Abstract
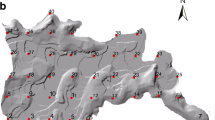
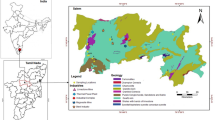
In this research, heavy metal accumulation pattern was investigated using the data measured from the soil, paddy plants, and irrigation water samples in Jessore district in Bangladesh with the aid of principal component analysis. A total of 28 samples representing farmland soil and irrigation water along with paddy plant were collected from 28 locations in the Jessore district in November 2016. In agricultural soil, arsenic (As) and nickel (Ni) were found 2.78 and 1.11 times more concentrated than their background values. In addition, 89% of the sample sites exhibited enhanced As concentrations relative to the background value. Principal component analysis (PCA) of soil data showed strong homogeneity in many species (e.g., Ni, Cu, Fe, and As) to reflect intense agricultural activities. In contrast, Pb showed no such homogeneity in soil accumulation pattern. In plant samples, Cu, Fe, and As were strongly correlated and homologous. This homology of pollution was in agreement with the pollution homology in the agricultural soil in which the plants were grown. In irrigation water, Cu and Ni were homologous. Observation of spatial distribution and other variables indicated that the accumulation of any particular metal in paddy plants was correlated with its content in soil and irrigation water, which was influenced by the soil organic matter, soil/water pH, and other metals present in that environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin, M. J., Cotter-Howells, J., & Meharg, A. A. (2002). Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water. Plant and Soil, 240(2), 311–319.
Alam, M. G. M., Snow, E. T., & Tanaka, A. (2003). Arsenic and heavy metal contamination of vegetables grown in Samta village, Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 308(1–3), 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00651-4.
Arber, C. E., Li, A., Houlden, H., & Wray, S. (2016). Review: Insights into molecular mechanisms of disease in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: unifying theories. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 42(3), 220–241.
Atafar, Z., Mesdaghinia, A., Nouri, J., Homaee, M., Yunesian, M., Ahmadimoghaddam, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1), 83–89.
BADC. (2012). Statistical report on irrigation in Jessore, Bangladesh Agricultural Development Corporation (BADC), Ministry of Agriculture, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, Dhaka.
Balabanova, B., Stafilov, T., & Baceva, K. (2015). Application of principal component analysis in the assessment of essential and toxic metals in vegetable and soil from polluted and referent areas. Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 21(3).
BBAR. (2012). Fertilizer recommendation GUIDE-2012 soils Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council, Farmgate, Dhaka, Pub. No. 45.
BBS. (2008). Agricultural census. Dhaka: Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
BGS (British Geological Survey). (1999). Groundwater studies for arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Vol. S1: 1-33. Review of existing data. Dubai: Mott MacDonald Ltd.
Cerny, C. A., & Kaiser, H. F. (1977). A study of a measure of sampling adequacy for factor-analytic correlation matrices. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 12(1), 43–47.
Chakraborti, D., Rahman, M. M., Mukherjee, A., Alauddin, M., Hassan, M., Dutta, R. N., Pati, S., Mukherjee, S. C., Roy, S., Quamruzzman, Q., Rahman, M., Morshed, S., Islam, T., Sorif, S., Selim, M., Islam, M. R., & Hossain, M. M. (2015). Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh—21 years of research. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 31, 237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.01.003.
Crichton, R. R., Wilmet, S., Legssyer, R., & Ward, R. J. (2002). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of iron homeostasis and toxicity in mammalian cells. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 91(1), 9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0162-0134(02)00461-0.
Das, H., Mitra, A. K., Sengupta, P., Hossain, A., Islam, F., & Rabbani, G. (2004). Arsenic concentrations in rice, vegetables, and fish in Bangladesh: a preliminary study. Environment International, 30(3), 383–387.
Dey, R. K. (2002). Arsenic health problem. In M. F. Ahmed & C. M. Ahmed (Eds.), Arsenic mitigation in Bangladesh (pp. 59–76). Dhaka: Local Govt. Division.
Dziuban, C. D., & Shirkey, E. C. (1974). When is a correlation matrix appropriate for factor analysis? Psychological Bulletin, 81, 358–361.
Fabrigar, L. R., Wegener, D. T., MacCallum, R. C., & Strahan, E. J. (1999). Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychological Methods, 4, 272–299.
Forti, E., Salovaara, S., Cetin, Y., Bulgheroni, A., Tessadri, R., Jennings, P., et al. (2011). In vitro evaluation of the toxicity induced by nickel soluble and particulate forms in human airway epithelial cells. Toxicology in Vitro, 25(2), 454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2010.11.013.
Fuentealba, I. C., & Aburto, E. M. (2003). Animal models of copper-associated liver disease. [journal article]. Comparative Hepatology, 2(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-5926-2-5.
Hayton, J. C., Allen, D. G., & Scarpello, V. (2004). Factor retention decisions in exploratory factor analysis: a tutorial on parallel analysis. Organizational Research Methods, 7(2), 191–205.
Heikens, A. (2006). Arsenic contamination of irrigation water, soil and crops in Bangladesh: risk implications for sustainable agriculture and food safety in Asia. FAO, UN. Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific.
Horn, J. L. (1965). A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis. Psychometrica., 30, 179–185.
Hossain, M. (2006). Arsenic contamination in Bangladesh—an overview. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 113(1), 1–16.
Huda, A. S. N., Mekhilef, S., & Ahsan, A. (2014). Biomass energy in Bangladesh: current status and prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 30, 504–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.10.028.
Huq, S. M. I., Joardar, J. C., Parvin, S., Correll, R., & Naidu, R. (2006). Arsenic contamination in food-chain: transfer of arsenic into food materials through groundwater irrigation. Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition, 24(3), 305–316.
Islam, M. S., & Masunaga, S. (2014). Trace metals contamination in soil and foodstuffs around the industrial area of Dhaka city, Bangladesh and health risk assessment. In International Forum for Sustainable Asia and the Pacific (ISAP2014) Poster Session for Young Researchers,
Juhasz, A. L., Smith, E., Weber, J., Rees, M., Rife, A., Kuchel, T., Sansom, L., & Naidu, R. (2006). In vivo assessment of arsenic bioavailability in rice and its significance for human health risk assessment. Environ Health Perspectives, 114, 1826–1831.
Kaiser, H. F. (1970). A second generation little jiffy. Psychometrika, 35(4), 401–415.
Kashem, M., & Singh, B. (2001). Metal availability in contaminated soils: I. Effects of flooding and organic matter on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni andZn. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 61(3), 247–255.
Kinniburgh, D., & Smedley, P. (2001). Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh. BGS Techniqual Report. WC/00/19, V1, 1–21.
Kippler, M., Skröder, H., Rahman, S. M., Tofail, F., & Vahter, M. (2016). Elevated childhood exposure to arsenic despite reduced drinking water concentrations—a longitudinal cohort study in rural Bangladesh. Environment International, 86, 119–125.
Li, Z., Li, L., & Chen, G. P. J. (2005). Bioavailability of Cd in a soil–rice system in China: soil type versus genotype effects. Plant and Soil, 271(1), 165–173.
Li, Z., Ma, Z., van der Kuijp, T. J., Yuan, Z., & Huang, L. (2014). A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 843–853.
Loewenberg, S. (2016). In Bangladesh, arsenic poisoning is a neglected issue. The Lancet, 388(10058), 2336–2337.
Meacher, D. M., Menzel, D. B., Dillencourt, M. D., Bic, L. F., Schoof, R. A., Yost, L. J., Eickhoff, J. C., & Farr, C. H. (2002). Estimation of multimedia inorganic arsenic intake in the US population. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 8, 1697–1721.
Meharg, A. A., & Rahman, M. M. (2003). Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implications for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(2), 229–234.
Meharg, A. A., Sun, G., Williums, P. N., Adomako, E., Deacon, C., Zhu, Y.-G., Feldmann, J., & Raab, A. (2008). Inorganic arsenic levels in baby rice are of concern. Environmental Pollution, 152, 746–749.
Misra, M. (2017). Is peasantry dead? Neoliberal reforms, the state and agrarian change in Bangladesh. Journal of Agrarian Change, 17(3), 594–611.
Pal, S., Patra, A. K., Reza, S. K., Wildi, W., & Pote-Wembonyama, J. (2010). Use of bio-resources for remediation of soil pollution. Natural Resources, 1(2), 110–125.
Papanikolaou, G., & Pantopoulos, K. (2005). Iron metabolism and toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 202(2), 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.06.021.
Parkpian, P., Leong, S. T., Laortanakul, P., & Thunthaisong, N. (2003). Regional monitoring of lead and cadmium contamination in a tropical grazing land site, Thailand. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 85(2), 157–173.
Rahman, S. (2013). Pesticide consumption and productivity and the potential of IPM in Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 445, 48–56.
Rattan, R., Datta, S., Chhonkar, P., Suribabu, K., & Singh, A. (2005). Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater—a case study. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 109(3), 310–322.
Roveda, L. F., Cuquel, F. L., Motta, A. C., & Melo, V. d. F. (2016). Organic compounds with high Ni content: Effects on soil and strawberry production. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 20(8), 722–727.
Smith, A. H., Lingas, E. O., & Rahman, M. (2000). Contamination of drinking-water by arsenic in Bangladesh: a public health emergency. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 78(9), 1093–1103.
Souza, D. M. d., Morais, P. A. d. O., Matsushige, I., & Rosa, L. A. (2016). Development of alternative methods for determining soil organic matter. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 40.
Sun, C., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Sun, L., & Yu, H. (2013). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere, 92(5), 517–523.
Tani, M., Jahiruddin, M., Egashira, K., Kurosawa, K., Moslehuddin, A., & Rahman, M. (2012). Dietary intake of arsenic by households in Marua village in Jessore. Journal of Environmental Science and Natural Resources, 5(1), 283–288.
Voroney, R., & Heck, R. (2007). The soil habitat. Soil Microbiology, Ecology, and Biochemistry, 25–49.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37(1), 29–38.
Williams, P. N., Zhang, H., Davison, W., Meharg, A. A., Hossain, M., Norton, G. J., Brammer, H., & Islam, M. R. (2011). Organic matter-solid phase interactions are critical for predicting arsenic release and plant uptake in Bangladesh paddy soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(14), 6080–6087.
Xu, X. Y., Mcgrath, S. P., Meharg, A. A., & Zhao, F. I. (2008). Growing rice aerobically markedly decreased accumulation. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(15), 5574–5579.
Yang, P., Yang, M., Mao, R., & Shao, H. (2014). Multivariate-statistical assessment of heavy metals for agricultural soils in northern China. The Scientific World Journal, 2014.
Zeng, F., Ali, S., Zhang, H., Ouyang, Y., Qiu, B., Wu, F., & Zhang, G. (2011). The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution, 159(1), 84–91.
Zhao, F., Ma, J., Meharg, A., & McGrath, S. (2009). Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytologist, 181(4), 777–794.
Zhao, K., Liu, X., Xu, J., & Selim, H. (2010). Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181(1), 778–787.
Zou, J., Dai, W., Gong, S., & Ma, Z. (2015). Analysis of spatial variations and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils of Beijing suburbs. PLoS One, 10(2), e0118082.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by the R&D Project of Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Bangladesh, and Jessore University of Science and Technology (JUST), Bangladesh. We are thankful to the GIS Laboratory, CSIRL, JUST, Bangladesh, and the Department of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, JUST, Bangladesh.
Funding
The corresponding author (KHK) acknowledges support made in part by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (No. 2016R1E1A1A01940995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Md. Shahedur Rahman and Polsh Kumar Biswas conducted the laboratory work. Md. Shahedur Rahman, Syed Mahfuz Al Hasan, and Md. Mahfuzur Rahman performed the data analysis and manuscript preparation. S Lee, KH Kim, Shaikh Mizanur Rahman, and Md. Rezuanul Islam designed and supervised the work. All of the authors were involved in the explication of data and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.S., Biswas, P.K., Al Hasan, S.M. et al. The occurrences of heavy metals in farmland soils and their propagation into paddy plants. Environ Monit Assess 190, 201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6577-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6577-7