Abstract
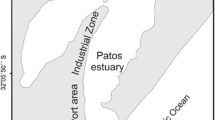
Arsenic concentrations and speciation of 55 mangrove surface sediment samples from the south-eastern coast of NSW, Australia, have been measured. Arsenic concentrations were in the range 1.6–8.6 μg/g dry mass. All arsenic concentration values were well below 20 μg/g, the ANZEC/ARMCANZ interim sediment quality guideline-low trigger value. The bulk sediment pH was 6.0–7.3 and Eh −80 to −260 mV. The sediments contained variable silt–clay (2–30 % w/w), iron (668–12721 μg/g), manganese (1–115 μg/g), sulphur (70–18400 μg/g) and carbon (5–90 mg/g) concentrations. Arsenic concentrations correlated with silt and clay content, iron and manganese concentrations, indicating silt–clay particles covered and coated with iron and manganese (oxy) hydroxides scavenged arsenic. Arsenic extracted with 0.5 M phosphoric acid (68–95 %) was present only as inorganic arsenic (55–91 %), indicating that other arsenic species such as arsenobetaine derived from marine animal tissues rapidly degrade in sediments. The unextractable arsenic was correlated with increases in organic carbon, iron and manganese content. In conclusion, the cycling of arsenic in mangrove sediments is essentially the cycling of inorganic arsenic and primarily controlled by the redox cycling of carbon, sulphur, iron and manganese.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alongi, D.M. (1998). Coastal Ecosystem processes CRC Marine Science Series, 3. In M. J. Kennish and P. L. Lutz (Eds.), CRC Marine Science Series, CRC Press: Boca Raton, USA. ISBN 0-8493-8426-5.
ANZECC and ARMCANZ. (2000). Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh water and marine water quality; Vol. 1, pp. 3.4–5. Sediment Quality Guidelines 2000, Canberra, Australia.
Belzile, N., & Tessier, A. (1990). Interactions between arsenic and iron oxyhydroxides in lacustrine sediments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 103–109.
Bird, F.L. (1994). The effects of bioturbation in Port Phillip Bay. Port Phillip Bay Environmental Study, Technical Report 14, pp. 1–22. CSIRO Institute of Natural Resources and Environment: Melbourne.
Boyle, E. A., Edmond, J. M., & Sholkovitz, E. R. (1977). The mechanism of iron removal in estuaries. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41, 1313–1324.
Bradl, H. B. (2004). Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 277, 1–18.
Brannon, J. M., & Patrick, W. H. (1987). Fixation, transformation and mobilization of arsenic sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 21, 450–459.
Breithaupt, J., Smoak, J. M., Smith, T. J. III., Sanders, C. J., & Hoare, A. (2012). Organic carbon burial rates in mangrove sediments: Strengthening the global budget. Global Biogeochemical Cycles. doi:10.1029/2012GB004375.
Burton, E. D., Sullivan, L. A., Bush, R. T., & Powell, B. (2008). Iron-sulfide and trace element behaviour in sediments of Coombabah Lake, Southern Moreton Bay (Australia). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56, 1353–1376.
Casado-Martinez, M. C., Duncan, E., Smith, B. D., Maher, W. A., & Rainbow, P. S. (2012). Arsenic toxicity in a sediment-dwelling polychaete: Detoxification and arsenic metabolism. Ecotoxicology, 21, 576–590.
Chatterjee, M., Massolo, S., Sarkar, S. K., Bhattacharya, A. K., Bhattacharya, B. D., Satpathy, K. K., & Saha, S. (2009). An assessment of trace element contamination in intertidal sediment cores of Sunderban mangrove wetland, India for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150, 307–322.
Clarke, M. W., McConchie, D., Lewis, D. W., & Saenger, P. (1998). Redox stratification and heavy metal partitioning in Avicennia-dominated mangrove sediments—a geochemical model. Chemical Geology, 149, 147–171.
Coker, V. S., Gault, A. G., Pearce, C. I., Van der Laan, G., Telling, N. D., Charnock, J. M., et al. (2006). XAS and XMCD evidence for species-dependent partitioning of arsenic during microbial reduction of ferrihydrite to magnetite. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 7745–7750.
Deborde, J., Marchand, C., Molnar, N., Della Patrona, L., & Meziane, T. (2015). Concentrations and fractionation of carbon, iron, sulfur, nitrogen and phosphorus in mangrove sediments along an intertidal gradient (Semi-arid climate, New Caledonia). Journal of Marine science and Engineering, 3, 52–72.
Dixit, S., & Hering, J. G. (2003). Comparison of Arsenic (V) and Arsenic (III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 4182–4189.
Du Laing, G., Chapagain, S. K., Dewispelaere, M., Meers, E., Tack, F. M. G., Kazama, F., et al. (2009). Presence and mobility of arsenic in estuarine wetland soils of the Scheldt estuary (Belgium). Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 11, 873–881.
Duncan, E. G., Maher, W. A., & Foster, S. D. (2015). The formation and fate of organoarsenic species in marine ecosystems: Do existing experimental approaches appropriately simulate ecosystem complexity? Environmental Chemistry, 12, 149–162.
Ellwood, M. J., & Maher, W. (2003). Measurement of arsenic species in marine sediments by high-performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Analytical Chimica Acta, 477, 279–291.
Farquhar, M. L., Charnock, J. M., Livens, F. R., & Vaughan, D. J. (2002). Mechanisms of arsenic uptake from aqueous solution by interaction with goethite, lepidocrocite, mackinawite and pyrite: An x-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 1757–1762.
Fauser, P., Sanderson, H., Hedegaard, R. V., Sloth, J. J., Larsen, M. M., Krongaard, T., et al. (2013). Occurrence and sorption properties of arsenicals in marine sediments. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 4679–4691.
Foster, S., & Maher, W. A. (2010). Decomposition of arsenotibosides from marine macroalgae in simulated rock pools. In J. S. Jean, J. Bundschuh, & P. Bhattacharya (Eds.), Arsenic in geosphere and human diseases (pp. 230–232). Boca Raton, USA: CRC Press.
Foster, S., Maher, W., Krikowa, F., & Apte, S. (2007). A microwave-assisted sequential extraction of water and dilute acid soluble arsenic species from marine plant and animal tissues. Talanta, 71, 537–549.
Gibbons, J. D. (1993). Nonparametric statistics—an introduction. In Quantitative Applications in Social Science 07-090 (p. 87). Newbury Park London: Sage Publications.
Guo, T., DeLaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H, Jr. (1997). The influence of sediment redox chemistry on chemically active forms of arsenic, cadmium, chromium and zinc in estuarine sediment. Environment International, 23, 305–316.
Han, X., Li, Y.-L., & Gu, J.-D. (2011). Oxidation of As(III) by MnO2 in the absence and presence of Fe(II) uder acidic conditons. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75, 368–379.
Hanaoka, K., Tagawa, S., & Kaise, T. (1992). The degradation of arsenobetaine to inorganic arsenic by sedimentary microorganisms. Hydrobiologia, 235(236), 623–628.
Handley, K. M., McBeth, J. M., Charnock, J. M., Vaughan, D. J., Wincott, P. L., Polya, D. A., & Lloyd, J. R. (2013). Effect of iron redox transformations on arsenic solid-phase associations in an arsenic-rich, ferruginous hydrothermal sediment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 102, 124–142.
Harbison, P. (1986). Mangrove muds—a sink and source for trace metals. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 17, 246–250.
Hohmann, C., Morin, G., Ona-Nguema, G., Guigner, J.-M., Brown, G. E., & Kappler, A. (2011). Molecular-level modes of As binding to Fe(III) (oxyhydr)oxides precipitated by the anaerobic nitrate-reducing Fe(II)-oxidising Acidovorax sp. Strain BoFeN1. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75, 4699–4712.
Hossain, M., Williams, P. N., Mestrot, A., Norton, G. J., Deacon, C. M., & Merhag, A. A. (2012). Spatial heterogeneity and kinetic regulation of arsenic dynamics in mangrove sediments: The Sundarbans, Bangladesh. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 8645–8652.
Jacks, G., Slejkovec, Z., Morth, M., & Bhattacharya, P. (2013). Redox—cycling of arsenic along the pathways in sulfidic-meta sediment areas in northern Sweden. Applied Geochemistry, 35, 35–43.
Jenkinson, A. V., & McOrist, G. D. (1999). Selenium contamination, redistribution and remobilisation in sediments of Lake Macquarie, NSW. Organic Geochemistry, 30, 1287–1299.
Kirby, J., Maher, W., Chariton, A., & Krikowa, F. (2002). Arsenic concentrations and speciation in a temperate mangrove ecosystem, NSW, Australia. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 16, 192–201.
Kirby, J., Maher, W., Ellwood, M., & Krikowa, F. (2004). Arsenic species determination in biological tissues by HPLC–ICP–MS and HPLC–HG–ICP–MS. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 57, 957–966.
Kostka, J. E., & Luther, G. W, I. I. I. (1994). Partitioning and speciation of solid phase iron in saltmarsh sediments. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta, 58, 1701–1710.
Kristensen, E., Bouillon, S., Dittmar, T., & Marchand, C. (2008). Organic carbon dynamics in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Aquatic Botany, 89, 201–219.
Livesley, S. J., & Andrusiak, S. M. (2012). Temperate mangrove and salt marsh sediments are a small methane and nitrous oxide source but important carbon store. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science, 97, 19–27.
Maher, W. A. (1983). Inorganic arsenic in marine organisms. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 14, 308–310.
Maher, W. A. (1985). Mode of occurrence and speciation of arsenic in some pelagic and estuarine sediments. Chemical Geology, 47, 333–345.
Maher, W., Forstner, S., Krikowa, F., Snitch, P., Chapple, G., & Craig, P. (2001). Measurement of trace metals and phosphorus in marine animal and plant tissues by low volume microwave digestion and ICPMS. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 22, 361–369.
Maher, W. A., Foster, S. D., Taylor, A. M., Krikowa, F., Duncan, E., & Chariton, A. C. (2011). Arsenic distribution and species in two Zostera capricorni seagrass ecosystems, New South Wales, Australia. Environmental Chemistry, 8, 9–18.
Mamindy-Pajany, Y., Hurel, C., Geret, F., Galgani, F., Battaglia-Brunet, F., Marmier, N., & Romeo, M. (2013). Arsenic in marine sediments from French Mediterranean ports; Geochemical partitioning, bioavailability and ecotoxicology. Chemosphere, 90, 2730–2736.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Review, arsenic around the world, a review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Manning, B. A., & Goldberg, S. (1977). Adsorption and stability of arsenic (III) at clay-mineral–water interface. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 2005–2011.
Masscheleyn, P. H., Delaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H. (1991). Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 25, 1414–1419.
Mathijs, S., Tack, J., van Speybroeck, D., & Koedam, N. (1999). Mangrove species zonation and soil redox state, sulphide concentration and salinity in Gazi Bay (Kenya), a preliminary study. Mangroves and Salt Marshes, 3, 243–249.
McCall, P. L., Tevesz, M. J. S. (Eds.). (1982). Chapter 3. The effects of Benthos on physical properties of freshwater sediments. In Animal-sediment relations—the biogenic alteration of sediments. Topics in Geobiology 100 (pp. 105–176). New York: Springer.
McCready, S., Birch, G. F., & Long, E. R. (2006). Metallic and organic contaminants in sediments of Sydney Harbour, Australia and vicinity—a chemical dataset for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environmental International, 32, 455–465.
Meadows, P. S., & Tait, J. (1989). Modification of sediment permeability and shear strength by two burrowing invertebrates. Marine Biology, 101, 75–82.
Moore, J. N., Ficklin, W. H., & Johns, C. (1988). Partitioning of arsenic and metals in reducing sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 22, 432–437.
Morgan, B., Rate, A. W., & Button, E. D. (2012). Trace element reactivity in FeS-rich estuarine sediments: Influence of formation environment and acid sulphate soil drainage. Science of the Total Environment, 438, 463–476.
Munksgaard, N. C., & Parry, D. L. (2002). Metals, arsenic and lead Isotopes in near-pristine estuarine and marine coastal sediments from Northern Australia. Marine and Fresh Water Research, 53, 719–729.
Nath, B., Birch, G., & Chaudhuri, P. (2014). Assessment of sediment quality in Avicennia marina-dominated embayments of sydney estuary: The potential use of pneumatophores (aerial roots) as a bio-indicator of trace metal contamination. Science of the Total Environment, 472, 1010–1022.
Noel, V., Marchand, C., Juillot, F., Ona-Nguema, Mg, Viollier, E., Marakovic, G., et al. (2014). Exafs analysis of iron cycling in mangrove sediments downstream of a lateritized ultramafic watershed (Vavouto Bay, New Caledonia). Geochemical Cosmochimica Acta, 136, 211–228.
Parveen, R., Zahir, E., & Siddiqui, A. F. (2013). Arsenic enrichment in mangroves and sediments along the Karachi coast, Pakistan. Journal of Coastal Life Medicine, 1, 59–64.
Peters, G. M., Maher, W. A., Jolley, D., Carroll, B. I., Gomes, V. G., Jenkinson, A. V., & McOrist, G. D. (1999). Selenium contamination, redistribution and remobilisation in sediments of Lake Macquarie, New South Wales. Organic Geochemistry, 30, 1287–1300.
Preda, M., & Cox, M. E. (2002). Trace metal occurrence and distribution in sediments and mangroves, Pumicestone region, southeast Queensland, Australia. Environment International, 28, 433–449.
Price, A., Maher, W., Kirby, J., Krikowa, F., Duncan, E., Taylor, A., & Potts, J. (2012). Distribution of arsenic species in an open seagrass ecosystem: Relationship to trophic groups, habitats and feeding zones. Environmental Chemistry, 9, 77–88.
Qui, Y.-W., Yu, K.-F., Zhang, G., & Wang, W.-X. (2011). Accumulation and partitioning of seven trace metals in mangroves and sediment cores from three estuarine wetlands of Hainan Island, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190, 631–638.
Redman, A. D., Macalady, D. L., & Ahmann, D. (2002). Natural organic matter affects arsenic speciation and sorption onto hematite. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 2889–2896.
Reimer, K. J., & Thompson, A. J. (1988). Arsenic speciation in marine interstitial water. The occurrence of organoarsenicals. Biogeochemistry, 6, 211–237.
Rhoads, D. C., & Boyer, L. F. (1982). Chapter 1. The effects of marine benthos on physical properties of sediments: A successional perspective. In P. L. McCall & M. J. S. Tevesz (Eds.), Animal-sediment relations (pp. 3–52). New York: Plenum Press.
Root, R. A., Vlassopoulos, D., Rivera, N. A., Rafferty, M. T., Andrews, C., & O’Day, P. A. (2009). Speciation and natural attenuation of arsenic and iron in a tidally influenced shallow aquifer. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73, 5528–5553.
Saalfield, S. L., & Bostick, B. C. (2009). Changes in iron, sulfur and arsenic speciation associated with bacterial sulfate reduction in ferrihydrite-rich systems. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 8787–8793.
Silva, C. A. R., Lacerda, L. D., & Rezende, C. E. (1990). Metals reservoir in a red mangrove forest. Biotropica, 22, 339–345.
Standards Association of Australia (1977). Australian standard 1289. Method of testing soils for engineering purposes. Standards Association of Australia, Standards House, 80 Arthur St North Sydney, N. S. W.
Tam, N. F. Y., & Wong, W. S. (2000). Spatial variation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Hong Kong mangrove swamps. Environmental Pollution, 110, 195–210.
Telford, K., Maher, W., Krikowa, F., & Foster, S. (2008). Measurement of total antimony and antimony species in mine contaminated soils by ICP–MS and HPLC–ICP–MS. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 10, 136–140.
Tufano, K., & Fendorf, S. (2008). Confounding impacts of iron reduction on arsenic retention. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 4777–4783.
Tufano, K., Reyes, C., Saltikov, C. W., & Fendorf, S. (2008). Reductive processes controlling arsenic retention: Revealing the relative importance of iron and arsenic reduction. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 8283–8289.
Tukai, R., Maher, W. A., McNaught, I. J., & Ellwood, M. J. (2002). Occurrence and chemical form of arsenic in marine macroalgae from the east coast of Australia. Marine & Freshwater Research, 53, 1–10.
Wang, X., Wang, J., & Zhang, J. (2012). Comparisons of three methods for organic and inorganic carbon in calcareous soils of Northwestern China. PLoS one, 7, e44334.
Waring, J., Maher, W. A., & Krikowa, F. (2005). Trace metal bioaccumulation in eight common Australian polychaeta. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 8, 1149–1157.
Wasserman, J. C., Figueiredo, A. M. G., Pellegatti, F., & Siva-Filho, E. V. (2001). Elemental composition of sediment cores from a mangrove environment using neutron activation analysis. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 72, 129–146.
Watts, M. J., Barlow, T. S., Button, M., Sarkar, S. K., Bhattacharya, B. D., Aftab Alam, Md, & Gomes, A. (2013). Arsenic speciation in polychaetes (Annelida) and sediments from the intertidal mudflat of Sundarban mangrove wetland, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35, 13–25.
Whaley-Martin, K. J., Koch, I., Moriarty, M., & Reimer, K. J. (2012). Arsenic speciation in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) along a highly contaminated arsenic gradient. Environmental Science and Technology, 46, 3110–3118.
Whaley-Martin, K. J., Koch, I., & Reimer, K. J. (2013). Determination of arsenic species in edible periwinkles (Littorina littorea) by HPLC-ICPMS and XAS along a contaminated gradient. Science of the Total Environment, 456(457), 148–153.
Whalley, C., Rowlatt, S., Bennett, M., & Lovell, D. (1999). Total arsenic in Sediments from the Western North Sea and the Humber Estuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 38, 394–400.
Widerlund, A., & Ingri, J. (1995). Early diagenesis of arsenic in sediments of the Kalix River Estuary, Northern Sweden. Chemical Geology, 1995(125), 185–196.
Xu, W., Wang, H., Liu, R., Zhao, X., & Qu, J. (2011). Arsenic release from arsenic-bearing Fe–Mn binary oxide: Effects of Eh condition. Chemosphere, 83, 1020–1027.
Yoshinaga, M., Cai, Y., & Rosen, B. P. (2011). Demethylation of methylarsonic acid by a microbial community. Environmental Microbiology, 13, 1205–1215.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Endeavour fellowship scheme for support of. S. Hettiarachchi and the Ecochemistry laboratory for funding to carry out this investigation. We are also grateful to P. Ceeney, T. Long, D. Purcell and A. Taylor for assistance with the collection of sediment samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hettiarachchi, S.R., Maher, W.A., Krikowa, F. et al. Factors influencing arsenic concentrations and species in mangrove surface sediments from south-east NSW, Australia. Environ Geochem Health 39, 209–219 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9821-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9821-5