Abstract
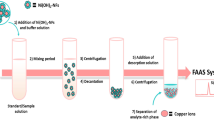
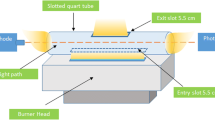
In this study, a new analytical strategy was developed to determine trace cadmium in aqueous samples with high sensitivity and accuracy. A combination of magnetic nickel nanoparticles (Ni-MNPs) based dispersive solid-phase extraction (DSPE) and flame atomic absorption spectrometry fitted with a slotted quartz tube (SQT-FAAS) lowered the detection limit of cadmium. The magnetic Ni nanoparticles were synthesized, characterized, and thoroughly optimized in a stepwise approach. The quartz tube was custom cut in the laboratory to suit the specifics of the flame burner. Using the optimized conditions, a limit of detection value of 0.58 μg/L and limit of quantification value of 1.93 μg/L were obtained. To demonstrate accuracy and applicability of the developed method, well water samples were analyzed for their Cd content, and matrix effect on the extraction yield was investigated. The percent recovery results calculated ranged from 93.8 to 108.2%, with corresponding standard deviation values ranging from 1.7 to 7.7. These results established the developed method as sensitive, accurate, and precise for determination of cadmium at trace levels.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Ai, L., Tian, T., & Jiang, J. (2017). Ultrathin graphene layers encapsulating nickel nanoparticles derived metal–organic frameworks for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 5(6), 4771–4777.
Akkaya, E., Aylin Kasa, N., Çetin, G., & Bakirdere, S. (2017). A new method for the determination of cadmium at ultratrace levels using slotted quartz tube-flame atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration with stearic acid coated magnetite nanoparticles. [Article]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 32(12), 2433–2438. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ja00303j.
Akkaya, E., Erulas, F. A., Büyükpinar, Ç., & Bakirdere, S. (2019). Accurate and sensitive determination of lead in black tea samples using cobalt magnetic particles based dispersive solid-phase microextraction prior to slotted quartz tube-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chemistry, 297, 124947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.06.014.
Álvarez Méndez, J., Barciela García, J., García Martín, S., Peña Crecente, R. M., & Herrero Latorre, C. (2015). Determination of cadmium and lead in urine samples after dispersive solid-liquid extraction on multiwalled carbon nanotubes by slurry sampling electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. [Article]. Spectrochimica Acta - Part B Atomic Spectroscopy, 106, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2015.01.008.
Arslan, Y., Kendüzler, E., & Ataman, O. Y. (2011). Indium determination using slotted quartz tube-atom trap-flame atomic absorption spectrometry and interference studies. Talanta, 85(4), 1786–1791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2011.07.006.
Çelik, B., Akkaya, E., Bakirdere, S., & Aydin, F. (2018). Determination of indium using vortex assisted solid phase microextraction based on oleic acid coated magnetic nanoparticles combined with slotted quartz tube-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. [Article]. Microchemical Journal, 141, 7–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.04.031.
de la Rosa, G., Peralta-Videa, J. R., Montes, M., Parsons, J. G., Cano-Aguilera, I., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2004). Cadmium uptake and translocation in tumbleweed (Salsola kali), a potential Cd-hyperaccumulator desert plant species: ICP/OES and XAS studies. Chemosphere, 55(9), 1159–1168.
Djedjibegovic, J., Larssen, T., Skrbo, A., Marjanović, A., & Sober, M. (2012). Contents of cadmium, copper, mercury and lead in fish from the Neretva river (Bosnia and Herzegovina) determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Food Chemistry, 131(2), 469–476.
Huang, C., & Hu, B. (2008). Silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified with γ-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane for fast and selective solid phase extraction of trace amounts of Cd, Cu, Hg, and Pb in environmental and biological samples prior to their determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 63(3), 437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2007.12.010.
Keskin, G., Bakirdere, S., & Yaman, M. (2015). Sensitive determination of lead, cadmium and nickel in soil, water, vegetable and fruit samples using STAT-FAAS after preconcentration with activated carbon. [Article]. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 31(10), 881–889. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713484650.
Li, Z., Wei, L., Gao, M., & Lei, H. (2005). One-pot reaction to synthesize biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 17(8), 1001–1005.
Michalcová, A., Svobodová, P., Nováková, R., Len, A., Heczko, O., Vojtěch, D., Marek, I., & Novák, P. (2014). Structure and magnetic properties of nickel nanoparticles prepared by selective leaching. Materials Letters, 137, 221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.09.012.
Mirabi, A., Dalirandeh, Z., & Rad, A. S. (2015). Preparation of modified magnetic nanoparticles as a sorbent for the preconcentration and determination of cadmium ions in food and environmental water samples prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. [Article]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 381, 138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.12.071.
Nawrot, T., Plusquin, M., Hogervorst, J., Roels, H. A., Celis, H., Thijs, L., Vangronsveld, J., van Hecke, E., & Staessen, J. A. (2006). Environmental exposure to cadmium and risk of cancer: A prospective population-based study. [Article]. Lancet Oncology, 7(2), 119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70545-9.
Rajput, S., Singh, L. P., Pittman Jr., C. U., & Mohan, D. (2017). Lead (Pb2+) and copper (Cu2+) remediation from water using superparamagnetic maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized by flame spray pyrolysis (FSP). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 492, 176–190.
Registry, A. f. T. S. a. D. (2012). Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp.asp?id=48&tid=15.
Saljooghi, A. S., & Saljoghi, Z. S. (2011). Natural analcime zeolite modified with 2,3,5,6-tetra(2-pyridyl)pyrazine for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of cadmium by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 28(9), 771–778. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233711422730.
Wen, X., Deng, Q., Wang, J., Yang, S., & Zhao, X. (2013). A new coupling of ionic liquid based-single drop microextraction with tungsten coil electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 105, 320–325.
Wierucka, M., & Biziuk, M. (2014). Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 59, 50–58.
Zhong, W.-S., Ren, T., & Zhao, L.-J. (2016). Determination of Pb (lead), Cd (cadmium), Cr (chromium), Cu (copper), and Ni (nickel) in Chinese tea with high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 24(1), 46–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yağci, Ö., Akkaya, E. & Bakirdere, S. Nano-sized magnetic Ni particles based dispersive solid-phase extraction of trace Cd before the determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with slotted quartz tube: a new, accurate, and sensitive quantification method. Environ Monit Assess 192, 583 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08548-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08548-z