Abstract
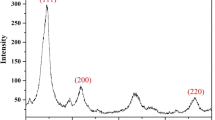
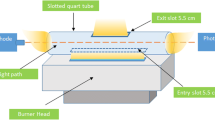
In this work, a dispersive solid-phase extraction method based on Ni(OH)2 nanoflowers (Ni(OH)2-NFs-DSPE) was developed to separate and preconcentrate copper ions from tap water samples for determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). Ni(OH)2-NFs was synthesized using a homogeneous precipitation technique and used as sorbent for copper preconcentration. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy were used to characterize the synthesized sorbent. All experimental variables were carefully optimized to achieve a high enhancement factor of 107.5-folds with respect to the detection sensitivity of the conventional FAAS. The proposed method’s analytical parameters including LOD, LOQ, and linear range were determined as 1.33 μg/L, 4.42 μg/L, and 3.0–40 μg/L, respectively. To assess the applicability and reliability of the developed method, optimal conditions were applied to tap water samples and satisfactory percent recoveries (94–103%) were obtained for the samples spiked at 20 and 30 μg/L. This validated the accuracy and feasibility of the developed method to real samples. The developed method can be described as a simple, efficient, and rapid analytical approach for the accurate determination of trace copper ions in water samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be available on reasonable request.
References
Anekthirakun, P., & Imyim, A. (2019). Separation of silver ions and silver nanoparticles by silica based-solid phase extraction prior to ICP-OES determination. Microchemical Journal, 145, 470–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.11.008
Asfaram, A., Dil, E. A., Arabkhani, P., Sadeghfar, F., & Ghaedi, M. (2020). Magnetic Cu: CuO-GO nanocomposite for efficient dispersive micro-solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from vegetable, fruit, and environmental water samples by liquid chromatographic determination. Talanta, 218, 121131.
Augusto, F., Hantao, L. W., Mogollón, N. G. S., & Braga, S. C. G. N. (2013). New materials and trends in sorbents for solid-phase extraction. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 43, 14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2012.08.012
Azizi, M., Seidi, S., & Rouhollahi, A. (2018). A novel N, N′-bis(acetylacetone)ethylenediimine functionalized silica-core shell magnetic nanosorbent for manetic dispersive solid phase extraction of copper in cereal and water samples. Food Chemistry, 249, 30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.12.085
Azzouz, A., Kailasa, S. K., Lee, S. S., Rascón, A. J., Ballesteros, E., Zhang, M., & Kim, K. -H. (2018). Review of nanomaterials as sorbents in solid-phase extraction for environmental samples. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 108, 347–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.009
Bakhshizadeh Aghdam, M., Farajzadeh, M. A., & Afshar Mogaddam, M. R. (2022). Facile preparation of carbonized cellulose nanoparticles and their application for the dispersive solid phase extraction prior to dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of pesticide residues from vegetable and fruit juices. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 110, 104527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104527
Bost, M., Houdart, S., Oberli, M., Kalonji, E., Huneau, J. F., & Margaritis, I. (2016). Dietary copper and human health: Current evidence and unresolved issues. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 35, 107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2016.02.006
Budipramana, Y., Ersam, T., & Kurniawan, F. (2014). Synthesis nickel hydroxide by electrolysis at high voltage. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 9, 2074–2077.
Buszewski, B., & Szultka, M. (2012). Past, present, and future of solid phase extraction: A review. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 42, 198–213.
Cheng, Z., Xu, J., Zhong, H., Li, D., Zhu, P., & Yang, Y. (2010). A facile and novel synthetic route to Ni(OH)2 nanoflowers. Superlattices and Microstructures, 48, 154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2010.05.013
Chisvert, A., Cárdenas, S., & Lucena, R. (2019). Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 112, 226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.12.005
Duran, C., Gundogdu, A., Bulut, V. N., Soylak, M., Elci, L., Sentürk, H. B., & Tüfekci, M. (2007). Solid-phase extraction of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (FAAS). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146, 347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.029
Ensafi, A. A., & Shiraz, A. Z. (2008). On-line separation and preconcentration of lead (II) by solid-phase extraction using activated carbon loaded with xylenol orange and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 150, 554–559.
Jiang, C. Y., Sun, X. W., Lo, G. Q., Kwong, D. L., & Wang, J. X. (2007). Improved dye-sensitized solar cells with a ZnO-nanoflower photoanode. Applied Physics Letters, 90, 263501.
Kalal, H., Panahi, H. A., Framarzi, N., Moniri, E., Naeemy, A., Hoveidi, H., & Abhari, A. (2011). New chelating resin for preconcentration and determination of molybdenum by inductive couple plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 8, 501–512.
Khairnar, N. A., & Gite, V. V. (2020). Selective solid-phase extraction of trace copper ions in an aqueous solution using ion-imprinted polymer. Materials Today: Proceedings, 29, 807–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.755
Khan, W. A., Arain, M. B., & Soylak, M. (2020). Nanomaterials-based solid phase extraction and solid phase microextraction for heavy metals food toxicity. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 145, 111704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111704
Kharisov, B. I. (2008). A review for synthesis of nanoflowers. Recent Patents on Nanotechnology, 2, 190–200.
Kobylinska, N., Kostenko, L., Khainakov, S., & Garcia-Granda, S. (2020). Advanced core-shell EDTA-functionalized magnetite nanoparticles for rapid and efficient magnetic solid phase extraction of heavy metals from water samples prior to the multi-element determination by ICP-OES. Microchimica Acta, 187, 289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04231-9
Köseoğlu, K., Ulusoy, H. İ, Yilmaz, E., & Soylak, M. (2020). Simple and sensitive determination of vitamin A and E in the milk and egg yolk samples by using dispersive solid phase extraction with newly synthesized polymeric material. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103482
Lemos, V. A., Teixeira, L. S. G., Bezerra, M. D. A., Costa, A. C. S., Castro, J. T., Cardoso, L. A. M., de Jesus, D. S., Santos, E. S., Baliza, P. X., & Santos, L. N. (2008). New materials for solid-phase extraction of trace elements. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews, 43, 303–334.
Li, B., Ai, M., & Xu, Z. (2010). Mesoporous β-Ni (OH) 2: Synthesis and enhanced electrochemical performance. Chemical Communications, 46, 6267–6269.
Limchoowong, N., Sricharoen, P., Areerob, Y., Nuengmatcha, P., Sripakdee, T., Techawongstien, S., & Chanthai, S. (2017). Preconcentration and trace determination of copper (II) in Thai food recipes using Fe3O4@ Chi–GQDs nanocomposites as a new magnetic adsorbent. Food Chemistry, 230, 388–397.
Liu, H., Han, Z., Wang, Q., Wang, X., Wu, D., & Wang, X. (2021). Surface construction of Ni(OH)2 nanoflowers on phase-change microcapsules for enhancement of heat transfer and thermal response. Applied Surface Science, 562, 150211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150211
Liu, Y., Chen, M., & Yongmei, H. (2013). Study on the adsorption of Cu(II) by EDTA functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic nano-particles. Chemical Engineering Journal, 218, 46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.027
Liu, Y., Ji, X., & He, Z. (2019). Organic–inorganic nanoflowers: From design strategy to biomedical applications. Nanoscale, 11, 17179–17194. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR05446D
Lui, G., Liao, J. -Y., Duan, A., Zhang, Z., Fowler, M., & Yu, A. (2013). Graphene-wrapped hierarchical TiO 2 nanoflower composites with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1, 12255–12262.
Ma, W., Wang, L., Xue, J., & Cui, H. (2016). A bottom-up strategy for exfoliation-free synthesis of soluble α-Ni (OH) 2 monolayer nanosheets on a large scale. RSC Advances, 6, 85367–85373.
Nabavi, S. N., Sajjadi, S. M., & Lotfi, Z. (2020). Novel magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent in ultrasound-assisted micro-solid-phase extraction for rapid pre-concentration of some trace heavy metal ions in environmental water samples: Desirability function. Chemical Papers, 74, 1143–1159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00954-z
Ozdemir, S., Turkan, Z., Kilinc, E., Bayat, R., Soylak, M., & Sen, F. (2022). Preconcentrations of Cu (II) and Mn (II) by magnetic solid-phase extraction on Bacillus cereus loaded γ-Fe2O3 nanomaterials. Environmental Research, 209, 112766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112766
Ozkantar, N., Yilmaz, E., Soylak, M., & Tuzen, M. (2020). Pyrocatechol violet impregnated magnetic graphene oxide for magnetic solid phase microextraction of copper in water, black tea and diet supplements. Food Chemistry, 321, 126737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126737
Rajabi, M., Rahimi, M., Hemmati, M., & Najafi, F. (2018). Chemically functionalized silica nanoparticles-based solid-phase extraction for effective pre-concentration of highly toxic metal ions from food and water samples. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 32, e4012. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4012
Ramos, L. (2012). Critical overview of selected contemporary sample preparation techniques. Journal of Chromatography A, 1221, 84–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.11.011
Salehi, N., Moghimi, A., & Shahbazi, H. (2021). Magnetic nanobiosorbent (MG-Chi/Fe3O4) for dispersive solid-phase extraction of Cu (II), Pb (II), and Cd (II) followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry determination. IET Nanobiotechnology, 15, 575.
Saydan Kanberoglu, G., Yilmaz, E., & Soylak, M. (2020). Fabrication and characterization of SiO2@Fe3O4@nanodiamonds for vortex-assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction of lead in cigarette samples prior to FAAS detection. Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society, 17, 1627–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-020-01882-6
Shende, P., Kasture, P., & Gaud, R. S. (2018). Nanoflowers: The future trend of nanotechnology for multi-applications. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology, 46, 413–422.
Socas-Rodríguez, B., Herrera-Herrera, A. V., Asensio-Ramos, M., & Hernández-Borges, J. (2015). Dispersive solid-phase extraction. Analytical Separation Science. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527678129.assep056
Soylak, M., & Koksal, M. (2019). Deep eutectic solvent microextraction of lead(II), cobalt(II), nickel(II) and manganese(II) ions for the separation and preconcentration in some oil samples from Turkey prior to their microsampling flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Microchemical Journal, 147, 832–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.04.006
Soylak, M., & Tuzen, M. (2008). Coprecipitation of gold(III), palladium(II) and lead(II) for their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 656–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.027
Tang, S., Zhang, H., & Lee, H. K. (2016). Advances in sample extraction. Analytical Chemistry, 88, 228–249.
Ulusoy, H. İ, Yılmaz, E., & Soylak, M. (2019). Magnetic solid phase extraction of trace paracetamol and caffeine in synthetic urine and wastewater samples by a using core shell hybrid material consisting of graphene oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotube/Fe3O4/SiO2. Microchemical Journal, 145, 843–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.11.056
Wan Ibrahim, W. A., Abd Ali, L. I., Sulaiman, A., Sanagi, M. M., & Aboul-Enein, H. Y. (2014). Application of solid-phase extraction for trace elements in environmental and biological samples: A review. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 44, 233–254.
Wang, L., Liu, Z., Han, J., Li, R., & Huang, M. (2019). Stepwise synthesis of Au@ CdS-CdS nanoflowers and their enhanced photocatalytic properties. Nanoscale Research Letters, 14, 1–9.
Wang, R., Jayakumar, A., Xu, C., & Lee, J. -M. (2016). Ni (OH) 2 nanoflowers/graphene hydrogels: A new assembly for supercapacitors. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 4, 3736–3742.
Wang, Y., Gao, S., Zang, X., Li, J., & Ma, J. (2012). Graphene-based solid-phase extraction combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for a sensitive determination of trace amounts of lead in environmental water and vegetable samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 716, 112–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.007
Yang, G., Fen, W., Lei, C., Xiao, W., & Sun, H. (2009). Study on solid phase extraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for the determination of nickel, silver, cobalt, copper, cadmium and lead with MCI GEL CHP 20Y as sorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 162, 44–49.
Yavuz, E., Tokalıoğlu, Ş, & Patat, Ş. (2018). Core–shell Fe3O4 polydopamine nanoparticles as sorbent for magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction of copper from food samples. Food Chemistry, 263, 232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.134
Yi, X., Liu, C., Liu, X., Wang, P., Zhou, Z., & Liu, D. (2019). Magnetic partially carbonized cellulose nanocrystal-based magnetic solid phase extraction for the analysis of triazine and triazole pesticides in water. Microchimica Acta, 186, 1–8.
Zhang, S., Niu, H., Hu, Z., Cai, Y., & Shi, Y. (2010). Preparation of carbon coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their application for solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217, 4757–4764.
Zhao, G., Zhang, H., Fan, Q., Ren, X., Li, J., Chen, Y., & Wang, X. (2010). Sorption of copper(II) onto super-adsorbent of bentonite–polyacrylamide composites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 661–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.08.135
Funding
The authors thank Yıldız Technical University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project Number: FBA-2021–4725) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Meltem Şaylan: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, visualization, writing—original draft; Rabia Demirel: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, writing—original draft; Merve Fırat Ayyıldız: conceptualization, methodology, validation; Dotse Selali Chormey: conceptualization, methodology, validation; Gülten ÇETİN: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, validation; Sezgin Bakırdere: conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, supervision, validation, visualization, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Şaylan, M., Demirel, R., Ayyıldız, M.F. et al. Nickel hydroxide nanoflower–based dispersive solid-phase extraction of copper from water matrix. Environ Monit Assess 195, 133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10653-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10653-0