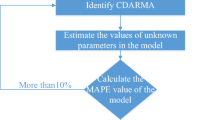
Abstract
Prediction of renewable energy consumption structure (RECS) can provide important guidance for energy development planning and energy structure transformation. The RECS refer to the proportion of various renewable energy consumptions and belong to compositional data, which could reflect the structural shapes of a complete system better. The multivariate compositional data’s vector autoregressive model (CDVAR) on the basis of the Simplex space and its algebraic system is proposed in this study aiming at the multi-dimensional small sample size. Firstly, the algebraic system of the Simplex space is introduced and the statistics of the compositional data are defined. Secondly, the novel model with the form of the compositional data is obtained and the least square parameter estimation of the model is derived according to Aitchison geometry. Third, the validation of the novel model is verified by the data on RECS in countries (China, USA, and Canada). The validation presents that the proposed model performs better in fitting, prediction, stability, and applicability compared with other five models under transformation. Last, the proposed model is applied to analyze and forecast the RECS of the above countries in 2021–2025 to provide an important basis for the optimization of the RECS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aburomman, A. A., & Reaz, M. B. I. (2017). A survey of intrusion detection systems based on ensemble and hybrid classifiers. Computers and Security, 65, 135–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cose.2016.11.004
Aitchison, J., & Egozcue, J. J. (2005). Compositional data analysis: Where are we and where should we be heading? Mathematical Geology, 37(7), 829–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-005-7383-7
Aitchison, J., Barceló-Vidal, C., Martín-Fernández, J. A., & Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. (2000). Logratio analysis and compositional distance. Mathematical Geology, 32(3), 271–275. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007529726302
Alenazi, A. (2021). A review of compositional data analysis and recent advances. Communications in Statistics: Theory and Methods. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2021.2014890
Alsaleh, M., & Abdul-Rahim, A. S. (2018). Bioenergy industry and the growth of the energy sector in the EU-28 region: Evidence from panel cointegration analysis. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 10, 053103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032323
Alsaleh, M., & Abdul-Rahim, A. S. (2019a). Financial development and bioenergy consumption in the EU28 region: Evidence from panel auto-regressive distributed lag bound approach. Resources, 8, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8010044
Alsaleh, M., & Abdul-Rahim, A. S. (2019b). Determinants of bioenergy consumption in the European continental countries: Evidence using GMM estimation. Pertanika Journal of Social Science and Humanities, 8, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8010043
Alsaleh, M., & Abdul-Rahim, A. S. (2021). Bioenergy consumption and economic growth in the EU-28 region: Evidence from a panel cointegration model. GeoJournal, 86, 1245–1260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10124-z
Baloch, Z. A., Tan, Q., Kamran, H. W., Nawaz, M. A., Albashar, G., & Hameed, J. (2022). A multi-perspective assessment approach of renewable energy production: Policy perspective analysis. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 24(2), 2164–2192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01524-8
Baye, R.S., Olper, A., Ahenkan, A., Musah Surugu, I.J., Weniga Anuga, S., & Darkwah, S. (2021). Renewable energy consumption in Africa: Evidence from a bias corrected dynamic panel. Science of the Total Enivronment, 766, 142583.
Chen, H., Xiao, X., & Wen, J. (2021). Novel multivariate compositional data’s model for structurally analyzing sub-industrial energy consumption with economic data. Neural Computing and Applications, 33(8), 3713–3735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05227-5
Chen, Y. (2018). Factors influencing renewable energy consumption in China: An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data. Journal of Cleaner Production, 174, 605–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.011
Ding, S., Tao, Z., Li, R. J., & Qin, X. H. (2022). A novel seasonal adaptive grey model with the data-restacking technique for monthly renewable energy consumption forecasting. Expert Systems with Applications., 208, 11811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118115
Duan, H., Wang, S., He, C., & Huang, J. (2021). Application of a novel grey Bernoulli model to predict the global consumption of renewable energy. Energy Reports, 7, 7200–7211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.10.070
Egozcue, J. J., & Pawlowsky-Glahn, V. (2005). Groups of parts and their balances in compositional data analysis. Mathematical Geology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-005-7381-9
Egozcue, J. J., Pawlowsky-Glahn, V., Mateu-Figueras, G., & Barceló-Vidal, C. (2003). Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Mathematical Geology, 35(3), 279–300. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023818214614
Erb, I. (2021). Power transformations of relative count data as a shrinkage problem. Springer. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.09215
Ferrers, N. M. (1876). An elementary treatise on trilinear co-ordinates: The model of reciprocal polars, and the theroy of projections. Macmillan and Company.
Gao, M. Y., Yang, H. L., Xiao, Q. Z., & Goh, M. (2022). COVID-19 lockdowns and air quality: Evidence from grey spatiotemporal forecasts. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seps.2022.101228
Gu, J., Cui, B., & Lu, S. (2021). A classification framework for multivariate compositional data with Dirichlet feature embedding. Knowledge-Based Systems, 212, 106614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106614
Gulraiz, A., Zaidi, S. S. H., & Samad, A. (2021). Pattern recognition approach to predict renewable energy consumption. International Multi-Topic ICT Conference. https://doi.org/10.1109/IMTIC53841.2021.9719779
He, Y. Y., Chen, Y., Zhang, W. Y., & Wang, Y. (2022). Optimizing energy consumption structure in Chongqing of China to achieve low-carbon and sustainable development based on compositional data. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 52, 10240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2022.102340
Hoyyi, A., Tarno, I., Maruddani, D. A., & Rahmawati, R. (2018). Vector autoregressive model approach for forecasting outflow cash in Central Java. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1025/1/012105
Hu, S., & Li, R. (2021). Investigating the effects of the united states’ economic slowdown related to the covid-19 pandemic on energy consumption in other countries—a global vector autoregressive model. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14112984
Huang, Y. S., Yang, L., Gao, C., Jiang, Y. Q., & Dong, Y. L. (2019). A novel prediction approach for short-term renewable energy consumption in China based on improved gaussian process regression. Energies, 12, 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12214181
Ilechukwu, N., & Lahiri, S. (2022). Renewable-energy consumption and international trade. Energy Reports., 8, 10624–10629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.08.209
Jiang, P., Yang, H., Li, H., & Wang, Y. (2021). A developed hybrid forecasting system for energy consumption structure forecasting based on fuzzy time series and information granularity. Energy, 219, 119599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119599
Khan, F., Saeed, A., & Ali, S. (2020). Modelling and forecasting of new cases, deaths and recover cases of COVID-19 by using vector autoregressive model in Pakistan. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 140, 110189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110189
Khatibi, A., Jahangir, M. H., Astaraei, F. R., & Mohabbati, F. (2022). Predicting the renewable energy consumption in 2026 by using a recursive moving average model. International Journal of Ambient Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2022.2031288
Li, S. (2021). Analysis of energy transformation path under the vision of "Double carbon" Lishifeng. https://doi.org/10.15937/j.cnki.issn1001-8263.2021.12.006
Ma, X., Wang, C., Dong, B., Gu, G., Chen, R., & Li, Y. (2019). Carbon emissions from energy consumption in China: Its measurement and driving factors. Science of the Total Environment, 648(27), 1411–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.183
Morris, B. (2003). The components of the wired spanning forest are recurrent. Probability Theory and Related Fields, 125(2), 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00440-002-0236-0
Pawlowsky -Glahn, V., & Egozcue, J.J. (2001). Geometric approach to statistical analysis on the simplex. Stochastic Enivironmental Research and Rsik Assessment, 15(5), 384–398
Pawlowsky-Glahn, V., & Egozcue, J. J. (2016). Spatial analysis of compositional data: A historical review. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 164, 28–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.12.010
Rao, C. J., Gao, M. Y., Wen, J. H., & Goh, M. (2022). Multi-attribute group decision making method with dual comprehensive clouds under information environment of dual uncertain Z-numbers. Information Sciences, 602, 106–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.04.031
Salahodjaev, R., Sharipov, K., Rakhmanov, N., & Khabirov, D. (2022). Tourism, renewable energy and CO2 emissions: evidence from Europe and Central Asia. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01993-x
Tlili, I. (2015). Renewable energy in Saudi Arabia: Current status and future potentials. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 17(4), 859–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-014-9579-9
Von Eynatten, H., Pawlowsky-Glahn, V., & Egozcue, J. J. (2002). Understanding perturbation on the simplex: A simple method to better visualize and interpret compositional data in ternary diagrams. Mathematical Geology, 34(3), 249–257. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014826205533
Wang, Z.-X., Wang, Z.-W., & Li, Q. (2020). Forecasting the industrial solar energy consumption using a novel seasonal GM(1,1) model with dynamic seasonal adjustment factors. Energy, 200, 117460.
Wang, Bi, Wu, Ying., Liu, Peng., Chen, S. (2022). Study on regional heterogeneity of influencing factors of renewable energy development. Jounal of BeiJing insititute of technology (Social sciences edition). https://doi.org/10.15918/j.jbitss1009-3370.2022.5679
Wang, H., Huang, W., & Liu, Q. (2003). Forecast analysis for Beijing’s industry Structure. Jounal of Systems Sciences and Information, 6788, 123–127.
Wang, H., Shangguan, L., Guan, R., & Billard, L. (2015). Principal component analysis for compositional data vectors. Computational Statistics, 30(4), 1079–1096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-015-0570-1
Wang, H., Shangguan, L., Wu, J., & Guan, R. (2013). Multiple linear regression modeling for compositional data. Neurocomputing, 122, 490–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.025
Wei, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, H., Li, Y., & Jiang, Z. (2019). Predicting population age structures of China, India, and Vietnam by 2030 based on compositional data. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212772
Wu, W., Ma, X., Zeng, B., Wang, Y., & Cai, W. (2019). Forecasting short-term renewable energy consumption of China using a novel fractional nonlinear grey Bernoulli model. Renewable Energy, 140(2019), 70–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.03.006
Xiao, X. P., & Li, X. (2022). A novel compositional data model for predicting the energy consumption structures of Europe, Japan, and China. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02547-5
Zhang, K., Yin, K. D., & Yang, W. D. (2022). Predicting bioenergy power generation structure using a newly developed grey compositional data model: A case study in China. Renewable Energy, 198, 695–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.08.050
Zhang, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhu, Y., Zhang, J., Ren, Q., & Huang, T. (2021). Effects of redispersible polymer powders on the structural build-up of 3D printing cement paste with and without hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Construction and Building Materials, 267, 120551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120551
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editor for providing valuable comments. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Xiao, X. & Chen, H. A novel method for forecasting renewable energy consumption structure based on compositional data: evidence from China, the USA, and Canada. Environ Dev Sustain 26, 5299–5333 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-02935-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-02935-5