fishes (Catla catla, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, Labeo rohita and Ctenopharyngodon idella), African. J Microbiol Res 6:5110–5120
Cordero H, Morcillo P, Cuesta A, Brinchmann MF, Esteban MA (2016a) Differential proteome profile of skin mucus of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) after probiotic intake and/or overcrowding stress. J Proteome 132:41–50
Cordero H, Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MÁ (2016b) Changes in the levels of humoral immune activities after storage of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) skin mucus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 58:500–507
Dawood MAO, El-Dakar A, Mohsen M, Abdelraouf E, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2014) Effects of using exogenous digestive enzymes or natural enhancer mixture on growth, feed utilization, and body composition of rabbitfish, Siganus rivulatus. J Agric Sci Technol B 4(3B)
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015a) Effects of heat killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) supplemental diets on growth performance, stress resistance and immune response of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 442:29–36
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015b) Interaction effects of dietary supplementation of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and β-glucan on growth performance, digestibility and immune response of juvenile red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish shellfish Immunol 45:33–42
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2015c) Effects of partial substitution of fish meal by soybean meal with or without heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum (LP20) on growth performance, digestibility, and immune response of Amberjack, Seriola dumerili Juveniles. BioMed Research International Article ID 514196
Dawood MAO, Koshio S (2016a) Vitamin C supplementation to optimize growth, health and stress resistance in aquatic animals. Rev Aquac. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12163
Dawood MAO, Koshio S (2016b) Recent advances in the role of probiotics and prebiotics in carp aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 454:243–251
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, El Basuini MF, Hossain MS, Nhu TH, Dossou S, Moss AS (2016a) Effects of dietary supplementation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus or/and Lactococcus lactis on the growth, gut microbiota and immune responses of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Fish Shellfish Immunol 49:275–285
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2016b) Effects of dietary inactivated Pediococcus pentosaceus on growth performance, feed utilization and blood characteristics of red sea bream, Pagrus major juvenile. Aquacult Nutr 22(4):923–932
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S (2016c) Immune responses and stress resistance in red sea bream, Pagrus major, after oral administration of heat-killed Lactobacillus plantarum and vitamin C. Fish Shellfish Immunol 54:266–275
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, El-Sabagh M, Esteban MA, Zaineldin AI (2016d) Probiotics as an environment-friendly approach to enhance red sea bream, Pagrus major growth, immune response and oxidative status. Fish Shellfish Immunol 57:170–178
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, El-Sabagh M, Billah MM, Zaineldin AI, Zayed MM, Omar AAED (2017a) Changes in the growth, humoral and mucosal immune responses following β-glucan and vitamin C administration in red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 470:214–222
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, El-Sabagh M, Yokoyama S, Wang WL, Yukun Z, Olivier A (2017b) Physiological response, blood chemistry profile and mucus secretion of red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed diets supplemented with Lactobacillus rhamnosus under low salinity stress. Fish Physiol Biochem 43(1):179–192
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, El Basuini MF, Hossain MS, Nhu TH, Moss AS, Dossou S, Wei H (2017c) Dietary supplementation of β-glucan improves growth performance, the innate immune response and stress resistance of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquac Nutr 23(1):148–159
Dawood MAO, Koshio S and Esteban MÁ, (2017d) Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Reviews in Aquaculture. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/raq.12209
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Abdel-Daim MM, Van Doan H (2018) Probiotic application for sustainable aquaculture. Rev Aquac. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12272
Dhanaraj M, Haniffa M, Arun A, Singh S, Muthu R, Manikandaraja D et al (2009) Antibacterial activity of skin and intestinal mucus of five different freshwater fish species viz., Channa striatus, C. micropeltes, C. marulius, C. punctatus and C. gachua. J. Sci, Malay, pp 257–262
Dossou, S., Koshio, S., Ishikawa, M., Yokoyama, S., Dawood, M.A.O., El Basuini, M.F., Olivier, A., Zaineldin, A.I., 2018a. Growth performance, blood health, antioxidant status and immune response in red sea bream (Pagrus major) fed Aspergillus oryzae fermented rapeseed meal (RM-Koji). Fish Shellfish Immunol 75, 253–262
Dossou, S., Koshio, S., Ishikawa, M., Yokoyama, S., Dawood, M.A.O., El Basuini, M.F., El-Hais, A.M. and Olivier, A., 2018b. Effect of partial replacement of fish meal by fermented rapeseed meal on growth, immune response and oxidative condition of red sea bream juvenile, Pagrus major. Aquaculture 490, 228–235
El Basuini MF, El-Hais AM, Dawood MA, Abou-Zeid AES, EL-Damrawy SZ, Khalafalla MMES, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Dossou S (2016) Effect of different levels of dietary copper nanoparticles and copper sulfate on growth performance, blood biochemical profiles, antioxidant status and immune response of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Aquaculture 455:32–40
El Basuini MF, El-Hais AM, Dawood MAO, Abou-Zeid AS, EL-Damrawy SZ, Khalafalla MS, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Dossou S (2017) Effects of dietary copper nanoparticles and vitamin C supplementations on growth performance, immune response and stress resistance of red sea bream, Pagrus major. Aquaculture Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12508/abstract
Fast MD, Sims DE, Burka JF, Mustafa A, Ross NW (2002) Skin morphology and humoral non-specific defense parameters of mucus and plasma in rainbow trout, coho and Atlantic salmon. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 132:645–657
Gao J, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Nose D, Ren T (2013) Interactive effects of vitamin C and E supplementation on growth, fatty acid composition, and lipid peroxidation of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus, fed with dietary oxidized fish oil. J World Aquac Soc 44(4):536–546
Gasque P (2004) Complement: a unique innate immune sensor for danger signals. Mol Immunol 41:1089
Goth L (1991) A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta 196(2):143–151
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Arizcun M, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2014) Comparative skin mucus and serum humoral defence mechanisms in the teleost gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Fish Shellfish Immunol 36:545–551
Han D, Xie S, Liu M, Xiao X, Liu H, Zhu X, Yang Y (2011) The effects of dietary selenium on growth performances, oxidative stress and tissue selenium concentration of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquac Nutr 17(3):e741–e749
Holland M, Claire H, Lambris JD (2002) The complement system in teleosts. Fish Shellfish Immunol 12:399–420
Hossain MS, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Sony NM, Dawood MAO, Kader MA, Bulbul M, Fujieda T (2016) Efficacy of nucleotide related products on growth, blood chemistry, oxidative stress and growth factor gene expression of juvenile red sea bream. Pagrus major Aquaculture 464:8–16
Iida T, Takahashi T, Wakabayashi H (1989) Decrease in the bactericidal activity of normal serum during the spawning period of rainbow trout. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 55:463–465
Kakuta I, Kurokura H, Nakamura H, Yamauchi K (1996) Enhancement of the nonspecific defense activity of the skin mucus of red sea bream by oral administration of bovine lactoferrin. Suisanzoshoku 44:197–202
Khan KU, Zuberi A, Nazir S, Fernandes JBK, Jamil Z, Sarwar H (2016) Effects of dietary selenium nanoparticles on physiological and biochemical aspects of juvenile Tor putitora. Turk J Zool 40(5):704–712
Kim KW, Wang X, Choi SM, Park GJ, Koo JW, Bai SC (2003) No synergistic effects by the dietary supplementation of ascorbic acid, α-tocopheryl acetate and selenium on the growth performance and challenge test of Edwardsiella tarda in fingerling Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. Aquac Res 34(12):1053–1058
Kiron V (2012) Fish immune system and its nutritional modulation for preventive health care. Anim Feed Sci Technol 173(1):111–133
Köhrle J, Brigelius-Flohé R, Böck A, Gärtner R, Meyer O, Flohé L (2000) Selenium in biology: facts and medical perspectives. Biol Chem 381(9–10):849–864
Kouba A, Velíšek J, Stará A, Masojídek J and Kozák P (2014) Supplementation with sodium selenite and selenium-enriched microalgae biomass show varying effects on blood enzymes activities, antioxidant response, and accumulation in common barbel (Barbus barbus). BioMed research international, 2014
Kumar, S., Sahu, N.P., Pal, A.K., Choudhury, D., Yengkokpam, S., Mukherjee, S.C., 2005. Effect of dietary carbohydrate on haematology, respiratory burst activity and histological changes in L. rohita juveniles. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19, 331–344
Le KT, Fotedar R (2014) Immune responses to Vibrio anguillarum in yellowtail kingfish, Seriola lalandi, fed selenium supplementation. J World Aquac Soc 45:138–148
Lee S, Nambi RW, Won S, Katya K, Bai SC (2016) Dietary selenium requirement and toxicity levels in juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 464:153–158
Liu LW, Liang XF, Li J, Fang JG, Yuan XC, Li J, Alam MS (2018) Effects of dietary selenium on growth performance and oxidative stress in juvenile grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Aquac Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12667
Lorentzen M, Maage A, Julshamn K (1994) Effects of dietary selenite or selenomethionine on tissue selenium levels of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 121(4):359–367
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lygren B, Sveier H, Hjeltnes B, Waagbo R (1999) Examination of the immunomodulatory properties and the effect on disease resistance of dietary bovine lactoferrin and vitamin C fed to Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) for a short-term period. Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:95–107
Magnadóttir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151
Moe YY, Koshio S, Teshima S, Ishikawa M, Matsunaga Y, Panganiban AJ (2004) Effect of vitamin C derivatives on the performance of larval kuruma shrimp, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Aquaculture 242:501–512
Naderi M, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Ghaedi A (2017a) Combined or individual effects of dietary vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles on humoral immune status and serum parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high stocking density. Aquaculture 474:40–47
Naderi M, Keyvanshokooh S, Salati AP, Ghaedi A (2017b) Effects of dietary vitamin E and selenium nanoparticles supplementation on acute stress responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) previously subjected to chronic stress. Aquaculture 473:215–222
National Research Council (NRC) (2011) Nutrient Requirements of Fish and Prawn. National Academies Press, Washington, DC, USA, pp 207–209
Ræder ILU, Paulsen SM, Smalås AO, Willassen NP (2007) Effect of fish skin mucus on the soluble proteome of Vibrio salmonicida analysed by 2-D gel electrophoresis and tandem mass spectrometry. Microb Pathog 42(1):36–45
Rayman MP (2004) The use of high-selenium yeast to raise selenium status: how does it measure up? Br J Nutr 92(4):557–573
Ruangsri J, Fernandes JMO, Brinchmann M, Kiron V (2010) Antimicrobial activity in the tissues of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:879–886
Saffari S, Keyvanshokooh S, Zakeri M, Johari SA, Pasha-Zanoosi H, Mozanzadeh MT (2018) Effects of dietary organic, inorganic, and nanoparticulate selenium sources on growth, hemato-immunological, and serum biochemical parameters of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Fish Physiol Biochem:1–11
Salinas I, Abelli L, Bertoni F, Picchietti S, Roque A, Furones D, Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2008) Monospecies and multispecies probiotic formulations produce different systemic and local immunostimulatory effects in the gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 25(1):114–123
Saurabh S, Sahoo P (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239
Skalickova S, Milosavljevic V, Cihalova K, Horky P, Richtera L, Adam V (2017) Selenium nanoparticles as a nutritional supplement. Nutrition 33:83–90
Song SK, Beck BR, Kim D, Park J, Kim J, Kim HD, Ringø E (2014) Prebiotics as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 40(1):40–48
Subramanian S, Ross NW, MacKinnon SL (2008) Comparison of antimicrobial activity in the epidermal mucus extracts of fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 150:85–92
Suzuki Y, Hashiura Y, Matsumura K, Matsukawa T, Shinohara A, Furuta N (2010) Dynamic pathways of selenium metabolism and excretion in mice under different selenium nutritional statuses. Metallomics 2(2):126–132
Wang WF, Mai KS, Zhang WB, Xu W, Ai QH, Liufu ZG, Li HT (2012) Dietary selenium requirement and its toxicity in juvenile abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Aquaculture 330–333:42–46
Yano T (1992) Assays of hemolytic complement activity. In: Stolen JS, Fletcher TC, Anderson DP, Kaattari SL, Rowley AF, editors. Techniques in fish immunology. Fair Haven, NJ: SOS Publications. pp. 131–41
Yano T (1997) 3 the nonspecific immune system: humoral defense. Fish Physiology 15:105–157
Zaineldin AI, Hegazi S, Koshio S, Ishikawa M, Bakr A, El-Keredy AM, Dawood MAO, Dossou S, Wang W, Yukun Z (2018) Bacillus subtilis as probiotic candidate for red sea bream: growth performance, oxidative status, and immune response traits. Fish Shellfish Immunol 79:303–312
Zakęś, Z., Kowalska, A., Demska-Zakęś, K., Jeney, G., Jeney, Z., 2008. Effect of two medicinal herbs (Astragalus radix and Lonicera japonica) on the growth performance and body composition of juvenile pikeperch [Sander lucioperca (L.)]. Aquac Res 39(11):1149–1160
Zhou X, Wang Y, Gu Q, Li W (2009) Effects of different dietary selenium sources (selenium nanoparticle and selenomethionine) on growth performance, muscle composition and glutathione peroxidase enzyme activity of crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquaculture 291(1):78–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors were responsible for data collection, data analysis, interpretation and writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 580 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dawood, M.A.O., Koshio, S., Zaineldin, A.I. et al. Dietary supplementation of selenium nanoparticles modulated systemic and mucosal immune status and stress resistance of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Fish Physiol Biochem 45, 219–230 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0556-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0556-3