Abstract
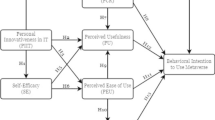
Although mobile learning systems offer several benefits for students, academic staff and universities, from easily access and learning anywhere and anytime, the use and acceptance of this new technology in Jordan still very low. However, acceptance of mobile learning by students is crucial to the success of mobile learning. The factors that affect the use and user acceptance of mobile learning are still controversial. Thus, this study mainly proposes an integrated model, with the aim of identifying the most influential factors that may encourage or impede students and universities in Jordan in moving towards acceptance and adoption of mobile learning applications. The proposed model was evaluated empirically with 1200 students from both two groups of universities that already used the mobile learning technology and non-adopters universities in Jordan. The model aims to examine the impact of 11 factors on the adoption of mobile learning applications that were categorised based on four fundamental constructs are: (i) technological factors (security, privacy, compatibility, relative advantage and trust), (ii) organizational factors (resistance to change and technology readiness), (iii) cultural factors and (iv) quality factors (quality of system, quality of content and quality of service). The key findings include: (1) resistance to change, security and privacy concerns still limit mobile learning acceptance and adoption in Jordanian universities; (2) some factors like compatibility, technology readiness, and culture were found to have a negative effect on the intention to use of the mobile learning; (3) five factors (relative advantage, trust, quality of system, quality of content and quality of service) were found to have a positive effect on the intention to use of the mobile learning; and (4) our research also found that the effect of these factors differed in universities that already used the mobile learning and non-adopters. Finally, it is expected that the findings of this research can assist university decision makers, mobile learning application providers and the research community in introducing better strategies for encouraging adoption and acceptance of this technology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Al-Aish, A., & Love, S. (2013). Factors influencing students’ acceptance of m-learning: an investigation in higher education. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 14(5).
Almaiah, M. A. (2018). Acceptance and usage of a mobile information system services in University of Jordan. Education and Information Technologies, 1–23.
Almaiah, M.A., & Alamri, M.M (2018). Proposing a new technical quality requirements for mobile learning applications. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 96(19).
Almaiah, M. A., & Alismaiel, O. A. (2018). Examination of factors influencing the use of mobile learning system: An empirical study. Education and Information Technologies, 1–25.
Almaiah, M. A., & Almulhem, A (2018). A conceptual framework for determining the success factors of e-learning system implementation using Delphi technique. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 96(17).
Almaiah, M. A., & Jalil, M. A. (2014). Investigating students' perceptions on mobile learning services. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies (iJIM), 8(4), 31–36.
Almaiah, M. A., & Man, M. (2016). Empirical investigation to explore factors that achieve high quality of mobile learning system based on students’ perspectives. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 19(3), 1314–1320.
Almaiah, M. A., Jalil, M. A., & Man, M. (2016a). Extending the TAM to examine the effects of quality features on mobile learning acceptance. Journal of Computers in Education, 3(4), 453–485.
Almaiah, M. A., Jalil, M. A., & Man, M. (2016b). Preliminary study for exploring the major problems and activities of mobile learning system: A case study of Jordan. Journal of Theoretical & Applied Information Technology, 93(2).
Almaiah, M. A., Jalil, M. A., & Man, M. (2016). Extending the TAM to examine the effects of quality features on mobile learning acceptance. Journal of Computers in Education, 3(4), 453–485.
Almarashdeh, I. A., Sahari, N., Zin, N. A. M., & Alsmadi, M. (2010). The success of learning management system among distance learners in Malaysian Universities. Journal of Theoretical & Applied Information Technology, 21(2).
Althunibat, A. (2015). Determining the factors influencing students’ intention to use m-learning in Jordan higher education. Computers in Human Behavior, 52, 65–71.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179–211.
Bagozzi, R. P., & Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the academy of marketing science, 16(1), 74–94.
Balakrishnan, V., & Gan, C. L. (2016). Students’ learning styles and their effects on the use of social media technology for learning. Telematics and Informatics, 33(3), 808–821.
Behera, S. K. (2013). E-and M-learning: A comparative study. International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their Implications, 4(3), 65–78.
Bentler, P. M., & Bonett, D. G. (1980). Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures. Psychological Bulletin, 88(3), 588.
Bere, A., & Rambe, P. (2016). An empirical analysis of the determinants of mobile instant messaging appropriation in university learning. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28(2), 172–198.
Buchanan, T., Sainter, P., & Saunders, G. (2013). Factors affecting faculty use of learning technologies: Implications for models of technology adoption. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 25(1), 1–11.
Chen, X., & Zhang, X. (2016). How environmental uncertainty moderates the effect of relative advantage and perceived credibility on the adoption of Mobile health services by Chinese organizations in the big data era. International Journal of Telemedicine and Applications, 2016, 1–11.
Cheng, Y. M. (2012). Effects of quality antecedents on e-learning acceptance. Internet Research, 22(3), 361–390.
Cheon, J., Lee, S., Crooks, S. M., & Song, J. (2012). An investigation of mobile learning readiness in higher education based on the theory of planned behavior. Computers & Education, 59(3), 1054–1064.
Chung, H. H., Chen, S. C., & Kuo, M. H. (2015). A study of EFL college students’ acceptance of mobile learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 176, 333–339.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13, 319–340.
Delone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: a ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9840-1.
Dobre, I. (2015). Learning Management Systems for higher education-an overview of available options for Higher Education Organizations. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 180, 313–320.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Wastell, D., Laumer, S., Henriksen, H. Z., Myers, M. D., Bunker, D., et al. (2015). Research on information systems failures and successes: Status update and future directions. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(1), 143–157.
Fishbein, M., & Ajzen, I. (1975). Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: An introduction to theory and research. Philosophy and Rhetoric, 10(2), 130–132.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Journal of marketing research, 382–388.
Gao, T., Sultan, F., & Rohm, A. J. (2010). Factors influencing Chinese youth consumers' acceptance of mobile marketing. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 27(7), 574–583.
Gu, J. C., Lee, S. C., & Suh, Y. H. (2009). Determinants of behavioral intention to mobile banking. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(9), 11605–11616.
Guo, X., Sun, Y., Wang, N., Peng, Z., & Yan, Z. (2013). The dark side of elderly acceptance of preventive mobile health services in China. Electronic Markets, 23(1), 49–61.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long Range Planning, 46(1-2), 1–12.
Hao, S., Dennen, V. P., & Mei, L. (2017). Influential factors for mobile learning acceptance among Chinese users. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65(1), 101–123.
Hirschheim, R., & Newman, M. (1988). Information systems and user resistance: theory and practice. The Computer Journal, 31(5), 398–408.
Hsia, J. W. (2016). The effects of locus of control on university students’ mobile learning adoption. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28(1), 1–17.
Hsu, C. L., Lu, H. P., & Hsu, H. H. (2007). Adoption of the mobile internet: An empirical study of multimedia message service (MMS). Omega, 35(6), 715–726.
Hyman, J. A., Moser, M. T., & Segala, L. N. (2014). Electronic reading and digital library technologies: Understanding learner expectation and usage intent for mobile learning. Educational Technology Research and Development, 62(1), 35–52.
Iqbal, S., & Qureshi, I. A. (2012). M-learning adoption: A perspective from a developing country. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed. Learning, 13(3), 147–164.
Jaradat, M. I. R. M. (2014). Understanding individuals' perceptions, determinants and the moderating effects of age and gender on the adoption of mobile learning: developing country perspective. International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation, 8(3-4), 253–275.
Joo, Y. J., Lee, H. W., & Ham, Y. (2014). Integrating user interface and personal innovativeness into the TAM for mobile learning in Cyber University. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 26(2), 143–158.
Joo, Y. J., Kim, N., & Kim, N. H. (2016). Factors predicting online university students’ use of a mobile learning management system (m-LMS). Educational Technology Research and Development, 64(4), 611–630.
Keengwe, J., & Bhargava, M. (2014). Mobile learning and integration of mobile technologies in education. Education and Information Technologies, 19(4), 737–746.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Methodology in the social sciences.
Kline, R. B. (2011). Convergence of structural equation modeling and multilevel modeling. na.
Lai, C. L., Hwang, G. J., Liang, J. C., & Tsai, C. C. (2016). Differences between mobile learning environmental preferences of high school teachers and students in Taiwan: A structural equation model analysis. Educational Technology Research and Development, 64(3), 533–554.
Laumer, S., Maier, C., Eckhardt, A., & Weitzel, T. (2016a). Work routines as an object of resistance during information systems implementations: Theoretical foundation and empirical evidence. European Journal of Information Systems, 25(4), 317–343.
Laumer, S., Maier, C., Eckhardt, A., & Weitzel, T. (2016b). User personality and resistance to mandatory information systems in organizations: A theoretical model and empirical test of dispositional resistance to change. Journal of Information Technology, 31(1), 67–82.
Leung, K., Bhagat, R. S., Buchan, N. R., Erez, M., & Gibson, C. B. (2005). Culture and international business: Recent advances and their implications for future research. Journal of international business studies, 36(4), 357–378.
Lian, J. W., Yen, D. C., & Wang, Y. T. (2014). An exploratory study to understand the critical factors affecting the decision to adopt cloud computing in Taiwan hospital. International Journal of Information Management, 34(1), 28–36.
Lin, K. Y., & Lu, H. P. (2011). Why people use social networking sites: An empirical study integrating network externalities and motivation theory. Computers in human behavior, 27(3), 1152–1161.
Liew, T. W., Tan, S. M., & Ismail, H. (2017). Exploring the effects of a non-interactive talking avatar on social presence, credibility, trust, and patronage intention in an e-commerce website. Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences, 7(1), 42.
Liu, Y., Li, H., & Carlsson, C. (2010). Factors driving the adoption of m-learning: An empirical study. Computers & Education, 55(3), 1211–1219.
MacCallum, R. C., & Austin, J. T. (2000). Applications of structural equation modeling in psychological research. Annual review of psychology, 51(1), 201–226.
Martin, F., & Ertzberger, J. (2013). Here and now mobile learning: An experimental study on the use of mobile technology. Computers & Education, 68, 76–85.
Mohammadi, H. (2015). Investigating users’ perspectives on e-learning: An integration of TAM and IS success model. Computers in Human Behavior, 45, 359–374.
Nov, O., & Ye, C. (2009). Resistance to change and the adoption of digital libraries: An integrative model. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 60(8), 1702–1708.
Obiria, P. B., & Kimwele, M. W. (2017). A location-based privacy-preserving m-learning model to enhance distance education in Kenya. Journal of Computers in Education, 4(2), 147–169.
Ozdamli, F., & Cavus, N. (2011). Basic elements and characteristics of mobile learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28, 937–942.
Ozkan, S., & Koseler, R. (2009). Multi-dimensional students’ evaluation of e-learning systems in the higher education context: An empirical investigation. Computers & Education, 53(4), 1285–1296.
Ozturk, T., & Guven, B. (2016). Evaluating Students' Beliefs in Problem Solving Process: A Case Study. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science & Technology Education, 12(3), 411–429.
Park, S. Y., Nam, M. W., & Cha, S. B. (2012). University students' behavioral intention to use mobile learning: Evaluating the technology acceptance model. British Journal of Educational Technology, 43(4), 592–605.
Park, E., & Kim, K. J. (2014). An integrated adoption model of mobile cloud services: exploration of key determinants and extension of technology acceptance model. Telematics and Informatics, 31(3), 376–385.
Park, S. Y., Lee, H. D., & Kim, S. Y. (2016). South Korean university students’ mobile learning acceptance and experience based on the perceived attributes, system quality and resistance. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 1–9.
Park, E., Kim, S., Kim, Y., & Kwon, S. J. (2017). Smart home services as the next mainstream of the ICT industry: Determinants of the adoption of smart home services. Universal Access in the Information Society, 1–16.
Ramzan, K., Taibah, K., Tahir, A. I., Al-Tassan, N., Berhan, A., Khater, A. M., et al. (2014). ILDR1: Novel mutation and a rare cause of congenital deafness in the Saudi Arabian population. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 57(6), 253–258.
Rehman, M., Esichaikul, V., & Kamal, M. (2012). Factors influencing e-government adoption in Pakistan. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 6(3), 258–282.
Rogers, E. M. (1995). Lessons for guidelines from the diffusion of innovations. Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety, 21(7), 324–328.
Rubin, H. J., & Rubin, I. S. (2011). Qualitative interviewing: The art of hearing data. Newcastle upon Tyne: Sage.
Safa, N. S., Von Solms, R., & Furnell, S. (2016). Information security policy compliance model in organizations. Computers & Security, 56, 70–82.
Sánchez-Prieto, J. C., Olmos-Migueláñez, S., & García-Peñalvo, F. J. (2016). Informal tools in formal contexts: Development of a model to assess the acceptance of mobile technologies among teachers. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 519–528.
Sarrab, M., Al-Shih, H., & Rehman, O. M. H. (2013). Exploring major challenges and benefits of mlearning adoption. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 3(4), 826.
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2009). Research methods for business students. London: Pearson Education.
Sharples, M., Taylor, J., & Vavoula, G. (2010). A theory of learning for the mobile age. In Medienbildung in neuen Kulturräumen (pp. 87–99). VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften.
Shin, C., Hong, J. H., & Dey, A. K. (2012). Understanding and prediction of mobile application usage for smart phones. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing (pp. 173-182). ACM.
Shin, W. S., & Kang, M. (2015). The use of a mobile learning management system at an online university and its effect on learning satisfaction and achievement. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 16(3).
Siponen, M., Mahmood, M. A., & Pahnila, S. (2014). Employees’ adherence to information security policies: An exploratory field study. Information & management, 51(2), 217–224.
Song, Y., & Kong, S. C. (2017). Affordances and constraints of BYOD (bring your own device) for learning in higher education: Teachers’ perspectives. In Emerging practices in scholarship of learning and teaching in a digital era (pp. 105–122). Singapore: Springer.
Su, C. H., & Cheng, C. H. (2015). A mobile gamification learning system for improving the learning motivation and achievements. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 31(3), 268–286.
Thomas, T. D., Singh, L., & Gaffar, K. (2013). The utility of the UTAUT model in explaining mobile learning adoption in higher education in Guyana. International Journal of Education and Development using Information and Communication Technology, 9(3), 71.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27, 425–478.
Wang, Y. S., Wu, M. C., & Wang, H. Y. (2009). Investigating the determinants and age and gender differences in the acceptance of mobile learning. British Journal of Educational Technology, 40(1), 92–118.
Widaman, K. F., & Thompson, J. S. (2003). On specifying the null model for incremental fit indices in structural equation modeling. Psychological Methods, 8(1), 16.
Yamakawa, P., Delgado, C., Díaz, E., Garayar, E., & Laguna, H. (2013). Factors influencing the use of mobile technologies in a university environment: A case from Latin America. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Education (IJICTE), 9(2), 24–38.
Zarmpou, T., Saprikis, V., Markos, A., & Vlachopoulou, M. (2012). Modeling users’ acceptance of mobile services. Electronic Commerce Research, 12(2), 225–248.
Zhou, T. (2014). Examining continuance usage of mobile internet services from the perspective of resistance to change. Information Development, 30(1), 22–31.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Faisal University for the financial support with number 186014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almaiah, M.A., Al Mulhem, A. Analysis of the essential factors affecting of intention to use of mobile learning applications: A comparison between universities adopters and non-adopters. Educ Inf Technol 24, 1433–1468 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9840-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-018-9840-1