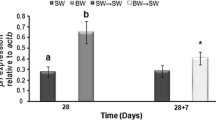
Abstract
Aquaculture industry in the Mediterranean region exhibits a growing interest for the Mediterranean meager Argyrosomus regius. Some preliminary works showed a good growth performance of the species in nearly isosmotic salinities. However, the patterns of alteration of prolactin (Prl) as well as growth hormone (Gh)/insulin growth factor-1 (Igf1) axis at the molecular level are not yet described in this species. Therefore, we cloned and sequenced partial cDNAs for pituitary prolactin (prl) and growth hormone (gh), hepatic insulin-like growth factor (igf1), and β-actin (actb). Expression patterns of these transcripts were tested in juveniles of A. regius acclimated to four different environmental salinities: (1) 5 ‰ (hyposmotic); (2) 12 ‰ (isosmotic); (3) 38 ‰ (hyperosmotic; seawater control); and (4) 55 ‰ (extremely hyperosmotic). All investigated transcripts shared high sequence identities with their counterparts in other perciformes. prl mRNA levels showed inverse pattern with increasing salinities. gh mRNA enhanced significantly in both 12 and 55 ‰ salinity groups in comparison with the control group, while igf1 showed its maximum expression levels under the nearly isosmotic environment. The results indicated clear sensitivity of prl, gh and igf1 to changes in environmental salinity, which can possibly control the euryhalinity capacity of this species.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breves JP, Seale AP, Moorman BP, Lerner DT, Moriyama S, Hopkins KD, Grau EG (2014) Pituitary control of branchial NCC, NKCC and Na+, K+-ATPase α-subunit gene expression in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J Comp Physiol B 184(4):513–523
Cárdenas S (2010) Crianza de la corvina Argyrosomus regius. Cuad Acuic 3:12–57
Chen S, Pu L, Xie F, Zou Z, Jiang Y, Han K, Wang Y, Zhang Z (2015) Differential expression of three estrogen receptors mRNAs in tissues, growth development, embryogenesis and gametogenesis from large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Gen Comp Endocrinol 216:134–151
Deane EE, Woo NYS (2004) Differential gene expression associated with euryhalinity in sea bream (Sparus sarba). Am J Physiol 287:R1054–R1063
Deane EE, Woo NYS (2005a) Cloning and characterization of sea bream Na+-K+-ATPase α and β subunit genes: in vitro effects of hormones on transcriptional and translational expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331:1229–1238
Deane EE, Woo NY (2005b) Upregulation of the somatotropic axis is correlated with increased G6PDH expression in Black Sea bream adapted to iso-osmotic salinity. Ann NY Acad Sci 1040:293–296
Deane EE, Woo NY (2009) Modulation of fish growth hormone levels by salinity, temperature, pollutants and aquaculture related stress: a review. Rev Fish Biol Fish 19:97–120
El-Shebly AA, El-Kady MAH (2007) Preliminary observations on the pond culture of meagre Argyrosomus regius (Asso, 1801) (Sciaenidae) in Egypt. J Fish Aquat Sci 2:345–352
FAO (2005–2015) Cultured aquatic species information programme. Argyrosomus regius. Cultured Aquatic Species Information Programme. Text by Stipa P; Angelini M. In: FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department [online]. Rome. Updated 10 Feb 2005 (Cited 12 Aug 2016). http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Argyrosomus_regius/en#tcNA00D9.ESTRODONDEVA
Fuentes J, Brinca L, Guerreiro PM, Power DM (2010) PRL and GH synthesis and release from the sea bream (Sparus auratus L.) pituitary gland in vitro in response to osmotic challenge. Gen Comp Endocrinol 168(1):95–102
Huang X, Hui MN, Liu Y, Yuen DS, Zhang Y, Chan WY, Lin HR, Cheng SH, Cheng CH (2009) Discovery of a novel prolactin in non-mammalian vertebrates: evolutionary perspectives and its involvement in teleost retina development. PLoS ONE 4(7):e6163
Jiménez MT, Pastor E, Grau A, Alconchel JI, Sánchez R, Cárdenas S (2005) Review of sciaenid culture around the world, with a special focus on the meagre Argyrosomus regius (Asso, 1801). Bol Inst Esp Oceanogr 21:169–175
Kültz D (2013) Osmosensing. In: McCormick SD, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Euryhaline fishes, vol 32. Academic Press, New York, pp 45–68
Kwasek K, Wick M, Dabrowski K (2015). Muscle protein characteristic and its association with faster growth in percids and other teleosts. In: Kestemont P, Dabrowski K, Summerfelt RC (eds) Biology and culture of percid fishes (pp 339–352). Springer, Dordrecht
Laiz-Carrión R, Fuentes J, Redruello B, Guzmán JM, del Río MPM, Mancera JM (2009) Expression of pituitary prolactin, growth hormone and somatolactin is modified in response to different stressors (salinity, crowding and food-deprivation) in gilthead sea bream Sparus auratus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162:293–300
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \(2^{{ - \Delta \Delta {\text{C}}_{\text{T}} }}\) method. Methods 25:402–408
Mancera JM, McCormick SD (1998) Osmoregulatory actions of the GH/IGF-1 axis in non-salmonid teleosts. Comp Biochem Physiol 121B:43–48
Mancera JM, McCormick SD (2007) Role of prolactin, growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor and cortisol in teleost osmoregulation. In: Baldisserotto B, Mancera JM, Kapoor BG (eds) Fish osmoregulation. Science Publishers, pp 497–515
Manzon LA (2002) The role of prolactin in fish osmoregulation: a review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 125(2):291–310
McCormick SD (1995) Hormonal control of gill Na+, K+-ATPase and chloride cell function. In: Wood CM, Shuttleworth TJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol 14. Academic Press, New York, pp 285–315
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
Moghadam HK, Ferguson MM, Rexroad CE 3rd, Coulibaly I, Danzmann RG (2007) Genomic organization of the IGF1, IGF2, MYF5, MYF6 and GRF/PACAP genes across Salmoninae genera. Anim Genet 38(5):527–532
Mohammed-Geba K, Mancera JM, Martínez-Rodríguez G (2015) Acclimation to different environmental salinities induces molecular endocrine changes in the GH/IGF-I axis of juvenile gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). J Comp Physiol B 185(1):87–101
Monfort MC (2010) Present market situation and prospects of meagre (Argyrosomus regius), as an emerging species in Mediterranean aquaculture. Studies and Reviews. General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean. No. 89. Rome, FAO
Muñoz JL, Rodríguez-Rúa A, Bustillos P et al (2008) Crecimiento de corvina Argyrosomus regius (Asso, 1801) en estanques de tierra a distintas salinidades. IV Jornadas de Acuicultura en el Litoral Suratlántico. Nuevos retos. Cartaya, Huelva, Spain
Riley LG, Hirano T, Grau EG (2003) Effects of transfer from seawater to fresh water on the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-I axis and prolactin in the Tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Comp Biochem Physiol 136B(4):647–655
Sakamoto T, McCormick SD (2006) Prolactin and growth hormone in fish osmoregulation. Gen Comp Endocrinol 147(1):24–30
Sakamoto T, Ogasawara T, Hirano T (1990) Growth hormone kinetics during adaptation to a hyperosmotic environment in rainbow trout. J Comp Physiol B 160(1):1–6
Schultz ET, McCormick SD (2013) Euryhalinity in an evolutionary context. In: McCormick SD, Farrell AP, Brauner CJ (eds) Euryhaline fishes, vol 32. Academic Press, New York, pp 478–533
Specker JL, King DS, Nishioka RS, Shirahata K, Yamaguchi K, Bern HA (1985) Isolation and partial characterization of a pair of prolactins released in vitro by the pituitary of cichlid fish, Oreochromis mossambicus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7490–7494
Suzuki R, Kaneko T, Hirano T (1991) Effects of osmotic pressure on prolactin and growth hormone secretion from organ-cultured eel pituitary. J Comp Physiol B 161(2):147–153
Takei Y, McCormick SD (2013) Hormonal control of fish euryhalinity. Euryhaline fishes. Fish Physiol 32:69–123
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tiago DM, Laizé V, Cancela ML (2008) Alternatively spliced transcripts of Sparus aurata insulin-like growth factor 1 are differentially expressed in adult tissues and during early development. Gen Comp Endocrinol 157:107–115
Uchida K, Yoshikawa-Ebesu JS, Kajimura S, Yada T, Hirano T, Grau EG (2004) In vitro effects of cortisol on the release and gene expression of prolactin and growth hormone in the tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 135(1):116–125
Vargas-Chacoff L, Astola A, Arjona FJ, Del Río MM, García-Cózar F, Mancera JM, Martínez-Rodríguez G (2009) Gene and protein expression for prolactin, growth hormone and somatolactin in Sparus aurata: seasonal variations. Comp Biochem Physiol 153B(1):130–135
Vargas-Chacoff L, Ruiz-Jarabo I, Pascoa I, Gonçalves O, Mancera JM (2014) Yearly growth and metabolic changes in earthen pond-cultured meagre Argyrosomus regius. Scientia Mar 78:193–202
Vélez EJ, Lutfi E, Azizi S, Perelló M, Salmerón C, Riera-Codina M, Ibarz A, Fernández-Borràs J, Blasco J, Capilla E, Navarro I, Gutiérrez J (2016) Understanding fish muscle growth regulation to optimize aquaculture production. Aquaculture. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.07.004
Whittamore JM (2012) Osmoregulation and epithelial water transport: lessons from the intestine of marine teleost fish. J Comp Physiol B 182(1):1–39
Woo NYS, Kelly SP (1995) Effects of salinity and nutritional status on growth and metabolism of Sparus sarba in a closed seawater system. Aquaculture 135:229–238
Wood AW, Duan C, Bern HA (2005) Insulin-like growth factor signaling in fish. Int Rev Cytol 243:215–285
Gonzalez RJ (2012) The physiology of hyper-salinity tolerance in teleost fish: a review. J Comp Physiol B 182(3):321–329
Yamaguchi Y, Moriyama S, Lerner DT, Gordon Grau E, Seale AP (2016) Autocrine positive feedback regulation of prolactin release from tilapia prolactin cells and its modulation by extracellular osmolality. Endocrinology. doi:10.1210/en.2015-1969#sthash.5kykoEND.dpuf
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhang L, Zhu T, Tian J, Li X, Lin H (2004) Two distinct cytochrome P450 aromatases in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides): cDNA cloning and differential mRNA expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 92(1–2):39–50
Zou S, Kamei H, Modi Z, Duan C (2009) Zebrafish IGF genes: gene duplication, conservation and divergence, and novel roles in midline and notochord development. PLoS ONE 4(9):e7026
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out as a part of the Spanish-Egyptian joint project AP/039755/11(Development of molecular, physiological and immunological biomarkers for the detection of stress related to the Mediterranean meager aquaculture Argyrosomus regius) awarded from the Spanish agency of international cooperation (Agencia Española de Cooperación Internacional, AECID) and the Egyptian Academy of Scientific Research and Technology, to Juan Miguel Mancera (Universidad de Cádiz, Spain) and Khaled Mohammed-Geba (Menofia University, Egypt). The authors would like to express their thanks to Prof. Saber Abd El-Rahman Sakr, head of the Zoology Department, Faculty of Science, Menofia University, Egypt, for his sincere help during the development of the project´s strategies and bureaucratic work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper follows the ZFIN Zebrafish Nomenclature Guidelines for gene and protein names and symbols (https://wiki.zfin.org/display/general/ZFIN+Zebrafish+Nomenclature+Guidelines).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed-Geba, K., González, A.A., Suárez, R.A. et al. Molecular performance of Prl and Gh/Igf1 axis in the Mediterranean meager, Argyrosomus regius, acclimated to different rearing salinities. Fish Physiol Biochem 43, 203–216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0280-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0280-9