Abstract
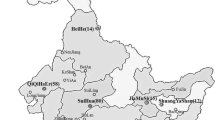
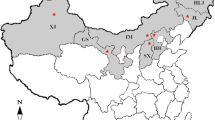
Three hundred and fifty six isolates of Rhizoctonia solani were obtained from potato stems and tubers in the main potato growing regions of China between 2011 and 2014. On the basis of the hyphal anastomosis and sequence analysis of the internal transcribed spacers of the ribosomal DNA, 249 isolates (69.94 %) were identified to anastomosis group (AG)-3 PT, 44 (12.36 %) to AG-5, 39 (10.96 %) to AG-4-HGI, 12 (3.37 %) to AG-4-HGII, seven (1.97 %) to AG-4-HGIII, three (0.84 %) to AG-2-1, one (0.28 %) to AG-1-IB, and one (0.28 %) to AG-11. All these AGs could be isolated from potato cankered subterranean stems, whereas isolates obtained from sclerotia on tubers just belonged to AG-3 PT, AG-4-HGI, and AG-5. The selected 56 isolates representing different AGs and subgroups were able to cause brown, dry lesions on potato subterranean stems with disease incidences ranging from 21.43 to 92.87 %. The lesions caused by AG-3 PT isolates were deeply sunken, while those caused by isolates of other AGs were slightly sunken. Taken together, AG-3 PT of R. solani was the predominant pathogen causing stem canker and black scurf on potatoes in China. To our knowledge, this is the first detailed report of the AG composition of R. solani populations causing potato disease in China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, H., & Tsuboki, K. (1978). Anastomosis groups of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn from potatoes. Bulletin of Hokkaido Prefectural Agricultural Experiment Stations, 40, 61–70.
Anguiz, R., & Martin, C. (1989). Anastomosis groups, pathogenicity, and other characteristics of Rhizoctonia solani isolated from potatoes in Peru. Plant Disease, 73, 199–201.
Balali, G. R., Neate, S. M., Scott, E. S., Whisson, D. L., & Wicks, T. J. (1995). Anastomosis group and pathogenicity of isolates of Rhizoctonia solani from potato crops in South Australia. Plant Pathology, 44, 1050–1057.
Bandy, B. P., Leach, S. S., & Tavantzis, S. M. (1988). Anastomosis group 3 is the major cause of Rhizoctonia disease of potato in Maine. Plant Disease, 72, 596–598.
Banville, G. J. (1978). Studies on the Rhizoctonia disease of potatoes. American Journal of Potato Research, 55, 56.
Banville, G. J. (1989). Yield losses and damage to potato plants caused by Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. American Potato Journal, 66, 821–834.
Banville, G. J., Carling, D. E., & Otrysko, B. E. (1996). Rhizoctonia diseases on potato. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control (pp. 321–330). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Bartz, F. E., Cubeta, M. A., Toda, T., Naito, S., & Ivors, K. L. (2010). An in planta method for assessing the role of Basidiospores in Rhizoctonia foliar disease of tomato. Plant Disease, 94, 515–520.
Budge, G. E., Shaw, M. W., Lambourne, C., Jennings, P., Clayburn, R., Boonham, N., & McPherson, M. (2009). Characterization and origin of infection of Rhizoctonia solani associated with Brassica oleracea crops in the UK. Plant Pathology, 58, 1059–1070.
Campion, C., Chatot, C., Perraton, B., & Andrivon, D. (2003). Anastomosis groups, pathogenicity and sensitivity to fungicides of Rhizoctonia solani isolates collected on potato crops in France. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109, 983–992.
Carling, D. E. (1996). Grouping in Rhizoctonia solani by the anastomosis reaction. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control (pp. 37–47). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Carling, D. E., & Leiner, R. H. (1990). Effect of temperature on virulence of Rhizoctonia solani and other Rhizoctonia on potato. Phytopathology, 80, 930–934.
Carling, D. E., Leiner, R. H., & Kebler, K. M. (1987). Characterization of a new anastomosis group (AG-9) of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 77, 1609–1612.
Carling, D. E., Leiner, R. H., & Westphale, P. C. (1989). Symptoms, signs and yield reduction associated with Rhizoctonia disease of potato induced by tuber-borne inoculum of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3. American Potato Journal, 66, 693–701.
Carling, D. E., Brainard, K. A., Virgen-Calleros, G., & Olalde-Portugal, V. (1998). First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-7 on potato in Mexico. Plant Disease, 82, 127.
Carling, D. E., Baird, R. E., Gitaitis, R. D., Brainard, K. A., & Kuninaga, S. (2002a). Characterization of AG-13, a newly reported anastomosis group of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 92, 893–899.
Carling, D. E., Kuninaga, S., & Brainard, K. A. (2002b). Hyphal anastomosis reactions, rDNA-internal transcribed spacer sequences, and virulence levels among subsets of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group-2 (AG-2) and AG-BI. Phytopathology, 92, 43–50.
Ceresini, P. C., Shew, H. D., Vilgalys, R. J., & Cubeta, M. A. (2002). Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 from potato and tobacco in North Carolina. Mycologia, 94, 437–449.
Cubeta, M. A., & Vilgalys, R. (1997). Population biology of the Rhizoctonia solani complex. Phytopathology, 87, 480–484.
Das, S., Shah, F. A., Butler, R. C., Falloon, R. E., Stewart, A., Raikar, S., & Pitman, A. R. (2014). Genetic variability and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with black scurf of potato in New Zealand. Plant Pathology, 63, 651–666.
Editorial Board of China Agriculture Yearbook. (2013). China agriculture yearbook (p. 214). Beijing: China Agriculture Press (In Chinese).
Escande, A. R., & Echandi, E. (1991). Protection of potato from Rhizoctonia canker with binucleate Rhizoctonia fungi. Plant Pathology, 40, 197–202.
Ferrucho, R. L., Ceresini, P. C., Ramirez-Escobar, U. M., McDonald, B. A., Cubeta, M. A., & García-Domínguez, C. (2013). The population genetic structure of Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT from potato in the Colombian Andes. Phytopathology, 103, 862–869.
Gonzalez, D., Carling, D. E., Kuninaga, S., Vilgalys, R., & Cubeta, M. A. (2001). Ribosomal DNA systematics of Ceratobasidium and Thanatephorus with Rhizoctonia anamorphs. Mycologia, 93, 1138–1150.
Grosch, R., Schneider, J. H. M., Peth, A., Waschke, A., Franken, P., Kofoet, A., & Jabaji-Hare, S. H. (2007). Development of a specific PCR assay for the detection of Rhizoctonia solani AG 1-IB using SCAR primers. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 102, 806–819.
Hide, G. A., & Firmager, J. P. (1990). Effects of an isolate of Rhizoctonia solani Kühn AG8 from diseased barley on the growth and infection of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum). Potato Research, 33, 229–234.
James, W. C., & McKenzie, A. R. (1972). The effect of tuberborne sclerotia of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn on the potato crop. American Journal of Potato Research, 49, 296–301.
Jing, Y., Li, X. N., & Yu, J. F. (2012). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani from cotton in northern China. Mycosystema, 31, 540–547 (In Chinese).
Kronland, W. C., & Stanghellini, M. E. (1988). Clean slide technique for the observation of anastomosis and nuclear condition of Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology, 78, 820–822.
Kuninaga, S., Natsuaki, T., Takeuchi, T., & Yokosawa, R. (1997). Sequence variation of the rDNA ITS regions within and between anastomosis groups in Rhizoctonia solani. Current Genetics, 32, 237–243.
Kuninaga, S., Nicoletti, R., Lahoz, E., & Naito, S. (2000). Ascription of Nt-isolates of Rhizoctonia solani to anastomosis group 2-1 (AG-2-1) on account of rDNA-ITS sequence similarity. Journal of Plant Pathology, 82, 61–64.
Kuramae, E. E., Buzeto, A. L., Ciampi, M. B., & Souza, N. L. (2003). Identification of Rhizoctonia solani AG 1-IB in lettuce, AG 4 HG-I in tomato and melon, and AG 4 HG-III in broccoli and spinach, in Brazil. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 109, 391–395.
Lehtonen, M. J., Ahvenniemi, P., Wilson, P. S., German-Kinnari, M., & Valkonen, J. P. T. (2008). Biological diversity of Rhizoctonia solani (AG-3) in a northern potato-cultivation environment in Finland. Plant Pathology, 57, 141–151.
Li, J., Xia, H. B., & Yu, J. F. (2011). The anastomosis groups of the corn sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia spp. in northeastern China. Mycosystema, 30, 392–399 (In Chinese).
Li, X. N., Xu, N. N., & Yu, J. F. (2014). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani from black scurf of potato in northern China. Mycosystema, 33, 584–593 (In Chinese).
Maimaiti, Y., Guo, Q. Y., & Fulati, D. (2007). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn isolated from cotton and their vegetative compatibility groups in the south of Xinjiang. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 30, 10–13 (In Chinese).
Mathew, F. M., Lamppa, R. S., Chittem, K., Chang, Y. W., Botschner, M., Kinzer, K., & Markell, S. G. (2012). Characterization and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani isolates affecting Pisum sativum in North Dakota. Plant Disease, 96, 666–672.
Ogoshi, A. (1996). Introduction—the genus Rhizoctonia. In B. Sneh, S. Jabaji-Hare, S. Neate, & G. Dijst (Eds.), Rhizoctonia species: Taxonomy, molecular biology, ecology, pathology and disease control (pp. 1–9). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Platt, H. W. (1989). Potato growth and tuber production as affected by inoculation of cut and whole seed with Rhizoctonia solani (AG 3) and the use of seed treatment fungicides. American Journal of Potato Research, 66, 365–378.
Platt, H. W., Canale, F., & Gimenez, G. (1993). Effects of tuber-borne inoculum of Rhizoctonia solani and fungicidal seed potato treatment of plant growth and Rhizoctonia disease in Canada and Uruguay. American Journal of Potato Research, 70, 553–559.
Rauf, C. A., Ahmad, I., & Ashraf, M. (2007). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn isolates from potato in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 39, 1335–1340.
Sharon, M., Kuninaga, S., Hyakumachi, M., Naito, S., & Sneh, B. (2008). Classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using rDNA-ITS sequence analysis supports the genetic basis of the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience, 49, 93–114.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2011). MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2731–2739.
Tian, X. Y., Meng, M. L., Zhang, X. Y., Dong, R. L., & Hu, J. (2011). Identification of anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani on potato plant. Chinese Potato, 25, 298–301 (In Chinese).
Toda, T., Mghalu, J. M., Priyatomojo, A., & Hyakumachi, M. (2004). Comparison of sequences for the internal transcribed spacer region in Rhizoctonia solani AG 1-ID and other subgroups of AG 1. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 70, 270–272.
Tsror, L. (2010). Biology, epidemiology and management of Rhizoctonia solani on potato. Journal of Phytopathology, 158, 649–658.
Virgen-Calleros, G., Olalde-Portugal, V., & Carling, D. E. (2000). Anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani on potato in central Mexico and potential for biological and chemical control. American Journal of Potato Research, 77, 219–224.
Wang, Y., Yang, Z. H., Qin, Y. X., & Zhu, J. H. (2013). Analysis on anastomosis groups of Rhizoctonia solani AG2-1 and AG3 from potato (Solanum tuberosum). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 21, 230–237 (In Chinese).
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In M. A. Innis, D. J. Gelfand, J. J. Sninsky, & T. J. White (Eds.), PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications (pp. 315–322). New York: Academic.
Woodhall, J. W., Lees, A. K., Edwards, S. G., & Jenkinson, P. (2007). Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani from potato in Great Britain. Plant Pathology, 56, 286–295.
Woodhall, J. W., Lees, A. K., Edwards, S. G., & Jenkinson, P. (2008). Infection of potato by Rhizoctonia solani: effect of anastomosis group. Plant Pathology, 57, 897–905.
Woodhall, J. W., Belcher, A. R., Peters, J. C., Kirk, W. W., & Wharton, P. S. (2012a). First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG2-2IIIB infecting potato stems and stolons in the United States. Plant Disease, 96, 460.
Woodhall, J. W., Wharton, P. S., & Peters, J. C. (2012b). First report of Rhizoctonia solani AG4 HG-II infecting potato stems in Idaho. Plant Disease, 96, 1701.
Woodhall, J. W., Adams, I. P., Peters, J. C., Harper, G., & Boonham, N. (2013). A new quantitative real-time PCR assay for Rhizoctonia solani AG3-PT and the detection of AGs of Rhizoctonia solani associated with potato in soil and tuber samples in Great Britain. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 136, 273–280.
Yanar, Y., Yllmaz, G., Cesmeli, I., & Coskun, S. (2005). Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from potatoes in Turkey and screening potato cultivars for resistance to AG-3 isolates. Phytoparasitica, 33, 370–376.
Yang, Y. G., & Wu, X. H. (2012). First report of potato stem canker caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-5 in China. Plant Disease, 96, 1579.
Yang, Y. G., & Wu, X. H. (2013). First report of potato stem canker caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG4 HGII in Gansu Province, China. Plant Disease, 97, 840.
Yang, J. H., Guo, Q. Y., & Ji, L. (2005). Study on anastomosis groups Rhizoctonia solani isolated from six Leguminaceous crops in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 42, 382–385 (In Chinese).
Yang, Y. G., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. J., & Wu, X. H. (2014). Anastomosis groups and pathogenicity of binucleate Rhizoctonia isolates associated with stem canker of potato in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 139, 535–544.
Zhao, S. F., Li, G. Y., & Du, Y. J. (2002). Beet root rot disease and prevention and control. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 39, 150–152 (in Chinese).
Zhou, S. Y., Ji, Z., Zhao, C. D., Liu, Y., & Li, B. D. (2012a). Anastomosis grouping and genetic diversity of maize pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in Shandong. Mycosystema, 31, 31–39 (In Chinese).
Zhou, X. K., Gao, Z. G., Zhang, X. X., Zhang, S., Li, Z. Z., & Gao, J. X. (2012b). Construction of UP-PCR system and genetic diversity analysis of Rhizoctonia solani. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 43, 33–38 (In Chinese).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to N. Kondo (Graduate School of Agriculture, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan) for kindly providing reference strains. This work was supported by Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT1042). Mention of trade names or commercial products in this report is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table
(DOC 532 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zhao, C., Guo, Z. et al. Anastomosis group and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia solani associated with stem canker and black scurf of potato in China. Eur J Plant Pathol 143, 99–111 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0668-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0668-x