Abstract
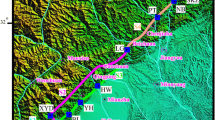
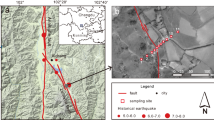
Investigating the emissions of soil gas including radon, mercury and carbon dioxide (222Rn, Hg and CO2) from the solid earth to the atmosphere through active fault zones is of great significance for accession of atmospheric environment. In this study, the concentrations and fluxes of 222Rn, Hg and CO2 were measured at the main active fault zones at the western margin of the Ordos block, China. The concentrations of 222Rn, Hg and CO2 were in the range of 0–60.1 kBq m−3, 3–81 ng m−3 and 0.04–9.23%, respectively, while the fluxes of 222Rn, Hg and CO2 are in the range of 1.99–306.99 mBq m−2 s−1, 0–15.12 ng m−2 h−1 and 0–37.91 g m−2d−1, respectively. Most of the major fault zones at the study area are CO2 risk-free regions (CO2 concentration in soil gas < 5%). However, the extend of 222Rn pollution at the fault zones of F1, F4, F5 and F9 (the fault number) and that of Hg pollution at the fault zones of F2, F4, F5 and F7 were higher than the pollution level of 1. The annual emission of Hg and CO2 from the western margin of the Ordos block was estimated to be 2.03 kg and 0.70 Mt, respectively. Comprehensive analyses indicated that the higher emission rates of soil gases from the active fault zones were related to the seismic activities. The results suggest that the earthquake activity is a dominant factor enhancing the emission of 222Rn, Hg and CO2 from the solid earth through active fault zones and, furthermore, resulting great impact on the atmospheric environment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baixeras, C., Erlandsson, B., Font, L., & Jönsson, G. (2001). Radon emanation from soil samples. Radiation Measurements, 34, 441–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1350-4487(01)00203-7
Bajwa, B. S., Sharma, N., Walia, V., & Virk, H. S. (2003). Measurements of natural radioactivity in some water and soil samples of Punjab state, India. Indoor and Built Environment, 12, 357–361. https://doi.org/10.1177/142032603035631
Baxter, P. J., Baubron, J. C., & Coutinho, R. (1999). Health hazards and disaster potential of ground gas emissions at furnas volcano, São Miguel, Azores. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 92(1), 95–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0273(99)00070-0
Bem, H., Długosz-Lisiecka, M., Mazurek-Rudnicka, D., & Szajerski, P. (2021). Occurrence of 222Rn and 226,228Ra in underground water and 222Rn in soil and their mutual correlations for underground water supplies in southern Greater Poland. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43, 3099–3114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00792-z
Bonforte, A., Federico, C., Giammanco, S., Guglielmino, F., Liuzzo, M., & Neri, M. (2013). Soil gases and SAR measurements reveal hidden faults on the sliding flank of Mt. Etna (Italy). Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 251, 27–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.08.010
Cao, G. (2001). Earthquake research in Inner Mongolia (pp. 1–174). Beijing: Seismological Press.
Capaccioni, B., Tassi, F., Cremonini, S., Sciarra, A., & Vaselli, O. (2015). Ground heating and methane oxidation processes at shallow depth in Terre Calde di Medolla (Italy): Observations and conceptual model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120, 3065–3076. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011635
Caracausi, A., Paternoster, M., & Nuccio, P. M. (2015). Mantle CO2 degassing at Mt. Vulture volcano (Italy): Relationship between CO2 outgassing of volcanoes and the time of their last eruption. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 411, 268–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.11.049
Chavrit, D., Humler, E., & Grasset, O. (2014). Mapping modern CO2 fluxes and mantle carbon content all along the mid-ocean ridge system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 387, 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.11.036
Chen, Z., Li, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, J., Zhou, X., & Du, J. (2018). Radon emission from soil gases in the active fault zones in the Capital of China and its environmental effects. Scientific Reports, 8(16772), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35262-1
Chen, Z., Li, Y., Liu, Z., Zheng, G., Xu, W., Yan, W., & Yi, L. (2019). CH4 and CO2 emissions from mud volcanoes on the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, NW China: Origin, output, and relation to regional tectonics. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jb016822
Chiodini, G., Granieri, D., Avino, R., Caliro, S., Costa, A., Minopoli, C., & Vilardo, G. (2010). Non-volcanic CO2 Earth degassing: Case of Mefite d’Ansanto (southern Apennines), Italy. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(L11303), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010gl042858
Cinelli, G., Tositti, L., Capaccioni, B., Brattich, E., & Mostacci, D. (2015). Soil gas radon assessment and development of a radon risk map in Bolsena, Central Italy. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37, 305–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9649-9
Ciotoli, G., Lombardi, S., & Annunziatellis, A. (2007). Geostatistical analysis of soil gas data in a high seismic intermontane basin: Fucino Plain, central Italy. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B05407), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JB004044
Cui, Y. J., Li, Y., Si, X. Y., Yang, L. X., Liu, Z. F., Sun, F. X., Li, X. Y., Zheng, H. W., & Du, J. G. (2019). Tectonic controls on near-surface variations in CH4 and CO2 concentrations along the northwestern margin of the Ordos Block, China. Geofluids, 7909483, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7909483
Doăn, T., Sumino, H., Nagao, K., Notsu, K., Tuncer, M. K., & Celik, C. (2009). Adjacent releases of mantle helium and soil CO2 from active faults: Observations from the Marmara region of the North Anatolian Fault zone, Turkey. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 10(11), Q11009. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GC002745
El-Arabi, A. M., Abbady, A., Ahmed, N. K., Michel, R., El-Kamel, A. H., & Abbady, A. G. E. (2006). Assessment of radon-222 concentrations and exhalation rates of rocks and building materials. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics, 44(4), 287–291.
Evans, W. C., Sorey, M. L., Kennedy, B. M., Stonestrom, D. A., Rogie, J. D., & Shuster, D. L. (2001). High CO2 emissions through porous media: Transport mechanisms and implications for flux measurement and fractionation. Chemical Geology, 177, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00379-X
Fu, C. C., Yang, T. F., Du, J., Walia, V., Chen, Y. G., Liu, T. K., & Chen, C. H. (2008). Variations of helium and radon concentrations in soil gases from an active fault zone in southern Taiwan. Radiation Measurements, 43, 348–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.03.035
Fu, C. C., Yang, T. F., Tsai, M. C., Lee, L. C., Liu, T. K., Walia, V., Chen, C. H., Chang, W. Y., Kumar, A., & Lai, T. H. (2017). Exploring the relationship between soil degassing and seismic activity by continuous radon monitoring in the Longitudinal Valley of eastern Taiwan. Chemical Geology, 469, 163–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.12.042
Fu, C. C., Yang, T. F., Walia, V., & Chen, C. H. (2005). Reconnaissance of soil gas composition over the buried fault and fracture zone in southern Taiwan. Geochemical Journal, 39, 427–439. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.39.427
Gao, L., Hou, D., Li, J., Li, S., Dai, Y., Xiong, F., & Yang, H. (2016). Movement characteristics and present seismic activity of Ordos Block. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 7(6), 451–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geog.2016.07.008
Gerlach, T. M., Doukas, M. P., Mcgee, K. A., & Kessler, R. (2001). Soil efflux and total emission rates of magmatic CO2 at the Horseshoe Lake tree kill, Mammoth mountain, California, 1995–1999. Chemical Geology, 177, 101–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00385-5
Gold, T. (1979). Terrestrial sources of carbon and earthquake outgassing. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1(3), 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-5457.1979.tb00616.x
Gray, J. E., Theodorakos, P. M., Fey, D. L., & Krabbenhoft, D. P. (2015). Mercury concentrations and distribution in soil, water, mine waste leachates, and air in and around mercury mines in the Big Bend region, Texas, USA. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 37, 35–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-014-9628-1
Han, X., Li, Y., Du, J., Zhou, X., Xie, C., & Zhang, W. (2014). Rn and CO2 geochemistry of soil gas across the active fault zones in the capital area of China. Natural Hazards and Earth System Science, 14(10), 2803–2815. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-14-2803-2014
Harrison, J. (2003). Invited editorial: Carcinogenic risk from hot particle exposures-has ICRP got it right? Journal of Radiological Protection, 23(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1088/0952-4746/23/1/002
He, D., Li, D., Wu, X., & Wen, Z. (2009). Basic types and structural characteristics of uplifts: An overview of sedimentary basins in China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(2), 321–346.
Hinkle, M. E. (1994). Environmental conditions affecting concentrations of He, CO2, O2 and N2 in soil-gases. Applied Geochemistry, 9(1), 53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(94)90052-3
Italiano, F., Bonfanti, P., Ditta, M., Petrini, R., & Slejko, F. (2009). Helium and carbon isotopes in the dissolved gases of Friuli Region (NE Italy): Geochemical evidence of CO2 production and degassing over a seismically active area. Chemical Geology, 266(1–2), 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.022
Italiano, F., Martinelli, G., & Plescia, P. (2008). CO2 degassing over seismic areas: The role of mechanochemical production at the study case of central apennines. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 165, 75–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-007-0291-7
Italiano, F., Sasmaz, A., Yuce, G., & Okan, O. O. (2013). Thermal fluids along the east anatolian fault zone (EAFZ): Geochemical features and relationships with the tectonic setting. Chemical Geology, 339, 103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.07.027
Italiano, F., Yuce, G., Uysal, I. T., Gasparon, M., & Morelli, G. (2014). Insights into mantle-type volatiles contribution from the dissolved gases in artesian waters of the Great Artesian Basin, Australia. Chemical Geology, 378–379, 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.04.013
Jia, J. D., He, G. Q., Li, M. S., Zhou, D. H., & Zhang, L. X. (1997). Structural feature of basement in the Ordos basin and its control to Paleozoic gas. Geological Journal of China Universities, 3(2), 144–153. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jung, N. H., Han, W. S., Han, K., & Park, E. (2015). Regional-scale advective, diffusive, and eruptive dynamics of CO2 and brine leakage through faults and wellbores. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(5), 3003–3025. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JB011722
Jung, N. H., Han, W. S., Watson, Z. T., Graham, J. P., & Kim, K. Y. (2014). Fault-controlled CO2 leakage from natural reservoirs in the colorado plateau, east-central Utah. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 403, 358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.07.012
Kämpf, H., Bräuer, K., Schumann, J., Hahne, K., & Strauch, G. (2013). CO2 discharge in an active, non-volcanic continental rift region (czech republic): Characterisation (δ13C, 3He/4He) and quantification of diffuse and vent CO2 emissions. Chemical Geology, 339, 71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.08.005
Kulongoski, J. T., Hilton, D. R., Barry, P. H., Esser, B. K., Hillegonds, D., & Belitz, K. (2013). Volatile fluxes through the Big bend section of the san Andreas fault, California: Helium and carbon-dioxide systematics. Chemical Geology, 339, 92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.09.007
Lehmann, B. E., Lehmann, M., Neftel, A., & Tarakanov, S. V. (2000). Radon-222 monitoring of soil diffusivity. Geophysical Research Letter, 27(23), 3917–3920. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999gl008469
Lewicki, J. L., Hilley, G. E., Dobeck, L., Mcling, T. L., Kennedy, B. M., Bill, M., & Marino, B. D. V. (2013). Geologic CO2 input into groundwater and the atmosphere, soda springs, ID, USA. Chemical Geology, 339, 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.06.013
Li, H., Xu, Z., Niu, Y., Kong, G., Huang, Y., Wang, H., Si, J., Sun, Z., Pei, J., Gong, Z., Chevalier, M. L., & Liu, D. (2014). Structural and physical property characterization in the Wenchuan earthquake Fault Scientific Drilling project - hole 1 (WFSD-1). Tectonophysics, 619–620, 86–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.08.022
Li, J., Zhou, X. C., Shi, H. Y., Sun, F. X., Lu, L. N., Chen, C., Zeng, L. H., & Chen, Z. (2018). Environmental impact of CO2, Rn and Hg emissions from the main faults of northwest region of the Beijing region, China. Environmental Chemistry, 37(5), 931–941. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, R., & Li, Y. (2008). Tectonic evolution of the western margin of the ordos basin (Central China). Russian Geology and Geophysics, 49(1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgg.2007.12.002
Li, Y., Du, J., Wang, X., Zhou, X., Xie, C., & Cui, Y. (2013). Spatial variations of soil gas geochemistry in the Tangshan area of Northern China. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 24(3), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.3319/tao.2012.11.26.01(tt)
Lindqvist, O., Johansson, K., Aastrup, M., Andersson, A., Bringmark, L., Hovsenius, G., Håkansson, L., Iverfeldt, Å., Meili, M., & Timm, B. (1991). Mercury in the Swedish environment - Recent research on causes, consequences and corrective methods. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 55, 1–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542429
Liu, Z. F. (2020). Soil gas geochemistry characteristics in the western margin of the Ordos block, China. Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, China Earthquake Administration, 1–76 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, J., Xie, F., & Lv, Y. (2016). Seismic hazard assessments for the ordos block and its periphery in China. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 84(1), 70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2016.02.007
Liu, Z. F., Li, Y., Chen, Z., Cui, Y. J., Lu, C., Yang, J., & Zhao, Y. X. (2019). Gas emission from active fault zones around the Jilantai faulted depression basin and its implications for fault activities. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 41(5), 613–632. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lombardi, S., & Voltattorni, N. (2010). Rn, He and CO2 soil gas geochemistry for the study of active and inactive faults. Applied Geochemistry, 25(8), 2803–2815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.05.006
Lubin, J. H., Wang, Z. Y., Boice, J. D., Jr., Xu, Z. Y., Blot, W. J., De Wang, L., & Kleinerman, R. A. (2004). Risk of lung cancer and residential radon in China: Pooled results of two studies. International Journal of Cancer, 109(1), 132–137. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.11683
Martinelli, G. (2020). Previous, current, and future trends in research into earthquake precursors in geofluids. Geosciences, 10(189), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10050189
Martinelli, G., & Plescia, P. (2003). Carbon dioxide and methane emissions from calcareous-marly rock under stress: Experimental tests results. Annals of Geophysics, 48, 167–173. https://doi.org/10.4401/ag-3191
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geological Journal, 2(3), 108–118.
Papp, B., Deák, F., Horváth, Á., Kiss, Á., Rajnai, G., & Szabó, C. (2008). A new method for the determination of geophysical parameters by radon concentration measurements in bore-hole. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99(11), 1731–1735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.05.005
Park, S., Bae, J., Nam, B. H., & Yoo, K. Y. (2008). Aetiology of cancer in Asia. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 9(3), 371–380.
Pfanz, H., Yüce, G., Gulbay, A. H., & Gokgoz, A. (2019). Deadly CO2 gases in the Plutonium of Hierapolis (Denizli, Turkey). Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 11(4), 1359–1371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12520-018-0599-5
Phuong, N. K., Harijoko, A., Itoi, R., & Unoki, Y. (2012). Water geochemistry and soil gas survey at Ungaran geothermal field, central Java, Indonesia. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 229, 23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.04.004
Pirrone, N., Cinnirella, S., Feng, X., Finkelman, R. B., Friedli, H., Leaner, J., Mason, R., Mukherjee, A. B., Stracher, G. B., Streets, D. G., & Telmer, K. (2010). Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 5951–5964. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5951-2010
Ring, U., Uysal, I. T., Yüce, G., Ünal-İmer, E., Italiano, F., Imer, A., & Zhao, J. (2016). Recent mantle degassing recorded by carbonic spring deposits along sinistral strike-slip faults, south-central Australia. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 454, 304–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.017
Rizzo, A. L., Uysal, I. T., Mutlu, M., Unal-Imer, E., Dirik, K., Yüce, G., Caracausi, A., Italiano, F., Misseri, M., Temel, A., Bayari, S., Özyurt, N., & Zhao, J. (2019). Geochemistry of fluid inclusions in travertines from Western and Northern Turkey: Inferences on the role of active faults in fluids circulation. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 20(11), 5473–5498. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GC008453
Tao, M. X., Xu, Y. C., Shi, B. G., Jiang, Z. T., Shen, P., Li, X. B., & Sun, M. L. (2005). Characteristics of mantle degassing and deep-seated geological structures in different typical fault zones of China. Science in China, Series D: Earth Sciences, 48(7), 1074–1088.
Tennant, R., Johnston, H. J., & Wells, J. B. (1961). Acute bilateral pneumonitis associated with the inhalation of mercury vapor-report of 5 cases. Connecticut Medicine, 25, 106–109.
The Research Group on “Active Fault System around Ordos Massif”, State Seismological Bureau (SSB). (1988). Active fault system around Ordos massif. Seismological Press, Beijing, 1–335 (in Chinese).
Toutain, J. P., & Baubron, J. C. (1999). Gas geochemistry and seismotectonics: A review. Tectonophysics, 304(1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00295-9
Varley, N. R., & Flowers, A. G. (1993). Radon in soil gas and its relationship with some major faults of SW England. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 15(2–3), 145–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02627832
Walia, V., Yang, T. F., Hong, W. L., Lin, S. J., Fu, C. C., Wen, K. L., & Chen, C. H. (2009). Geochemical variation of soil-gas composition for fault trace and earthquake precursory studies along the Hsincheng fault in NW Taiwan. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 67, 1855–1863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2009.07.004
Wang, X., Li, Y., Du, J., & Zhou, X. (2014). Correlations between radon in soil gas and the activity of seismogenic faults in Tangshan area, North China. Radiation Measurements, 60, 8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2013.11.001
Wang, Y., Wang, M., & Shen, Z. K. (2017). Block-like versus distributed crustal deformation around the northeastern Tibetan plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 140, 31–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.02.040
Wang, Y., Zhang, S., & Yuce, G. (2018). Gas geochemistry: From conventional to unconventional domains. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 89(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.08.023
Wei, Y., & Wang, Y. (2004). Comparison of enrichment patterns of various energy resources in ordos basin. Oil and Gas Geology, 25(4), 385–392. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wesnousky, S. G., Jones, L. M., Scholz, C. H., & Deng, Q. (1984). Historical seismicity and rates of crustal deformation along the margins of the Ordos block, north China. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 74(5), 1767–1783.
Winkler, R., Ruckerbauer, F., & Bunzl, K. (2001). Radon concentration in soil gas: A comparison of the variability resulting from different methods, spatial heterogeneity and seasonal fluctuations. Science of the Total Environment, 272(1), 273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00704-5
Yang, Y., Li, Y., Guan, Z. J., Chen, Z., Zhang, L., Lv, C. J., & Sun, F. X. (2018). Correlations between the radon concentrations in soil gas and the activity of the Anninghe and the Zemuhe faults in Sichuan, southwestern of China. Applied Geochemistry, 89, 23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.11.006
Yıldırım, G., Mutlu, H., Karabacak, V., Uysal, I. T., Dirik, K., Temel, A., Yüce, G., & Zhao, J. X. (2020). Temporal changes in geochemical-isotopic systematics of the late Pleistocene Akkaya travertines (Turkey) - Implications for fluid flow circulation and seismicity. Geochemistry, 80(4), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125630
Yin, A., & Harrison, T. M. (2000). Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28, 211–280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
Yuce, G., Fu, C. C., D’Alessandro, W., Gulbay, A. H., Lai, C. W., Bellomo, S., Yang, T. F., Italiano, F., & Walia, V. (2017). Geochemical characteristics of soil radon and carbon dioxide within the dead sea fault and Karasu fault in the Amik basin (Hatay), Turkey. Chemical Geology, 469, 129–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.01.003
Yuce, G., & Gasparon, M. (2013). Preliminary Risk Assessment of Radon in Groundwater: A case study from Eskisehir. Turkey Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 49(2), 163–179. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2013.739562
Yuce, G., Italiano, F., D’Alessandro, W., Yalcin, T. H., Yasin, D. U., Gulbay, A. H., Ozyurt, N. N., Rojay, B., Karabacak, V., Bellomo, S., Brusca, L., Yang, T., Fu, C. C., Lai, C. W., Ozacar, A., & Walia, V. (2014). Origin and interactions of fluids circulating over the Amik Basin (Hatay-Turkey) and relationships with the hydrologic, geologic and tectonic settings. Chemical Geology, 388, 23–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.09.006
Yuce, G., Ugurluoglu, Y. D., Nadar, N., Yalcin, H. T., Yaltirak, C., Streil, T., & Oeser, V. (2010). Monitoring of earthquake precursors by multi-parameter stations in Eskisehir Region (Turkey). Applied Geochemistry, 25(4), 572–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.01.013
Zhan, Y., Zhao, G., Wang, J., Tang, J., Chen, X., Deng, Q., Xuan, F., & Zhao, J. (2005). Crustal electric structure of Haiyuan arcuate tectonic region in the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang plateau, China. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27(4), 431–440. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang, Y. Q., Shi, W., & Dong, S. (2011). Changes of late Mesozoic tectonic regimes around the Ordos Basin (north China) and their geodynamic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(6), 1254–1276. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng, G., Ma, X., Guo, Z., Hilton, D. R., Xu, W., Liang, S., Fan, Q., & Chen, W. (2017). Gas geochemistry and methane emission from Dushanzi mud volcanoes in the southern Junggar Basin, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 149, 184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.08.023
Zheng, G., Xu, S., Liang, S., Shi, P., & Zhao, J. (2013). Gas emission from the Qingzhu river after the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake, Southwest China. Chemical Geology, 339, 187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.10.032
Zhou, X., Chen, Z., & Cui, Y. (2016). Environmental impact of CO2, Rn, Hg degassing from the rupture zones produced by Wenchuan MS 8.0 earthquake in western Sichuan. China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 38(5), 1067–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9773-1
Zhou, X., Du, J., Chen, Z., Cheng, J., Tang, Y., Yang, L., Xie, C., Cui, Y., Liu, L., Yi, L., Yang, P., & Li, Y. (2010). Geochemistry of soil gas in the seismic fault zone produced by the Wenchuan MS 8.0 earthquake, southwestern China. Geochemical Transactions, 11(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1467-4866-11-5
Zhou, X. C., Sun, F. X., Chen, Z., Lü, C. J., Li, J., Wu, K. T., & Du, J. G. (2017). Degassing of CO2, CH4, Rn and Hg in the rupture zones produced by Wenchuan MS 8.0 earthquake. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(1), 291–303. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Acknowledgements
This study was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2019YFC1509203), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41402298, 42073063), the Basic Science Research Plan of the Institute of Earthquake Science, China Earthquake Administration (Nos. 2020IEF0704, 2019IEF0303).
Funding
The National Key Research and Development Program of China (No.2019YFC1509203), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41402298, 42073063), the Basic Science Research Plan of the Institute of Earthquake Science, China Earthquake Administration (Nos. 2020IEF0704, 2019IEF0303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.L. and Z.C. were involved in conceptualization, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript preparation and verification, and review process; Y.L. was involved in methods elaboration and validation, manuscript verification and corrections, and review process; R.H. was involved in experimental works, data analysis and interpretation, and manuscript preparation; and Z.Z. was involved in methods validation and manuscript verification; Y.Z., L.L. and C.L. were involved in investigation, data acquisition, data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this paper.
Human and animal rights
Not applicable since the manuscript has not been involved the use of any animal or human data or tissue.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Li, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Environmental impacts of 222Rn, Hg and CO2 emissions from the fault zones in the western margin of the Ordos block, China. Environ Geochem Health 45, 457–472 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01350-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01350-5