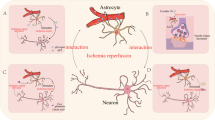
Abstract
Post-stroke depression (PSD) is a frequent and disabling complication of stroke that affects up to one-third of stroke survivors. The pathophysiology of PSD involves multiple mechanisms, including neurochemical, neuroinflammatory, neurotrophic, and neuroplastic changes. Astrocytes are a type of glial cell that is plentiful and adaptable in the central nervous system. They play key roles in various mechanisms by modulating neurotransmission, inflammation, neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity. This review summarizes the latest evidence of astrocyte involvement in PSD from human and animal studies, focusing on the alterations of astrocyte markers and functions in relation to monoamine neurotransmitters, inflammatory cytokines, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glutamate excitotoxicity. We also discuss the potential therapeutic implications of targeting astrocytes for PSD prevention and treatment. Astrocytes could be new candidates for antidepressant medications and other interventions that aim to restore astrocyte homeostasis and function in PSD.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdullahi W, Tripathi D, Ronaldson PT (2018) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 315(3):C343–C356. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018
Alexopoulos GS, Meyers BS, Young RC, Campbell S, Silbersweig D, Charlson M (1997) ‘Vascular depression’ hypothesis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54(10):915–922. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830220033006
Allaman I, Fiumelli H, Magistretti PJ, Martin JL (2011) Fluoxetine regulates the expression of neurotrophic/growth factors and glucose metabolism in astrocytes. Psychopharmacology 216(1):75–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2190-y
Allen NJ, Eroglu C (2017) Cell biology of astrocyte-synapse interactions. Neuron 96(3):697–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.056
Altshuler LL, Abulseoud OA, Foland-Ross L, Bartzokis G, Chang S, Mintz J, Hellemann G, Vinters HV (2010) Amygdala astrocyte reduction in subjects with major depressive disorder but not bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 12(5):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-5618.2010.00838.x
Alvarez JI, Katayama T, Prat A (2013) Glial influence on the blood brain barrier. Glia 61(12):1939–1958. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22575
Andersen JV, Markussen KH, Jakobsen E, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS, Rosenberg PA, Aldana BI (2021) Glutamate metabolism and recycling at the excitatory synapse in health and neurodegeneration. Neuropharmacology 196:108719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108719
Aten S, Du Y, Taylor O, Dye C, Collins K, Thomas M, Kiyoshi C, Zhou M (2022) Chronic stress impairs the structure and function of astrocyte networks in an animal model of depression. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03663-4
Ayerbe L, Ayis S, Wolfe CD, Rudd AG (2013) Natural history, predictors and outcomes of depression after stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry 202(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.111.107664
Bai S, Guo W, Feng Y, Deng H, Li G, Nie H, Guo G, Yu H, Ma Y, Wang J, Chen S, Jing J, Yang J, Tang Y, Tang Z (2020) Efficacy and safety of anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment of major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91(1):21–32. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2019-320912
Bellot-Saez A, Stevenson R, Kekesi O, Samokhina E, Ben-Abu Y, Morley JW, Buskila Y (2021) Neuromodulation of astrocytic K(+) clearance. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052520
Bernard R, Kerman IA, Thompson RC, Jones EG, Bunney WE, Barchas JD, Schatzberg AF, Myers RM, Akil H, Watson SJ (2011) Altered expression of glutamate signaling, growth factor, and glia genes in the locus coeruleus of patients with major depression. Mol Psychiatry 16(6):634–646. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2010.44
Brandebura AN, Paumier A, Onur TS, Allen NJ (2023) Astrocyte contribution to dysfunction, risk and progression in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 24(1):23–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-022-00641-1
Carrard A, Elsayed M, Margineanu M, Boury-Jamot B, Fragniere L, Meylan EM, Petit JM, Fiumelli H, Magistretti PJ, Martin JL (2018) Peripheral administration of lactate produces antidepressant-like effects. Mol Psychiatry 23(2):392–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.179
Chandley MJ, Szebeni K, Szebeni A, Crawford J, Stockmeier CA, Turecki G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, Ordway GA (2013) Gene expression deficits in pontine locus coeruleus astrocytes in men with major depressive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 38(4):276–284. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.120110
Chen HH, Zhang N, Li WY, Fang MR, Zhang H, Fang YS, Ding MX, Fu XY (2015) Overexpression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus protects against post-stroke depression. Neural Regen Res 10(9):1427–1432. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.165510
Chen B, Zhang M, Ji M, Gong W, Chen B, Zorec R, Stenovec M, Verkhratsky A, Li B (2021) The association between antidepressant effect of SSRIs and astrocytes: conceptual overview and meta-analysis of the literature. Neurochem Res 46(10):2731–2745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03225-6
Chen H, Liu F, Sun D, Zhang J, Luo S, Liao Q, Tian F (2022) The potential risk factors of early-onset post-stroke depression from immuno-inflammatory perspective. Front Immunol 13:1000631. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1000631
Chen H, Huang X, Zeng C, Sun D, Liu F, Zhang J, Liao Q, Luo S, Xu W, Xiao Y, Zeng D, Song M, Tian F (2023) The role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 in early-onset post-stroke depression. Front Immunol 14:1125634. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1125634
Cheng SY, Zhao YD, Li J, Chen XY, Wang RD, Zeng JW (2014) Plasma levels of glutamate during stroke is associated with development of post-stroke depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 47:126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.05.006
Chi CH, Huang YY, Ye SZ, Shao MM, Jiang MX, Yang MY, Wu Q, Shao B, Li XM (2021) Interleukin-10 level is associated with post-stroke depression in acute ischaemic stroke patients. J Affect Disord 293:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.06.037
Christ GJ, Moreno AP, Melman A, Spray DC (1992) Gap junction-mediated intercellular diffusion of Ca2+ in cultured human corporal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol 263(2 Pt 1):C373-383. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C373
Cobb JA, O’Neill K, Milner J, Mahajan GJ, Lawrence TJ, May WL, Miguel-Hidalgo J, Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA (2016) Density of GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes is decreased in left hippocampi in major depressive disorder. Neuroscience 316:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.12.044
Codeluppi SA, Chatterjee D, Prevot TD, Bansal Y, Misquitta KA, Sibille E, Banasr M (2021) Chronic stress alters astrocyte morphology in mouse prefrontal cortex. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 24(10):842–853. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyab052
Colombo E, Farina C (2016) Astrocytes: key regulators of neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol 37(9):608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2016.06.006
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ni Z, Dong Y, Cai G, Foncelle A, Ma S, Sang K, Tang S, Li Y, Shen Y, Berry H, Wu S, Hu H (2018) Astroglial Kir4.1 in the lateral habenula drives neuronal bursts in depression. Nature 554(7692):323–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25752
Della Vecchia S, Marchese M, Santorelli FM, Sicca F (2021) Kir4.1 dysfunction in the pathophysiology of depression: a systematic review. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102628
Diaz-Castro B, Robel S, Mishra A (2023) Astrocyte endfeet in brain function and pathology: open questions. Annu Rev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-091922-031205
Dolotov OV, Inozemtseva LS, Myasoedov NF, Grivennikov IA (2022) Stress-induced depression and alzheimer’s disease: focus on astrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094999
Dong R, Han Y, Jiang L, Liu S, Zhang F, Peng L, Wang Z, Ma Z, Xia T, Gu X (2022) Connexin 43 gap junction-mediated astrocytic network reconstruction attenuates isoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. J Neuroinflammation 19(1):64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-022-02424-y
Du Preez A, Onorato D, Eiben I, Musaelyan K, Egeland M, Zunszain PA, Fernandes C, Thuret S, Pariante CM (2021) Chronic stress followed by social isolation promotes depressive-like behaviour, alters microglial and astrocyte biology and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in male mice. Brain Behav Immun 91:24–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.07.015
Durkee C, Kofuji P, Navarrete M, Araque A (2021) Astrocyte and neuron cooperation in long-term depression. Trends Neurosci 44(10):837–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2021.07.004
Ernst C, Nagy C, Kim S, Yang JP, Deng X, Hellstrom IC, Choi KH, Gershenfeld H, Meaney MJ, Turecki G (2011) Dysfunction of astrocyte connexins 30 and 43 in dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex of suicide completers. Biol Psychiatry 70(4):312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.03.038
Fang Y, Ding X, Zhang Y, Cai L, Ge Y, Ma K, Xu R, Li S, Song M, Zhu H, Liu J, Ding J, Lu M, Hu G (2022) Fluoxetine inhibited the activation of A1 reactive astrocyte in a mouse model of major depressive disorder through astrocytic 5-HT(2B)R/beta-arrestin2 pathway. J Neuroinflammation 19(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-022-02389-y
Feng D, Zhou J, Liu H, Wu X, Li F, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Wang L, Chao M, Wang Q, Qin H, Ge S, Liu Q, Zhang J, Qu Y (2022) Astrocytic NDRG2-PPM1A interaction exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Sci Adv 8(39):eabq2423. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abq2423
Fernandez AM, Hernandez E, Guerrero-Gomez D, Miranda-Vizuete A, Torres Aleman I (2018) A network of insulin peptides regulate glucose uptake by astrocytes: Potential new druggable targets for brain hypometabolism. Neuropharmacology 136(Pt B):216–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.034
Forsyth RJ (1996) Astrocytes and the delivery of glucose from plasma to neurons. Neurochem Int 28(3):231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-0186(95)00094-1
Frank D, Kuts R, Tsenter P, Gruenbaum BF, Grinshpun Y, Zvenigorodsky V, Shelef I, Natanel D, Brotfain E, Zlotnik A, Boyko M (2019) The effect of pyruvate on the development and progression of post-stroke depression: a new therapeutic approach. Neuropharmacology 155:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.035
Freitas AE, Egea J, Buendia I, Gomez-Rangel V, Parada E, Navarro E, Casas AI, Wojnicz A, Ortiz JA, Cuadrado A, Ruiz-Nuno A, Rodrigues ALS, Lopez MG (2016) Agmatine, by improving neuroplasticity markers and inducing Nrf2, prevents corticosterone-induced depressive-like behavior in mice. Mol Neurobiol 53(5):3030–3045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9182-6
Frizzo ME, Ohno Y (2021) Perisynaptic astrocytes as a potential target for novel antidepressant drugs. J Pharmacol Sci 145(1):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2020.11.002
Fullana N, Gasull-Camos J, Tarres-Gatius M, Castane A, Bortolozzi A, Artigas F (2020) Astrocyte control of glutamatergic activity: Downstream effects on serotonergic function and emotional behavior. Neuropharmacology 166:107914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107914
Gao HQ, Zhu HY, Zhang YQ, Wang LX (2008) Reduction of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma serotonin in patients with post-stroke depression: a preliminary report. Clin Invest Med 31(6):E351–E356. https://doi.org/10.25011/cim.v31i6.4921
Genel O, Pariante CM, Borsini A (2021) The role of AQP4 in the pathogenesis of depression, and possible related mechanisms. Brain Behav Immun 98:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2021.08.232
Gos T, Schroeter ML, Lessel W, Bernstein HG, Dobrowolny H, Schiltz K, Bogerts B, Steiner J (2013) S100B-immunopositive astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in the hippocampus are differentially afflicted in unipolar and bipolar depression: a postmortem study. J Psychiatr Res 47(11):1694–1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2013.07.005
Gruenbaum BF, Kutz R, Zlotnik A, Boyko M (2020) Blood glutamate scavenging as a novel glutamate-based therapeutic approach for post-stroke depression. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 10:2045125320903951. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045125320903951
Gules E, Iosifescu DV, Tural U (2020) Plasma neuronal and glial markers and anterior cingulate metabolite levels in major depressive disorder: a pilot study. Neuropsychobiology 79(3):214–221. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505782
Guo J, Wang J, Sun W, Liu X (2022) The advances of post-stroke depression: 2021 update. J Neurol 269(3):1236–1249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-021-10597-4
Gur S, Taler M, Bormant G, Blattberg D, Nitzan U, Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Brill L, Krivoy A, Weizman A, Hochman E (2020) Lack of association between unipolar or bipolar depression and serum aquaporin-4 autoantibodies. Brain Behav Immun 88:930–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.001
Hama S, Yamashita H, Shigenobu M, Watanabe A, Kurisu K, Yamawaki S, Kitaoka T (2007) Post-stroke affective or apathetic depression and lesion location: left frontal lobe and bilateral basal ganglia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 257(3):149–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0698-7
Hasler G, van der Veen JW, Tumonis T, Meyers N, Shen J, Drevets WC (2007) Reduced prefrontal glutamate/glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in major depression determined using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(2):193–200. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.64.2.193
Hidese S, Hattori K, Sasayama D, Tsumagari T, Miyakawa T, Matsumura R, Yokota Y, Ishida I, Matsuo J, Yoshida S, Ota M, Kunugi H (2020) Cerebrospinal fluid neuroplasticity-associated protein levels in patients with psychiatric disorders: a multiplex immunoassay study. Transl Psychiatry 10(1):161. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0843-5
Howren MB, Lamkin DM, Suls J (2009) Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med 71(2):171–186. https://doi.org/10.1097/PSY.0b013e3181907c1b
Hu J, Zhou W, Zhou Z, Yang Q, Han J, Yan Y, Dong W (2019) Predictive value of inflammatory indicators for post-stroke depression in patients with ischemic stroke. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 39(6):665–671. https://doi.org/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.06.06
Iadecola C, Buckwalter MS, Anrather J (2020) Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential. J Clin Invest 130(6):2777–2788. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI135530
Ilut S, Stan A, Blesneag A, Vacaras V, Vesa S, Fodoreanu L (2017) Factors that influence the severity of post-stroke depression. J Med Life 10(3):167–171
Jackson RJ, Meltzer JC, Nguyen H, Commins C, Bennett RE, Hudry E, Hyman BT (2022) APOE4 derived from astrocytes leads to blood-brain barrier impairment. Brain 145(10):3582–3593. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awab478
Jantas D, Lech T, Golda S, Pilc A, Lason W (2018) New evidences for a role of mGluR7 in astrocyte survival: possible implications for neuroprotection. Neuropharmacology 141:223–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.08.035
Jimenez I, Sobrino T, Rodriguez-Yanez M, Pouso M, Cristobo I, Sabucedo M, Blanco M, Castellanos M, Leira R, Castillo J (2009) High serum levels of leptin are associated with post-stroke depression. Psychol Med 39(7):1201–1209. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291709005637
Kang S, Li J, Bekker A, Ye JH (2018) Rescue of glutamate transport in the lateral habenula alleviates depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in ethanol-withdrawn rats. Neuropharmacology 129:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.11.013
Karaahmet OZ, Gurcay E, Avluk OC, Umay EK, Gundogdu I, Ecerkale O, Cakci A (2017) Poststroke depression: risk factors and potential effects on functional recovery. Int J Rehabil Res 40(1):71–75. https://doi.org/10.1097/MRR.0000000000000210
Khakh BS, Sofroniew MV (2015) Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nat Neurosci 18(7):942–952. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4043
Kilb W, Kirischuk S (2022) GABA release from astrocytes in health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232415859
Kim JS, Choi-Kwon S (2000) Poststroke depression and emotional incontinence: correlation with lesion location. Neurology 54(9):1805–1810. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.54.9.1805
Kim Y, Kim SH, Kim YS, Lee YH, Ha K, Shin SY (2011) Imipramine activates glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor via early growth response gene 1 in astrocytes. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35(4):1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2011.02.012
Kim JM, Stewart R, Bae KY, Kim SW, Kang HJ, Shin IS, Kim JT, Park MS, Kim MK, Park SW, Kim YH, Kim JK, Cho KH, Yoon JS (2012) Serotonergic and BDNF genes and risk of depression after stroke. J Affect Disord 136(3):833–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2011.09.029
Kim JM, Stewart R, Kang HJ, Kim SY, Kim SW, Shin IS, Park MS, Kim HR, Shin MG, Cho KH, Yoon JS (2013) A longitudinal study of BDNF promoter methylation and genotype with poststroke depression. J Affect Disord 149(1–3):93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2013.01.008
Kim JM, Kang HJ, Kim JW, Bae KY, Kim SW, Kim JT, Park MS, Cho KH (2017a) Associations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Interleukin-1beta levels and polymorphisms with post-stroke depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 25(12):1300–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jagp.2017.07.012
Kim SK, Nabekura J, Koizumi S (2017b) Astrocyte-mediated synapse remodeling in the pathological brain. Glia 65(11):1719–1727. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23169
Klingbeil J, Brandt ML, Wawrzyniak M, Stockert A, Schneider HR, Baum P, Hoffmann KT, Saur D (2021) Association of lesion location and depressive symptoms poststroke. Stroke 52(3):830–837. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031889
Köhler-Forsberg O, Lydholm CN, Hjorthøj C, Nordentoft M, Mors O, Benros ME (2019) Efficacy of anti-inflammatory treatment on major depressive disorder or depressive symptoms: meta-analysis of clinical trials. Acta Psychiatr Scand 139(5):404–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/acps.13016
Kong H, Zeng XN, Fan Y, Yuan ST, Ge S, Xie WP, Wang H, Hu G (2014) Aquaporin-4 knockout exacerbates corticosterone-induced depression by inhibiting astrocyte function and hippocampal neurogenesis. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(5):391–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12222
Larsen BR, MacAulay N (2017) Activity-dependent astrocyte swelling is mediated by pH-regulating mechanisms. Glia 65(10):1668–1681. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23187
Legg LA, Rudberg AS, Hua X, Wu S, Hackett ML, Tilney R, Lindgren L, Kutlubaev MA, Hsieh CF, Barugh AJ, Hankey GJ, Lundstrom E, Dennis M, Mead GE (2021) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for stroke recovery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11(11):CD009286. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009286.pub4
Leng L, Zhuang K, Liu Z, Huang C, Gao Y, Chen G, Lin H, Hu Y, Wu D, Shi M, Xie W, Sun H, Shao Z, Li H, Zhang K, Mo W, Huang TY, Xue M, Yuan Z, Zhang X, Bu G, Xu H, Xu Q, Zhang J (2018) Menin deficiency leads to depressive-like behaviors in mice by modulating astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation. Neuron 100(3):551-563 e557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.08.031
Li J, Zhao YD, Zeng JW, Chen XY, Wang RD, Cheng SY (2014) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in post-stroke depression. J Affect Disord 168:373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2014.07.011
Li Z, Xu H, Xu Y, Lu G, Peng Q, Chen J, Bi R, Li J, Chen S, Li H, Jin H, Hu B (2021) Morinda officinalis oligosaccharides alleviate depressive-like behaviors in post-stroke rats via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome to inhibit hippocampal inflammation. CNS Neurosci Ther 27(12):1570–1586. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13732
Li L, Zhou J, Han L, Wu X, Shi Y, Cui W, Zhang S, Hu Q, Wang J, Bai H, Liu H, Guo W, Feng D, Qu Y (2022a) The specific role of reactive astrocytes in stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 16:850866. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2022.850866
Li S, Fang Y, Zhang Y, Song M, Zhang X, Ding X, Yao H, Chen M, Sun Y, Ding J, Wang Q, Lu M, Wu G, Hu G (2022b) Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activates neurotoxic astrocytes in depression-like mice. Cell Rep 41(4):111532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111532
Liang J, Yue Y, Jiang H, Geng D, Wang J, Lu J, Li S, Zhang K, Wu A, Yuan Y (2018) Genetic variations in the p11/tPA/BDNF pathway are associated with post stroke depression. J Affect Disord 226:313–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.09.055
Liu Z, Chopp M (2016) Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 144:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.008
Liu F, Wu J, Gong Y, Wang P, Zhu L, Tong L, Chen X, Ling Y, Huang C (2017) Harmine produces antidepressant-like effects via restoration of astrocytic functions. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 79(Pt B):258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.06.012
Liu J, Mo JW, Wang X, An Z, Zhang S, Zhang CY, Yi P, Leong ATL, Ren J, Chen LY, Mo R, Xie Y, Feng Q, Chen W, Gao TM, Wu EX, Feng Y, Cao X (2022a) Astrocyte dysfunction drives abnormal resting-state functional connectivity in depression. Sci Adv 8(46):eabo2098. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abo2098
Liu X, Gu XH, Zheng LL, Xu LJ, Yang YJ, Yang G, Wu HJ, Chen ZZ, Wang W (2022b) Autophagy promotes membrane trafficking of NR2B to alleviate depression by inhibiting AQP4 expression in mice. Exp Cell Res 419(1):113298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113298
Lowenbach H, Greenhill MH (1947) The effect of oral administration of lactic acid upon the clinical course of depressive states. J Nerv Ment Dis 105(4):343–358. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005053-194704000-00001
Lu X, Duan J, Cheng Q, Lu J (2020) The association between serum growth differentiation factor-15 and 3-month depression after acute ischemic stroke. J Affect Disord 260:695–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.09.037
Lu L, Yang LK, Yue J, Wang XS, Qi JY, Yang F, Feng B, Liu SB (2021) Scutellarin alleviates depression-like behaviors induced by LPS in mice partially through inhibition of astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation. Neurosci Lett 765:136284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136284
Lu Q, Xiong J, Yuan Y, Ruan Z, Zhang Y, Chai B, Li L, Cai S, Xiao J, Wu Y, Huang P, Zhang H (2022) Minocycline improves the functional recovery after traumatic brain injury via inhibition of aquaporin-4. Int J Biol Sci 18(1):441–458. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.64187
Luykx JJ, Laban KG, van den Heuvel MP, Boks MP, Mandl RC, Kahn RS, Bakker SC (2012) Region and state specific glutamate downregulation in major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of (1)H-MRS findings. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36(1):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.05.014
Ma Q, Li R, Wang L, Yin P, Wang Y, Yan C, Ren Y, Qian Z, Vaughn MG, McMillin SE, Hay SI, Naghavi M, Cai M, Wang C, Zhang Z, Zhou M, Lin H, Yang Y (2021) Temporal trend and attributable risk factors of stroke burden in China, 1990–2019: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 6(12):e897–e906. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00228-0
Mak KK, Kong WY, Mak A, Sharma VK, Ho RC (2013) Polymorphisms of the serotonin transporter gene and post-stroke depression: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(3):322–328. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-303791
Marques BL, Oliveira-Lima OC, Carvalho GA, de Almeida Chiarelli R, Ribeiro RI, Parreira RC, da Madeira Freitas EM, Resende RR, Klempin F, Ulrich H, Gomez RS, Pinto MCX (2020) Neurobiology of glycine transporters: from molecules to behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 118:97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.07.025
Martinez-Lozada Z, Guillem AM, Robinson MB (2016) Transcriptional regulation of glutamate transporters: from extracellular signals to transcription factors. Adv Pharmacol 76:103–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2016.01.004
Medeiros GC, Roy D, Kontos N, Beach SR (2020) Post-stroke depression: A 2020 updated review. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 66:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.011
Medina A, Watson SJ, Bunney W Jr, Myers RM, Schatzberg A, Barchas J, Akil H, Thompson RC (2016) Evidence for alterations of the glial syncytial function in major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 72:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.10.010
Michel M, Fiebich BL, Kuzior H, Meixensberger S, Berger B, Maier S, Nickel K, Runge K, Denzel D, Pankratz B, Schiele MA, Domschke K, van Elst LT, Endres D (2021) Increased GFAP concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with unipolar depression. Transl Psychiatry 11(1):308. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-021-01423-6
Michinaga S, Koyama Y (2019) Dual roles of astrocyte-derived factors in regulation of blood-brain barrier function after brain damage. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030571
Mitchell AJ, Sheth B, Gill J, Yadegarfar M, Stubbs B, Yadegarfar M, Meader N (2017) Prevalence and predictors of post-stroke mood disorders: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of depression, anxiety and adjustment disorder. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 47:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2017.04.001
Morris PL, Robinson RG, Raphael B, Hopwood MJ (1996) Lesion location and poststroke depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 8(4):399–403. https://doi.org/10.1176/jnp.8.4.399
Nagy C, Suderman M, Yang J, Szyf M, Mechawar N, Ernst C, Turecki G (2015) Astrocytic abnormalities and global DNA methylation patterns in depression and suicide. Mol Psychiatry 20(3):320–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.21
Nagy EE, Frigy A, Szasz JA, Horvath E (2020) Neuroinflammation and microglia/macrophage phenotype modulate the molecular background of post-stroke depression: a literature review. Exp Ther Med 20(3):2510–2523. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8933
Nie Y, Wen L, Li H, Song J, Wang N, Huang L, Gao L, Qu M (2022) Tanhuo formula inhibits astrocyte activation and apoptosis in acute ischemic stroke. Front Pharmacol 13:859244. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.859244
Oh DH, Son H, Hwang S, Kim SH (2012) Neuropathological abnormalities of astrocytes, GABAergic neurons, and pyramidal neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortices of patients with major depressive disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 22(5):330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.09.001
O’Leary LA, Belliveau C, Davoli MA, Ma JC, Tanti A, Turecki G, Mechawar N (2021) Widespread decrease of cerebral vimentin-immunoreactive astrocytes in depressed suicides. Front Psychiatry 12:640963. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.640963
Pan SM, Pan Y, Tang YL, Zuo N, Zhang YX, Jia KK, Kong LD (2022a) Thioredoxin interacting protein drives astrocytic glucose hypometabolism in corticosterone-induced depressive state. J Neurochem 161(1):84–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15489
Pan SM, Zhou YF, Zuo N, Jiao RQ, Kong LD, Pan Y (2022b) Fluoxetine increases astrocytic glucose uptake and glycolysis in corticosterone-induced depression through restricting GR-TXNIP-GLUT1 Pathway. Front Pharmacol 13:872375. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.872375
Pellerin L (2018) Neuroenergetics: astrocytes have a sweet spot for glucose. Curr Biol 28(21):R1258–R1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.09.042
Peng L, Huang J (2012) Astrocytic 5-HT(2B) receptor as in vitro and in vivo target of SSRIs. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 7(3):243–253. https://doi.org/10.2174/157488912803252078
Peng L, Verkhratsky A, Gu L, Li B (2015) Targeting astrocytes in major depression. Expert Rev Neurother 15(11):1299–1306. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.2015.1095094
Popa-Wagner A, Dinca I, Yalikun S, Walker L, Kroemer H, Kessler C (2006) Accelerated delimitation of the infarct zone by capillary-derived nestin-positive cells in aged rats. Curr Neurovasc Res 3(1):3–13. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720206775541732
Proia P, Di Liegro CM, Schiera G, Fricano A, Di Liegro I (2016) Lactate as a metabolite and a regulator in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091450
Rajkowska G, Legutko B, Moulana M, Syed M, Romero DG, Stockmeier CA, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ (2018) Astrocyte pathology in the ventral prefrontal white matter in depression. J Psychiatr Res 102:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.04.005
Rana T, Behl T, Shamsuzzaman M, Singh S, Sharma N, Sehgal A, Alshahrani AM, Aldahish A, Chidambaram K, Dailah HG, Bhatia S, Bungau S (2022) Exploring the role of astrocytic dysfunction and AQP4 in depression. Cell Signal 96:110359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110359
Rappeneau V, Blaker A, Petro JR, Yamamoto BK, Shimamoto A (2016) Disruption of the glutamate-glutamine cycle involving astrocytes in an animal model of depression for males and females. Front Behav Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00231
Revuelta M, Elicegui A, Moreno-Cugnon L, Buhrer C, Matheu A, Schmitz T (2019) Ischemic stroke in neonatal and adult astrocytes. Mech Ageing Dev 183:111147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2019.111147
Rosa CE, Soares JC, Figueiredo FP, Cavalli RC, Barbieri MA, Schaufelberger MS, Salmon CEG, Del-Ben CM, Santos AC (2017) Glutamatergic and neural dysfunction in postpartum depression using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 265:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.04.008
Shan D, Zheng Y, Froud K (2021) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a clinical biomarker in predicting the development of post-stroke depression: a review of evidence. Cureus. 13(6):e15662. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.15662
Shiroyama T, Fukuyama K, Okada M (2021) Distinct effects of escitalopram and vortioxetine on astroglial l-glutamate release associated with connexin43. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221810013
Shu X, Sun Y, Sun X, Zhou Y, Bian Y, Shu Z, Ding J, Lu M, Hu G (2019) The effect of fluoxetine on astrocyte autophagy flux and injured mitochondria clearance in a mouse model of depression. Cell Death Dis 10(8):577. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1813-9
Song S, Huang H, Guan X, Fiesler V, Bhuiyan MIH, Liu R, Jalali S, Hasan MN, Tai AK, Chattopadhyay A, Chaparala S, Sun M, Stolz DB, He P, Agalliu D, Sun D, Begum G (2021) Activation of endothelial Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by protective astrocytes repairs BBB damage in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 199:101963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101963
Steinacker P, Al Shweiki MR, Oeckl P, Graf H, Ludolph AC, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C, Otto M (2021) Glial fibrillary acidic protein as blood biomarker for differential diagnosis and severity of major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 144:54–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.09.012
Stenovec M, Li B, Verkhratsky A, Zorec R (2020) Astrocytes in rapid ketamine antidepressant action. Neuropharmacology 173:108158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108158
Sun C, Lin L, Yin L, Hao X, Tian J, Zhang X, Ren Y, Li C, Yang Y (2022) Acutely inhibiting AQP4 With TGN-020 improves functional outcome by attenuating edema and peri-infarct astrogliosis after cerebral ischemia. Front Immunol 13:870029. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.870029
Suzuki A, Stern SA, Bozdagi O, Huntley GW, Walker RH, Magistretti PJ, Alberini CM (2011) Astrocyte-neuron lactate transport is required for long-term memory formation. Cell 144(5):810–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.018
Takano K, Yamasaki H, Kawabe K, Moriyama M, Nakamura Y (2012) Imipramine induces brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in cultured astrocytes. J Pharmacol Sci 120(3):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.12039fp
Tang WK, Tang N, Liao CD, Liang HJ, Mok VC, Ungvari GS, Wong KS (2013) Serotonin receptor 2C gene polymorphism associated with post-stroke depression in Chinese patients. Genet Mol Res 12(2):1546–1553. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.May.13.8
Tene O, Hallevi H, Molad J, Usher S, Seyman E, Bornstein NM, Shenhar-Tsarfaty S, Ben Assayag E (2021) CCR5-Delta32 polymorphism: a possible protective factor for post-stroke depressive symptoms. J Psychiatry Neurosci 46(4):E431–E440. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.200197
Tokunaga N, Takimoto T, Nakamura Y, Hisaoka-Nakashima K, Morioka N (2022) Downregulation of connexin 43 potentiates amitriptyline-induced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in primary astrocytes through lysophosphatidic acid receptor(1/3), Src, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Eur J Pharmacol 925:174986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174986
Tong X, Ao Y, Faas GC, Nwaobi SE, Xu J, Haustein MD, Anderson MA, Mody I, Olsen ML, Sofroniew MV, Khakh BS (2014) Astrocyte Kir41 ion channel deficits contribute to neuronal dysfunction in Huntington’s disease model mice. Nat Neurosci 17(5):694–703. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3691
Torres-Platas SG, Nagy C, Wakid M, Turecki G, Mechawar N (2016) Glial fibrillary acidic protein is differentially expressed across cortical and subcortical regions in healthy brains and downregulated in the thalamus and caudate nucleus of depressed suicides. Mol Psychiatry 21(4):509–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.65
Tural U, Irvin MK, Iosifescu DV (2022) Correlation between S100B and severity of depression in MDD: a meta-analysis. World J Biol Psychiatry 23(6):456–463. https://doi.org/10.1080/15622975.2021.2013042
Valenza M, Facchinetti R, Steardo L, Scuderi C (2019) Altered waste disposal system in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: focus on astrocytic aquaporin-4. Front Pharmacol 10:1656. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01656
Vandebroek A, Yasui M (2020) Regulation of AQP4 in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051603
Villa RF, Ferrari F, Moretti A (2018) Post-stroke depression: mechanisms and pharmacological treatment. Pharmacol Ther 184:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.11.005
Wang X, Li YH, Li MH, Lu J, Zhao JG, Sun XJ, Zhang B, Ye JL (2012) Glutamate level detection by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with post-stroke depression. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262(1):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-011-0209-3
Wang Q, Jie W, Liu J-H, Yang J-M, Gao T-M (2017) An astroglial basis of major depressive disorder? An Overview Glia 65(8):1227–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23143
Wang YJ, Li ZX, Gu HQ, Zhai Y, Zhou Q, Jiang Y, Zhao XQ, Wang YL, Yang X, Wang CJ, Meng X, Li H, Liu LP, Jing J, Wu J, Xu AD, Dong Q, Wang D, Wang WZ, Ma XD, Zhao JZ (2022) China stroke statistics: an update on the 2019 report from the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in neurological diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for neurological diseases, The Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for chronic and non-communicable disease control and prevention, Chinese Center for disease control and prevention and Institute for Global Neuros. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7(5):415–450. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2021-001374
Wijeratne T, Sales C (2021) Understanding why post-stroke depression may be the norm rather than the exception: the anatomical and neuroinflammatory correlates of post-stroke depression. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10081674
Xie X-H, Lai W-T, Xu S-X, Di Forti M, Zhang J-Y, Chen M-M, Yao L-H, Wang P, Hao K-K, Rong H (2023) Hyper-inflammation of astrocytes in patients of major depressive disorder: evidence from serum astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles. Brain Behav Immun 109:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2022.12.014
Xiong Z, Zhang K, Ren Q, Chang L, Chen J, Hashimoto K (2019) Increased expression of inwardly rectifying Kir4.1 channel in the parietal cortex from patients with major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 245:265–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.11.016
Yang X, Yun Y, Wang P, Zhao J, Sun X (2022) Upregulation of RCAN1.4 by HIF1alpha alleviates OGD-induced inflammatory response in astrocytes. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 9(8):1224–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.51624
Yao S, Xu M-D, Wang Y, Zhao S-T, Wang J, Chen G-F, Chen W-B, Liu J, Huang G-B, Sun W-J, Zhang Y-Y, Hou H-L, Li L, Sun X-D (2023a) Astrocytic lactate dehydrogenase a regulates neuronal excitability and depressive-like behaviors through lactate homeostasis in mice. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36209-5
Yao S, Xu MD, Wang Y, Zhao ST, Wang J, Chen GF, Chen WB, Liu J, Huang GB, Sun WJ, Zhang YY, Hou HL, Li L, Sun XD (2023b) Astrocytic lactate dehydrogenase a regulates neuronal excitability and depressive-like behaviors through lactate homeostasis in mice. Nat Commun 14(1):729. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36209-5
Yu D, Cheng Z, Ali AI, Wang J, Le K, Chibaatar E, Guo Y (2019) Down-expressed GLT-1 in PSD astrocytes inhibits synaptic formation of NSC-derived neurons in vitro. Cell Cycle 18(1):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1560201
Zhang HY, Wang Y, He Y, Wang T, Huang XH, Zhao CM, Zhang L, Li SW, Wang C, Qu YN, Jiang XX (2020) A1 astrocytes contribute to murine depression-like behavior and cognitive dysfunction, which can be alleviated by IL-10 or fluorocitrate treatment. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01871-9
Zhang L, Verwer RWH, Zhao J, Huitinga I, Lucassen PJ, Swaab DF (2021) Changes in glial gene expression in the prefrontal cortex in relation to major depressive disorder, suicide and psychotic features. J Affect Disord 295:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.098
Zhang C, Wang X, Zhu Q, Mei Y, Zhang Z, Xu H (2022) Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in poststroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Psychiatry. 13:876557. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.876557
Zhang X, Wang CB, Duan LH, Long JJ, Xiao P, Wang YL, Zhang XH, Liu Q (2023) Correlation research of serum substance P, CCK-8, and 5-HT values with depression levels in stroke survivors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 27(4):1248–1254
Zhao Q, Guo Y, Yang D, Yang T, Meng X (2016) Serotonin transporter gene 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism as a protective factor against the progression of post-stroke depression. Mol Neurobiol 53(3):1699–1705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9120-7
Zhao A, Ma B, Xu L, Yao M, Zhang Y, Xue B, Ren J, Chang D, Liu J (2021) Jiedu tongluo granules ameliorates post-stroke depression rat model via regulating NMDAR/BDNF signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 12:662003. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.662003
Zhao J, Sun J, Zheng Y, Zheng Y, Shao Y, Li Y, Fei F, Xu C, Liu X, Wang S, Ruan Y, Liu J, Duan S, Chen Z, Wang Y (2022a) Activated astrocytes attenuate neocortical seizures in rodent models through driving Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase. Nat Commun 13(1):7136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34662-2
Zhao YF, Verkhratsky A, Tang Y, Illes P (2022b) Astrocytes and major depression: the purinergic avenue. Neuropharmacology 220:109252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109252
Zhou L, Wang T, Yu Y, Li M, Sun X, Song W, Wang Y, Zhang C, Fu F (2022) The etiology of poststroke-depression: a hypothesis involving HPA axis. Biomed Pharmacother 151:113146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113146
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82170865), Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province (2020Q140), Science and Technology Innovation Program of Weifang Medical University (04101401), and Taishan Scholars Project of Shandong Province (tsqn202211365).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DQJ and XLH were responsible for conceptualization, methodology, data curation, and writing and original draft preparation; JLL and XDS were responsible for supervision, writing, reviewing, and editing of the manuscript, and funding acquisition; others were responsible for data curation and investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, D., Hou, X., Guo, X. et al. Astrocytes in Post-Stroke Depression: Roles in Inflammation, Neurotransmission, and Neurotrophin Signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 3301–3313 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01386-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01386-w