Abstract
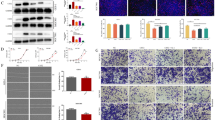
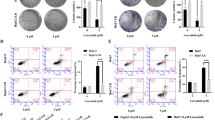
PRPF19 seems to play either tumor-promoting or anti-tumor roles depending on cancer types. This study aimed to clarify the potential role and mechanism of PRPF19 in bladder cancer. PRPF19 expression and its correlation with patients’ overall survival were analyzed in bladder cancer. The effects of PRPF19 on the viability, apoptosis, DNA damage repair, and gemcitabine sensitivity in human bladder cancer cells (T24 and 5637) were analyzed through loss- or gain-of-function methods. Moreover, the influences of DDB1 small interfering RNA on these indexes were evaluated in bladder cancer cells. At last, rescue experiment using DDB1 overexpression was carried out to confirm whether PRPF19 functioned via regulating DDB1. PRPF19 was highly expressed in bladder cancer tissues and cells. Elevated PRPF19 expression was related to shorter overall survival of bladder cancer patients. Downregulation of PRPF19 inhibited cell proliferation, promoted cell apoptosis, increased the number of γ-H2AX-positive cells, and reduced the mRNA and protein levels of DDB1 and BRCA1. Meanwhile, knockdown of PRPF19 decreased the IC50 of gemcitabine and promoted gemcitabine-induced cell apoptosis. Whereas, PRPF19 overexpression significantly decreased gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. DDB1 downregulation suppressed cell proliferation and BRCA1 expression, but elevated the number of γ-H2AX-positive cells and gemcitabine sensitivity. Upregulation of DDB1 attenuated γ-H2AX-positive cell number, BRCA1 expression and IC50 of gemcitabine that were affected by PRPF19 silencing. In conclusion, PRPF19 expression was upregulated in bladder cancer. It promoted cell growth and DNA damage repair, and decreased gemcitabine sensitivity via positively regulating DDB1 expression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Shanmugam I, Bsaili M, Hromas R, Shaheen M (2014) The role of the human psoralen 4 (hPso4) protein complex in replication stress and homologous recombination. J Biol Chem 289:14009–14019
Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Comperat EM, Dominguez Escrig JL et al (2022) European association of urology guidelines on non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (Ta, T1, and carcinoma in situ). Eur Urol 81:75–94
Benjamin AB, Zhou X, Isaac O, Zhao H, Song Y, Chi X et al (2014) PRP19 upregulation inhibits cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinomas by p21-mediated induction of cell cycle arrest. Biomed Pharmacother 68:463–470
Chanarat S, Strasser K (2013) Splicing and beyond: the many faces of the Prp19 complex. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:2126–2134
Dariane C, Timsit MO (2022) DNA-damage-repair gene alterations in genitourinary malignancies. Eur Surg Res 63:155–164
de Moura TR, Mozaffari-Jovin S, Szabo CZK, Schmitzova J, Dybkov O, Cretu C et al (2018) Prp19/Pso4 is an autoinhibited ubiquitin ligase activated by stepwise assembly of three splicing factors. Mol Cell 69:979–992
Font A, Taron M, Gago JL, Costa C, Sanchez JJ, Carrato C et al (2011) BRCA1 mRNA expression and outcome to neoadjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in bladder cancer. Ann Oncol 22:139–144
Gao X, Liu J, Fan D, Li X, Fang Z, Yan K et al (2022) Berberine enhances gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity in bladder cancer by downregulating Rad51 expression through inactivating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol Rep 47:33
He Y, Huang C, Cai K, Liu P, Chen X, Xu YI et al (2021) PRPF19 promotes tongue cancer growth and chemoradiotherapy resistance. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53:893–902
Iovine B, Iannella ML, Bevilacqua MA (2011) Damage-specific DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1): a protein with a wide range of functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1664–1667
Khan A, Dellago H, Terlecki-Zaniewicz L, Karbiener M, Weilner S, Hildner F et al (2017) SNEV(hPrp19/hPso4) regulates adipogenesis of human adipose stromal cells. Stem Cell Rep 8:21–29
Li X, Heyer WD (2008) Homologous recombination in DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance. Cell Res 18:99–113
Lord CJ, Ashworth A (2012) The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature 481:287–294
Lu JL, Xia QD, Lu YH, Liu Z, Zhou P, Hu HL et al (2020) Efficacy of intravesical therapies on the prevention of recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancer Med 9:7800–7809
Mahajan K (2016) hPso4/hPrp19: a critical component of DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint complexes. Oncogene 35:2279–2286
Mahajan KN, Mitchell BS (2003) Role of human Pso4 in mammalian DNA repair and association with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10746–10751
Man X, Piao C, Lin X, Kong C, Cui X, Jiang Y (2019) USP13 functions as a tumor suppressor by blocking the NF-kB-mediated PTEN downregulation in human bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR 38:259
Marechal A, Li JM, Ji XY, Wu CS, Yazinski SA, Nguyen HD et al (2014) PRP19 transforms into a sensor of RPA-ssDNA after DNA damage and drives ATR activation via a ubiquitin-mediated circuitry. Mol Cell 53:235–246
Mehlich D, Lomiak M, Sobiborowicz A, Mazan A, Dymerska D, Szewczyk LM et al (2021) MLK4 regulates DNA damage response and promotes triple-negative breast cancer chemoresistance. Cell Death Dis 12:1111
Meng Y, Qiu L, Zeng X, Hu X, Zhang Y, Wan X et al (2022) Targeting CRL4 suppresses chemoresistant ovarian cancer growth by inducing mitophagy. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:388
Messing EM, Tangen CM, Lerner SP, Sahasrabudhe DM, Koppie TM, Wood DP Jr et al (2018) Effect of intravesical instillation of gemcitabine vs saline immediately following resection of suspected low-grade non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer on tumor recurrence: SWOG S0337 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 319:1880–1888
Mullane SA, Werner L, Guancial EA, Lis RT, Stack EC, Loda M et al (2016) Expression levels of DNA damage repair proteins are associated with overall survival in platinum-treated advanced urothelial carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 14:352–359
Mun JY, Baek SW, Park WY, Kim WT, Kim SK, Roh YG et al (2020) E2F1 promotes progression of bladder cancer by modulating RAD54L involved in homologous recombination repair. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239025
Ohi MD, Vander Kooi CW, Rosenberg JA, Ren L, Hirsch JP, Chazin WJ et al (2005) Structural and functional analysis of essential pre-mRNA splicing factor Prp19p. Mol Cell Biol 25:451–460
Prasanna T, Craft P, Balasingam G, Haxhimolla H, Pranavan G (2017) Intravesical gemcitabine versus intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin for the treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: an evaluation of efficacy and toxicity. Front Oncol 7:260
Qiu D, Hu J, Hu J, Yu A, Othmane B, He T et al (2021) PMEPA1 is a prognostic biomarker that correlates with cell malignancy and the tumor Microenvironment in bladder cancer. Front Immunol 12:705086
Sharma A, Singh K, Almasan A (2012) Histone H2AX phosphorylation: a marker for DNA damage. Methods Mol Biol 920:613–626
Sun S, Jiang K, Zeng J (2022) Differential expression of DNA damage repair genes after chemoradiotherapy and inhibition rate in different bladder cancer cells. Transl Androl Urol 11:1336–1344
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin 71:209–249
Teoh JY, Huang J, Ko WY, Lok V, Choi P, Ng CF et al (2020) Global trends of bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and their associations with tobacco use and gross domestic product per capita. Eur Urol 78:893–906
Wang SC (2014) PCNA: a silent housekeeper or a potential therapeutic target? Trends Pharmacol Sci 35:178–186
Wang JYJ (2019) Cell death response to DNA damage. Yale J Biol Med 92:771–779
Wojtuszkiewicz A, Assaraf YG, Maas MJ, Kaspers GJ, Jansen G, Cloos J (2015) Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer: the relevance in oncogenesis, treatment and drug resistance. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 11:673–689
Xie R, Chen X, Cheng L, Huang M, Zhou Q, Zhang J et al (2021) NONO inhibits lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer via alternative splicing of SETMAR. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther 29:291–307
Xiong Y, Ju L, Yuan L, Chen L, Wang G, Xu H et al (2021) KNSTRN promotes tumorigenesis and gemcitabine resistance by activating AKT in bladder cancer. Oncogene 40:1595–1608
Yano K, Takahashi RU, Shiotani B, Abe J, Shidooka T, Sudo Y et al (2021) PRPF19 regulates p53-dependent cellular senescence by modulating alternative splicing of MDM4 mRNA. J Biol Chem 297:100882
Yin J, Zhu JM, Shen XZ (2012) New insights into pre-mRNA processing factor 19: a multi-faceted protein in humans. Biol Cell 104:695–705
Yin J, Wang L, Zhu JM, Yu Q, Xue RY, Fang Y et al (2016) Prp19 facilitates invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/twist1 pathway. Oncotarget 7:21939–21951
Yin M, Grivas P, Wang QE, Mortazavi A, Emamekhoo H, Holder SL et al (2020) Prognostic value of DNA damage response genomic alterations in relapsed/advanced urothelial cancer. Oncologist 25:680–688
Yu XN, Zhang GC, Liu HN, Zhu JM, Liu TT, Song GQ et al (2022) Pre-mRNA processing factor 19 functions in DNA damage repair and radioresistance by modulating cyclin D1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 27:390–403
Zhai X, Kong N, Wang C, Qin W, Dong S, Zhai H et al (2023) PRPF19 limits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication through targeting and degrading viral capsid protein. J Virol 97:e0161422
Zhang Y, Lei Y, Xu J, Hua J, Zhang B, Liu J et al (2019) Role of damage DNA-binding protein 1 in pancreatic cancer progression and chemoresistance. Cancers 11:1998
Zhou W, Xu Y, Zhang J, Zhang P, Yao Z, Yan Z et al (2022) MiRNA-363-3p/DUSP10/JNK axis mediates chemoresistance by enhancing DNA damage repair in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 36:1861–1869
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JY and SG designed the study, conducted the experiments, collected and analyzed the data. JY wrote the original manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they all have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10616_2023_599_MOESM1_ESM.jpeg
BRCA1 expression in bladder cancer tissues and normal samples in TCGA database predicted by Starbase v3.0 software. Supplementary material 1 (JPEG 69.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Ge, S. PRPF19 functions in DNA damage repair and gemcitabine sensitivity via regulating DDB1 in bladder cancer cells. Cytotechnology 76, 85–96 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-023-00599-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-023-00599-7