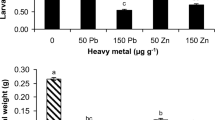
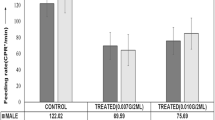
Abstract
Insects are exposed to cadmium stress since cadmium pollution has increasingly become a serious global environmental issue. However, until now few studies have paid attention to the effect of heavy metals on insect reproductive behaviors. In our study, the courtship behaviors, mating behaviors and fecundity of beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) exposed to different concentrations of cadmium in artificial diets at larval stage were studied. The results showed that cadmium stress changed the courtship rhythm by significantly advancing or delaying the courtship starting time. Low dose of cadmium (0.2 mg/kg) increased the courtship frequency in the first two scotophases, but in the fourth phase, the two cadmium treatments reduced the frequency. The total courtship duration was significantly shortened in the first six scotophases except high dose of cadmium treatment (51.2 mg/kg) in the sixth dark phase. Paired adults did not mate after the seventh scotophase under low cadmium exposure, while high cadmium stress made the paired adults just copulate in the first four scotophases. The daily mating rate and total mating rate decreased with the increase in cadmium concentration. The number of eggs of low cadmium treatment was higher than that of control, but the difference was not significant; the number of eggs in high cadmium treatment was lower than that of control and low cadmium treatment. Our results indicate that cadmium exposure can disrupt the courtship rhythm for females and has negative influences on copulation behavior and high cadmium stress can reduce fecundity. Hence, the insect population increase will be affected by heavy metal pollution. Our study will provide scientific reference for environmental risk assessment of heavy metal pollution.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All authors guarantee that all data and materials support our published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Altesor P, Horas VR, Arcia MP, Rossini C, Zarbin PHG, Gonzalez A (2010) Reproductive behaviour of Crocidosema (=Epinotia) aporema (Walsingham) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae): temporal pattern of female calling and mating Neotrop Entomol 39(3):324–329
Babin-Fenske J, Anand M (2011) Patterns of insect communities along a stress gradient following decommissioning of a Cu–Ni smelter. Environ Pollut 159(10):3036–3043
Castrovillo PJ, Cardè RT(1979) Environmental regulation of female calling and male pheromone response periodicities in the codling moth (Laspeyresiapomonella). J Insect Physiol 25(8):659–667
Clark DC, Haynes KF (1992a) Sublethal effects of cypermethrin on chemical communication, courtship, and oviposition in the cabbage looper (Lepidoptera: noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 85(5):1771–1778
Clark DC, Haynes KF (1992b) Sublethal effects of chlordimeform on chemical communication and other reproductive behaviors in the female cabbage looper moth (Lepidoptera: noctuidae). Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 19(2):105–117
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech J (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Ann Rev Entomol 57:81–106
Eeva T, Rainio K, Suominen O (2010) Effects of pollution on land snail abundance, size and diversity as resources for pied flycatcher, Ficedula hypoleuca. Sci Total Environ 408(19):4165–4169
Firebaugh A, Haynes KJ (2016) Experimental tests of light-pollution impacts on nocturnal insect courtship and dispersal. Oecologia 182(4):1203–1211
Floyd JP, Crowder LA (1981) Sublethal effects of permethrin on pheromone response and mating of male pink bollworm moths. J Econ Entomol 74(5):634–638
Gao HH, Zhao HY, Du C, Deng MM, Du EX, Hu ZQ, Hu XS (2012) Life table evaluation of survival and reproduction of the aphid, Sitobion avenae, exposed to cadmium. J Insect Sci 12(44):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.012.4401
Haynes KF, Baker TC (1985) Sublethal effects of permethrin on the chemical communication system of the pink bollworm moth, Pectinophora gossypiella. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 2(3):283–293
Hensbergen PJ, Van Velzen MJ, Nugroho RA, Donker MH, Van Straalen NM (2000) Metallothionein-bound cadmium in the gut of the insect Orchesella cincta (Collembola) in relation to dietary cadmium exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 125(1):17–24
Hossain S, Latifa GA, Prianqa, Ai Nayeem A (2019) Review of cadmium pollution in Bangladesh. J Health Pollut 9(23):190913
Huang D, Kong J, Seng Y (2012) Effects of the heavy metal cu2+ on growth, development, and population dynamics of Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 105(1):288–294.
Huang Y, Wang LY, Wang WJ, Li TQ, He ZL, Yang XE (2019) Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 651:3034–3042
Hunt RE, Haynes KF (1990) Periodicity in the quantity and blend ratios of pheromone components in glands and volatile emissions of mutant and normal cabbage looper moths, Trichoplusia ni. J Insect Physiol 36(10):769–774
Lalouette L, Pottier MA, Wycke MA, Boitard C, Bozzolan F, Maria A, Demondion E, Chertemps T, Lucas P, Renault D, Maibeche M, Siaussat D (2016) Unexpected effects of sublethal doses of insecticide on the peripheral olfactory response and sexual behavior in a pest insect. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(4):3073–3085
Li G, Chen YH, Yang T, Lv GF (2019a) Screening study and edible safety analysis of vegetables in mild cadmium contaminated field. Hubei Agric Sci 58(17):109–112
Li LJ, Liu XM, Duan YH, Guo YP, Cheng B, Guo J, Xi YY, Ma EB (2006) Accumulation of cadmium and copper by female Oxya chinensis (Orthopera: Acridoidea) in soil-plant-insect system. J Enviorn Sci 18(2):341–346
Li P, Pan XW, Ye JZ, Zeng SD, Yang CL (2020) Study on pollution condition of lead and cadmiumn in vegetables in Zhanjiang. Mod Agric Sci Technol 2:213–215
Li XW, Jia XT, Xiang HM, Diao HL, Yan Y, Wang Y, Ma RY (2019b) The effect of photoperiods and light intensity on mating behavior and reproduction of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Environ Entomol 48(5):1035–1041
Ma T, Shi XH, Lin N, Wang ZB, Xiao Q, Sun ZH, Wen XJ (2019) Temporal pattern of adult emergence and sexual behavior of Scopula subpunctaria (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Phytoparasitica 47(1):17–29
Mcbride MB (2002) Cadmium uptake by crops estimated from soil total Cd and pH. Soil Sci 167(1):62–67
Moore RF (1988) Inhibition of chemical communication between male and female bollworms (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) by sublethal amounts of permethrin. J Econ Entomol 81(1):78–82
Navarro-roldan MA, Gemeno C (2017) Sublethal effects of neonicotinoid insecticide on calling behavior and pheromone production of Tortricid moths. J Chem Ecol 43(9):881–890
Oves M, Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahmad E (2012) Soil contamination, nutritive value, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals: an overview. In: Zaidi A., Wani P., Khan M. (eds) Toxicity of Heavy Metals to Legumes and Bioremediation. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-0730-0_1. pp. 1–27.
Owens A, Cochard C, Durrant J, Farnworth B, Perkin E, Seymoure B (2020) Light pollution is a driver of insect declines. Biol Conserv 241:108259
Phelan PL, Baker TC (1990) Comparative study of courtship in twelve phycitine moths (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Insect Behav 3(3):303–326
Płachetka-Bożek A, Kafel A, Augustyniak M (2018) Reproduction and development of Spodoptera exigua from cadmium and control strains under differentiated cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:138–145
Sadowski JA, Grace JL, Moore AJ (2002) Complex courtship behavior in the striped ground cricket, Allonemobius socius (Orthoptera: Gryllidae): does social environment affect male and female behavior? J Insect Behav 15(1):69–84
Sadowski J, Moore A, Brodie E.,III(1999) The evolution of empty nuptial gifts in a dance fly, Empis snoddyi (Diptera: Empididae): bigger isn't always better. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 45:161–166
Stanger-Hall KF, Lloyd JE(2015) Flash signal evolution in Photinus fireflies: Character displacement and signal exploitation in a visual communication system. Evolution 69(3):666–682
Su HH, Hu MM, Tim HS, Yang YZ (2014) Accumulation and excretion of cadmium in three successive generations of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and impact on the population increase. J Econ Entomol 107(1):223–229.
Su HH, Yang Y, Qian YY, Ye ZB, Chen YQ, Yang YZ (2019) Effects of lead stress on Vg expression in the beet armyworm over five successive generations. J Integr Agric 18(1):134–142
Ullah F, Gul H, Desneux N, Tariq K, Ali A, Gao XW, Song DL (2019a) Clothianidin-induced sublethal effects and expression changes of vitellogenin and ecdysone receptors genes in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol Gen 39(2):137–149
Ullah F, Gul H, Desneux N, Qu YY, Xiao X, Khattak AM, Gao XW, Song DL (2019b) Acetamiprid-induced hormetic effects and vitellogenin gene (Vg) expression in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol Gen 39(2):259–270
Wan TL, Liu S, Tang QY, Cheng JA (2014) Heavy metal bioaccumulation and mobility from rice plants to Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae) in China. Environ Entomol 43(3):654–661
Wei BG, Yang LS (2009) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94(2):99–107
Wei HY, Du JW (2004) Sublethal effects of larval treatment with deltamethrin on moth sex pheromone communication system of the Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. Pest Biochem Physiol 80(1):12–20
Yang QQ, Li ZY, Lu XN, Duan QN, Huang L, Bi J (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Yang ZH, Du JW (2003) Effects of sublethal deltamethrin on the chemical communication system and PBAN activity of Asian corn borer,Ostrinia furnacalis (Güenee). J Chem Ecol 29(7):1611–1619
Zhang ZS, Wang QC, Lü XG, Zheng DM, Sun XJ, Zhang XY, Zhang SQ (2009) Heavy metal contents in insects collected from the Huludao city suffering pollution by zinc smelting and cholor-alkai production. Environ Sci 30(7):2077–2081
Zhou HC, Du JW, Huang YP (2005) Effects of sublethal doses of malathion on responses to sex pheromones by male Asian corn borer moths,Ostrinia furnacalis (Guenée). J Chem Ecol 31(7):1645–1656
Zhuang P, Zou HL, Shu WS (2009) Biotransfer of heavy metals along a soil-plant-insect-chicken food chain: field study. J Food Qual 21(6):849–853
Zou JC, Sun Y, Yang Y, Yang YZ, Zhang ZX, Wang SY, Su HH (2017) Cadmium stress significantly affects the flight performance of Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) adults. Acta Entomol Sin 60(9):1021–1030
Zvereva LE(2010) Responses of terrestrial arthropods to air pollution: a meta-analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:297–311
Acknowledgements
We thank Jeannie McDonald (Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Department, Cornell University, NY, USA) very much for her contribution to the manuscript revision.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project, China (2016ZX08012-004-010) and (2019ZX08012-004-010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HS, methodology: ZY, ZZ, YC, formal analysis and investigation: JW, ZY, ZZ, writing—original draft preparation: JW, HS, ZY, ZZ; writing—review and editing: HS, JW, funding acquisition: YY, supervision: YY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to publish
All the authors are in agreement with the publishment.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Wu, J., Zhang, Z. et al. Effects of cadmium stress at different concentrations on the reproductive behaviors of beet armyworm Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Ecotoxicology 30, 402–410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02365-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-021-02365-x