Abstract
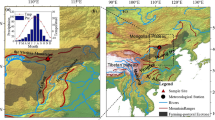
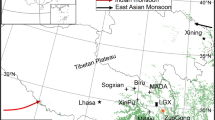
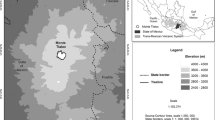
Chinese pine (Pinus tabulaeformis) is a highly climate-sensitive species. Presently, the Huanglong Mountains are covered by widespread forests dominated by Chinese pine and thus has a great potential for dendrochronological studies. To increase the knowledge of NDVI changes of the Loess Plateau and their potential influences on the environmental changes, the regional tree-ring chronology from the Huanglong Mountains was used to investigate climate/NDVI relationships. Standard dendrochronological methods were applied to a regional tree-ring series of Pinus tabulaeformis from the Huanglong Mountains, the Loess Plateau. The relationships between ring widths and NDVI/climate factors were investigated by the simple and spatial correlation analysis. The results of the correlation analysis indicated that mean temperature has negative influences on tree growth, while the tree-ring widths of Chinese pine reflect the variations of the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). Herein the standard tree-ring width series was used to develop June–July NDVI for the Huanglong Mountains during the period AD 1812–2012, and it explained 41.2 % of the total NDVI variance during the period AD 1982–2006. The results of the spatial analysis show that the reconstructed NDVI has strong drought signals for the Huanglong Mountains. Drought events in the NDVI series are compared to the historical records and climate data in the study area, and show common drought events over much of Shaanxi. These drought-caused famines have had strong influences on the people of Shaanxi during the past 201 years. The moving correlation between March–July temperature and the NDVI reconstruction showed that the recent warming is the most important driving force of the drying trend and the resulting in tree growth decline during the last 30 years. Our reconstructed NDVI is significantly correlated with sea surface temperature in the Indian and the western Pacific Oceans. The linkages to the Indian and Pacific Oceans suggest the connection of regional NDVI variations to large-scale ocean–atmosphere–land circulation systems. Our NDVI reconstruction provides the long-term perspective on the vegetation dynamics of the Huanglong Mountains and is used to guide expectations of future forest variations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, Q. G. (2001). Soil erosion and management on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 11, 53–70.
Cai, Q. F., & Liu, Y. (2013). Climatic response of Chinese pine and PDSI variability in the middle Taihang Mountains, north China since 1873. Trees, 27, 419–427.
Cai, Q. F., Liu, Y., Song, H. M., & Sun, J. Y. (2008). Tree-ring-based reconstruction of the April to September mean temperature since 1826 AD for north-central Shaanxi Province, China. Science in China Series D, 51, 1099–1106.
Chen, F., Yuan, Y. J., Wei, W. S., Fan, Z. A., Yu, S. L., Zhang, T. W., et al. (2013). Reconstructed precipitation for the north-central China over the past 380 years and its linkages to East Asian summer monsoon variability. Quaternary International, 283, 36–45.
Chen, F., Yuan, Y. J., Wei, W. S., Yu, S. L., Fan, Z. A., Zhang, R. B., et al. (2012). Tree-ring-based reconstruction of precipitation for the Changling Mountains, China, since A.D. 1691. International Journal of Biometeorology, 56, 765–774.
Chen, F., Yuan, Y. J., Zhang, R. B., & Qin, L. (2014). A tree-ring based drought reconstruction (AD 1760–2010) for the Loess Plateau and its possible driving mechanisms. Global and Planetary Change, 122, 82–88.
Cook, E. R., & Kairiukstis, L. A. (1990). Methods of dendrochronology. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Press.
D’Arrigo, R. D., Malmstrom, C. M., Jacoby, G. C., Los, S. O., & Bunker, D. E. (2000). Correlation between maximum latewood density of annual tree rings and NDVI based estimates of forest productivity. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21, 2329–2336.
Fang, K. Y., Gou, X. H., Chen, F. H., Liu, C., Davi, N., Li, J. B., et al. (2012). Tree-ring based reconstruction of drought variability (1615–2009) in the Kongtong Mountain area, northern China. Global and Planetary Change, 81–82, 190–197.
Fritts, H. C. (1976). Tree rings and climate. London: Academic Press.
Hao, Z., Zheng, J., Wu, G., Zhang, X., & Ge, Q. (2010). 1876–1878 severe drought in North China: Facts, impacts and climatic background. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(26), 3001–3007.
He, J. C., & Shao, X. M. (2006). Relationships between tree-ring width index and NDVI of grassland in Delingha. Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 1106–1114.
Holmes, R. L. (1983). Computer-assisted quality control in tree-ring dating and measurement. Tree-Ring Bulletin, 43, 69–95.
Kang, Y. X., Yue, J. W., & Zhang, Q. M. (2007). Classification of Quercus liaotungensis communities and biodiversity in the Huanglong Mountain. Journal-Northwest Forestry University, 22(3), 7–10. (in Chinese).
Leblanc, D., & Terrell, M. (2001). Dendroclimatic analyses using Thornthwaite–Mather-Type evapotranspiration models: A bridge between dendroecology and forest simulation models. Tree-Ring Research, 57, 55–66.
Li, Y. (2000). Effects of forest on water circle on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Natural Resources, 16, 427–432.
Liang, E., Shao, X., Kong, Z., & Lin, J. (2003). The extreme drought in the 1920s and its effect on tree growth deduced from tree ring analysis: A case study in North China. Annals of Forest Science, 60, 145–152.
Liu, Y., Shi, J., Shishov, E., Vaganov, E., Yang, K., Cai, Q., et al. (2004). Reconstruction of May–July precipitation in the north Helan Mountain, Inner Mongolia since A.D. 1726 from tree-ring late-wood widths. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49, 2487–2492.
Liu, Y., Wu, X. D., Shao, X. M., Liu, H. B., An, Z. S., Zhu, Y. Z., et al. (1997). Seasonal precipitation and temperature reconstruction based on tree-ring density and stable carbon isotope. Science in China Series D, 27, 271–277.
Lu, Z. W., & Cao, X. P. (2010). Strategies and measures of close-to-nature forest management in Huanglongshan Forest Bureau. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 30, 7–10. (in Chinese).
Osborn, T. J., Briffa, K. R., & Jones, P. D. (1997). Adjusting variance for sample-size in tree-ring chronologies and other regional mean timeseries. Dendrochronologia, 15, 89–99.
Qiang, J. H., Zhan, P. X., & Chen, G. L. (2007). A study on remote monitoring of the growth status natural forests of Chinese pine based on the NDVI. Journal-Northwest Forestry University, 22, 149–151.
Rayner, N. A., Parker, D. E., Horton, E. B., Folland, C. K., Alexander, L. V., Rowell, D. P., et al. (2003). Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. Journal Geophysical Research, 108(D14), 4407.
Robinson, A. R. (1981). Erosion and sediment control in China’s Yellow River Basin. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 36, 125–127.
Shi, Y. F., Shen, Y. P., Kang, E. S., Li, D. L., Ding, Y. J., Zhang, G. W., et al. (2007). Recent and future climate change in northwest China. Climate Change, 80, 379–393.
Sun, J. Y., Liu, Y., Sun, B., & Wang, R. Y. (2012). Tree-ring based PDSI reconstruction since 1853 AD in the source of the Fenhe River Basin, Shanxi Province, China. Science in China Series D, 55, 1847–1854.
Sun, J. Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Y. C., Bao, G., & Sun, B. (2013). Tree-ring based runoff reconstruction of the upper Fenhe River basin, North China, since 1799 AD. Quaternary International, 283, 117–124.
Trouet, V., & Van Oldenborgh, G. J. (2013). KNMI Climate Explorer: A web-based research tool for high-resolution paleoclimatology. Tree-Ring Research, 69, 3–13.
Tucker, C. J., Pinzon, J. E., Brown, M. E., Slayback, D. A., Pak, E. W., Mahoney, R., et al. (2005). An extended AVHRR 8-km NDVI data set compatible with MODIS and SPOT vegetation NDVI data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26, 4485–4498.
Vicente-Serrano, S. M., Beguería, S., & López-Moreno, J. I. (2010). A Multi-scalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index—SPEI. Journal of Climate, 23, 1696–1718.
Wang, H. (2001). The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 18, 376–386.
Wei, X., Huang, M., Shao, M., Li, L., Zhang, X., & Horton, R. (2013). Shrubs increase soil resources heterogeneity along semiarid grass slopes in the Loess Plateau Original Research Article. Journal of Arid Environments, 88, 175–183.
Wigley, T., Briffa, K. R., & Jones, P. D. (1984). On the average value of correlated time series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. Journal of Climate and Applied Meteorology, 23, 201–213.
Wu, R. G., & Wang, B. (2002). A contrast of the east Asian summer monsoon-ENSO relationship between 1962–77 and 1978–93. Journal of Climate, 15, 3266–3279.
Yuan, L. (1994). The disaster history of the Northwest of China. Lanzhou: Gansu People’s Publishing House.
Zhao, X. N., Zhang, B. Q., & Wu, P. T. (2014). Changes in key driving forces of soil erosion in the Middle Yellow River Basin: Vegetation and climate. Natural Hazards, 70, 957–968.
Zhou, T., Yu, R., Zhang, J., Drange, H., Cassou, C., Deser, C., & Okumura, Y. (2009). Why the western Pacific subtropical high has extended westward since the late 1970s. Journal of Climate, 22, 2199–2215.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Public Benefit (Meteorology) Research Foundation of China (GYHY(QX)201506001-14), Excellent Youth Science and Technology Innovation Personnel Training Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (qn2015yx040), and the Young Talent Training Plan of Meteorological Departments of China Meteorological Administration. We thank the reviewers very much whose comments greatly benefitted this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Chen, F., Zhang, R. et al. Seasonal dynamics of vegetation of the central Loess Plateau (China) based on tree rings and their relationship to climatic warming. Environ Dev Sustain 19, 2535–2546 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9870-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9870-z