Abstract
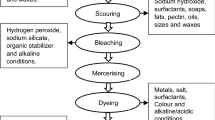
Effective treatment of textile effluent prior to discharge is necessary in order to avert the associated adverse health impacts on human and aquatic life. In the present investigation, coagulation/flocculation processes were evaluated for the effectiveness of the individual treatment. Effectiveness of the treatment was evaluated based on the physicochemical characteristics. The quality of the pre-treated and post-flocculation treated effluent was further evaluated by determination of cytotoxicity and inflammatory activity using RAW264.7 cell cultures. Cytotoxicity was determined using WST-1 assay. Nitric oxide (NO) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were used as biomarkers of inflammation. NO was determined in cell culture supernatant using the Griess reaction assay. The IL-6 secretion was determined using double antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunoassay (DAS ELISA). Cytotoxicity results show that raw effluent reduced the cell viability significantly (P < 0.001) compared to the negative control. All effluent samples treated by coagulation/flocculation processes at 1 in 100 dilutions had no cytotoxic effects on RAW264.7 cells. The results on inflammatory activities show that the raw effluent and effluent treated with 1.6 g/L of Fe-Mn oxide induced significantly (P < 0.001) higher NO production than the negative control. The inflammatory results further show that the raw effluent induced significantly (P < 0.001) higher production of IL-6 than the negative control. Among the coagulants/flocculants evaluated Al2(SO4)3.14H2O at a dosage of 1.6 g/L was the most effective to remove both toxic and inflammatory pollutants. In conclusion, the inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 cells can be used as sensitive biomarkers for monitoring the effectiveness of coagulation/flocculation processes used for textile effluent treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo, S. A., Shai, L. J., Cholo, M. C., Anderson, R., & du Toit, D. (2014). Assessment of the pro-inflammatory activity of water sampled from major water treatment facilities in the greater Pretoria region. Water SA, 40(2), 379–384.
Anouzla, A., Abrouki, Y., Souabi, S., Safi, M., & Rhbal, H. (2009). Color and COD removal of disperse dye solution by a novel coagulant: application of statistical design for the optimization and regression analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1302–1306.
APHA (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC, USA.: American Public Health Association (APHA), AWWA, WEF,.
Barnes, T. C., Anderson, M. E., & Moots, R. J. (2011). The many faces of interleukin-6: the role of IL-6 in inflammation, vasculopathy, and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. International Journal of Rheumatology. doi:10.1155/2011/721608.
Bolto, B., & Gregory, J. (2007). Organic polyelectrolytes in water treatment. Water Research, 41, 2301–2324.
Ciabatti, I., Tognotti, F., & Lombardi, L. (2010). Treatment and reuse of dyeing effluents by potassium ferrate. Desalination, 250, 222–228.
Connelly, L., Jacobs, A.T., Palacios-Callender, M., Moncada, S., Hobbs, A.J. (2003). Macrophage endothelial nitric-oxide synthase autoregulates cellular activation and pro-inflammatory protein expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(29), 26480–26487.
Di Bella, G., Giustra, M. G., & Freni, G. (2014). Optimisation of coagulation/flocculation for pre-treatment of high strength and saline wastewater: performance analysis with different coagulant doses. Chemical Engineering Journal, 254, 283–292.
Dulov, A., Dulova, N., & Trapido, M. (2011). Combined physicochemical treatment of textile and mixed industrial wastewater. Ozone: Science & Engineering: The Journal of the International Ozone Association, 33(4), 285–293.
El-Gohary, F., & Tawfik, A. (2009). Decolorization and COD reduction of disperse and reactive dyes wastewater using chemical-coagulation followed by sequential batch reactor (SBR) process. Desalination, 249, 1159–1164.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Decontamination of textile wastewater via TiO2/activated carbon composite materials. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 159, 130–143.
Galleano, M., Simontacchi, M., Puntarulo, S. (2004). Nitric oxide and iron: effect of iron overload on nitric oxide production in endotoxemia. Molecular Aspects of Medicine, 25(1-2), 141–154.
Gatidou, G., Thomaidis, N. S., Stasinakis, A. S., & Lekkas, T. D. (2007). Simultaneous determination of the endocrine disrupting compound nonylphenol, nonylphenol ethoxylates, triclosan and bisphenol A in wastewater and sewage sludge by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1138, 32–41.
Ghaly, A. E., Ananthashankar, R., Alhattab, M., & Ramakrishnan, V. V. (2014). Production, characterization and treatment of textile effluents: a critical review. Journal Chemical Engineering Process Technology, 5, 182.
He, Y., Sun, X., Huang, C., Long, X. R., Lin, X., Zhang, L., Lv, X. W., & Li, J. (2014). MiR-146a regulates IL-6 production in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264. 7 macrophage cells by inhibiting Notch1. Inflammation, 37(1), 71–82.
Hendricks, R., & Pool, E. J. (2012). Rapid in vitro tests to determine the toxicity of raw wastewater and treated sewage effluents. Water SA, 38(5), 807–812.
Hussain, S., Shaikh, S., & Farooqui, M. (2013). COD reduction of waste water streams of active pharmaceutical ingredient—atenolol manufacturing unit by advanced oxidation-Fenton process. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 17, 199–202.
Hymery, N., Masson, F., Barbier, G., & Coton, E. (2014). Cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity of cyclopiazonic acid on human cells. Toxicology In Vitro, 28(5), 940–947.
Jeon, C.-M., Shin, I.-S., Shin, N.-R., Hong, J.-M., Kwon, O.-K., Kim, H.-S., et al. (2014). Siegesbeckia glabrescens attenuates allergic airway inflammation in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and OVA induced asthma murine model. International Immunopharmacology, 22(2), 414–419.
Kang, Y. H., & Biswas, S. K. (2013). Basophil-macrophage dialog in allergic inflammation. Immunity, 38(3), 408–410.
Kasraie, S., & Werfel, T. (2013). Role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Mediators of Inflammation, 2013.
Kim, J. H., Kim, Y. S., Hwang, J. W., Han, Y. K., Lee, J. S., Kim, S. K., Jeon, Y. J., Moon, S. H., Jeon, B. T., Bahk, Y. Y., & Park, P. J. (2014). Sulfated chitosan oligosaccharides suppress LPS-induced NO production via JNK and NF-κB inactivation. Molecules, 19, 18232–18247. doi:10.3390/molecules191118232.
Klemola, K., Pearson, J., Lindstrom-Seppä, P. (2007). Evaluating the toxicity of reactive dyes and dyed fabrics with the HaCaT cytotoxicity test. Autex Research Journal, 7 (3), 217–223.
Kobayashi, Y. (2010). The regulatory role of nitric oxide in proinflammatory cytokine expression during the induction and resolution of inflammation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 88(6), 1157–1162.
Kumar, P., Prasad, B., Mishra, I. M., & Chand, S. (2008). Decolorization and COD reduction of dyeing wastewater from a cotton textile mill using thermolysis and coagulation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 635–645.
Malinauskiene, L., Zimerson, E., Bruze, M., Ryberg, K., Isaksson, M. (2011). Textile dyes disperse orange 1 and yellow 3 contain more than one allergen as shown by patch testing with thin-layer chromatograms. Dermatitis, 22(6), 335–343.
Malinauskiene, L., Zimerson, E., Bruze, M., Ryberg, K., & Isaksson, M. (2012). Are allergenic disperse dyes used for dyeing textiles? Contact Dermatitis, 67(3), 141–148. doi:10.1159/000357021.
Mathur, N., Bhatnagar, P., Nagar, P., Bijarnia, M.K. (2005). Mutagenicity assessment of effluents from textile/dye industries of Sanganer, Jaipur (India): A case study. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 61 (1), 105–113.
Martín, M. A., González, I., Berrios, M., Siles, J. A., & Martín, A. (2011). Optimization of coagulation–flocculation process for wastewater from sauce manufacturing using factorial design of experiments derived. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172, 771–782.
Mattila, J. T., & Thomas, A. C. (2014). Nitric oxide synthase: non-canonical expression pattern. Frontiers in Immunology, 5, 478. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00478.
Mazumder, D. (2011). Process evaluation and treatability study of wastewater in a textile dyeing industry. International Journal of Energy and Environment, 2(6), 1053–1066.
Mihara, M., Hashizume, M., Yoshida, H., Suzuki, M., & Shiina, M. (2012). IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clinical Science, 122(4), 143–159.
Moreira, A. P., & Hogaboam, C. M. (2011). Macrophages in allergic asthma: fine-tuning their pro-and anti-inflammatory actions for disease resolution. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research, 31(6), 485–491.
Mukhlish, M., Zobayer, B., Huq, M. M., Ferdous, K., Mazumder, M., Salatul, I., Khan, M., Maksudur, R., & Islam, M. A. (2013). Treatment of textile effluent of Fokir knitwear in Bangladesh using coagulation-flocculation and adsorption methods. International Research Journal of Environment Science, 2(6), 49–53.
Nygaard, U., Kralund, H. H., & Sommerlund, M. (2013). Allergic contact dermatitis induced by textile necklace. Case reports in Dermatology, 5(3), 336–339.
Oller, I., Malato, S., & Sánchez-Pérez, J. A. (2011). Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—a review. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20), 4141–4166.
Parmar, K.A., Prajapati, S., Patel, R., Dabhi, Y. (2011). Effective use of ferrous sulfate and alum as a coagulant in treatment of dairy industry wastewater. Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 6(9), 42–45.
Pool, E. J., van Wyk, J. H., & Leslie, A. J. (2000). Inflammatory activity as an indicator of water quality: the use of human whole blood cultures. Journal of Immunoassay, 21(4), 387–399.
Pothitou, P., & Voutsa, D. (2008). Endocrine disrupting compounds in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants in Northern Greece. Chemosphere, 73, 1716–1723.
Roponen, M., Toivola, M., Meklin, T., Ruotsalainen, M., Komulainen, H., Nevalainen, A., & Hirvonen, M. R. (2001). Differences in inflammatory responses and cytotoxicity in RAW264.7 macrophages induced by Streptomyces Anulatus grown on different building materials. Indoor Air, 11(3), 179–184.
Ryberg, K., Isaksson, M., Gruvberger, B., Hindsén, M., Zimerson, E., & Bruze, M. (2006). Contact allergy to textile dyes in southern Sweden. Contact Dermatitis, 54(6), 313–321.
Sabur, M. A., Khan, A. A., & Safiullah, S. (2012). Treatment of textile wastewater by coagulation precipitation method. Journal of Scientific Research, 4(3), 623–633.
Scheller, J., Chalaris, A., Schmidt-Arras, D., & Rose-John, S. (2011). The pro-and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 1813(5), 878–888.
Schmidt, H. H., Warner, T. D., Nakane, M. A. S. A. K. I., Förstermann, U., & Murad, F. E. R. I. D. (1992). Regulation and subcellular location of nitrogen oxide synthases in RAW264. 7 macrophages. Molecular Pharmacology, 41(4), 615–624.
Sher, F., Malik, A., & Liu, H. (2013). Industrial polymer effluent treatment by chemical coagulation and flocculation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 1, 684–689.
Verma, Y. (2008). Toxicity assessment of dye containing industrial effluents by acute toxicity test using Daphnia magna. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 24, 491–500.
Verma, A. K., Dash, R. R., & Bhunia, P. (2012). A review on chemical coagulation/flocculation technologies for removal of colour from textile wastewaters. Journal of Environmental Management, 93, 154–168.
Ward, R. J., Crichton, R. R., Taylor, D. L., Della Corte, L., Srai, S. K., & Dexter, D. T. (2011). Iron and the immune system. Journal of Neural Transmission, 118(3), 315–328.
Weiss, G., Werner-Felmayer, G., Werner, E. R., Grünewald, K., Wachter, H., & Hentze, M. W. (1994). Iron regulates nitric oxide synthase activity by controlling nuclear transcription. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 180(3), 969–976.
Xu, X., Wu, X., Wang, Q., Cai, N., Zhang, H., Jiang, Z., Wan, M., & Oda, T. (2014). Immunomodulatory effects of alginate oligosaccharides on murine macrophage RAW264. 7 cells and their structure–activity relationships. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62(14), 3168–3176.
Zapata, A., Velegraki, T., Sánchez-Pérez, J. A., Mantzavinos, D., Maldonado, M. I., & Malato, S. (2009a). Solar photo-Fenton treatment of pesticides in water: effect of iron concentration on degradation and assessment of ecotoxicity and biodegradability. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 88, 448–454.
Zapata, A., Oller, I., Bizani, E., Sánchez-Pérez, J. A., Maldonado, M. I., & Malato, S. (2009b). Evaluation of operational parameters involved in solar photo-Fenton degradation of a commercial pesticide mixture. Catalysis Today, 144, 94–99.
Zayas, P. T., Geissler, G., & Hernandez, F. (2007). Chemical oxygen demand reduction in coffee wastewater through chemical flocculation and advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 300–305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
The project was funded by funds from the NRF of South Africa (Grant number 74016).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makene, V.W., Tijani, J.O., Petrik, L.F. et al. Evaluation of cytotoxicity and inflammatory activity of wastewater collected from a textile factory before and after treatment by coagulation-flocculation methods. Environ Monit Assess 188, 471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5441-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5441-x