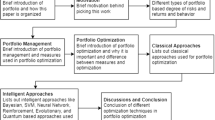
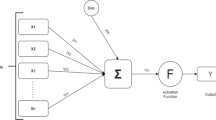
Abstract
In this paper, a two-stage swarm intelligence based hybrid feed-forward neural network approach is designed for optimal feature selection and joint optimization of trainable parameters of neural networks in order to forecast the close price of Nifty 50, Sensex, S&P 500, DAX and SSE Composite Index for multiple-horizon (1-day ahead, 5-days-ahead and 10-days ahead) forecasting. Although the neural network can deal with complex non-linear and uncertain data but defining its architecture in terms of number of input features in the input layer, the number of neurons in the hidden layer and optimizing the weights is a challenging problem. The back-propagation algorithm is frequently used in the neural network and has a drawback to getting stuck in local minima and overfitting the data. Motivated by this, we introduce a swarm intelligence based hybrid neural network model for automatic search of features and other hlearnable neural networks' parameters. The proposed model is a combination of discrete particle swarm optimization (DPSO), particle swarm optimization (PSO) and Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm (LM) for training the feed-forward neural networks. The DPSO attempts to search automatically the optimum number of features and the optimum number of neurons in the hidden layer of FFNN whereas PSO, simultaneously tune the weights and bias in different layers of FFNN. This paper also compares the forecasting efficiency of proposed model with another hybrid model obtained by integrating binary coded genetic algorithm and real coded genetic algorithm with FFNN. Simulation results indicate that the proposed model is effective for obtaining the optimized feature subset and network structure and also shows superior forecasting accuracy.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABC:
-
Artificial Bee Colony
- ACO:
-
Ant Colony Optimization
- ACRO:
-
Artificial Chemical Reaction Optimization
- ADI:
-
Accumulation Distribution Index
- ADX:
-
Average Directional Index
- ANNs:
-
Artificial Neural Networks
- ANFIS:
-
Adaptive Network Fuzzy Inference System
- ARCH:
-
Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity
- ARIMA:
-
Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average
- ARMA:
-
Autoregressive Moving Average
- ARV:
-
Average Relative Variance
- ATR:
-
Average True Range
- BBBC:
-
Big-Bang-Big Crunch (BBBC) Optimization
- BCGA:
-
Binary Coded Genetic Algorithm
- BFO:
-
Bacterial Foraging Optimization
- BP:
-
Back-Propagation
- BSE:
-
Bombay Stock Exchange
- CCI:
-
Commodity Channel Index
- CI:
-
Computational Intelligence
- CL:
-
Close Price
- DE:
-
Differential Evolution
- DJIA:
-
Dow Jones Industrial Average
- DNN:
-
Dynamic Neural Network
- DPSO:
-
Discrete Particle Swarm Optimization
- EC:
-
Evolutionary Computation
- ELM:
-
Extreme Learning Machine
- EMA:
-
Exponential Moving Average
- ENN:
-
Elman Neural Network
- ES:
-
Exponential Smoothing
- FCRBFNN:
-
Fully Complex-valued Radial Basis Function Neural Network
- FFNN:
-
Feed-Forward Neural Network
- FL:
-
Fuzzy Logic
- FLANN:
-
Functional Link Artificial Neural Network
- GA:
-
Genetic Algorithm
- GARCH:
-
Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity
- GRNN:
-
Generalized Regression Neural Network
- GWO:
-
Gray Wolf Optimization
- HI:
-
High Price
- HS:
-
Harmony Search
- IHHO:
-
Improved Harris's hawks optimization
- ISCA:
-
Improved Sine Cosine Algorithm
- IT2FS:
-
Interval Type-2 Fuzzy System
- %K:
-
Stochastic %K
- LM:
-
Levenberg–Marquardt Algorithm
- LMBP:
-
Levenberg–Marquardt Back-Propagation
- LO:
-
Low Price
- MAAPE:
-
Mean Arctangent Absolute Percentage Error
- MACD:
-
Moving Average Convergence Divergence
- MOEA:
-
Multi-objective Evolutionary Optimization
- MOMM:
-
Multiobjective Model-Metric (MOMM) Learning
- MSE:
-
Mean Squared Error
- MTM:
-
Momentum
- NAS:
-
Neural Architecture Search
- NIA:
-
Nature Inspired Algorithm
- OBV:
-
On-Balance Volume
- OHLC:
-
Open High Low Close
- OP:
-
Open Price
- PSO:
-
Particle Swarm Optimization
- QRNN:
-
Quantile Regression Neural Network
- %R:
-
William %R
- RBFNN:
-
Radial Basis Functional Neural network
- RCGA:
-
Real Coded Genetic Algorithm
- RMSE:
-
Root Mean Squared Error
- RNN:
-
Recurrent Neural Network
- ROC:
-
Rate of Change
- RSI:
-
Relative Strength Index
- RW:
-
Random Walk
- SI:
-
Swarm Intelligence
- SMA:
-
Simple Moving Average
- SMAPE:
-
Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error
- TA:
-
Technical Analysis
- TSI:
-
True Strength Index
- UI:
-
Ulcer Index
References
Adebiyi, A. A., Adewumi, A. O., & Ayo, C. K. (2014). Comparison of ARIMA and artificial neural networks models for stock price prediction. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2014, 1–7.
Ariyo, A. A., Adewumi, A. O., & Ayo, C. K. (2014). Stock price prediction using the ARIMA model. In UKSim-AMSS 16th international conference on computer modelling and simulation (pp. 106–112). IEEE.
Atsalakis, G. S., & Valavanis, K. P. (2009). Surveying stock market forecasting techniques–part II: Soft computing methods. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(3), 5932–5941.
Azadeh, A., Saberi, M., Ghaderi, S., Gitiforouz, A., & Ebrahimipour, V. (2008). Improved estimation of electricity demand function by integration of fuzzy system and data mining approach. Energy Conversion and Management, 49(8), 2165–2177.
Baldominos, A., Saez, Y., & Isasi, P. (2020). On the automated, evolutionary design of neural networks: Past, present, and future. In Neural computing and applications (pp. 1–27).
Bartlett, P., & Downs, T. (1990). Training a neural network with a genetic algorithm. University of Queensland.
Basheer, I. A., & Hajmee, M. (2000). Artificial neural networks: Fundamentals, computing, design, and application. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 43(1), 3–31.
Bisoi, R., & Dash, P. K. (2014). A hybrid evolutionary dynamic neural network for stock market trend analysis and prediction using unscented Kalman filter. Applied Soft Computing, 19, 41–56.
Botchkarev, A. (2018). Performance metrics (error measures) in machine learning regression, forecasting and prognostics: Properties and typology (pp. 1–37). arXiv preprint. https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.03006.
Box, G. E., Jenkins, G. M., Reinsel, G. C., & Ljung, G. M. (2015). Time series analysis: Forecasting and control (5th ed.). Wiley.
Chen, W., Jiang, M., & Jiang, C. (2019). Constructing a multilayer network for stock market. Soft Computing 1–17.
Chiang, W. C., Enke, D., Wu, T., & Wang, R. (2016). An adaptive stock index trading decision support system. Expert Systems with Applications, 59, 195–207.
Darwish, A., Hassanien, A. E., & Das, S. (2020). A survey of swarm and evolutionary computing approaches for deep learning. Artificial Intelligence Review, 53(3), 1767–1812.
Elsken, T., Metzen, J. H., & Hutter, F. (2018). Efficient multi-objective neural architecture search via lamarckian evolution. arXiv preprint. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.09081.
Elsken, T., Metzen, J. H., Hutter, F. (2018). Neural architecture search: A survey. arXiv preprint. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.05377.
Elsken, T., Metzen, J. H., & Hutter, F. (2018). Neural architecture search: A survey. arXiv preprint. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.05377.
Fama, E. (1970). Efficient capital markets: A review of theory and empirical work. . R. Lowbridge (Module Leader).
Gao, S., Zhou, M., Wang, Y., Cheng, J., Yachi, H., & Wang, J. (2018). Dendritic neuron model with effective learning algorithms for classification, approximation, and prediction. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 30(2), 601–614.
Gocken, M., Ozcalici, M., Boru, A., & Dosdogru, A. T. (2016). Integrating metaheuristics and artificial neural networks for improved stock price prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 44, 320–331.
Gocken, M., Ozcalici, M., Boru, A., & Dosdogru, A. T. (2019). Stock price prediction using hybrid soft computing models incorporating parameter tuning and input variable selection. Neural Computing and Applications, 31(2), 577–592.
Goh, A. T. (1995). Back-propagation neural networks for modeling complex systems. Artificial Intelligence in Engineering, 9(3), 143–151.
Gong, Z., Chen, H., Yuan, B., & Yao, X. (2018). Multiobjective learning in the model space for time series classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 49(3), 918–932.
Guresen, E., Gulgun, K., & Daim, T. U. (2011a). Using artificial neural network models in stock market index prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(8), 10389–10397.
Guresen, E., Kayakutlu, G., & Daim, T. U. (2011b). Using artificial neural network models in stock market index prediction. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(8), 10389–10397.
Guyon, I., & Elisseeff, A. (2003). An introduction to variable and feature selection. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3, 1157–1182.
Hagan, M. T., & Menhaj, M. B. (1994). Training feedforward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5(6), 989–993.
Haleh, H., Moghaddam, B. A., & Ebrahimijam, S. (2011). A new approach to forecasting stock price with EKF data fusion. International Journal of Trade, Economics and Finance, 2(2), 109–114.
Han, H. G., Lu, W., Hou, Y., & Qiao, J. F. (2016). An adaptive-PSO-based self-organizing RBF neural network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(1), 104–117.
Haupt, R. L., & Haupt, S. E. (2004). Practical genetic algorithms (pp. 51–56). Wiley.
Haykin, S. (1999). Neural network: A comprehensive foundation (2nd ed.). Prentice Hall.
Holland, J. H. (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press.
Hu, H., Ao, Y., Bai, Y., Cheng, R., & Xu, T. (2020). An improved Harris’s Hawks optimization for SAR target recognition and stock market index prediction. IEEE Access, 8, 65891–65910.
Hu, H., Tang, L., Zhang, S., & Wang, H. (2018). Predicting the direction of stock markets using optimized neural networks with Google Trends. Neurocomputing, 285, 188–195.
Hyndman, R. J., & Koehler, A. B. (2006). Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. International Journal of Forecasting, 22(4), 679–688.
Ibrahim, D. (2016). An overview of soft computing. Procedia Computer Science, 102, 34–38.
Inthachot, M., Boonjing, V., & Intakosum, S. (2016). Artificial neural network and genetic algorithm hybrid intelligence for predicting Thai stock price index trend. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2016, 1–8.
Jang, J. S. (1993). ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685.
Kapanova, K. G., Dimov, I., & Sellier, J. M. (2018). A genetic approach to automatic neural network architecture optimization. Neural Computing and Applications, 29(5), 1481–1492.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN'95-international conference on neural networks (Vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948). IEEE.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. C. (1997). A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics. Computational cybernetics and simulation (Vol. 5, pp. 4104–4108).
Kim, K. J. (2006). Artificial neural networks with evolutionary instance selection for financial forecasting. Expert Systems with Applications, 30(3), 519–526.
Kim, S., & Kim, H. (2016). A new metric of absolute percentage error for intermittent demand forecasts. International Journal of Forecasting, 32(3), 669–679.
Kohonen, T. (1988). An introduction to neural computing. Neural Networks, 1(1), 3–16.
Kristjanpoller, W., & Minutolo, M. C. (2018). A hybrid volatility forecasting framework integrating GARCH, artificial neural network, technical analysis and principal components analysis. Expert Systems with Applications, 109, 1–11.
Kumar, G., Jain, S., & Singh, U. P. (2020). Stock market forecasting using computational intelligence: A survey. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 1–33.
Kumar, D., Meghwani, S. S., & Thakur, M. (2016). Proximal support vector machine based hybrid prediction models for trend forecasting in financial markets. Journal of Computational Science, 17, 1–13.
Kumar, S. (2004). Neural networks: A classical approach (2nd ed., pp. 61–65). Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Lin, C. S., Chiu, S. H., & Lin, T. Y. (2012). Empirical mode decomposition-based least squares support vector regression for foreign exchange rate forecasting. Economic Modelling, 29(6), 2583–2590.
Liu, C., Barret, Z., Maxim, N., Jonathon, S., Wei, H., Li-Jia, L., Li, F. F., Alan, Y., Jonathan, H., & Kevin, M. (2018). Progressive neural architecture search. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 19–34).
Liu, F., & Wang, J. (2012). Fluctuation predictions of stock market index by Legendre neural network with random time strength function. Neurocomputing, 83, 12–21.
Lu, C. J., Lee, T. S., & Chiu, C. C. (2009). Financial time series forecasting using independent component analysis and support vector regression. Decision Support Systems, 47(2), 115–125.
Mandziuk, J., & Jaruszewicz, M. (2011). Neuro-genetic system for stock index prediction. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 22(2), 93–123.
Menkhoff, L. (1997). Examining the use of technical currency analysis. International Journal of Finance and Economics, 2(4), 307–318.
Mirjalili, S., & Lewis, A. (2013). S-shaped versus V-shaped transfer functions for binary particle swarm optimization. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 9, 1–14.
More, J. J. (1978). The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm: Implementation and theory. In Numerical analysis (pp. 105–116). Springer.
Nassirtoussi, A. K., Wah, T. Y., & Ling, D. N. C. (2011). A novel FOREX prediction methodology based on fundamental data. African Journal of Business Management, 5(20), 8322–8330.
Nayak, S. C., Kumar, K. V., & Jilla, K. (2020). ACRRFLN: Artificial chemical reaction of recurrent functional link networks for improved stock market prediction. In Computational intelligence in data mining (pp. 311–325). Springer.
Nayak, S. C., Misra, B. B., & Behera, H. S. (2019). ACFLN: Artificial chemical functional link network for prediction of stock market index. Evolving Systems, 10(4), 567–592.
Pradeepkumar, D., & Ravi, V. (2017). Forecasting financial time series volatility using particle swarm optimization trained quantile regression neural network. Applied Soft Computing, 58, 35–52.
Qiu, M. Y., Song, Y., & Akagi, F. (2016). Application of artificial neural network for the prediction of stock market returns: The case of the Japanese stock market. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 85, 1–7.
Ren, G., Cao, Y., Wen, S., Huang, T., & Zeng, Z. (2018). A modified Elman neural network with a new learning rate scheme. Neurocomputing, 286, 11–18.
Reza, H., Shahrabi, J., & Hadavandi, E. (2015). A bat-neural network multi-agent system (BNNMAS) for stock price prediction: Case study of DAX stock price. Applied Soft Computing, 29, 196–210.
Rout, M., & Koudjonou, K. M. (2020). An evolutionary algorithm based hybrid parallel framework for Asia foreign exchange rate prediction. In Nature inspired computing for data science (pp. 279–295). Springer.
Sahoo, S., & Mohanty, M. N. (2020). Stock market price prediction employing artificial neural network optimized by Gray Wolf optimization. In New paradigm in decision science and management (pp. 77–87). Springer.
Sakshi, S., & Kumar, R. (2019). A neuro-genetic technique for pruning and optimization of ANN weights. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 33(1), 1–26.
Sands, T. M., Tayal, D., Morris, M. E., & Monteiro, S. T. (2015). Robust stock value prediction using support vector machines with particle swarm optimization. In IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC) (pp. 3327–3331). IEEE.
Senapati, M. R., Das, S., & Mishra, S. (2018). A novel model for stock price prediction using hybrid neural network. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (india): Series B, 99(6), 555–563.
Shynkevich, Y., McGinnity, T. M., Coleman, S. A., Belatreche, A., & Li, Y. (2017). Forecasting price movement using technical indicators: Investing the impact of varying window length. Neurocomputing, 264, 71–88.
Si, Y. W., & Yin, J. (2013). OBST-based segmentation approach to financial time series. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 26(10), 2581–2596.
Technical analysis. [Online]. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/technical-analysis-4689657. Accessed March 20, 2020.
Technical analysis library in python. [Online]. Retrieved from https://technical-analysis-library-inpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ta.html. Accessed May 30, 2020.
Technical indicators. [Online]. Retrieved from https://school.stockcharts.com/doku.php?id=technicalindicators. Accessed March 30, 2020
Theil, H. (1966). Applied economic forecasting. North-Holland Pub. Co.
Ulke, V., Sahin, A., & Subasi, A. (2018). A comparison of time series and machine learning models for inflation forecasting: Empirical evidence from the USA. Neural Computing and Applications, 30(5), 1519–1527.
Vaisla, K. S., & Bhatt, A. K. (2010). Ananalysis of the performance of artificial neural network technique for stock market forecasting. International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, 2(6), 2104–2109.
Wang, J., & Kumbasar, T. (2019). Parameter optimization of interval Type-2 fuzzy neural networks based on PSO and BBBC methods. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 6(1), 247–257.
Wang, J., & Wang, J. (2015). Forecasting stock market indexes using principle component analysis and stochastic time effective neural networks. Neurocomputing, 156, 68–78.
Wang, J. J., Wang, J. Z., Zhang, Z. G., & Guo, S. P. (2012). Stock index forecasting based on a hybrid model. Omega, 40(6), 758–766.
Webb, A. R. (2003). Statistical pattern recognition (pp. 307–352). Wiley.
Wright, A. H. (1991) Genetic algorithms for real parameter optimization. In Foundations of genetic algorithms (Vol. 1, pp. 205–218).
Xiong, T., Bao, Y., Hu, Z., & Chiong, R. (2015). Forecasting interval time series using a fully complex-valued RBF neural network with DPSO and PSO algorithms. Information Sciences, 305, 77–92.
Yan, W. (2012). Toward automatic time-series forecasting using neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 23(7), 1028–1039.
Yang, F., Chen, Z., Li, J., & Tang, L. (2019). A novel hybrid stock selection method with stock prediction. Applied Soft Computing, 80, 820–831.
Yao, J., Tan, C. L., & Poh, H. L. (1999). Neural networks for technical analysis: A study on KLCI. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance, 2(2), 221–241.
Yao, X. (1999). Evolving artificial neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE, 87(9), 1423–1447.
Yeh, W. C. (2009). A two-stage discrete particle swarm optimization for the problem of multiple multi-level redundancy allocation in series systems. Expert System Application, 36, 9192–9200.
Yu, L., & Liu, H. (2003). Feature selection for high-dimensional data: A fast correlation-based filter solution. In Proceedings of the 20th international conference on machine learning (pp. 856–863).
Zhang, D. Y., Song, H. W., & Chen, P. (2008). Stock market forecasting model based on a hybrid ARMA and support vector machines. In International conference on management science and engineering 15th annual conference proceedings (pp. 1312–1317). IEEE.
Zhong, X., & Enke, D. (2017). Forecasting daily stock market return using dimensionality reduction. Expert Systems with Applications, 67, 126–139.
Zhou, T., Gao, S., Wang, J., Chu, C., Todo, Y., & Tang, Z. (2016). Financial time series prediction using a dendritic neuron model. Knowledge-Based Systems, 105, 214–224.
Funding
No funding received from any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GK: Conceptualization, writing-original draft preparation, software, visualization. UPS: Methodology, result validation, writing- reviewing and editing. SJ: Writing- reviewing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, G., Singh, U.P. & Jain, S. Swarm Intelligence Based Hybrid Neural Network Approach for Stock Price Forecasting. Comput Econ 60, 991–1039 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-021-10176-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10614-021-10176-9