Abstract
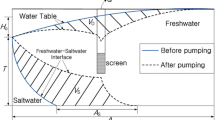
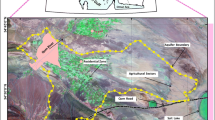
In the present work, a simulation-optimization method is employed in order to manage saltwater intrusion in two unconfined coastal aquifers in Crete, Greece. The optimization formulation seeks to maximize groundwater withdrawal rates while maintaining the saltwater intrusion front at the current location or inhibiting it at locations closer to the coast. A combination of a groundwater flow model (MODFLOW) with the Ghyben-Herzberg saltwater front approximation and a sequential implementation of the Simplex algorithm (GWM) are employed. The results show that under the current pumping strategies, the saltwater intrusion front will continue to move inland, posing a serious threat to the groundwater quality of these regions. Optimal groundwater withdrawal scenarios that take into consideration the water needs of the local communities and environmental concerns are presented and discussed. In both case studies, significant reductions in pumping are required in order for the saltwater intrusion front to retract closer to the shoreline.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Werner, A. D., Bakker, M., Post, V. E. A., Vandenbohede, A., Lu, C., Ataie-Ashtiani, B., Simmons, C. T., & Barry, A. (2013). Seawater intrusion processes, investigation, and management: recent advances and future challenges. Advances in Water Resources, 51, 3–26.
Karatzas, G. P., & Dokou, Z. (2015). Optimal management of saltwater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of Malia, Crete (Greece). Hydrogeology Journal, 23(6), 1181–1194.
Pinder, G. F., & Cooper, H. H. (1970). A numerical technique for calculating transient position of saltwater front. Water Resources Research, 6(3), 875–882.
Milnes, E., & Renard, P. (2004). The problem of salt recycling and seawater intrusion in coastal irrigated plains: an example from the Kiti aquifer (southern Cyprus). Journal of Hydrology, 288(3–4), 327–343.
Giambastiani, B. M. S., Antonellini, M., Essink, G. H. P. O., & Stuurman, R. J. (2007). Saltwater intrusion in the unconfined coastal aquifer of Ravenna (Italy): a numerical model. Journal of Hydrology, 340(1–2), 91–104.
Kopsiaftis, G., Mantoglou, A., & Giannoulopoulos, P. (2009). Variable density coastal aquifer models with application to an aquifer on Thira Island. Desalination, 237(1–3), 65–80.
Kourakos, G., & Mantoglou, A. (2009). Pumping optimization of coastal aquifers based on evolutionary algorithms and surrogate modular neural network models. Advances in Water Resources, 32(4), 507–521.
Dokou, Z., & Karatzas, G. P. (2012). Saltwater intrusion estimation in a karstified coastal system using density-dependent modelling and comparison with the sharp-interface approach. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 57(5), 985–999.
Reilly, T. E., & Goodman, A. S. (1985). Quantitative-analysis of saltwater fresh-water relationships in groundwater systems-a historical-perspective. Journal of Hydrology, 80(1–2), 125–160.
Mantoglou, A., Papantoniou, M., & Giannoulopoulos, P. (2004). Management of coastal aquifers based on nonlinear optimization and evolutionary algorithms. Journal of Hydrology, 297(1–4), 209–228.
Mantoglou, A. (2003). Pumping management of coastal aquifers using analytical models of saltwater intrusion. Water Resources Research. doi:10.1029/2002WR001891.
Guvanasen, V., Wade, S. C., & Barcelo, M. D. (2000). Simulation of regional ground water flow and salt water intrusion in Hernando County, Florida. Ground Water, 38(5), 772–783.
Ababou, R., & Al-Bitar, A. (2004). Salt water intrusion with heterogeneity and uncertainty: mathematical modelling and analyses. Developments in Water Science, 55, 1559–1571.
Karterakis, S. M., Karatzas, G. P., Nikolos, I. K., & Papadopoulou, M. P. (2007). Application of linear programming and differential evolutionary optimization methodologies for the solution of coastal subsurface water management problems subject to environmental criteria. Journal of Hydrology, 342(3–4), 270–282.
Koukadaki, M. A., Karatzas, G. P., Papadopoulou, M. P., & Vafidis, A. (2007). Identification of the saline zone in a coastal aquifer using electrical tomography data and simulation. Water Resources Management, 21(11), 1881–1898.
Papadopoulou, M. P., Varouchakis, E. A., & Karatzas, G. P. (2010). Terrain discontinuity effects in the regional flow of a complex karstified aquifer. Environmental Modeling and Assessment, 15(5), 319–328.
Shamir, U., Bear, J., & Gamliel, A. (1984). Optimal annual operation of a coastal aquifer. Water Resources Research, 20, 435–444.
Uddameri, V., & Kuchanur, Z. M. (2007). Simulation-optimization approach to assess groundwater availability in Refugio County, TX. Environment Geology, 51, 921–929.
Gorelick, S. M., Voss, C. I., Gill, P. E., Murray, W., Saunders, M. A., & Wright, M. H. (1984). Aquifer reclamation design: the use of contaminant transport simulation combined with non-linear programming. Water Resources Research, 20(4), 415–427.
Willis, R., & Finney, B. A. (1988). Planning model for optimal control of saltwater intrusion. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 114(2), 163–178.
Finney, B. A., Samsuhadi, & Willis, R. (1992). Quasi-three-dimensional optimization model of Jakarta Basin. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 118(1), 18–31.
Gharbi, A., & Peralta, R. C. (1994). Integrated embedding optimization applied to salt Lake valley aquifers. Water Resources Research, 30(3), 817–832.
Reinelt, P. (2005). Seawater intrusion policy analysis with a numerical spatially heterogeneous dynamic optimization model. Water Resources Research, 41(W05006).
Cheng, A. H.-D., Halhal, D., Naji, A., & Ouazar, D. (2000). Pumping optimization in saltwater-intruded coastal aquifers. Water Resources Research, 36(8), 2155–2165.
Cai, X., McKinney, D. C., & Lasdon, L. S. (2001). Solving non-linear water management models using a combined genetic algorithm and linear programming approach. Advances in Water Resources, 24, 667–676.
Dhar, A., & Datta, B. (2009). Saltwater intrusion management of coastal aquifers. I: linked simulation-optimization. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 14(12), 1263–1272.
Mantoglou, A., & Papantoniou, M. (2008). Optimal design of pumping networks in coastal aquifers using sharp interface models. Journal of Hydrology, 361, 52–63.
Kourakos, G., & Mantoglou, A. (2011). Simulation and multi-objective management of coastal aquifers in semi-arid regions. Water Resources Management, 25, 1063–1074.
Papadopoulou, M. P., Varouchakis, E. A., & Karatzas, G. P. (2009). Simulation of complex aquifer behavior using numerical and geostatistical methodologies. Desalination, 237, 42–53.
Varouchakis, E. A., Karatzas, G. P., & Giannopoulos, G. P. (2014). Impact of irrigation scenarios and precipitation projections on the groundwater resources of Viannos basin in the island of Crete. Greece. Environmental Earth Sciences. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3913-2.
Llopis-Albert, C., & Pulido-Velazquez, D. (2014). Discussion about the validity of sharp-interface models to deal with seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers. Hydrological Processes, 28(10), 3642–3654.
Ahlfeld, D.P., Barlow P.M., & Mulligan, A.E. (2005). GWM—a groundwater-management process for the U.S. Geological Survey modular ground-water model (MODFLOW-2000). USA: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2005–1072.
Paritsis, S.N. (2005). Simulation of seawater intrusion into the Tymbaki aquifer, South Central Crete, Greece. Heraklion, Crete, Greece: Department of Management of Water Resources of the Region of Crete.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dokou, Z., Dettoraki, M., Karatzas, G.P. et al. Utilizing Successive Linearization Optimization to Control the Saltwater Intrusion Phenomenon in Unconfined Coastal Aquifers in Crete, Greece. Environ Model Assess 22, 115–128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-016-9529-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-016-9529-z