Abstract
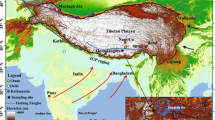
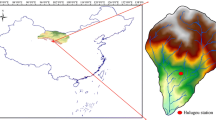
Remote region is normally considered a receptor of long-range transported pollutants. Monitoring stations are important platforms for investigating the atmospheric environment of remote regions. However, the potential contribution of very local sources around these stations may produce important influences on its atmospheric environment, which is still barely studied. In this study, major ions of precipitation were investigated simultaneously at a typical remote station (Nam Co station) and other sites nearby on the Tibetan Plateau (TP) — the so-called “The Third Pole” in the world. The results showed that despite low values compared to those of other remote regions, the concentrations of major ions in precipitation of Nam Co station (e.g., Ca2+: 32.71 μeq/L; \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\): 1.73 μeq/L) were significantly higher than those at a site around 2.2 Km away (Ca2+: 11.47 μeq/L; \(\mathrm{SO}_4^{2-}\): 0.64 μeq/L). This provides direct evidence that atmospheric environment at Nam Co station is significantly influenced by mineral dust and pollutants emitted from surface soil and anthropogenic pollutants of the station itself. Therefore, numbers of other related data reported on the station are influenced. For example, the aerosol concentration and some anthropogenic pollutants reported on Nam Co station should be overestimated. Meanwhile, it is suggested that it is cautious in selecting sites for monitoring the atmospheric environment at the remote station to reduce the potential influence from local sources.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the funding of this study are available within the article.
References
Adhikari, S., Zhang, F., Adhikari, N. P., Zeng, C., Pant, R. R., Ram, K., Liu, Y., Ahmed, N., Xu, J., Tripathee, L., Zhang, Q., Bhuiyan, M. A. Q., & Ahsan, M. A. (2021). Atmospheric wet deposition of major ionic constituents and inorganic nitrogen in Bangladesh: implications for spatiotemporal variation and source apportionment. Atmospheric Research, 250, 105414.
Adhikari, S., Zhang, F., Zeng, C., Tripathee, L., Adhikari, N. P., Xu, J., & Wang, G. (2019). Precipitation chemistry and stable isotopic characteristics at Wengguo in the northern slopes of the Himalayas. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 76, 289–313.
Ahmed, M. S., Bhuyan, P., Sarkar, S., & Hoque, R. R. (2022). Seven-year study of monsoonal rainwater chemistry over the mid-Brahmaputra plain, India: assessment of trends and source regions of soluble ions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29, 25276–25295.
Cao, J.-J., Xu, B.-Q., He, J.-Q., Liu, X.-Q., Han, Y.-M., Wang, G.-h., Zhu, C.-s., 2009. Concentrations, seasonal variations, and transport of carbonaceous aerosols at a remote Mountainous region in western China. Atmospheric Environment 43, 4444-4452.
Chen, P., Kang, S., Bai, J., Sillanpää, M., & Li, C. (2015). Yak dung combustion aerosols in the Tibetan Plateau: chemical characteristics and influence on the local atmospheric environment. Atmospheric Research, 156, 58–66.
Cong, Z., Kang, S., Smirnov, A., & Holben, B. (2009). Aerosol optical properties at Nam Co, a remote site in central Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Research, 92, 42–48.
Dong, Z., Brahney, J., Kang, S., Elser, J., Wei, T., Jiao, X., & Shao, Y. (2020). Aeolian dust transport, cycle and influences in high-elevation cryosphere of the Tibetan Plateau region: new evidences from alpine snow and ice. Earth-Science Reviews, 211, 103408.
Dong, Z., Kang, S., Qin, X., Li, X., Qin, D., & Ren, J. (2015). New insights into trace elements deposition in the snow packs at remote alpine glaciers in the northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Science of the Total Environment, 529, 101–113.
Dong, Z., Qin, D., Kang, S., Ren, J., Chen, J., Cui, X., Du, Z., & Qin, X. (2014). Physicochemical characteristics and sources of atmospheric dust deposition in snow packs on the glaciers of western Qilian Mountains, China. Tellus Series B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 66(1), 20956.
Duan, K. Q., Thompson, L. G., Yao, T., Davis, M. E., & Mosley-Thompson, E. (2007). A 1000 year history of atmospheric sulfate concentrations in southern Asia as recorded by a Himalayan ice core. Geophysical Research Letters, 34.
Gu, Y., Du, J., Tang, Y., Qiao, X., Bossard, C., & Deng, G. P. (2013). Challenges for sustainable tourism at the Jiuzhaigou World Natural Heritage site in western China. Natural Resources Forum, 37, 103–112.
Kang, S., Chen, P., Li, C., Liu, B., & Cong, Z. (2016). Atmospheric aerosol elements over the Inland Tibetan Plateau: concentration, seasonality, and transport. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 16, 789–800.
Kang, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Dong, Z., Li, C., Wang, C., Chen, P., & Rawat, B. (2020). Chapter Three - chemical components and distributions in glaciers of the Third Pole. In C. M. Sharma, S. Kang, & L. Tripathee (Eds.), Water quality in the third pole (pp. 71–134). Elsevier.
Kang, S. C., Mayewski, P. A., Qin, D. H., Yan, Y. P., Zhang, D. Q., Hou, S. G., & Ren, J. W. (2002). Twentieth century increase of atmospheric ammonia recorded in Mount Everest ice core. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 107.
Kang, S. C., Zhang, Q. G., Qian, Y., Ji, Z. M., Li, C. L., Cong, Z. Y., Zhang, Y. L., Guo, J. M., Du, W. T., Huang, J., You, Q. L., Panday, A. K., Rupakheti, M., Chen, D. L., Gustafsson, O., Thiemens, M. H., & Qin, D. H. (2019). Linking atmospheric pollution to cryospheric change in the Third Pole region: current progress and future prospects. National Science Review, 6, 796–809.
Kumar, P., Yadav, S., & Kumar, A. (2014). Sources and processes governing rainwater chemistry in New Delhi, India. Natural Hazards, 74, 2147–2162.
Li, C., Bosch, C., Kang, S., Andersson, A., Chen, P., Zhang, Q., Cong, Z., Chen, B., Qin, D., & Gustafsson, Ö. (2016a). Sources of black carbon to the Himalayan–Tibetan Plateau glaciers. Nature Communications, 7, 12574.
Li, C., Kang, S., & Yan, F. (2018a). Importance of local black carbon emissions to the fate of glaciers of the Third Pole. Environmental Science & Technology, 52, 14027–14028.
Li, C., Yan, F., Kang, S., Chen, P., Han, X., Hu, Z., Zhang, G., Hong, Y., Gao, S., Qu, B., Zhu, Z., Li, J., Chen, B., & Sillanpää, M. (2017a). Re-evaluating black carbon in the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau: concentrations and deposition. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 11899–11912.
Li, C. L., Chen, P. F., Kang, S. C., Yan, F. P., Tripathee, L., Wu, G. J., Qu, B., Sillanpaa, M., Yang, D., Dittmar, T., Stubbins, A., & Raymond, P. A. (2018b). Fossil fuel combustion emission from South Asia influences precipitation dissolved organic carbon reaching the remote Tibetan Plateau: isotopic and molecular evidence. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 123, 6248–6258.
Li, C. L., Kang, S. C., Zhang, Q. G., & Kaspari, S. (2007). Major ionic composition of precipitation in the Nam Co region, Central Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Research, 85, 351–360.
Li, C. L., Yan, F. P., Kang, S. C., Yan, C. Q., Hu, Z. F., Chen, P. F., Gao, S. P., Zhang, C., He, C. L., Kaspari, S., & Stubbins, A. (2021a). Carbonaceous matter in the atmosphere and glaciers of the Himalayas and the Tibetan plateau: an investigative review. Environment International, 146, 106281.
Li, J. G., Li, Z. X., & Feng, Q. (2017b). Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the chemical compositions of precipitation at a rapidly urbanized city in Northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76.
Li, Y., Yan, F., Kang, S., Zhang, C., Chen, P., Hu, Z., & Li, C. (2021b). Sources and light absorption characteristics of water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC) of atmospheric particles at a remote area in inner Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Research, 253, 105472.
Li, Y., Yan, Y., & Yun, X. (2015). The spatial structure of Tibet tourism based on tourism digital footprint. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 29, 176–182.
Li, Y.-C., Zhang, M., Shu, M., Ho, S. S. H., Liu, Z.-F., Wang, X.-X., & Zhao, X.-Q. (2016b). Chemical characteristics of rainwater in Sichuan basin, a case study of Ya’an. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 13088–13099.
Liu, B., Cong, Z., Wang, Y., Xin, J., Wan, X., Pan, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Zhang, G., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., & Kang, S. (2017). Background aerosol over the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau: observed characteristics of aerosol mass loading. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 17, 449–463.
Liu, B., Kang, S. C., Sun, J. M., Zhang, Y. L., Xu, R., Wang, Y. J., Liu, Y. W., & Cong, Z. Y. (2013). Wet precipitation chemistry at a high-altitude site (3,326 m a.s.l.) in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 5013–5027.
Liu, X., Xu, B., Yao, T., Wang, N., & Wu, G. (2008). Carbonaceous particles in Muztagh Ata ice core, West Kunlun Mountains, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53, 3379–3386.
Mao, R., Wu, H., He, J., Guo, Z., Wu, Y., & Wu, X. (2013). Spatiotemporal variation of albedo of Muztagh Glacier in the Kunlun Mountains and its relation to dust. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 35, 1133–1142.
Ming, J., Xiao, C., Sun, J., Kang, S., & Bonasoni, P. (2010). Carbonaceous particles in the atmosphere and precipitation of the Nam Co region, central Tibet. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 22, 1748–1756.
Mishra, S. K., Jain, S., Salunke, P., & Sahany, S. (2019). Past and future climate change over the Himalaya–Tibetan Highland: inferences from APHRODITE and NEX-GDDP data. Climatic Change, 156, 315–322.
Qiao, X., Du, J., Kota, S. H., Ying, Q., Xiao, W., & Tang, Y. (2018). Wet deposition of sulfur and nitrogen in Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China during 2015–2016: Possible effects from regional emission reduction and local tourist activities. Environmental Pollution, 233, 267–277.
Rao, P. S. P., Tiwari, S., Matwale, J. L., Pervez, S., Tunved, P., Safai, P. D., Srivastava, A. K., Bisht, D. S., Singh, S., & Hopke, P. K. (2016). Sources of chemical species in rainwater during monsoon and non-monsoonal periods over two mega cities in India and dominant source region of secondary aerosols. Atmospheric Environment, 146, 90–99.
Sharma, A., & Kulshrestha, U. C. (2020). Wet deposition and long-range transport of major ions related to snow at Northwestern Himalayas (India). Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 20, 1249–1265.
Singh, S., Gupta, G. P., Kumar, B., & Kulshrestha, U. C. (2014). Comparative study of indoor air pollution using traditional and improved cooking stoves in rural households of Northern India. Energy for Sustainable Development, 19, 1–6.
Tripathee, L., Guo, J., Kang, S., Paudyal, R., Sharma, C. M., Huang, J., Chen, P., Sharma Ghimire, P., Sigdel, M., & Sillanpää, M. (2020). Measurement of mercury, other trace elements and major ions in wet deposition at Jomsom: the semi-arid mountain valley of the Central Himalaya. Atmospheric Research, 234, 104691.
Wang, L., Shen, Z., Lu, D., Xu, H., Zhang, N., Lei, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, X., Wang, Q., & Cao, J. (2019a). Water-soluble ions and oxygen isotope in precipitation over a site in northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 76, 229–243.
Wang, W., Xu, W., Collett, J. L., Liu, D., Zheng, A., Dore, A. J., & Liu, X. (2019b). Chemical compositions of fog and precipitation at Sejila Mountain in the southeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Environmental Pollution, 253, 560–568.
Wei, T., Kang, S., Dong, Z., Qin, X., Shao, Y., & Rostami, M. (2020). Natural versus anthropogenic sources and seasonal variability of insoluble precipitation residues at Laohugou Glacier in northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114114.
Xu, X., Zhang, H., Lin, W., Wang, Y., Xu, W., & Jia, S. (2018). First simultaneous measurements of peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and ozone at Nam Co in the central Tibetan Plateau: impacts from the PBL evolution and transport processes. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 18, 5199–5217.
Yang, X., Davis, M. E., Acharya, S., & Yao, T. (2018). Asian monsoon variations revealed from stable isotopes in precipitation. Climate Dynamics, 51, 2267–2283.
Yang, Y. J., Liu, J. Q., Di, Y. A., Yang, J., Wen, T. X., Li, Y. W., & Shi, Y. Q. (2012). Major ionic composition of precipitation in the Shigatse region, Southern Tibetan Plateau. Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 1005.
Yao, T., Thompson, L., Yang, W., Yu, W., Gao, Y., Guo, X., Yang, X., Duan, K., Zhao, H., Xu, B., Pu, J., Lu, A., Xiang, Y., Kattel, D. B., & Joswiak, D. (2012). Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings. Nature Climate Change, 2, 663–667.
You, Q., Kang, S., Li, C., Li, M., & Liu, J. (2007). Variation features of meteorological elements at Namco Station, Tibetan Plateau. Meteorological Monthly, 33, 54–60.
Zeng, J., & Han, G. (2020). Rainwater chemistry reveals air pollution in a karst forest: temporal variations, source apportionment, and implications for the forest. Atmosphere, 11, 1315.
Zeng, J., Yue, F.-J., Li, S.-L., Wang, Z.-J., Wu, Q., Qin, C.-Q., & Yan, Z.-L. (2020). Determining rainwater chemistry to reveal alkaline rain trend in Southwest China: evidence from a frequent-rainy karst area with extensive agricultural production. Environmental Pollution, 266, 115166.
Zhang, Y. L., Kang, S. C., Li, C. L., Cong, Z. Y., & Zhang, Q. G. (2012). Wet deposition of precipitation chemistry during 2005-2009 at a remote site (Nam Co Station) in central Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 69, 187–200.
Zhao, Z., Wang, Q., Xu, B., Shen, Z., Huang, R., Zhu, C., Su, X., Zhao, S., Long, X., Liu, S., & Cao, J. (2017). Black carbon aerosol and its radiative impact at a high-altitude remote site on the southeastern Tibet Plateau. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 122, 5515–5530.
Zhu, L., Xie, M., & Wu, Y. (2010). Quantitative analysis of lake area variations and the influence factors from 1971 to 2004 in the Nam Co basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55, 1294–1303.
Zongxing, L., Qi, F., Wei, L., Tingting, W., Aifang, C., Yan, G., Xiaoyan, G., Yanhui, P., Jianguo, L., Rui, G., & Bing, J. (2014). Study on the contribution of cryosphere to runoff in the cold alpine basin: a case study of Hulugou River Basin in the Qilian Mountains. Global and Planetary Change, 122, 345–361.
Liu, Y. W., Xu, R., Wang, Y. S., Pan, Y. P., & Piao, S. L. (2015). Wet deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen at five remote sites in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15, 11683–11700.
Funding
This work was supported by the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (STEP) (2019QZKK0605), the NSFC (41971096, 41977397), CAS “Light of West China” Program (E0900104), and the State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science (SKLCS-ZZ-2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yixi Liu: methodology, investigation, resources, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. Chao Zhang: investigation, methodology, writing — review and editing. Fangping Yan: resources, investigation, writing — review and editing. Yinbo Xu: investigation. Pengling Wang: writing — review. Chaoliu Li: conceptualization, resources, methodology, investigation, validation, writing — review editing, supervision, project administration, and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical Responsibilities of Authors” as found in the instructions for authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhang, C., Yan, F. et al. Significant spatial variations of the atmospheric environment at remote site of the Tibetan Plateau — a case study on major ions of precipitation around Nam Co station. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1540 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12113-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12113-9