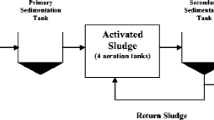
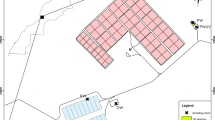
Abstract
Global water consumption has grown twice as fast as the population. Wastewater is therefore a valuable and renewable source and provides additional water for priority uses. Wastewater can also be a source of pollution; thus, its physico-chemical and biological compositions can present major risks to the environment and human health. The objective of this study was to assess the status of irrigation waters in terms of salinization, accumulation of metallic elements, and microbiological contamination by parasites and pathogenic bacteria. The study focused on the surface water of Oued Fès used for irrigation located downstream of the industrial zone of Doukkarat and upstream of the industrial zone of Ain Noukbi (wastewater) before the confluence with the Oued Sebou, as well as on the treated wastewater of the wastewater treatment plant. The physico-chemical and microbiological analyses were carried out in two periods: summer and winter. Metals were analyzed by ICP-AES. The chemical and bacteriological quality of the wastewater and treated wastewater was found to be poor. These were characterized by organic pollution, including biodegradable pollutants, while upstream the organic residues were not biodegradables. COD, BOD5, Kjeldahl nitrogen, as well as chloride ion (Cl−) are above the standard values. The highest concentrations of Cd, at 850 µg/l, Cu, at 690 µg/l and Mn, at 470 µg/l, largely exceed the international standards and requirements. In addition to fecal contamination, characterized by total coliforms and thermo-tolerant coliforms, other pathogens were present, including helminth eggs, both in the wastewater and in the treated wastewater. Other pathogens, such as Vibrio cholera, were found at all three sites whether in winter or summer, with the exception of the downstream of Oued Fez in winter. As for Salmonella, it was present in treated wastewater during the winter only. The water used for irrigation upstream of Oued Fez and the treated wastewater have poor to very poor quality. Therefore, for a better use of these waters, it is necessary to ensure their regular treatment in order to minimize the impacts on the environment and human health.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data pertinent to this study are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Change history
06 April 2023
The e-mail address of the corresponding authors is correctly placed under their respective affiliation.
11 May 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01549-0
References
Acosta, J. A., Jansen, B., Kalbitz, K., Faz, A., & Martínez-Martínez, S. (2011). Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere, 85(8), 1318–1324.
Azzaoui, S., El Hanbali, M., & Leblanc, M. (2002). Copper, lead, iron and manganese in the Sebou drainage basin; sources and impact on surface water quality. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 37(4), 773–784.
BaizeSterckeman, D. T. (2001). Of the necessity of knowledge of the natural pedo-geochemical background content in the evaluation of the contamination of soils by trace elements. Science of the Total Environment, 264(1–2), 127–139.
Belaid, N. (2010). Evaluation des impacts de l’irrigation par les eaux usées traitées sur les plantes et les sols du périmètre irrigué d’El Hajeb-Sfax: salinisation, accumulation et phytoabsorption des éléments métalliques , Limoges, 2010.
Benslama, S. (2021). Qualité des eaux d’irrigation et salinisation des sols dans une palmeraie dans la région de Ghardaïa – Cas de Zelfana. Thèse Doc. Etat, Univ. Ghardaïa, Algérienne, p 49.
Bissassa, M. (2016). Etude physico-chimique et géochimique de la qualité des eaux et sédiments d’Oued Fès et Sebou-Province Fès Maroc. Mémoir. MST. Etat, Univ. Fès, p 64.http://www.abhatoo.net.ma/content/download/51802/1093311/version/1/file/Etude+physico-chimique+et+g%C3%A9ochimique+de+la+qualit%C3%A9+des+eaux+et+s%C3%A9diments+d%E2%80%99Oued+F%C3%A8s+et+Sebou++Province+F%C3%A8s+Maroc.pdf
Bouchetara, M., Wotto, M., & Eyih, S. (2021). Les effets de la modernisation du secteur agricole sur la croissance économique: l’analyse comparative des stratégies nationales de l’Algérie, du Maroc et de la Tunisie. Dirassat Journal Economic Issue, 12(1), 735–752.
Brémond, R. & Vuichard, (1973). Paramètres de la qualité des eaux. Ministère de la protection de la nature et de l’environnement, Secrétariat.
Coulibaly-Kalpy, J., et al. (2017). Étude de la qualité des eaux usées des deux retenues du bassin du Gourou au carrefour de l’Indénié à Abidjan en 2012. Journal of Applied Biosciences, 113, 11138–11144.
Derfoufi, H., Legssyer, M., & Legssyer, B. (2019). Effect of physicochemical and microbiological parameters on the water quality of wadi Zegzel. Materials Today: Proceedings, 13, 730–738.
Derwich, E., Beziane, Z., Benaabidate, L, Belghyti, D. (2008). Evaluation de la qualité des eaux de surface des Oueds Fès et Sebou utilisées en agriculture maraîchère au Maroc. LARHYSS Journal P-ISSN 1112–3680/E-ISSN 2521–9782, no 7.
Diao, M. (2021). Gestion de l’eau. Le Maroc a opté pour une planification anticipative et à long terme. https://fnh.ma/article/developpement-durable/gestion-de-l-eau-le-maroc-a-opte-pour-une-planification-anticipative-et-a-long-terme-1
Dussart, B., & Fauré-Fremiet, E. P. (1966). Limnologie: l’étude des eaux continentales. Gauthier-Villars.
El Ouali, L., Zanibou, A., Bekhti, K., Zerrouq, F., & Merzouki, M. (2014). Contrôle de la qualité microbiologique des eaux usées domestiques et industrielles de la ville de Fès au Maroc (Microbiological Control wastewater domestic and industrial city of Fes Morocco). J. Mater. Environ. Sci., 5(2028–2508), 2325–2532.
Eldridge E. F. (1967). Water temperature: influences, effects, and control. Federal Water Pollution Control Administration, Portland, Oreg.(USA).
Er-Raioui, H., Khannous, S., Mohamed Cheihk, M. O., Mhamada, M., & Bouzid, S. (2012). The Moroccan Mediterranean coastline: A potential threatened by the urban discharge. The Open Environmental Pollution & Toxicology Journal, 3(1), 23–36.
FAO. (1994). Water quality for agriculture. FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 29. Revision, Rome, Italy, p. 174.
FAO. (2003). Wastewater treatment and use in agriculture. Rome, Italy: FAO irrigation and drainage. Consulté le: 15 mars 2022.
FAO. (2007). Agriculture and water scarcity: A programmatic approach to water use efficiency and agricultural productivity. Rome, Italy: FAO. Consulté le: 14 mars 2022.
Fonseca, R. C., Souza, N. A. D., Correa, T. C. L., Garcia, L. F., Reis, L. G. V. D., & Rodriguez, A. G. (2013). Assessment of toxic potential of Cerrado fruit seeds using Artemia salina bioassay. Food Science and Technology, 33(2), 251–256.
Ghazali, D., & Zaid, A. (2013). Study of the physico-chemical and bacteriological quality of the waters of the Ain Salama-Jerri spring (region of Meknes–Morocco). Larhyss J, 12, 25–36.
Gromaire, M.-C., Garnaud, S., Saad, M., & Chebbo, G. (2001). Contribution of different sources to the pollution of wet weather flows in combined sewers. Water Research, 35(2), 521–533.
Gupta, N., Pandey, P., & Hussain, J. (2017). Effect of physicochemical and biological parameters on the quality of river water of Narmada, Madhya Pradesh India. Water Science, 31(1), 11–23.
Hamaidi, M., & Kais, H. (2016). Evaluation De La Charge En Pathogenes Et De La Microfaune Dans Les Eaux De L’effluent Brute Et Traité Rejeté Dans Un Milieu Recepteur: Cas De La Station D’epuration De Médéa. Larhyss Journal, 26, 183–208.
Hamdy, A. (2002). Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources in the arid regions. Acta Horticulturae. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2002.573.18
Hamoda, M. F. (2004). Water strategies and potential of water reuse in the south Mediterranean countries. Desalination, 165, 31–41.
Horckmans, L., Swennen, R., Deckers, J., & Maquil, R. (2005). Local background concentrations of trace elements in soils: A case study in the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. CATENA, 59(3), 279–304.
Idrissi, Y. A., Alemad, A., Aboubaker, S., Daifi, H., Elkharrim, K., & Belghyti, D. (2015). Caractérisation physico-chimique des eaux usées de la ville d’Azilal-Maroc-/[Physico-chemical characterization of wastewater from Azilal city-Morocco-. International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies, 11(3), 556.
Jampani, M., Liedl, R., Hülsmann, S., Sonkamble, S., & Amerasinghe, P. (2020). Hydrogeochemical and mixing processes controlling groundwater chemistry in a wastewater irrigated agricultural system of India. Chemosphere, 239, 124741.
Karrouch, L., Chahlaoui, A., & Essahale, A. (2017). Anthropogenic impacts on the distribution and biodiversity of benthic macroinvertebrates and water quality of the Boufekrane River Meknes Morocco. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 5(07), 173.
Du Laing, G., De Vos, R., Vandecasteele, B., Lesage, E., Tack, F. M., & Verloo, M. G. (2008). Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 77(4), 589–602.
Lamri, D., & Belghyti, D. (2011). Bio-évaluation de la qualité des eaux par application des indices biotiques: Cas de l’oued Moulouya (Maroc). ScienceLib Editions Mersenne, 3(110905), 21.
Mahboubi, M. H., & Benyacoub, B. (2020). Les PME de la ville de Fès, et perspectives de financement participatif: Revue de littérature, hypothèses et modèle de recherche. Revue Internationale Des Sciences De Gestion, 3(1), 475–491.
Merghem, K. A., et al. (2016). Quality study of wastewater treated by Waste Water Treatment Plant (WWTP) in the city of Sana’a (Yemen) used for agriculture. Moroccan Journal of Chemistry, 4(3), 4–3.
Mufur, A. M., Awah, M. T., Nono, G. D. K., Tamfuh, P. A., Wotchoko, P., & Beyala, K. K. V. (2021). Physico-chemical and bacteriological characterisation of surface water in Bamenda (North West Cameroon). Applied Water Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01512-3
Ndiaye, M. L., Dieng, Y., Niang, S., Pfeifer, H. R., Tonolla, M., & Peduzzi, R. (2011). Effect of irrigation water on the incidence of Salmonella spp on lettuces produced by urban agriculture and sold on the markets in Dakar Senegal. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 5(19), 2885–2890.
Official Bulettin NBM. (2002). Bulletin officiel n° 5062 du 30 ramadan 1423, Ministry of the environment of Morocco.
El Ouali, L. A., Bekhti, K., Berrada, S., Zanibou, A., Fadil, F., & Merzouki, M. (2013). Contrôle de la qualité microbiologique des eaux usées domestiques et industrielles de la ville de Fès au Maroc. AGROBIOLOGIA, 3(1), 56–65.
Papaiacovou, I. (2001). Case study—wastewater reuse in Limassol as an alternative water source. Desalination, 138(1–3), 55–59.
Perrin, J.-L., Raïs, N., Chahinian, N., Moulin, P., & Ijjaali, M. (2014). Water quality assessment of highly polluted rivers in a semi-arid Mediterranean zone Oued Fez and Sebou River (Morocco). Journal of Hydrology, 510, 26–34.
Qadir, M., Sharma, B. R., Bruggeman, A., Choukr-Allah, R., & Karajeh, F. (2007). Non-conventional water resources and opportunities for water augmentation to achieve food security in water scarce countries. Agricultural Water Management, 87(1), 2–22.
Remon, M. (2018). Frédéric Lasserre, Alexandre Brun, Le partage de l’eau Une Réflexion Géopolitique. Revue Projet, 6, 94–94.
Rezouki, S., Allali, A., Berady, K., Habchaoui, J., Eloutassi, N., & Fadli, M. (2021a). The Impact of Physicochemical Parameters and Heavy Metals on the Biodiversity of Benthic Macrofauna in the Inaouene Wadi (Taza, North East Morocco). Journal of Ecological Engineering, 22(7), 231–241.
Rezouki, S., Allali, A., Touati, N., Mansouri, D., Eloutassi, N., & Fadli, M. (2021b). Spatio-temporal evolution of the physico-chemical parameters of the Inaouen wadi and its tributaries. Moroccan Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.48317/IMIST.PRSM/morjchem-v9i3.23521
Rodier, J. (1996). L’analyse de l’eau - 8ème édition - Eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer: Eaux naturelles, eaux résiduaires, eau de mer (p. 1996). Dunod.
Rodier, J., Legube, B., & Merlet, N. (2009). L’analyse de l’eau. Dunod.
Sayo, S., Kiratu, J. M., & Nyamato, G. S. (2020). Heavy metal concentrations in soil and vegetables irrigated with sewage effluent : A case study of Embu sewage treatment plant. Kenya: Scientific African. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00337
Scott, C. A., Faruqui, N. I., & Raschid-Sally, L. (2004). Wastewater use in irrigated agriculture: Confronting the livelihood and environmental realities. CABI. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851998237.0000
Tomczyk, P., & Wiatkowski, M. (2021). The Effects of hydropower plants on the physicochemical parameters of the Bystrzyca River in Poland. Energies, 14(8), 2075. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14082075
Funding
This work received no specific funding either internal or external.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FJ carried out the sampling and the physicochemical and microbiological analyses with the support of BAMRS, MT, ASM, MB, FK, MAMA-S, and JPG. She supervised the data and statistical calculations. LA and EN supervised the project. MAMA-S and JPG contributed to writing the original draft and editing the final version. All authors participated in the writing of the article and validated the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable as this is not a clinical study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: The seventh author name is corrected as “Farid Khallouki” and the last author name is corrected as “Amal Lahkimi”.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Faouzi, J., Rezouki, S., Bourhia, M. et al. Assessment of impacts of industrial effluents on physico-chemical and microbiological qualities of irrigation water of the Fez Rriver, Morocco. Environ Geochem Health 45, 3933–3946 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01449-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01449-9