Abstract
Heightened academic stress in the final years of schooling is a common concern, yet little is known about how stress changes over time and what individual, school and family factors are associated with distress. We conducted a systematic review to examine the nature of distress in students in their final two years of secondary school. Sixty studies were eligible for inclusion. The main findings indicated severity of distress differed across the 17 countries sampled and measures used. There was some consistencies suggesting about 1 in 6 students experienced excessive distress. Female gender and anxiety proneness were consistently associated with increased distress, and freedom from negative cognitions with reduced distress. There was some evidence that individual characteristics (perfectionism, avoidance, coping, self-efficacy, resilience), lifestyle (sleep, homework), school, family and peer connectedness were associated with distress. Overall at-risk students can be predicted by theoretical models of anxiety and distress targeted with psychological interventions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huan VS, See YL, Ang RP, Har CW (2008) The impact of adolescent concerns on their academic stress. Educ Rev 60(2):169–178
Ivancic L, Perrens B, Fildes J, Perry Y, Christensen H (2014) Youth mental health report. Mission Australia and Black Dog Institute, AU
McGraw K, Moore S, Fuller A, Bates G (2008) Family, peer and school connectedness in final year secondary school students. Aust Psychol 43(1):27–37
Dewald JF, Meijer AM, Oort FJ, Kerkhof GA, Bogels SM (2014) Adolescents' sleep in low-stress and high-stress (exam) times: a prospective quasi-experiment. Behav Sleep Med 12(6):493–506
Putwain D, Daly A (2014) Test anxiety prevalence and gender differences in a sample of English secondary school students. Educ Stud 40(5):554–570
Leonard NR, Gwadz MV, Ritchie A, Linick JL, Cleland CM, Elliott L, Grethel M (2015) A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools. Front Psychol 6:1028–1044
Chamberlain S, Daly AL, Spalding V (2011) The fear factor: students’ experiences of test anxiety when taking A-level examinations. Pastor Care Educ 29(3):193–205
Putwain D (2009) Assessment and examination stress in Key Stage 4. Br Educ Res J 35(3):391–411
Robinson JA, Alexander DJ, Gradisar MS (2009) Preparing for Year 12 examinations: predictors of psychological distress and sleep. Aust J Psychol 61(2):59–68
Putwain D, Daly A, Chamberlain S, Sadreddini S (2015) Academically buoyant students are less anxious about and perform better in high-stakes examinations. Brit J Educ Stud 85(3):247–263
Spielberger CD (1980) Preliminary professional manual for the Test Anxiety Inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto
King NJ, Ollendick TH, Prins PJ (2000) Test-anxious children and adolescents: psychopathology, cognition, and psychophysiological reactivity. Behav Chang 17(3):134–142
Putwain D (2008) Deconstructing test anxiety. Emot Behav Difficult 13(2):141–155
Gross C, Hen R (2004) The developmental origins of anxiety. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(7):545–552
Weems CF (2008) Developmental trajectories of childhood anxiety: Identifying continuity and change in anxious emotion. Dev Rev 28(4):488–502
Rapee RM (2001) The development of generalized anxiety. In: Vasey MW, Dadds MR (eds) The developmental psychopathology of anxiety. Oxford University Press, New York
Spence SH, Rapee RM (2016) The etiology of social anxiety disorder: an evidence-based model. Behav Res Ther 86:50–67
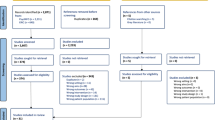
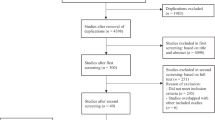
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
Critical Skills Appraisal Programme (2018) CASP Cohort Study Checklist [online]: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Critical Skills Appraisal Programme (2018) Qualitative Study Checklist [online]: https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Hodge GM, McCormick J, Elliott R (1997) Examination-induced distress in a public examination at the completion of secondary schooling. Brit J Educ Psychol 67(2):185–197
Smith L, Sinclair KE (2000) Transforming the HSC: affective implications. Change 3(2):67–79
Akca F (2011) The relationship between test anxiety and learned helplessness. Soc Behav Pers 39(1):101–111
Guner-Kucukkaya P, Isik I (2010) Predictors of psychiatric symptom scores in a sample of Turkish high school students. Nurse Health Sci 12(4):429–436
Moulds JD (2003) Stress manifestation in high school students: an Australian sample. Psychol Schools 40(4):391–402
Wilkinson-Lee AM, Zhang Q, Nuno VL, Wilhelm MS (2011) Adolescent emotional distress: the role of family obligations and school connectedness. J Youth Adolesc 40(2):221–230
Cunha M, Paiva MJ (2012) Text anxiety in adolescents: the role of self-criticism and acceptance and mindfulness skills. Span J Psychol 15(2):533–543
Locker J, Cropley M (2004) Anxiety, depression and self-esteem in secondary school children. Sch Psychol Int 25(3):333–345
Einstein DA, Lovibond PF, Gaston JE (2000) Relationship between perfectionism and emotional symptoms in an adolescent sample. Aust J Psychol 52(2):89–93
Lay CH, Edwards JM, Parker JD, Endler NS (1989) An assessment of appraisal, anxiety, coping, and procrastination during an examination period. Eur J Person 3(3):195–208
Peluso MA, Savalli C, Curi M, Gorenstein C, Andrade LH (2010) Mood changes in the course of preparation for the Brazilian university admission exam—a longitudinal study. Rev Bras Psiquitr 32(1):30–36
Smith L, Sinclair KE, Chapman ES (2002) Students' goals, self-efficacy, self-handicapping, and negative affective responses: an Australian senior school student study. Contemp Educ Psychol 27(3):471–485
Yeni Palabiyik P (2014) A study of Turkish high school students' burnout and proficiency levels in relation to their sex. Novitas-ROYAL 8(2):169–177
Lovibond S, Lovibond P (1995) Manual for the depression anxiety stress scales. Psychology Foundation of Australia, Sydney
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54(6):1063–1070
Kovacs M (1985) The children's depression inventory (CDI). Psychopharmacol Bull 21:995–998
Reynolds CR, Richmond BO (1978) What I think and feel: a revised measure of children's manifest anxiety. J Abnorm Child Psychol 6(2):271–280
Rosenberg M (1965) Society and the adolescent self-image. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Szafranski DD, Barrera TL, Norton PJ (2012) Test anxiety inventory: 30 years later. Anxiety Stress Coping 25(6):667–677
Szabó M (2010) The short version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21): factor structure in a young adolescent sample. J Adolesc 33(1):1–8
Willemsen J, Markey S, Declercq F, Vanhuele S (2011) Negative emotionality in a large community sample of adolescents: the factor structure and measurement invariance of the short version of the depression anxiety stress scales (DASS-21). Stress Health 27(3):120–128
Patrick J, Dyck M, Bramston P (2010) Depression Anxiety Stress Scale: is it valid for children and adolescents? J Clin Psychol 66(9):996–1007
Lin HJ, Yusoff MS (2013) Psychological distress, sources of stress and coping strategy in high school students. Int Med J 20(6):672–676
Goldberg DP (1972) The detection of psychiatric illness by questionnaire. London University Press, London
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Group P (1999) Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ primary care study. J Am Med Assoc 282(18):1737–1744
Beck AT, Rush AJ, Shaw BF, Emery G (1979) Cognitive therapy of depression. Guilford, New York
Yildirim I, Ergene T, Munir K (2007) High rates of depressive symptoms among senior high school students preparing for National University Entrance Examination in Turkey. IJSD 4(2):35–44
Lee M, Larson R (2000) The Korean "Examination Hell": long hours of studying, distress, and depression. J Youth Adolesc 29(2):249–271
Putwain D (2008) Do examinations stakes moderate the test anxiety–examination performance relationship? Educ Psychol 28(2):109–118
Putwain D (2008) Test anxiety and GCSE performance: the effect of gender and socio-economic background. EPIP 24(4):319–334
von der Embse NP, Witmer SE (2014) High-stakes accountability: student anxiety and large-scale testing. J Appl Sch Psychol 30(2):132–156
Putwain D (2007) Test anxiety in UK schoolchildren: prevalence and demographic patterns. Brit J Educ Psychol 77:579–593
Byrne B (2000) Relationships between anxiety, fear, self-esteem, and coping strategies in adolescence. J Adolesc 35(137):201–215
Chukwuorji JC, Nwonyi SK (2015) Test anxiety: contributions of gender, age, parent's occupation and self-esteem among secondary school students in Nigeria. J Psychol Afr 25(1):60–64
Ünal-Karagüven MH (2015) Demographic factors and communal mastery as predictors of academic motivation and test anxiety. J Educ Train Stud 3(3):1–12
Erzen E, Odacı H (2016) The effect of the attachment styles and self-efficacy of adolescents preparing for university entrance tests in Turkey on predicting test anxiety. Educ Psychol 36(10):1728–1741
Karatas H, Alci B, Aydin H (2013) Correlation among high school senior students' test anxiety, academic performance and points of University Entrance Exam. Educ Res Rev 8(13):919–926
Liu YY (2012) Students' perceptions of school climate and trait test anxiety. Psychol Rep 111(3):761–764
Lushington K, Wilson A, Biggs S, Dollman J, Martin J, Kennedy D (2015) Culture, extracurricular activity, sleep habits, and mental health: a comparison of senior high school Asian-Australian and Caucasian-Australian adolescents. Int J Ment Health 44(1–2):139–157
Rahafar A, Maghsudloo M, Farhangnia S, Vollmer C, Randler C (2016) The role of chronotype, gender, test anxiety, and conscientiousness in academic achievement of high school students. Chronobiol Int 33(1):1–9
Ringeisen T, Buchwald P (2010) Test anxiety and positive and negative emotional states during an examination. Special Issue Test Anxiety 14(4):431–447
Sari SA, Bilek G, Celik E (2018) Test anxiety and self-esteem in senior high school students: a cross-sectional study. Nord J Psychiatry 72(2):84–88
Yildirim I, Ergene T, Munir K (2007) Academic achievement, perfectionism and social support as predictors of test anxiety. Hacet U J Educ 34:287–296
Manley MJ, Rosemier RA (1972) Developmental trends in general and test anxiety among junior and senior high school students. J Genet Psychol 120(2):219–226
Christensen H (1979) Test anxiety and academic achievement in high school students. Percept Mot Ski 49(2):648
Aysan F, Thompson D, Hamarat E (2001) Test anxiety, coping strategies, and perceived health in a group of high school students: a Turkish sample. J Genet Psychol 162(4):402–411
Merikangas KR, He J, Burstein M, Swanson SA, Avenevoli S, Cui L et al (2010) Lifetime prevalence of mental disorders in US adolescents: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication-Adolescent Supplement (NCS-A). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(10):980–989
Lawrence D, Johnson S, Hafekost J, Boterhoven de Haan K, Sawyer M, Ainley J et al (2015) The mental health of children and adolescents: Report on the second Australian child and adolescent survey of mental health and wellbeing. Australian Government Department of Health, Canberra
Chin E, Williams MW, Taylor JE, Harvey ST (2017) The influence of negative affect on test anxiety and academic performance: an examination of the tripartite model of emotions. Learn Individ Differ 54:1–8
Segool NK, von der Embse NP, Mata AD, Gallant J (2014) Cognitive behavioral model of test anxiety in a high-stakes context: an exploratory study. School Ment Health 6(1):50–61
Sarason IG (1963) Test anxiety and intellectual performance. J Abnorm Soc Psychol 66(1):73–75
McCann SJ, Meen KS (1984) Anxiety, ability, and academic achievement. J Soc Psychol 124(2):257–258
Çırak Y (2016) University entrance exams from the perspective of senior high school students. J Educ Train Stud 4(9):177–185
Kouzma NM, Kennedy GA (2004) Self-reported sources of stress in senior high school students. Psychol Rep 94(1):314–316
Putwain D (2011) How is examination stress experienced by secondary students preparing for their General Certificate of Secondary Education examinations and how can it be explained? Int J Qual Stud Educ 24(6):717–731
Schmidt S, Tinti C, Levine LJ, Testa S (2010) Appraisals, emotions and emotion regulation: an integrative approach. Motiv Emot 34(1):63–72
Smyth E, Banks J (2012) High stakes testing and student perspectives on teaching and learning in the Republic of Ireland. Educ Assess Eval Acc 24(4):283–306
Liebert RM, Morris LW (1967) Cognitive and emotional components of test anxiety: a distinction and some initial data. Psychol Rep 20(3):975–978
Putwain D, Connors L, Symes W (2010) Do cognitive distortions mediate the test anxiety–examination performance relationship? Educ Psychol 30(1):11–26
Sud A, Sujata (2006) Academic performance in relation to self-handicapping, test anxiety and study habits of high school children. Psychol Stud 51(4):304–309
Putwain D, Daly A, Chamberlain S, Sadreddini S (2016) ‘Sink or swim’: buoyancy and coping in the cognitive test anxiety—academic performance relationship. Educ Psychol 36(10):1807–1825
Putwain D, Aveyard B (2018) Is perceived control a critical factor in understanding the negative relationship between cognitive test anxiety and examination performance? Sch Psychol Q 33(1):65–74
Frost RO, Marten P, Lahart C, Rosenblate R (1990) The dimensions of perfectionism. Cogn Ther Res 14(5):449–468
Hewitt PL, Flett GL (1991) Perfectionism in the self and social contexts: conceptualization, assessment, and association with psychopathology. J Pers Soc Psychol 60(3):456–470
Flett GL, Panico T, Hewitt PL (2011) Perfectionism, type A behavior, and self-efficacy in depression and health symptoms among adolescents. Curr Psychol 30(2):105–116
Eum K, Rice KG (2011) Test anxiety, perfectionism, goal orientation, and academic performance. Anxiety Stress Coping 24(2):167–178
Putwain D, Connors L, Symes W, Douglas-Osborn E (2012) Is academic buoyancy anything more than adaptive coping? Anxiety Stress Coping 25(3):349–358
Compas BE, Jaser SS, Bettis AH, Watson KH, Gruhn MA, Dunbar JP et al (2017) Coping, emotion regulation, and psychopathology in childhood and adolescence: a meta-analysis and narrative review. Psychol Bull 143(9):939–991
Putwain D, Symes W (2011) Perceived fear appeals and examination performance: facilitating or debilitating outcomes? Learn Individ Differ 21(2):227–232
Martin A, Marsh H (2009) Academic resilience and academic buoyancy: Multidimensional and hierarchical conceptual framing of causes, correlates and cognate constructs. Oxf Rev Educ 35(3):353–370
Martin A, Marsh H (2006) Academic resilience and its psychological and educational correlates: a construct validity approach. Psychol Schools 43(3):267–281
Putwain D, Daly A (2013) Do clusters of test anxiety and academic buoyancy differentially predict academic performance? Learn Individ Differ 27:157–162
Martin A, Colmar S, Davey L, Marsh H (2010) Longitudinal modelling of academic buoyancy and motivation: do the '5Cs' hold up over time? Br J Educ Psychol 80:473–496
Kouzma NM, Kennedy GA (2002) Homework, stress and mood disturbance in senior high school students. Psychol Rep 91(1):193–198
Akcoltekin A (2015) High school students’ time management skills in relation to research anxiety. Educ Res Rev 10(16):2241–2249
Astill RG, Verhoeven D, Vijzelaar RL, Van Someren EJ (2013) Chronic stress undermines the compensatory sleep efficiency increase in response to sleep restriction in adolescents. J Sleep Res 22(4):373–379
Baum KT, Desai A, Field J, Miller LE, Rausch J, Beebe DW (2014) Sleep restriction worsens mood and emotion regulation in adolescents. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 55(2):180–190
Sarchiapone M, Mandelli L, Carli V, Losue M, Wasserman C, Hadlaczky G et al (2014) Hours of sleep in adolescents and its association with anxiety, emotional concerns, and suicidal ideation. Sleep Med 15(2):248–254
Short MA, Gradisar M, Lack LC, Wright HR, Dohnt H (2013) The sleep patterns and well-being of Australian adolescents. J Adolesc 36(1):103–110
Ramsawh HJ, Stein MB, Belik SL, Jacobi F, Sareen J (2009) Relationship of anxiety disorders, sleep quality, and functional impairment in a community sample. J Psychiatr Res 43(10):926–933
Tsuno N, Besset A, Ritchie K (2005) Sleep and depression. J Clin Psychiatry 66(10):1254–1269
Riekie H, Aldridge JM, Afari E (2017) The role of the school climate in high school students’ mental health and identity formation: a South Australian study. Br Educ Res J 43(1):95–123
Putwain D, Symes W (2011) Teachers' use of fear appeals in the mathematics classroom: worrying or motivating students? Br J Educ Psychol 81(3):456–474
Symes W, Putwain D, Remedios R (2015) The enabling and protective role of academic buoyancy in the appraisal of fear appeals used prior to high stakes examinations. Sch Psychol Int 36(6):605–619
von der Embse NP, Schultz BK, Draughn JD (2015) Readying students to test: the influence of fear and efficacy appeals on anxiety and test performance. Sch Psychol Int 36(6):620–637
Ollendick TH, King NJ (1994) Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of internalizing problems in children: the role of longitudinal data. J Consult Clin Psychol 62(5):918–927
Rapee RM (2014) Preschool environment and temperament as predictors of social and nonsocial anxiety disorders in middle adolescence. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 53(3):320–328
Zuckerman M (1999) Diathesis-stress models. In: Zuckerman M (ed) Vulnerability to psychopathology: a biosocial model. American Psychological Association, Washington, US
Werner-Seidler A, Perry Y, Calear AL, Newby JM, Christensen H (2017) School-based depression and anxiety prevention programs for young people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev 51:30–47
Lowe C, Wuthrich VM, Hudson JL (2020) Randomised controlled trial of Study Without Stress: a Cognitive Behavioural Therapy group program to reduce academic stress in students in the final year of high school. In preparation
Wuthrich VM, Lowe C (2015) Study without stress program. Department of Psychology, Macquarie University, Sydney, AU, Centre for Emotional Health
Varlow M, Wuthrich V, Murrihy R, Remond L, Tuquiri R, Van Kessel J et al (2009) Stress literacy in Australian adolescents. Youth Stud Aust 28(4):29–34
Saeki E, Pendergast L, Segool NK, von der Embse NP (2015) Potential psychosocial and instructional consequences of the common core state standards: implications for research and practice. Contemp Sch Psychol 19(2):89–97
von der Embse NP, Pendergast LL, Segool N, Saeki E, Ryan S (2016) The influence of test-based accountability policies on school climate and teacher stress across four states. Teach Teach Educ 59:492–502
Daly AL, Chamberlain S, Spalding V (2011) Test anxiety, heart rate and performance in A-level French speaking mock exams: an exploratory study. Educ Res 53(3):321–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wuthrich, V.M., Jagiello, T. & Azzi, V. Academic Stress in the Final Years of School: A Systematic Literature Review. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 51, 986–1015 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-020-00981-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-020-00981-y