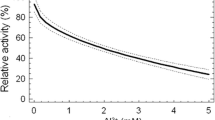
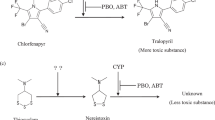
Abstract
The first step in xenobiotic detoxification in aquatic invertebrates is mainly governed by the cytochrome P450 mixed function oxidase system. The ability to measure cytochrome P450 activity provides an important tool to understand macroinvertebrates’ responses to chemical stressors. However, measurements of P450 activity in small aquatic invertebrates have had variable success and a well characterized assay is not yet available. The general lack of success has been scarcely investigated and it is therefore the focus of the present work. In particular, the suitability of the substrate selected for the assay, the sensitivity of the assay and the possible inhibition/attenuation of enzymatic activity caused by endogenous substances were investigated. 7-ethoxycoumarin-O-dealkylation activity of Daphnia magna, Chironomus riparius larvae and Hyalella azteca was assessed in vivo and in vitro and possible inhibition of enzymatic activity by macroinvertebrates homogenate was investigated. Activities of D. magna and C. riparius larvae measured in vivo were 1.37 ± 0.08 and 2.2 ± 0.2 pmol h−1 organism−1, respectively, while activity of H. azteca could not be detected. In vitro activity could be measured in C. riparius larvae only (500–1000 pmol h−1 mg microsomal protein−1). The optimization of the in vitro assay has been especially long and resource consuming and particularly for D. magna, substances that inhibited cytochrome P450 activity seemed to be released during tissue homogenization preventing activity measurements in vitro. We therefore recommend testing the P450 inhibition potential of homogenate preparations prior to any investigation of P450 activity in vitro in macroinvertebrates.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DTT:
-
DL-dithiothreitol
- ECOD:
-
7-ethoxycoumarin-O-dealkylation
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt dihydrate
- EROD:
-
7-ethoxyresorufin-O-dealkylation
- K2HPO4·3H2O:
-
Potassium phosphate dibasic trihydrate
- KH2PO4 :
-
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
- MFO:
-
Mixed function oxidase
- MgCl2·6H2O:
-
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
- NADPH:
-
ß-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2′-phosphate reduced tetrasodium salt hydrate
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
References
Aitio A (1978) A simple and sensitive assay of 7-ethoxycoumarin in deethylation. In: Leonard BJ (ed) Toxicological aspects of food safety, vol 1., Archives of toxicologySpringer, Berlin, p 275. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-66896-8_53
Anand SS, Bruckner JV, Haines WT, Muralidhara S, Fisher JW, Padilla S (2006) Characterization of deltamethrin metabolism by rat plasma and liver microsomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 212:156–166. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2005.07.021
Anderson TD, Zhu KY (2004) Synergistic and antagonistic effects of atrazine on the toxicity of organophosphorodithioate and organophosphorothioate insecticides to Chironomus tentans (Diptera : Chironomidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol 80:54–64. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2004.06.003
Bach J, Snegaroff J (1989) Effects of the fungicide prochloraz on xenobiotic metabolism in Rainbow trout: in vivo induction. Xenobiotica 19:1–9
Baldwin WS, Leblanc GA (1994) Identification of multiple steroid hydroxylases in Daphnia magna and their modulation by xenobiotics. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:1013–1021. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1994)13[1013:iomshi]2.0.co;2
Belden JB, Lydy MJ (2000) Impact of atrazine on organophosphate insecticide toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2266–2274. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2000)019<2266:ioaooi>2.3.co;2
Binelli A, Ricciardi F, Riva C, Provini A (2006) New evidences for old biomarkers: effects of several xenoblotics on EROD and AChE activities in Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Chemosphere 62:510–519. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.06.033
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Brander SM, Werner I, White JW, Deanovic LA (2009) Toxicity of a dissolved pyrethroid mixture to Hyalella azteca at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1493–1499
Brattsten LB, Wilkinson CF (1973) A microsomal enzyme inhibitor in the gut contents of the house cricket (Acheta domesticus). Comp Biochem Phys Part B Comp Biochem 45:59–70. doi:10.1016/0305-0491(73)90284-8
Cedergreen N (2014) Quantifying synergy: a systematic review of mixture toxicity studies within environmental toxicology. PLoS One 9:e96580. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096580
Cedergreen N, Kamper A, Streibig JC (2006) Is prochloraz a potent synergist across aquatic species? A study on bacteria, daphnia, algae and higher plants. Aquat Toxicol 78:243–252. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.03.007
Chalvet-Monfray K, Belzunces LP, Colin ME, Fleche C, Sabatier P (1996) Synergy between deltamethrin and prochloraz in bees: modeling approach. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:525–534. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<0525:sbdapi>2.3.co;2
Daborn P, Boundy S, Yen J, Pittendrigh B, Ffrench-Constant R (2001) DDT resistance in drosophila correlates with Cyp6g1 over-expression and confers cross-resistance to the neonicotinoid imidacloprid. Mol Genet Genomics 266:556–563. doi:10.1007/s004380100531
David RM, Jones HS, Panter GH, Winter MJ, Hutchinson TH, Chipman JK (2012) Interference with xenobiotic metabolic activity by the commonly used vehicle solvents dimethylsulfoxide and methanol in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae but not Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 88:912–917. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.018
EPA (2000) Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates, 2nd edn. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Feyereisen R (1999) Insect P450 enzymes. Annu Rev Entomol 44:507–533. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.44.1.507
Fisher T, Crane M, Callaghan A (2003) Induction of cytochrome P-450 activity in individual Chironomus riparius meigen larvae exposed to xenobiotics. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54:1–6. doi:10.1016/s0147-6513(02)00031-3
Gagnaire B, Geffard O, Noury P, Garric J (2010) In vivo indirect measurement of cytochrome P450-associated activities in freshwater gastropod molluscs. Environ Toxicol 25:545–553. doi:10.1002/tox.20515
Gilbert MD, Wilkinson CF (1975) An inhibitor of microsomal oxidation from gut tissues of the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Comp Biochem Phys Part B Comp Biochem 50:613–619. doi:10.1016/0305-0491(75)90099-1
Glockner R, Muller D (1995) Ethoxycoumarin O-deethylation (ECOD) activity in rat-liver slices exposed to beta-naphthoflavone (BNF) in vitro. Exp Toxicol Pathol 47:319–324
Godin SJ, Crow JA, Scollon EJ, Hughes MF, DeVito MJ, Ross MK (2007) Identification of rat and human cytochrome P450 isoforms and a rat serum esterase that metabolize the pyrethroid insecticides deltamethrin and esfenvalerate. Drug Metab Dispos Biol Fate Chem 35:1664–1671
Gonzalez-Mendoza D (2007) Enzymatic complex cytochrome P450 in plants. Rev Int Contam Ambient 23:177–183
Guengerich FP (2005) Human cytochrome P450 enzymes. In: de Ortiz Montellano P (ed) Cytochrome P450. Springer, New York, pp 377–530. doi:10.1007/0-387-27447-2_10
Hawker DW, Connell DW (1986) Bioconcentration of lipophilic compounds by some aquatic organisms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 11:184–197. doi:10.1016/0147-6513(86)90063-1
James MO (1984) Catalytic properties of cytochrome P-450 in hepatopancreas of the Spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Marine Environ Res 14:1–11. doi:10.1016/0141-1136(84)90066-7
James MO, Boyle SM (1998) Cytochromes P450 in crustacea. Comp Biochem Phys C-Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol. 121:157–172. doi:10.1016/s0742-8413(98)10036-1
Johnson RM, Dahlgren L, Siegfried BD, Ellis MD (2013) Acaricide, fungicide and drug interactions in honey bees (Apis mellifera). PLoS One 8:e54092. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054092
Jones HS, Panter GH, Hutchinson TH, Chipman JK (2010) Oxidative and conjugative xenobiotic metabolism in zebrafish larvae in vivo. Zebrafish 7:23–30. doi:10.1089/zeb.2009.0630
Kelly SL, Kelly DE (2013) Microbial cytochromes P450: biodiversity and biotechnology Where do cytochromes P450 come from, what do they do and what can they do for us? Philosophical Trans R Soc B-Biol Sci 368:17. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0476
Koenig S, Fernandez P, Sole M (2012) Differences in cytochrome P450 enzyme activities between fish and crustacea: relationship with the bioaccumulation patterns of polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs). Aquat Toxicol 108:11–17. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.10.016
Komagata O, Kasai S, Tomita T (2010) Overexpression of cytochrome P450 genes in pyrethroid-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:146–152. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.01.006
Kotze AC (2000) Oxidase activities in macrocyclic-resistant and -susceptible Haemonchus contortus. J Parasitol 86:873–876. doi:10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0873:oaimra]2.0.co;2
Kretschmann A, Ashauer R, Hitzfeld K, Spaak P, Hollender J, Escher BI (2011) Mechanistic toxicodynamic model for receptor-mediated toxicity of diazoxon, the active metabolite of diazinon, in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 45:4980–4987. doi:10.1021/es1042386
Livingstone DR (1998) The fate of organic xenobiotics in aquatic ecosystems: quantitative and qualitative differences in biotransformation by invertebrates and fish. Comp Biochem Phys a-Mol Integr Phys 120:43–49. doi:10.1016/s1095-6433(98)10008-9
Mayer RT, Jermyn JW, Burke MD, Prough RA (1977) Methoxyresorufin as a substrate for fluorometric assay of insect microsomal O-dealkylases. Pestic Biochem Physiol 7:349–354. doi:10.1016/0048-3575(77)90038-4
Mokry LE, Hoagland KD (1990) Acute toxicities of five synthetic pyrethroid insecticides to Daphnia magna and Ceriodaphnia dubia. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1045–1051. doi:10.1002/etc.5620090811
Moon JY, Lee DW, Park KH (1998) Inhibition of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase activity in rat liver microsomes by naturally occurring flavonoids: structure-activity relationships. Xenobiotica 28:117–126. doi:10.1080/004982598239623
Nillos MG, Chajkowski S, Rimoldi JM, Gan J, Lavado R, Schlenk D (2010) Stereoselective biotransformation of permethrin to estrogenic metabolites in fish. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1568–1575. doi:10.1021/tx100167x
Noury P, Geffard O, Tutundjian R, Garric J (2006) Non destructive in vivo measurement of ethoxyresorufin biotransformation by zebrafish prolarva: development and application. Environ Toxicol 21:324–331. doi:10.1002/tox.20184
OECD (2004) Test no. 202: Daphnia sp. Acute immobilisation test. In: OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
OECD (2010) Test no. 233: sediment-water chironomid life-cycle toxicity test using spiked water or spiked sediment. In: OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
OECD (2011) Test no. 235: Chironomus sp., acute immobilisation test. In: OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
OECD (2012) Test no. 211: Daphnia magna reproduction test. In: OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals, section 2: effects on biotic systems. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Ong CE, Pan Y, Mak JW, Ismail R (2013) In vitro approaches to investigate cytochrome P450 activities: update on current status and their applicability. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 9:1097–1113. doi:10.1517/17425255.2013.800482
Orrenius S, Berggren M, Moldeus P, Krieger RI (1971) Mechanism of inhibition of microsomal mixed-function oxidation by gut-contents inhibitor of southern armyworm (Prodenia-eridania). Biochem J 124:427–430
Pilling ED, Bromleychallenor KAC, Walker CH, Jepson PC (1995) Mechanism of synergism between the pyrethroid insecticide lambda-cyhalothrin and the imidazole fungicide prochloraz, in the honeybee (Apis-mellifera L.). Pestic Biochem Physiol 51:1–11. doi:10.1006/pest.1995.1001
Rewitz KF, Styrishave B, Lobner-Olesen A, Andersen O (2006) Marine invertebrate cytochrome P450: emerging insights from vertebrate and insect analogies. Comp Biochem Phys C-Toxicol Pharmacol 143:363–381. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.04.001
Routti H, Letcher RJ, Arukwe A, van Bavel B, Yoccoz NG, Chu SG, Gabrielsen GW (2008) Biotransformation of PCBs in relation to phase I and II xenobiotic-metabolizing enzyme activities in ringed seals (Phoca hispida) from Svalbard and the Baltic sea. Environ Sci Technol 42:8952–8958. doi:10.1021/es801682f
Rubach MN, Ashauer R, Maund SJ, Baird DJ, Van den Brink PJ (2010) Toxicokinetic variation in 15 freshwater arthropod species exposed to the insecticide chlorpyrifos. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:2225–2234. doi:10.1002/etc.273
Sigma-Aldrich (2013) Bradford Reagent : Technical bulletin. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Sigma/Bulletin/b6916bul.pdf
Snyder MJ (2000) Cytochrome P450 enzymes in aquatic invertebrates: recent advances and future directions. Aquat Toxicol 48:529–547. doi:10.1016/s0166-445x(00)00085-0
Stevenson BJ et al (2011) Cytochrome P450 6M2 from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae metabolizes pyrethroids: sequential metabolism of deltamethrin revealed. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:492–502. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2011.02.003
Sturm A, Hansen PD (1999) Altered cholinesterase and monooxygenase levels in Daphnia magna and Chironomus riparius exposed to environmental pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 42:9–15. doi:10.1006/eesa.1998.1721
Tian SM, Pan LQ, Zhang H (2014) Identification of a CYP3A-like gene and CYPs mRNA expression modulation following exposure to benzo a pyrene in the bivalve mollusk Chlamys farreri. Marine Environ Res 94:7–15. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.11.001
Timbrell JA (2008) Factors affecting toxic responses: metabolism. In: Principles of biochemical toxicology, 4th edn. CRC Press, pp 75–127. doi:10.3109/9781420007084-5
Uno T, Ishizuka M, Itakura T (2012) Cytochrome P450 (CYP) in fish. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34:1–13. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2012.02.004
Valles SM, Yu SJ (1996) German cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae) gut contents inhibit cytochrome P450 monooxygenases. J Econ Entomol 89:1508–1512
Vanderweiden MEJ, Tibosch HJH, Bleumink R, Sinnige TL, Vandeguchte C, Seinen W, Vandenberg M (1993) Cytochrome P450 1a induction in the Common carp (Cyprinus carpio) following exposure to contaminated sediments with halogenated polyaromatics. Chemosphere 27:1297–1309. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(93)90177-7
Venkatakrishnan K, von Moltke LL, Greenblatt DJ (2000) Effects of the antifungal agents on oxidative drug metabolism: clinical relevance. Clin Pharmacokinet 38:111–180. doi:10.2165/00003088-200038020-00002
Waxman DJ, Chang TK (2006) Use of 7-ethoxycoumarin to monitor multiple enzymes in the human CYP1, CYP2, and CYP3 families. Methods Mol Biol 320:153–156. doi:10.1385/1-59259-998-2:153
Weston DP, Poynton HC, Wellborn GA, Lydy MJ, Blalock BJ, Sepulveda MS, Colbourne JK (2013) Multiple origins of pyrethroid insecticide resistance across the species complex of a nontarget aquatic crustacean Hyalella azteca. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:16532–16537. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302023110
Yang Y, Chen S, Wu S, Yue L, Wu Y (2006) Constitutive overexpression of multiple cytochrome P450 genes associated with pyrethroid resistance in Helicoverpa armigera. J Econ Entomol 99:1784–1789
Zelnickova L et al (2013) Biochemical markers for the assessment of pollution of selected small streams in the Czech Republic. Neuroendocrinol Lett 34:109–115
Zhang M, Scott JG (1996) Cytochrome b5 is essential for cytochrome P450 6D1-mediated cypermethrin resistance in LPR House flies. Pestic Biochem Physiol 55:150–156
Acknowledgments
The authors thank laboratory technician Anja Weibell for taking good care of the organisms’ cultures and Post Doc Tomas Laursen for his suggestions on the cytochrome P450 in vitro assay as well as for solving practical issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gottardi, M., Kretschmann, A. & Cedergreen, N. Measuring cytochrome P450 activity in aquatic invertebrates: a critical evaluation of in vitro and in vivo methods. Ecotoxicology 25, 419–430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1600-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1600-z