Abstract
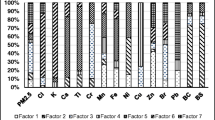
In this study, PM10 concentrations and elemental (Al, Fe, Sc, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Mo, Ag, Cd, Sn, Sb, Ba, Pb, and Bi) contents of particles were determined in Düzce, Turkey. The particulate matter samplings were carried out in the winter and summer seasons simultaneously in both urban and sub-urban sampling sites. The average PM10 concentration measured in the winter season was 86.4 and 27.3 μg/m3, respectively, in the urban and sub-urban sampling sites, while it was measured as 53.2 and 34.7 μg/m3 in the summer season. According to the results, it was observed that the PM10 levels and the element concentrations reached higher levels, especially at the urban sampling site, in the winter season. The positive matrix factorization model (PMF) was applied to the data set for source apportionment. Analysis with the PMF model revealed six factors for both the urban (coal combustion, traffic, oil combustion, industry, biomass combustion, and soil) and sub-urban (industry, oil combustion, traffic, road dust, soil resuspension, domestic heating) sampling sites. Loadings of grouped elements on these factors showed that the major sources of the elements in the atmosphere of Düzce were traffic, fossil fuel combustion, and metal industry-related emissions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque, M., Coutinho, M., Rodrigues, J., Ginja, J., & Borrego, C. (2017). Long-term monitoring of trace metals in PM10 and total gaseous mercury in the atmosphere of Porto, Portugal. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(3), 535–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.12.001.
Aldabe, J., Elustondo, D., Santamaría, C., Lasheras, E., Pandolfi, M., Alastuey, A., Querol, X., & Santamaría, J. M. (2011). Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 at rural, urban and traffic sites in Navarra (north of Spain). Atmospheric Research, 102, 191–205.
Alleman, L. Y., Lamaison, L., Perdrix, E., Robache, A., & Galloo, J. C. (2010). PM10 metal concentrations and source identification using positive matrix factorization and wind sectoring in a French industrial zone. Atmospheric Research, 96(4), 612–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2010.02.008.
Apeagyei, E., Bank, M. S., & Spengler, J. D. (2011). Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmospheric Environment, 45(13), 2310–2323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.11.015.
Argyropoulos, G., Manoli, E., Kouras, A., & Samara, C. (2012). Concentrations and source apportionment of PM10 and associated major and trace elements in the Rhodes Island, Greece. Science of the Total Environment, 432, 12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.076.
Ariola, V., D’Alessandro, A., Lucarelli, F., Marcazzan, G., Mazzei, F., Nava, S., Garcia-Orellana, I., Prati, P., Valli, G., Vecchi, R., & Zucchiatti, A. (2006). Elemental characterization of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 in the town of genoa (Italy). Chemosphere, 62(2), 226–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.05.004.
Artun, G. K., Polat, N., Yay, O. D., Üzmez, Ö. Ö., Arı, A., Tuygun, G. T., Elbir, T., Altug, H., Dumanoglu, Y., Dogeroglu, T., Dawood, A., Odabasi, M., & Gaga, E. O. (2017). An integrative approach for determination of air pollution and its health effects in a coal fired power plant area by passive sampling. Atmospheric Environment, 150, 331–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.11.025.
Behera, S. N., Cheng, J., Huang, X., Zhu, Q., Liu, P., & Balasubramanian, R. (2015). Chemical composition and acidity of size-fractionated inorganic aerosols of 2013-14 winter haze in Shanghai and associated health risk of toxic elements. Atmospheric Environment, 122, 259–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.09.053.
Bove, M. C., Brotto, P., Calzolai, G., Cassola, F., Cavalli, F., Fermo, P., Hjorth, J., Massabò, D., Nava, S., Piazzalunga, A., Schembari, C., & Prati, P. (2016). PM10 source apportionment applying PMF and chemical tracer analysis to shipborne measurements in the western Mediterranean. Atmospheric Environment, 125, 140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.11.009.
Bressi, M., Sciare, J., Ghersi, V., Mihalopoulos, N., Petit, J. E., Nicolas, J. B., Moukhtar, S., Rosso, A., Feron, A., Bonnaire, N., Poulakis, E., & Theodosi, C. (2014). Sources and geographical origins of fine aerosols in Paris (France). Atmospheric Chemistry and Physic, 14(16), 8813–8839. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-8813-2014.
Callen, M. S., Cruz, M. T., Lopez, J. M., Navarro, M. V., & Mastral, A. M. (2009). Comparison of receptor models for source apportionment of the PM10 in Zaragoza (Spain). Chemosphere, 76(8), 1120–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.04.015.
Calvo, A. I., Alves, C., Castro, A., Pont, V., Vicente, A. M., & Fraile, R. (2013). Research on aerosol sources and chemical composition: past, current and emerging issues. Atmospheric Research, 120-121, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.09.021.
Cheng, Y., Lee, S., Gu, Z., Ho, K., Zhang, Y., Huang, Y., Chow, J. C., Watson, J. G., Cao, J., & Zhang, R. (2015). PM2.5 and PM10-2.5 chemical composition and source apportionment near a Hong Kong roadway. Particuology, 18, 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2013.10.003.
Choi, J. K., Ban, S. J., Kim, Y. P., Kim, Y. H., Yi, S. M., & Zoh, K. D. (2015). Molecular marker characterization and source apportionment of particulate matter and its organic aerosols. Chemosphere, 134, 482–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.093.
Clements, N., Eav, J., Xie, M., Hannigan, M. P., Miller, S. L., Navidi, W., Peel, J. L., Schauer, J. J., Shafer, M. M., & Milford, J. B. (2014). Concentrations and source insights for trace elements in fine and coarse particulate matter. Atmospheric Environment, 89, 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.01.011.
Contini, D., Belosi, F., Gambaro, A., Cesari, D., Stortini, A. M., & Bove, M. C. (2012). Comparison of PM10 concentrations and metal content in three different sites of the Venice lagoon: an analysis of possible aerosol sources. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(11), 1954–1965. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61027-9.
Das, R., Khezri, B., Srivastava, B., Datta, S., Sikdar, P. K., Webster, R. D., & Wang, X. (2015). Trace element composition of PM2.5 and PM10 from Kolkata—a heavily polluted Indian metropolis. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 6(5), 742–750. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.083.
Dongarra, G., Manno, E., Varrica, D., & Vultaggio, M. (2007). Short communication mass levels, crustal component and trace elements in PM10 in Palermo, Italy. Atmospheric Environment, 41(36), 7977–7986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.015.
Dongarra, G., Manno, E., & Varrica, D. (2009). Possible markers of traffic-related emissions. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 154(1-4), 117–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0382-7.
Duce, R. A., Hoffman, G. L., & Zoller, W. H. (1975). Atmospheric trace metals at remote northern and southern hemisphere sites’ pollution or natural? Science, 187, 59–61.
Enamorado-Baez, S. M., Guzman-Gomez, J. M., Chamizo, E., & Abril, J. M. (2015). Levels of 25 trace elements in high-volume air filter samples from Seville (2001–2002), sources, enrichment factors and temporal variations. Atmospheric Research, 155, 118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.12.005.
Ergenekon, P., & Ulutaş, K. (2014). Heavy metal content of total suspended air particles in the heavily industrialized town of Gebze, Turkey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 92(1), 90–95.
Gao, Y., Arimoto, R., Duce, R. A., Lee, D. S., & Zhou, M. Y. (1992). Input of atmospheric trace elements and mineral matter to the Yellow Sea during the spring of a low-dust year. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97(D4), 3767–3777. https://doi.org/10.1029/91JD02686.
Gugamsetty, B., Wei, H., Liu, C. N., Awasthi, A., Hsu, S. C., Tsai, C. J., Roam, G. D., Wu, Y. C., & Chen, C. F. (2012). Source characterization and apportionment of PM10, PM2.5 and PM0.1 by using positive matrix factorization. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 12, 476–491.
Hien, P. D., Bac, V. T., & Thinh, N. T. H. (2004). PMF receptor modelling of fine and coarse PM10 in air masses governing monsoon conditions in Hanoi, northern Vietnam. Atmospheric Environment, 38(2), 189–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.09.064.
Hsu, C. Y., Chiang, H. C., Lin, S. L., Chen, M. J., Lin, T. Y., & Chen, Y. C. (2016). Elemental characterization and source apportionment of PM10 and PM2.5 in the western coastal area of central Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 541, 1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.122.
Huang, X., Betha, R., Tan, L. Y., & Balasubramanian, R. (2016). Risk assessment of bioaccesible trace elements in smoke haze aerosols using simulated lung fluids. Atmospheric Environment, 125, 505–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.06.034.
Jiang, N., Yin, S., Guo, Y., Li, J., Kang, P., Zhang, R., & Tang, X. (2017). Characteristics of mass concentration, chemical composition, source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 and health risk assessment in the emerging megacity in China. Atmospheric Pollution Research, in press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.07.005.
Karar, K., & Grupta, A. K. (2007). Source apportionment of PM10 at residential and industrial sites of an urban region of Kolkata, India. Atmospheric Research, 84(1), 30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2006.05.001.
Kim, E., Larson, T. V., Hopke, P. K., Slaughter, C., Sheppard, L. E., & Claiborn, C. (2003). Source identification of PM2.5 in an arid northwest U.S. city by positive matrix factorization. Atmospheric Research, 66(4), 291–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-8095(03)00025-5.
Koçak, M., Theodosi, C., Zarmpas, P., Im, U., Bougiatioti, A., Yenigün, O., & Mihalopoulos, N. (2011). Particulate matter (PM10) in İstanbul, origin, sources, areas and potential impact on surrounding regions. Atmospheric Environment, 45(38), 6891–6900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.10.007.
Kummer, U., Pacyna, J., Pacyna, E., & Friedrich, R. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal releases from the use phase of road transport in Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 43(3), 640–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.10.007.
Liu, Q., Liu, Y., Yin, J., Zhang, M., & Zhang, T. (2014). Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM10 during Asian dust storm and non-dust storm days in Beijing. Atmospheric Environment, 91, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.03.057.
Lopez, J. M., Callen, M. S., Murillo, R., Garcia, T., Navarro, M. V., Cruz, M. T., & Mastral, A. M. (2005). Levels of selected metals in ambient air PM10 in an urban site of Zaragoza (Spain). Environmental Research, 99(1), 58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2005.01.007.
Lopez, M. L., Ceppi, S., Palancar, G. G., Olcese, L. E., Tirao, G., & Toselli, B. M. (2011). Elemental concentration and source identification of PM10 and PM2.5 by SR-XRF in Cordoba City, Argentina. Atmospheric Environment, 45(31), 5450–5457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.07.003.
Maenhaut, W., Vermeylen, R., Claeys, M., Vercauteren, J., & Roekens, E. (2016). Sources of the PM10 aerosol in Flanders, Belgium, and re-assessment of the contribution from wood burning. Science of the Total Environment, 562, 550–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.074.
Manousakas, M., Diapouli, E., Papaefthymiou, H., Migliori, A., Karydas, A. G., Padilla-Alvarez, R., Bogovac, M., Kaiser, R. B., Jaksic, M., Bogdanovic-Radovic, I., & Eleftheriadis, K. (2015). Source apportionment by PMF on elemental concentrations obtained by PIXE analysis of PM10 samples collected at the vicinity of lignite power plants and mines in Megalopolis, Greece. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 349, 114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2015.02.037.
Mazzei, F., Alessandro, A. D., Lucarelli, F., Nava, S., Prati, P., Valli, G., & Vecchi, R. (2008). Chracterization of particulate matter sources in an urban environment. Science of the Total Environment, 401(1-3), 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.03.008.
McLennan, S. M. (2001). Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2(4), 1021–1024. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GC000109.
Moreno, T., Querol, X., Alastuey, A., & Gibbons, W. (2009). Identification of chemical tracers in the characterisation and source apportionment of inhalable inorganic airborne particles: an overview. Biomarkers, 14(sup1), 17–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13547500902965435.
Öztürk, F., & Keleş, M. (2016). Wintertime chemical compositions of coarse and fine fractions of particulate matter in Bolu Turkey. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(14), 14157–14172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6584-6.
Paatero, P. (1997). Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 37(1), 23–35.
Paatero, P., & Hopke, P. K. (2003). Discarding or downweighting high-noise variables in factor analytic models. Analytica Chimica Acta, 490(1-2), 277–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(02)01643-4.
Pekey, B., Bulut, Z. B., Pekey, H., Doğan, G., Zararsız, A., Efe, N., & Tuncel, G. (2010). Indoor/outdoor concentrations and elemental composition of PM10/PM2.5 in urban/industrial areas of Kocaeli City, Turkey. Indoor Air, 20(2), 112–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0668.2009.00628.x.
Polissar, A. V., Hopke, P. K., & Poirot, R. L. (2001). Atmospheric aerosol over Vermont: chemical composition and sources. Environmental Science and Technology, 35(23), 4604–4621. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0105865.
Richter, P., Grino, P., Ahumada, I., & Giordano, A. (2007). Total element concentration and chemical fractionation in airborne particulate matter from Santiago, Chile. Atmospheric Environment, 41(32), 6729–6738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.04.053.
Querol, X., Alastuey, A., Rodriguez, S., Plana, F., Ruiz, C. R., Cots, N., Massague, G., & Puig, O. (2001). PM10 and PM2.5 source apportionment in the Barcelona metropolitan area, Catalonia, Spain. Atmospheric Environment, 35(36), 6407–6419. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00361-2.
Querol, X., Viana, M., Alastuey, A., Amato, F., Moreno, T., Castillo, S., Pey, J., Rosa, J., Campa, A. S., Artinano, B., Salvador, P., Santos, S. G. D., Fernandez-Patier, R., Moreno-Grau, S., Negral, L., Minguillon, M. C., Monfort, E., Gil, J. I., Inza, A., Ortega, L. A., Santamaria, J. M., & Zabalza, J. (2007). Source origin of trace elements in PM from regional background urban and industrial sites of Spain. Atmospheric Environment, 41(34), 7219–7231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.05.022.
Romanazzi, V., Casazza, M., Malandrino, M., Maurino, V., Piano, A., Schilirò, T., & Gilli, G. (2014). PM10 size distribution of metals and environmental-sanitary risk analysis in the city of Torino. Chemosphere, 112, 210–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.034.
Sanches-Soberon, F., Rovira, J., Mari, M., Sierra, J., Nadal, M., Domingo, J. L., & Schuhmacher, M. (2015). Main components and human health risks assessment of PM10, PM2.5, PM1 in two areas influenced by cement plants. Atmospheric Environment, 120, 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.020.
Sharma, S. K., Mandal, T. K., Saxena, M., Rashmi, R., Sharma, A., & Gautam, R. (2014). Source apportionment of PM10 by using positive matrix factorization at an urban site of Delhi, India. Urban Climate, 10, 656–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2013.11.002.
Shen, R., Schafer, K., Schnelle-Kreis, J., Shao, L., Norra, S., Kramar, U., Michalke, B., Abbaszade, G., Streibel, T., Fricker, M., Chen, Y., Zimmermann, R., Emeis, S., & Schmid, H. P. (2016). Characteristics and sources of PM in seasonal perspective a case study from one year continuously sampling in Beijing. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 7(2), 235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2015.09.008.
Song, X., Yang, S., Shao, L., Fan, J., & Liu, Y. (2016). PM10 mass concentration, chemical composition, and sources in the typical coal-dominated industrial city of Pingdingshan, China. Science of the Total Environment, 571, 1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.115.
Talbi, A., Kerchich, Y., Kerbachi, R., & Boughedaoui, M. (2018). Assessment of annual air pollution levels with PM1, PM2.5, PM10 and associated heavy metals in Algiers, Algeria. Environmental Pollution, 232, 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.09.041.
Tan, J. H., Duan, J. C., Chai, F. H., He, K. B., & Hao, J. M. (2014). Source apportionment of size segregated fine/ultrafine particle by PMF in Beijing. Atmospheric Research, 139, 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.01.007.
Tecer, L. H., Tuncel, G., Karaca, F., Alagha, O., Suren, P., Zararsız, A., & Kırmaz, R. (2012). Metallic composition and source apportionment of fine and coarse particles using positive matrix factorization in the southern Black Sea atmosphere. Atmospheric Research, 118, 153–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.06.016.
Titos, G., Lyamani, H., Pandolfi, M., Alastuey, A., & Alados-Arboledas, L. (2014). Identification of fine (PM1) and coarse (PM10-1) sources of particulate matter in an urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 89, 593–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.03.001.
Türküm, A., Pekey, B., Pekey, H., & Tuncel, G. (2008). Comparison of sources affecting chemical compositions of aerosol and rainwater at different locations in Turkey. Atmospheric Research, 89(4), 315–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2008.03.010.
Upadhyay, N., Majestic, B. J., Prapaipong, P., & Herckes, P. (2009). Evaluation of polyurethane foam, polypropylene, quartz fiber, and cellulose substrates for multi-element analysis of atmospheric particulate matter by ICP-MS. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 394(1), 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2671-6.
USEPA IRIS (2015). US Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System. http://www.epa.gov/iris/supdocs/0276index.html.
USEPA Method IO-2.1 (1999) Compendium of methods for the determination of inorganic compounds in ambient Air; Compendium Method IO-2.1; EPA/625/R-96/010a. Sampling of ambient air for total suspended particulate matter (SPM) and PM10 using high volume (HV) sampler
USEPA Method IO-3.1, (1999) Compendium of methods for the determination of inorganic compounds in ambient air; EPA/ 625/R-96/010a. Selection, Preparation and Extraction of Filter Material.
USEPA, (2011). Exposure factors handbook 2011 edition (final) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-09/052F, 2011USEPA IRIS (2015). US Environmental Protection Agency, Integrated Risk Information System http://www.epa.gov/iris/supdocs/0276index.html.
USEPA, (2013). Regional screening level (RSL) summary table (TR = 1E_6, HQ = 1). http://www.epa.gov/region9/superfund/prg/.
USEPA, (2014). Positive matrix factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundementals & User Guide.
Wang, X., Bi, X., Sheng, G., & Fu, J. (2006). Chemical composition and source of PM10 and PM2.5 aerosols in Guangzhou, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 119(1-3), 425–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-9034-3.
Wang, J., Pan, Y., Tian, S., Chen, X., Wang, L., & Wang, Y. (2016). Size distributions and health risks particulate trace elements in rural areas in northeastern China. Atmospheric Research, 168, 191–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.08.019.
Yatın, M., Tuncel, S., Aras, N. K., Olmez, I., Aygun, S., & Tuncel, G. (2000). Atmospheric trace elements in Ankara, Turkey, 1. Factors affecting chemical composition of fine particles. Atmospheric Environment, 34(8), 1305–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00297-0.
Yatkın, S., & Bayram, A. (2008). Determination of major natural and anthropogenic source profiles for particulate matter and trace elements in Izmir, Turkey. Chemosphere, 71(4), 685–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.070.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Düzce University Scientific Research Projects Coordinator (DÜBAP) (Project number: 2014.06.02.219). The authors thank Düzce University Central Research Laboratory (DUBIT) for their valuable support to finalize the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozkurt, Z., O. Gaga, E., Taşpınar, F. et al. Atmospheric ambient trace element concentrations of PM10 at urban and sub-urban sites: source apportionment and health risk estimation. Environ Monit Assess 190, 168 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6517-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6517-6