Abstract
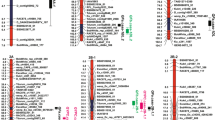
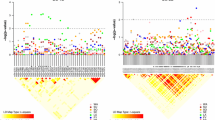
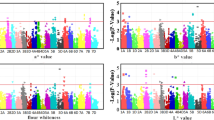
The color of flour and its end-use products is an important quality trait of wheat. Understanding the genetic basis of this trait is essential for improving wheat quality. In this study, quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping for 27 color-related traits of flour, starch, gluten, dough sheet, steamed bread, and baked bread was performed using a population of recombinant inbred lines (RILs) with 173 lines of F9:10, tested in four environments. For this purpose, a high-density genetic map constructed using a 90 K SNP array, Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers was used. A total of 43 additive QTLs were detected, including 25 large-effect QTLs, located on chromosomes 1A, 1B, 2A, 4B, 5B, and 7B. Four of these major QTLs, namely QFa7B.7-1, QFb7B.7-2, QFb7B.7-1 and QGb4B.4, made the highest contribution and accounted for 29.60, 29.02, 27.45, and 22.24% of the phenotypic variation, respectively. Six stable QTLs (QSa4B.4, QSl4B.4-1, QFa7B.7-2, QFb7B.7-1, QFb7B.7-2, and QBca7B.7) were detected in more than one environment with high PVE values. In addition, two robust QTL clusters contribution to 13 evaluated traits were identified on chromosomes 4B (RAC875_c27536_611-wsnp_Ku_c28756_38667953) and 7B (wPt-1196-Kukri_c2348_2340). A locus within the interval Ex_c101685_705-RAC875_c27536_611 of 4B also harbored many genes previously reported to affect wheat quality and yield. These detected QTLs may be used for further study and be used to improve wheat quality in wheat-breeding programs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeer AA, Hossam SEB, Rehab FMA, Somia MM, Emam A-R (2019) The effects of wheat flour and barley flour on the quality and properties of biscuits colored with synthetic and natural colorants. Not Sci Biol 11(1):30–38. https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb11110408
Akbari M, Wenzl P, Caig V, Carling J, Xia L, Yang S, Uszynski G, Mohler V, Lehmensiek A, Kuchel H, Hayden MJ, Howes N, Sharp P, Vaughan P, Rathmell B, Huttner E, Kilian A (2006) Diversity arrays technology (DArT) for high-throughput profiling of the hexaploid wheat genome. Theor Appl Genet 113:1409–1420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0365-4
Chao S, Zhang W, Akhunov E, Sherman J, Ma Y, Luo M, Dubcovsky J (2009) Analysis of gene-derived SNP marker polymorphism in US wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Mol Breed 23:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9210-6
Chen JS, Chen GF, Li QF, Zhang H, Shi CL, Sun CL, Deng ZY, Liu K, Gu ZQ, Tian JC (2014) Construction of genetic map using genotyping chips and QTL analysis of grain weight. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 47(24):4769–4779. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.24.001
Chen JH, Zhang FY, Zhao CJ, Lv GG, Sun CW, Pan YB, Guo XY, Chen F (2019) Genome-wide association study of six quality traits reveals the association of the TaRPP13L1 gene with flour color in Chinese bread wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 17(11):2106–2122. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13126
Deng ZY, Tian JC, Chen F, Li WJ, Zheng FF, Chen JS, Shi CL, Sun CL, Wang SY, Zhang YX (2015) Genetic dissection on wheat flour quality traits in two related populations. Euphytica 203:221–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1318-7
Garbus I, Carrera AD, Dubcovsky J, Echenique V (2009) Physical mapping of durum wheat lipoxygenase genes. Cereal Sci 50:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2009.02.008
Howitt CA, Cavanagh CR, Bowerman AF, Cazzonelli C, Rampling L, Mimica JL, Pogson BJ (2009) Alternative splicing, activation of cryptic exons and amino acid substitutions in carotenoid biosynthetic genes are associated with lutein accumulation in wheat endosperm. Func Integr Genomic 9:363–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-009-0121-3
Ishikawa G, Hayashi T, Nakamura K, Tanaka T, Kobayashi F, Saito M, Ito H, Ikenaga S, Taniguchi Y, Nakamura T (2020) Multifamily QTL analysis and comprehensive design of genotypes for high-quality soft wheat. PLoS ONE 15(3):e0230326. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230326
Ji MQ, Fang WQ, Li WS, Zhao YZ, Guo YX, Wang W, Chen GF, Tian JC, Deng ZY (2021) Genome wide association study of the whiteness and colour related traits of flour and dough sheets in common wheat. Sci Rep 11:8790. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-88241-4
Jiang XL, Li XJ, Li G, Li TT, Li XL, Yong HC, Ru ZG, Wang YD (2019) Stability of fresh dough sheet color and its correlation with wheat quality traits. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc 34(2):8–13. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2019.02.003
Johnson M, Kumar A, Oladzad-Abbasabadi A, Salsman E, Aoun M, Manthey FA, Elias EM (2019) Association mapping for 24 traits related to protein content, gluten strength, color, cooking and milling quality using balanced and unbalanced data in durum wheat [Triticum Turgidum L. Var. Durum (Desf.)]. Front Genet 10:717. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00717
Kang H, Kang CS, Kim H, Park CS (2015) Mapping of QTL for color of noodle dough sheet in a doubled haploid population. J Agr Sci-Camb 7(5):182–194. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v7n5p182
Kruger JE, Reed G (1988) Enzymes and colour. In: Pomeranz Y (ed) Wheat: chemistry and technology, vol 2. American Association Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, MN, pp 441–487
Kruger JE, Matsuo RR, Preston K (1992) A comparison of methods for the prediction of Cantonese noodle colour. Can J Plant Sci 72(4):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps92-128
Kumar J, Saripalli G, Gahlaut V, Goel N, Meher PK, Mishra KK, Mishra PC, Sehgal D, Vikram P, Sansaloni C, Singh S, Sharma PK, Gupta PK (2018) Genetics of Fe, Zn, b-carotene, GPC and yield traits in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using multi-locus and multitraits GWAS. Euphytica 214(11):219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2284-2
Li WH, Liu W, Liu L, You MS, Liu GT, Li BY (2011) QTL Mapping for wheat flour color with additive, epistatic, and QTL × environmental interaction effects. Agric Sci China 10(5):651–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60047-3
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Constructing genetics maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0 Whitehead Institute Technical Report. Whitehead Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA
Liu TT, An YL, Liu K, Wang FF, Xie CP, Zhang Y, Guan X, Tian JC, Chen JS (2017a) A genetic analysis of the quality of northern-style Chinese steamed bread. Mol Breed 37:41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0593-5
Liu TT, Liu K, Wang FF, Zhang Y, Li QF, Zhang KR, Xie CP, Tian JC, Chen JS (2017b) Conditional and unconditional QTLs mapping of gluten strength in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Integr Agr 16(10):2145–2155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61564-2
Liu K, Sun XX, Ning TY, Duan XX, Wang QL, Liu TT, An YL, Guan X, Tian JC, Chen JS (2018) Genetic dissection of wheat panicle traits using linkage analysis and a genome-wide association study. Theor Appl Genet 131(2):1073–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3059-9
Mares DJ, Campbell AW (2001) Mapping components of flour and noodle colour in Australian wheat. Aust J Agr Res 52(11–12):1297–1309. https://doi.org/10.1071/ar01048
Oliver JR, Blakeney AB, Allen HM (1992) Measurement of flour color in color space parameters. Cereal Chem 69(5):546–551
Parker GD, Langridge P (2000) Development of a STS marker linked to a major locus controlling flour color in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 6:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009638017859
Pestsova E, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2000) Isolation and mapping of microsatellite markers specific for the D genome of bread wheat. Genome 43:689–697. https://doi.org/10.1139/g00-042
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Roncallo PF, Cervigni GL, Jensen C, Miranda R, Carrera AD, Helguera M, Echenique V (2012) QTL analysis of main and epistatic effects for flour color traits in durum wheat. Euphytica 185(1):77–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0628-x
Sadequ A, Turner MA (2010) QTL Mapping of flour color in a hexaploid wheat doubled haploid population using diversity array technology. Thai J Agric Sci 43(2):103–108
Sun XD, Wang LK, Ren HB, Lan J (2002) The application of tristimulus colorimeter in the determination of flour color. Sci Technol Cereals Oils Foods 10(2):31–33
Sun XX, Liu TT, Ning TY, Liu K, Duan X, Wang XR, Wang QL, An YL, Guan X, Tian JC, Chen JS (2018) Genetic dissection of wheat kernel hardness using conditional QTL mapping of kernel size and protein-related traits. Plant Mol Biol Rep 34(6):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1061-z
Tsilo TJ, Hareland GA, Chao S, Anderson JA (2011) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of flour color and milling yield related traits using recombinant inbred lines in hard red spring wheat. Crop Sci 51(1):237–246. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.12.0711
Verlotta A, Simone VD, Mastrangelo AM, Cattivelli L, Papa R, Trono D (2010) Insight into durum wheat Lpx-B1: a small gene family coding for the lipoxygenase responsible for carotenoid bleaching in mature grains. BMC Plant Biol 10:263–269
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Wang DL, Zhu J, Li ZK, Paterson AH (1999) Mapping QTLs with epistatic effects and QTL × environment interactions by mixed linear model approaches. Theor Appl Genet 99:1255–1264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051331
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K, Allen A, Chao S, Huang BE, Maccaferri M, Salvi S, Milner SG, Cattivelli L, Mastrangelo AM, Whan A, Stephen S, Barker G, Wieseke R, Plieske J, Lillemo M, Mather D, Appels R (2014) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Wang FF, Liu TT, Li QF, An YL, Xie CP, Sun X, Liu K, Deng ZY, Tian JC, Chen JS (2016) QTL mapping of the pasting properties of wheat flour treated by papain digestion. Starch/stärke 68:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201600077
Wu P, Liu J, Chen GF, Zhao ZT, Yang Y, Li XY, Tang XZ, Tian JC (2018) Genome-wide association analysis between SNP Markers and Colour and texture related traits of steamed bread. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc 33(11):26–32. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2018.11.006
Zhai SN, He ZH, Wen WE, Jin H, Liu JD, Zhang Y, Liu ZY, Xia XC (2016a) Genome-wide linkage mapping of flour color-related traits and polyphenol oxidase activity in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 129:377–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2634-6
Zhai SN, Xia XC, He ZH (2016b) Carotenoids in staple cereals: metabolism, regulation, and genetic manipulation. Front Plant Sci 7:1197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01197
Zhai SN, Liu JD, Xu DA, Wen WE, Yan J, Zhang PP, Wan YX, Cao SH, Hao YF, Xia XC, Ma WJ, He ZH (2018) A Genome-wide association study reveals a rich genetic architecture of flour color-related traits in bread wheat. Front Plant Sci 9:1136. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01136
Zhai SN, He ZH, Wen WE, Liu JD, Jin H, Yan J, Zhang Y, Zhang PZ, Wan YX, Xia XC (2020) Genetic architecture of polyphenol oxidase activity in wheat flour by genome-wide association study. Crop Sci 60(3):1291–1293. https://doi.org/10.1002/csc2.20038
Zhang W, Dubcovsky J (2008) Association between allelic variation at the Phytoene synthase 1 gene and yellow pigment content in the wheat grain. Theor Appl Genet 116:635–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0697-8
Zhang X, Tian JC (2008) The color advantage of Chinese wheat with high whiteness and analysis of factors affecting color formation. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 41(2):347–353. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2008.02.005
Zhang KP, Chen GF, Zhao L, Liu B, Xu XB, Tian JC (2009a) Molecular genetic analysis of flour color using a doubled haploid population in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 165:471–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9756-8
Zhang X, Tian JC, Zhu DM (2009b) Correlation between quality traits and color of flour and dough sheet in RIL populations. J Chin Cereals Oils Assoc 24(6):1–6
Zhang YL, Wu YP, Xiao YG, He ZH, Zhang Y, Yan J, Zhang Y, Xia XC, Ma CX (2009c) QTL mapping for flour and noodle colour components and yellow pigment content in common wheat. Euphytica 165:435–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9744-z
Zhang SB, Lu QY, Yang HS, Meng DD (2011) Effects of protein content, glutenin-to-gliadin ratio, amylose content, and starch damage on textural properties of Chinese fresh white noodles. Cereal Chem 88(3):296–301. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-05-10-0072
Zhao Y, Sun HY, Wang YY, Pu YY, Kong FM, Li SS (2013) QTL mapping for the color, carotenoids and polyphenol oxidase activity of flour in recombinant inbred lines of wheat. Aust J Crop Sci 7(3):328–337
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971936), the Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (212102110273, 212102110267, 212102110298), the Major Project of Colleges and Universities of Henan Province (22A210016), and the Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province (ZR2019ZD15, 2019YQ028, 2019YQ014, 2019LZGC001-3, and 2017LZN047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. HL and JC conceived and designed the research. XJ wrote and revised the manuscript and analyzed the data. ZW collected the phenotypic data and participated in the statistics analysis. JZ, XL, and ZK helped with the statistics analysis. ZZ and QG provided valuable suggestions on the manuscript. JT revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
This manuscript did not contain any studies with human participants or animals and did not involve any endangered or protected species.
Consent for publication
Publication ethics have been followed during the preparation of manuscript. All authors approved the final version for submission. The manuscript has not been submitted to any other journal.
Informed consent
All authors approved the manuscript for submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Wang, Z., Zhao, J. et al. QTL analysis for 27 quality traits measured through the color of end-use products in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica 218, 121 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03055-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03055-3