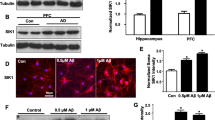
Abstract
Diabetic encephalopathy (DE) is one of the complications of diabetes mellitus with mild-to-moderate cognitive impairment. Trichostatin A (TSA) has been revealed to show protective effect on central nervous systems in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and hypoxic–ischemic brain injury. However, the effect and molecular mechanism of TSA on cognitive function of DE are unknown. Here, we demonstrated that cognitive function was damaged in diabetic mice versus normal mice and treatment with TSA improved cognitive function in diabetic mice. Proteomic analysis of the hippocampus revealed 174 differentially expressed proteins in diabetic mice compared with normal mice. TSA treatment reversed the expression levels of 111 differentially expressed proteins grouped into functional clusters, including the longevity regulating pathway, the insulin signaling pathway, peroxisomes, protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes. Furthermore, protein–protein interaction network analysis of TSA-reversed proteins revealed that UBA52, CAT, RPL29, RPL35A, CANX, RPL37, and PRKAA2 were the main hub proteins. Multiple KEGG pathway-enriched CAT and PRKAA2 levels were significantly decreased in the hippocampus of diabetic mice versus normal mice, which was reversed by TSA administration. Finally, screening for potential similar or ancillary drugs for TSA treatment indicated that HDAC inhibitors ISOX, apicidin, and panobinostat were the most promising similar drugs, and the PI3K inhibitor GSK-1059615, the Aurora kinase inhibitor alisertib, and the nucleophosmin inhibitor avrainvillamide-analog-6 were the most promising ancillary drugs. In conclusion, our study revealed that CAT and PRKAA2 were the key proteins involved in the improvement of DE after TSA treatment. ISOX, apicidin, and panobinostat were promising similar drugs and that GSK-1059615, alisertib, and avrainvillamide-analog-6 were promising ancillary drugs to TSA in the treatment of DE.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data of the present study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Sun et al. 2022) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD036588.
Abbreviations
- DE:
-
Diabetic encephalopathy
- TSA:
-
Trichostatin A
- T2DM:
-
Type II diabetes mellitus
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- PRKAA2:
-
Protein kinase AMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha 2
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- APP:
-
Beta-amyloid precursor protein
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- IRS:
-
Insulin receptor substrates
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- PPI:
-
Protein–protein interaction
- IOD:
-
Integrated optical density
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- CMap:
-
Connectivity Map
- ANOVA:
-
One-way Analysis of Variance
References
Akhtar A, Sah SP (2020) Insulin signaling pathway and related molecules: role in neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 135:104707
An J, Zhang X, Jia K, Zhang C, Zhu L, Cheng M, Li F, Zhao S, Hao J (2021) Trichostatin A increases BDNF protein expression by improving XBP-1s/ATF6/GRP78 axis in Schwann cells of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Biomed Pharmacother 133:111062
Andresen V, Erikstein BS, Mukherjee H, Sulen A, Popa M, Sornes S, Reikvam H, Chan KP, Hovland R, McCormack E, Bruserud O, Myers AG, Gjertsen BT (2016) Anti-proliferative activity of the NPM1 interacting natural product avrainvillamide in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis 7:e2497
Antal B, McMahon LP, Sultan SF, Lithen A, Wexler DJ, Dickerson B, Ratai EM, Mujica-Parodi LR (2022) Type 2 diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline: complementary findings from UK Biobank and meta-analyses. Elife 11:e73138
Baumeister P, Dong D, Fu Y, Lee AS (2009) Transcriptional induction of GRP78/BiP by histone deacetylase inhibitors and resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 8:1086–1094
Bei S, Li F, Li H, Li J, Zhang X, Sun Q, Feng L (2019) Inhibition of gastric cancer cell growth by a PI3K-mTOR dual inhibitor GSK1059615. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 511:13–20
Berger J, Dorninger F, Forss-Petter S, Kunze M (1863) Peroxisomes in brain development and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016:934–955
Biessels GJ, Despa F (2018) Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 14:591–604
Bilches Medinas D, Malik S, Yildiz-Bolukbasi E, Borgonovo J, Saaranen MJ, Urra H, Pulgar E, Afzal M, Contreras D, Wright MT, Bodaleo F, Quiroz G, Rozas P, Mumtaz S, Diaz R, Rozas C, Cabral-Miranda F, Pina R, Valenzuela V, Uyan O, Reardon C, Woehlbier U, Brown RH, Sena-Esteves M, Gonzalez-Billault C, Morales B, Plate L, Ruddock LW, Concha ML, Hetz C, Tolun A (2022) Mutation in protein disulfide isomerase A3 causes neurodevelopmental defects by disturbing endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis. EMBO J 41:e105531
Bryan MR, Bowman AB (2017) Manganese and the insulin-IGF signaling network in Huntington’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Adv Neurobiol 18:113–142
Chandramouli K, Qian PY (2009) Proteomics: challenges, techniques and possibilities to overcome biological sample complexity. Hum Genomics Proteomics 2009:239204
Dahabieh MS, Ha Z, Di Pietro E, Nichol JN, Bolt AM, Goncalves C, Dupere-Richer D, Pettersson F, Mann KK, Braverman NE, Del Rincon SV, Miller WH Jr (2017) Peroxisomes protect lymphoma cells from HDAC inhibitor-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 24:1912–1924
Dastidar SG, Nair D (2022) A ribosomal perspective on neuronal local protein synthesis. Front Mol Neurosci 15:823135
Demichev V, Messner CB, Vernardis SI, Lilley KS, Ralser M (2020) DIA-NN: neural networks and interference correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat Methods 17:41–44
Demir S, Nawroth PP, Herzig S, Ekim Ustunel B (2021) Emerging targets in type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications. Adv Sci (weinh) 8:e2100275
Frank CL, Ge X, Xie Z, Zhou Y, Tsai LH (2010) Control of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) persistence by multisite phosphorylation impacts cell cycle progression and neurogenesis. J Biol Chem 285:33324–33337
Galasso M, Gambino S, Romanelli MG, Donadelli M, Scupoli MT (2021) Browsing the oldest antioxidant enzyme: catalase and its multiple regulation in cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 172:264–272
Goth L, Vitai M (1996) Hypocatalasemia in hospital patients. Clin Chem 42:341–342
Habib LK, Lee MT, Yang J (2010) Inhibitors of catalase-amyloid interactions protect cells from beta-amyloid-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. J Biol Chem 285:38933–38943
Hetman M, Slomnicki LP (2019) Ribosomal biogenesis as an emerging target of neurodevelopmental pathologies. J Neurochem 148:325–347
Hirschler-Laszkiewicz I, Cavanaugh A, Hu Q, Catania J, Avantaggiati ML, Rothblum LI (2001) The role of acetylation in rDNA transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 29:4114–4124
Horikoshi M, Hara K, Ohashi J, Miyake K, Tokunaga K, Ito C, Kasuga M, Nagai R, Kadowaki T (2006) A polymorphism in the AMPKalpha2 subunit gene is associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Diabetes 55:919–923
Jo DS, Cho DH (2019) Peroxisomal dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Arch Pharmacal Res 42:393–406
Joazeiro CAP (2019) Mechanisms and functions of ribosome-associated protein quality control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:368–383
Kim W, Lee Y, McKenna ND, Yi M, Simunovic F, Wang Y, Kong B, Rooney RJ, Seo H, Stephens RM, Sonntag KC (2014) miR-126 contributes to Parkinson’s disease by dysregulating the insulin-like growth factor/phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Neurobiol Aging 35:1712–1721
Lee HJ, Seo HI, Cha HY, Yang YJ, Kwon SH, Yang SJ (2018) Diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease: mechanisms and nutritional aspects. Clin Nutr Res 7:229–240
Li X, Pan W, Yang GZ, Di YN, Zhao F, Zhu LY, Jiang ZH (2011) Proteome analysis of differential protein expression in brain of rats with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 119:265–270
Li Y, Xiang Q, Yao YH, Li JJ, Wang Y, Li XH (2020) Inactivated AMPK-alpha2 promotes the progression of diabetic brain damage by Cdk5 phosphorylation at Thr485 site. Biochimie 168:277–284
Liewer S, Huddleston A (2018) Alisertib: a review of pharmacokinetics, efficacy and toxicity in patients with hematologic malignancies and solid tumors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27:105–112
Liu Y, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2011) Deficient brain insulin signalling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Pathol 225:54–62
Mahalingam SS, Shukla N, Farre JC, Zientara-Rytter K, Subramani S (2021) Balancing the opposing principles that govern peroxisome homeostasis. Trends Biochem Sci 46:200–212
Martinez G, Vidal RL, Mardones P, Serrano FG, Ardiles AO, Wirth C, Valdes P, Thielen P, Schneider BL, Kerr B, Valdes JL, Palacios AG, Inestrosa NC, Glimcher LH, Hetz C (2016) Regulation of memory formation by the transcription factor XBP1. Cell Rep 14:1382–1394
Matsuura K, Otani M, Takano M, Kadoyama K, Matsuyama S (2018) Proteomic analysis of hippocampus and cortex in streptozotocin-induced diabetic model mice showing dementia. J Diabetes Res 2018:8953015
Meraner J, Lechner M, Schwarze F, Gander R, Jesacher F, Loidl P (2008) Cell cycle dependent role of HDAC1 for proliferation control through modulating ribosomal DNA transcription. Cell Biol Int 32:1073–1080
Mimura N, Yuasa S, Soma M, Jin H, Kimura K, Goto S, Koseki H, Aoe T (2008) Altered quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum causes cortical dysplasia in knock-in mice expressing a mutant BiP. Mol Cell Biol 28:293–301
Morgan M, Kabayama Y, Much C, Ivanova I, Di Giacomo M, Auchynnikava T, Monahan JM, Vitsios DM, Vasiliauskaite L, Comazzetto S, Rappsilber J, Allshire RC, Porse BT, Enright AJ, O’Carroll D (2019) A programmed wave of uridylation-primed mRNA degradation is essential for meiotic progression and mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res 29:221–232
Nandi A, Yan LJ, Jana CK, Das N (2019) Role of catalase in oxidative stress- and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:9613090
Peng Y, Liu J, Shi L, Tang Y, Gao D, Long J, Liu J (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction precedes depression of AMPK/AKT signaling in insulin resistance induced by high glucose in primary cortical neurons. J Neurochem 137:701–713
Rasmussen L, de Labio RW, Viani GA, Chen E, Villares J, Bertolucci PH, Minett TS, Turecki G, Cecyre D, Drigo SA, Smith MC, Payao SL (2015) Differential expression of ribosomal genes in brain and blood of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Curr Alzheimer Res 12:984–989
Salas-Perez F, Ramos-Lopez O, Mansego ML, Milagro FI, Santos JL, Riezu-Boj JI, Martinez JA (2019) DNA methylation in genes of longevity-regulating pathways: association with obesity and metabolic complications. Aging (albany NY) 11:1874–1899
Saltiel AR (2021) Insulin signaling in health and disease. J Clin Investig 131:e142241
Slavov N (2021) Increasing proteomics throughput. Nat Biotechnol 39:809–810
Steinberg GR, Carling D (2019) AMP-activated protein kinase: the current landscape for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18:527–551
Su Q, Li T, He PF, Lu XC, Yu Q, Gao QC, Wang ZJ, Wu MN, Yang D, Qi JS (2021) Trichostatin A ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathology and cognitive deficits by increasing albumin expression and Abeta clearance in APP/PS1 mice. Alzheimers Res Ther 13:7
Sun C, Zhou J (2008) Trichostatin A improves insulin stimulated glucose utilization and insulin signaling transduction through the repression of HDAC2. Biochem Pharmacol 76:120–127
Sun P, Wen H, Liu X, Ma Y, Jang J, Yu C (2022) Time trends in type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence across the BRICS from 1990 to 2019: an age-period-cohort analysis. BMC Public Health 22:65
Vasquez GE, Medinas DB, Urra H, Hetz C (2022) Emerging roles of endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis in brain development. Cells Dev 170:203781
Wu S, Lu Q, Ding Y, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Wang P, Mao X, Huang K, Xie Z, Zou MH (2019) Hyperglycemia-driven inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha2 induces diabetic cardiomyopathy by promoting mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes in vivo. Circulation 139:1913–1936
Wulff JE, Siegrist R, Myers AG (2007) The natural product avrainvillamide binds to the oncoprotein nucleophosmin. J Am Chem Soc 129:14444–14451
Yang CY, Liu CR, Chang IY, OuYang CN, Hsieh CH, Huang YL, Wang CI, Jan FW, Wang WL, Tsai TL, Liu H, Tseng CP, Chang YS, Wu CC, Chang KP (2020) Cotargeting CHK1 and PI3K synergistically suppresses tumor growth of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma in patient-derived xenografts. Cancers (basel) 12:1726
Yuan Q, Zhang X, Wei W, Zhao J, Wu Y, Zhao S, Zhu L, Wang P, Hao J (2022) Lycorine improves peripheral nerve function by promoting Schwann cell autophagy via AMPK pathway activation and MMP9 downregulation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pharmacol Res 175:105985
Zalewska T, Jaworska J, Sypecka J, Ziemka-Nalecz M (2020) Impact of a histone deacetylase inhibitor-trichostatin a on neurogenesis after hypoxia–ischemia in immature rats. Int J Mol Sci 21:3808
Zhang CH, Lv X, Du W, Cheng MJ, Liu YP, Zhu L, Hao J (2019) The Akt/mTOR cascade mediates high glucose-induced reductions in BDNF via DNMT1 in Schwann cells in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp Cell Res 383:111502
Zhou S, Ma Y, Xu R, Tang X (2022) Nanoparticles loaded with GSK1059615 combined with sorafenib inhibited programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 expression by negatively regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway, thereby reversing the drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib. J Biomed Nanotechnol 18:693–704
Funding
This research was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171365) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2021206086, H2021206098).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW, QZ, DK, and JH conceived and designed the experiment; WW, QZ, TJ, LZ, and JZ performed the experiments; WW, QZ, FL, SZ, DK, and JL analyzed the data; DK and JH wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Zhang, Q., Jin, T. et al. Quantitative Proteomics Characterization of the Effect and Mechanism of Trichostatin A on the Hippocampus of Type II Diabetic Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 4309–4332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01424-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01424-7