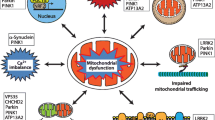
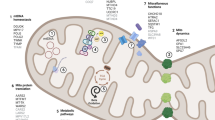
Abstract
Neurodegeneration is among the most critical challenges that involve modern societies and annually influences millions of patients worldwide. While the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is complicated, the role of mitochondrial is demonstrated. The in vitro and in vivo models and genome-wide association studies in human cases proved that specific genes, including PINK1, Parkin, DJ-1, SNCA, and LRRK2, linked mitochondrial dysfunction with PD. Also, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) plays an essential role in the pathophysiology of PD. Targeting mitochondria as a therapeutic approach to inhibit or slow down PD formation and progression seems to be an exciting issue. The current review summarized known mutations associated with both mitochondrial dysfunction and PD. The significance of mtDNA in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis and potential PD therapeutic approaches targeting mitochondrial dysfunction was then discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer's disease
- CDCrel-1:
-
Cell division control-related protein 1
- DA neuron:
-
Dopaminergic neuron
- ETC:
-
Electron transport chain
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
- HTRA2:
-
High-temperature requirement protein A2
- IBR:
-
In-between-ring
- LRRK2:
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2
- mtDNA:
-
Mitochondrial DNA
- NdufA10:
-
NADH dehydrogenase ubiquinone 1α sub-complex 10
- NESC:
-
Neuroepithelial stem cells
- NFκB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- Nrf2/ARE:
-
The nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/antioxidant receptor element
- PD:
-
Parkinson's disease
- PINK1:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced kinase 1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SNCA:
-
Alpha-synuclein
- TFAM:
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A
- TRAP1:
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1
- Ubl:
-
Ubiquitin-like
- UPS:
-
Ubiquitin–proteasome system
- UQ:
-
Ubiquitin
- VPS35:
-
Vascular protein sorting-associated protein 35
References
Abdelkader NF, Safar MM, Salem HA (2016) Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates apoptotic cascade in the rotenone model of parkinson’s disease: modulation of mitochondrial perturbations. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):810–817. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9043-8
Abrahams S, Miller HC, Lombard C, van der Westhuizen FH, Bardien S (2021) Curcumin pre-treatment may protect against mitochondrial damage in LRRK2-mutant Parkinson’s disease and healthy control fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Rep 27:101035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101035
Aerts L, Craessaerts K, De Strooper B, Morais VA (2015) PINK1 kinase catalytic activity is regulated by phosphorylation on serines 228 and 402. J Biol Chem 290(5):2798–2811
Aman Y, Ryan B, Torsetnes SB, Knapskog A-B, Watne LO, McEwan WA, Fang EF (2020) Enhancing mitophagy as a therapeutic approach for neurodegenerative diseases. Int Rev Neurobiol 155:169–202
Ammal Kaidery N, Thomas B (2018) Current perspective of mitochondrial biology in parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 117:91–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2018.03.001
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA, Aggarwal BB (2007) Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises. Mol Pharm 4(6):807–818. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp700113r
Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, de Bruijn MH, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreier PH, Smith AJ, Staden R, Young IG (1981) Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290(5806):457–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/290457a0
Andres RH, Huber AW, Schlattner U, Pérez-Bouza A, Krebs SH, Seiler RW, Wallimann T, Widmer HR (2005) Effects of creatine treatment on the survival of dopaminergic neurons in cultured fetal ventral mesencephalic tissue. Neuroscience 133(3):701–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.03.004
Anis E, Zafeer MF, Firdaus F, Islam SN, Anees Khan A, Ali A, Hossain MM (2020) Ferulic acid reinstates mitochondrial dynamics through PGC1α expression modulation in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Phytotherapy Research : PTR 34(1):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6523
Anvret A, Westerlund M, Sydow O, Willows T, Lind C, Galter D, Belin AC (2010) Variations of the CAG trinucleotide repeat in DNA polymerase γ (POLG1) is associated with parkinson’s disease in Sweden. Neurosci Lett 485(2):117–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.082
Arias-Fuenzalida J, Jarazo J, Qing X, Walter J, Gomez-Giro G, Nickels SL, Zaehres H, Schöler HR, Schwamborn JC (2017) FACS-assisted CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing facilitates parkinson’s disease modeling. Stem Cell Rep 9(5):1423–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.08.026
Athauda D, Maclagan K, Skene SS, Bajwa-Joseph M, Letchford D, Chowdhury K, Hibbert S, Budnik N, Zampedri L, Dickson J, Li Y, Aviles-Olmos I, Warner TT, Limousin P, Lees AJ, Greig NH, Tebbs S, Foltynie T (2017) Exenatide once weekly versus placebo in parkinson’s disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (london, England) 390(10103):1664–1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)31585-4
Balafkan N, Tzoulis C, Müller B, Haugarvoll K, Tysnes OB, Larsen JP, Bindoff LA (2012) Number of CAG repeats in POLG1 and its association with parkinson disease in the Norwegian population. Mitochondrion 12(6):640–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2012.08.004
Baloh RH, Salavaggione E, Milbrandt J, Pestronk A (2007) Familial parkinsonism and ophthalmoplegia from a mutation in the mitochondrial DNA helicase twinkle. Arch Neurol 64(7):998–1000. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.7.998
Barceló-Coblijn G, Golovko MY, Weinhofer I, Berger J, Murphy EJ (2007) Brain neutral lipids mass is increased in alpha-synuclein gene-ablated mice. J Neurochem 101(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04348.x
Beal MF, Matthews RT, Tieleman A, Shults CW (1998) Coenzyme Q10 attenuates the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) induced loss of striatal dopamine and dopaminergic axons in aged mice. Brain Res 783(1):109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(97)01192-x
Bender A, Koch W, Elstner M, Schombacher Y, Bender J, Moeschl M, Gekeler F, Müller-Myhsok B, Gasser T, Tatsch K, Klopstock T (2006a) Creatine supplementation in parkinson disease: a placebo-controlled randomized pilot trial. Neurology 67(7):1262–1264. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000238518.34389.12
Bender A, Krishnan KJ, Morris CM, Taylor GA, Reeve AK, Perry RH, Jaros E, Hersheson JS, Betts J, Klopstock T, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM (2006b) High levels of mitochondrial DNA deletions in substantia nigra neurons in aging and parkinson disease. Nat Genet 38(5):515–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1769
Bendor JT, Logan TP, Edwards RH (2013) The function of α-synuclein. Neuron 79(6):1044–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.09.004
Bennett JP Jr, Keeney PM (2020) Alzheimer’s and parkinson’s brain tissues have reduced expression of genes for mtDNA OXPHOS proteins, mitobiogenesis regulator PGC-1α protein and mtRNA stabilizing protein LRPPRC (LRP130). Mitochondrion 53:154–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2020.05.012
Bentley SR, Shan J, Todorovic M, Wood SA, Mellick GD (2014) Rare POLG1 CAG variants do not influence parkinson’s disease or polymerase gamma function. Mitochondrion 15:65–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2014.01.004
Berman SB, Chen YB, Qi B, McCaffery JM, Rucker EB 3rd, Goebbels S, Nave KA, Arnold BA, Jonas EA, Pineda FJ, Hardwick JM (2009) Bcl-x L increases mitochondrial fission, fusion, and biomass in neurons. J Cell Biol 184(5):707–719. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200809060
Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O, Andersson A, Dannaeus K, Heidrich J, Kortesmaa J, Mercer A, Nielsen E, Rönnholm H, Wikström L (2008) Peptide hormone exendin-4 stimulates subventricular zone neurogenesis in the adult rodent brain and induces recovery in an animal model of parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 86(2):326–338. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21483
Biju KC, Evans RC, Shrestha K, Carlisle DCB, Gelfond J, Clark RA (2018) Methylene blue ameliorates olfactory dysfunction and motor deficits in a chronic MPTP/probenecid mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 380:111–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.008
Blackinton J, Lakshminarasimhan M, Thomas KJ, Ahmad R, Greggio E, Raza AS, Cookson MR, Wilson MA (2009) Formation of a stabilized cysteine sulfinic acid is critical for the mitochondrial function of the parkinsonism protein DJ-1. J Biol Chem 284(10):6476–6485. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M806599200
Bonkowski MS, Sinclair DA (2016) Slowing ageing by design: the rise of NAD(+) and sirtuin-activating compounds. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(11):679–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.93
Boon JY, Dusonchet J, Trengrove C, Wolozin B (2014) Interaction of LRRK2 with kinase and GTPase signaling cascades. Front Mol Neurosci 7:64. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2014.00064
Borsche M, Pereira SL, Klein C, Grünewald A (2021) Mitochondria and parkinson’s disease: clinical, molecular, and translational aspects. J Parkinsons Dis 11(1):45–60
Bose A, Beal MF (2016) Mitochondrial dysfunction in parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 139:216–231
Braschi E, Goyon V, Zunino R, Mohanty A, Xu L, McBride HM (2010) Vps35 mediates vesicle transport between the mitochondria and peroxisomes. Curr Biol 20(14):1310–1315
Cannon JR, Geghman KD, Tapias V, Sew T, Dail MK, Li C, Greenamyre JT (2013) Expression of human E46K-mutated α-synuclein in BAC-transgenic rats replicates early-stage parkinson’s disease features and enhances vulnerability to mitochondrial impairment. Exp Neurol 240:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.11.007
Carbone C, Costa A, Provensi G, Mannaioni G, Masi A (2017) The hyperpolarization-activated current determines synaptic excitability, calcium activity and specific viability of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 11:187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00187
Castro-Caldas M, Carvalho AN, Rodrigues E, Henderson CJ, Wolf CR, Rodrigues CM, Gama MJ (2012) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid prevents MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell death in a mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 46(2):475–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8295-4
Chakraborty J, von Stockum S, Marchesan E, Caicci F, Ferrari V, Rakovic A, Klein C, Antonini A, Bubacco L, Ziviani E (2018) USP 14 inhibition corrects an in vivo model of impaired mitophagy. EMBO Mol Med 10(11):e9014
Chan SS, Copeland WC (2009) DNA polymerase gamma and mitochondrial disease: understanding the consequence of POLG mutations. Biochem Biophys Acta 1787(5):312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.10.007
Chandra G, Kundu M, Rangasamy SB, Dasarathy S, Ghosh S, Watson R, Pahan K (2018) Increase in Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Neuronal Cells by RNS60, a Physically-Modified Saline, via Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Mediated Upregulation of PGC1α. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 13(2):143–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-017-9771-4
Chandra G, Shenoi RA, Anand R, Rajamma U, Mohanakumar KP (2019) Reinforcing mitochondrial functions in aging brain: an insight into parkinson’s disease therapeutics. J Chem Neuroanat 95:29–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.12.004
Chang J-C, Wu S-L, Liu K-H, Chen Y-H, Chuang C-S, Cheng F-C, Su H-L, Wei Y-H, Kuo S-J, Liu C-S (2016) Allogeneic/xenogeneic transplantation of peptide-labeled mitochondria in parkinson’s disease: restoration of mitochondria functions and attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine–induced neurotoxicity. Transl Res 170(40–56):e43
Chang C-Y, Liang M-Z, Chen L (2019) Current progress of mitochondrial transplantation that promotes neuronal regeneration. Transl Neurodegener 8(1):1–12
Chang J-C, Chao Y-C, Chang H-S, Wu Y-L, Chang H-J, Lin Y-S, Cheng W-L, Lin T-T, Liu C-S (2021) Intranasal delivery of mitochondria for treatment of parkinson’s disease model rats lesioned with 6-hydroxydopamine. Sci Rep 11(1):1–14
Chen C, Vincent AE, Blain AP, Smith AL, Turnbull DM, Reeve AK (2020) Investigation of mitochondrial biogenesis defects in single substantia nigra neurons using post-mortem human tissues. Neurobiol Dis 134:104631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104631
Chinta SJ, Mallajosyula JK, Rane A, Andersen JK (2010) Mitochondrial α-synuclein accumulation impairs complex I function in dopaminergic neurons and results in increased mitophagy in vivo. Neurosci Lett 486(3):235–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.061
Chuang C-S, Chang J-C, Cheng F-C, Liu K-H, Su H-L, Liu C-S (2017) Modulation of mitochondrial dynamics by treadmill training to improve gait and mitochondrial deficiency in a rat model of parkinson’s disease. Life Sci 191:236–244
Chun HS, Low WC (2012) Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses mitochondria-dependent programmed cell death induced by sodium nitroprusside in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology 292(2–3):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2011.11.020
Cichewicz RH, Kouzi SA (2004) Chemistry, biological activity, and chemotherapeutic potential of betulinic acid for the prevention and treatment of cancer and HIV infection. Med Res Rev 24(1):90–114
Clark IE, Dodson MW, Jiang C, Cao JH, Huh JR, Seol JH, Yoo SJ, Hay BA, Guo M (2006) Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature 441(7097):1162–1166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04779
Copeland WC, Longley MJ (2003) DNA polymerase gamma in mitochondrial DNA replication and repair. TheScientificWorldJOURNAL 3:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2003.09
Cornelissen T, Spinazzi M, Martin S, Imberechts D, Vangheluwe P, Bird M, De Strooper B, Vandenberghe W (2020) CHCHD2 harboring parkinson’s disease-linked T61I mutation precipitates inside mitochondria and induces precipitation of wild-type CHCHD2. Hum Mol Genet 29(7):1096–1106. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddaa028
Costa LG, Garrick JM, Roquè PJ, Pellacani C (2016) Mechanisms of neuroprotection by quercetin: counteracting oxidative stress and more. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:2986796. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2986796
Coxhead J, Kurzawa-Akanbi M, Hussain R, Pyle A, Chinnery P, Hudson G (2016) Somatic mtDNA variation is an important component of parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 38:217 e211-217 e216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.036
Davidzon G, Greene P, Mancuso M, Klos KJ, Ahlskog JE, Hirano M, DiMauro S (2006) Early-onset familial parkinsonism due to POLG mutations. Ann Neurol 59(5):859–862. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20831
de Paula MR, Glaser V, Aguiar AS Jr, de Paula Ferreira PM, Ghisoni K, da Luz SD, Lanfumey L, Raisman-Vozari R, Corti O, De Paul AL (2018) De novo tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis is impaired in the inflammed striatum of parkin (−/−) mice. Cell Biol Int 42(6):725–733
Deng H, Wang P, Jankovic J (2018) The genetics of parkinson disease. Ageing Res Rev 42:72–85
Devi L, Raghavendran V, Prabhu BM, Avadhani NG, Anandatheerthavarada HK (2008) Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem 283(14):9089–9100. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710012200
Dolhun R, Presant EM, Hedera P (2013) Novel polymerase gamma (POLG1) gene mutation in the linker domain associated with parkinsonism. BMC Neurol 13:92. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-13-92
Dölle C, Flønes I, Nido GS, Miletic H, Osuagwu N, Kristoffersen S, Lilleng PK, Larsen JP, Tysnes OB, Haugarvoll K, Bindoff LA, Tzoulis C (2016) Defective mitochondrial DNA homeostasis in the substantia nigra in parkinson disease. Nat Commun 7:13548. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13548
Dorsey ER, Elbaz A, Nichols E, Abbasi N, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Adsuar JC, Ansha MG, Brayne C, Choi J-YJ (2018) Global, regional, and national burden of parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol 17(11):939–953
East DA, Campanella M (2016) Mitophagy and the therapeutic clearance of damaged mitochondria for neuroprotection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 79:382–387
Eerola J, Luoma PT, Peuralinna T, Scholz S, Paisan-Ruiz C, Suomalainen A, Singleton AB, Tienari PJ (2010) POLG1 polyglutamine tract variants associated with parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 477(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.04.021
Fares MB, Jagannath S, Lashuel HA (2021) Reverse engineering Lewy bodies: how far have we come and how far can we go? Nat Rev Neurosci 22(2):111–131
Ferreira AFF, Binda KH, Singulani MP, Pereira CPM, Ferrari GD, Alberici LC, Real CC, Britto LR (2020) Physical exercise protects against mitochondria alterations in the 6-hidroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res 387:112607
Fountaine TM, Wade-Martins R (2007) RNA interference-mediated knockdown of alpha-synuclein protects human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells from MPP(+) toxicity and reduces dopamine transport. J Neurosci Res 85(2):351–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21125
Funayama M, Ohe K, Amo T, Furuya N, Yamaguchi J, Saiki S, Li Y, Ogaki K, Ando M, Yoshino H, Tomiyama H, Nishioka K, Hasegawa K, Saiki H, Satake W, Mogushi K, Sasaki R, Kokubo Y, Kuzuhara S, Toda T, Mizuno Y, Uchiyama Y, Ohno K, Hattori N (2015) CHCHD2 mutations in autosomal dominant late-onset parkinson’s disease: a genome-wide linkage and sequencing study. Lancet Neurol 14(3):274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(14)70266-2
Geisler S, Holmström KM, Skujat D, Fiesel FC, Rothfuss OC, Kahle PJ, Springer W (2010) PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy is dependent on VDAC1 and p62/SQSTM1. Nat Cell Biol 12(2):119–131
Gerhardt E, Gräber S, Szego EM, Moisoi N, Martins LM, Outeiro TF, Kermer P (2011) Idebenone and resveratrol extend lifespan and improve motor function of HtrA2 knockout mice. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28855. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028855
Giannoccaro MP, La Morgia C, Rizzo G, Carelli V (2017) Mitochondrial DNA and primary mitochondrial dysfunction in parkinson’s disease. Mov Dis 32(3):346–363. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26966
Giorgio V, Schiavone M, Galber C, Carini M, Da Ros T, Petronilli V, Argenton F, Carelli V, Acosta Lopez MJ, Salviati L, Prato M, Bernardi P (2018) The idebenone metabolite QS10 restores electron transfer in complex I and coenzyme Q defects. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859(9):901–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.04.006
Grassi D, Howard S, Zhou M, Diaz-Perez N, Urban NT, Guerrero-Given D, Kamasawa N, Volpicelli-Daley LA, LoGrasso P, Lasmézas CI (2018) Identification of a highly neurotoxic α-synuclein species inducing mitochondrial damage and mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(11):E2634–E2643. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1713849115
Gray MW, Lang BF, Cedergren R, Golding GB, Lemieux C, Sankoff D, Turmel M, Brossard N, Delage E, Littlejohn TG, Plante I, Rioux P, Saint-Louis D, Zhu Y, Burger G (1998) Genome structure and gene content in protist mitochondrial DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 26(4):865–878. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.4.865
Grünewald A, Kasten M, Ziegler A, Klein C (2013) Next-generation phenotyping using the parkin example: time to catch up with genetics. JAMA Neurol 70(9):1186–1191
Grünewald A, Rygiel KA, Hepplewhite PD, Morris CM, Picard M, Turnbull DM (2016) Mitochondrial DNA depletion in respiratory chain-deficient parkinson disease neurons. Ann Neurol 79(3):366–378. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24571
Grünewald A, Kumar KR, Sue CM (2019) New insights into the complex role of mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 177:73–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.09.003
Gu G, Reyes PE, Golden GT, Woltjer RL, Hulette C, Montine TJ, Zhang J (2002) Mitochondrial DNA deletions/rearrangements in parkinson disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61(7):634–639. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/61.7.634
Gui Y-x, Xu Z-p, Lv W, Liu H-m, Zhao J-J, Hu X-Y (2012) Association of mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ gene POLG1 polymorphisms with parkinsonism in Chinese populations. PLoS ONE 7(12):e50086
Gureev AP, Popov VN (2019) Nrf2/ARE pathway as a therapeutic target for the treatment of parkinson diseases. Neurochem Res 44(10):2273–2279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-02711-2
Haleagrahara N, Siew CJ, Mitra NK, Kumari M (2011) Neuroprotective effect of bioflavonoid quercetin in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress biomarkers in the rat striatum. Neurosci Lett 500(2):139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.06.021
Hallberg BM, Larsson NG (2011) TFAM forces mtDNA to make a U-turn. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18(11):1179–1181. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2167
Heeman B, Van den Haute C, Aelvoet SA, Valsecchi F, Rodenburg RJ, Reumers V, Debyser Z, Callewaert G, Koopman WJ, Willems PH, Baekelandt V (2011) Depletion of PINK1 affects mitochondrial metabolism, calcium homeostasis and energy maintenance. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 7):1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.078303
Heo JY, Park JH, Kim SJ, Seo KS, Han JS, Lee SH, Kim JM, Park JI, Park SK, Lim K, Hwang BD, Shong M, Kweon GR (2012) DJ-1 null dopaminergic neuronal cells exhibit defects in mitochondrial function and structure: involvement of mitochondrial complex I assembly. PLoS ONE 7(3):e32629. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032629
Ho DH, Kim H, Kim J, Sim H, Ahn H, Kim J, Seo H, Chung KC, Park BJ, Son I, Seol W (2015) Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2) phosphorylates p53 and induces p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. Mol Brain 8:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-015-0145-7
Huang X, Wu BP, Nguyen D, Liu YT, Marani M, Hench J, Bénit P, Kozjak-Pavlovic V, Rustin P, Frank S, Narendra DP (2019) CHCHD2 accumulates in distressed mitochondria and facilitates oligomerization of CHCHD10. Hum Mol Genet 28(2):349. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddy340
Hudson G, Chinnery PF (2006) Mitochondrial DNA polymerase-gamma and human disease. Human Mol Genet 15(2):R244-252. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl233
Hudson G, Schaefer AM, Taylor RW, Tiangyou W, Gibson A, Venables G, Griffiths P, Burn DJ, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF (2007) Mutation of the linker region of the polymerase gamma-1 (POLG1) gene associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia and parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 64(4):553–557. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.64.4.553
Hudson G, Tiangyou W, Stutt A, Eccles M, Robinson L, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF (2009) No association between common POLG1 variants and sporadic idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24(7):1092–1094
Ikebe S-i, Tanaka M, Ozawa T (1995) Point mutations of mitochondrial genome in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Brain Res 28(2):281–295
Ikeda A, Nishioka K, Meng H, Takanashi M, Hasegawa I, Inoshita T, Shiba-Fukushima K, Li Y, Yoshino H, Mori A, Okuzumi A, Yamaguchi A, Nonaka R, Izawa N, Ishikawa KI, Saiki H, Morita M, Hasegawa M, Hasegawa K, Elahi M, Funayama M, Okano H, Akamatsu W, Imai Y, Hattori N (2019) Mutations in CHCHD2 cause α-synuclein aggregation. Hum Mol Genet 28(23):3895–3911. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz241
Inose Y, Izumi Y, Takada-Takatori Y, Akaike A, Koyama Y, Kaneko S, Kume T (2020) Protective effects of Nrf2-ARE activator on dopaminergic neuronal loss in Parkinson disease model mice: Possible involvement of heme oxygenase-1. Neurosci Lett 736:135268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135268
Inoue N, Ogura S, Kasai A, Nakazawa T, Ikeda K, Higashi S, Isotani A, Baba K, Mochizuki H, Fujimura H, Ago Y, Hayata-Takano A, Seiriki K, Shintani Y, Shintani N, Hashimoto H (2018) Knockdown of the mitochondria-localized protein p13 protects against experimental parkinsonism. EMBO Rep. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201744860
Invernizzi F, Varanese S, Thomas A, Carrara F, Onofrj M, Zeviani M (2008) Two novel POLG1 mutations in a patient with progressive external ophthalmoplegia, levodopa-responsive pseudo-orthostatic tremor and parkinsonism. Neuromuscul Dis 18(6):460–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2008.04.005
Irrcher I, Aleyasin H, Seifert EL, Hewitt SJ, Chhabra S, Phillips M, Lutz AK, Rousseaux MW, Bevilacqua L, Jahani-Asl A, Callaghan S, MacLaurin JG, Winklhofer KF, Rizzu P, Rippstein P, Kim RH, Chen CX, Fon EA, Slack RS, Harper ME, McBride HM, Mak TW, Park DS (2010) Loss of the Parkinson’s disease-linked gene DJ-1 perturbs mitochondrial dynamics. Hum Mol Genet 19(19):3734–3746. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq288
Ishikawa S, Taira T, Takahashi-Niki K, Niki T, Ariga H, Iguchi-Ariga SM (2010) Human DJ-1-specific transcriptional activation of tyrosine hydroxylase gene. J Biol Chem 285(51):39718–39731. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.137034
Jamebozorgi K, Taghizadeh E, Rostami D, Pormasoumi H, Barreto GE, Hayat SMG, Sahebkar A (2019) Cellular and molecular aspects of Parkinson treatment: future therapeutic perspectives. Mol Neurobiol 56(7):4799–4811
Janetzky B, Hauck S, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Jellinger K, Pantucek F, Zo R, Boissl KW, Reichmann H (1994) Unaltered aconitase activity, but decreased complex I activity in substantia nigra pars compacta of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 169(1–2):126–128
Jiang X, Li L, Ying Z, Pan C, Huang S, Li L, Dai M, Yan B, Li M, Jiang H, Chen S, Zhang Z, Wang X (2016) A small molecule that protects the integrity of the electron transfer chain blocks the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Mol Cell 63(2):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.016
Jin F, Wu Q, Lu YF, Gong QH, Shi JS (2008) Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol on 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 600(1–3):78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.005
Jin SM, Lazarou M, Wang C, Kane LA, Narendra DP, Youle RJ (2010) Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates PINK1 import and proteolytic destabilization by PARL. J Cell Biol 191(5):933–942. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201008084
Kakhlon O, Breuer W, Munnich A, Cabantchik ZI (2010) Iron redistribution as a therapeutic strategy for treating diseases of localized iron accumulation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88(3):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1139/y09-128
Karimi-Moghadam A, Charsouei S, Bell B, Jabalameli MR (2018) Parkinson disease from mendelian forms to genetic susceptibility: new molecular insights into the neurodegeneration process. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(6):1153–1178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-0587-4
Kasten M, Hartmann C, Hampf J, Schaake S, Westenberger A, Vollstedt EJ, Balck A, Domingo A, Vulinovic F, Dulovic M (2018) Genotype-phenotype relations for the Parkinson’s disease genes Parkin, PINK1, DJ1: MDSGene systematic review. Mov Disord 33(5):730–741
Kazlauskaite A, Kondapalli C, Gourlay R, Campbell DG, Ritorto MS, Hofmann K, Alessi DR, Knebel A, Trost M, Muqit MM (2014) Parkin is activated by PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of ubiquitin at Ser65. Biochemical Journal 460(1):127–141
Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ishrat T, Khan MB, Hoda MN, Khuwaja G, Raza SS, Khan A, Javed H, Vaibhav K, Islam F (2010) Resveratrol attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage and dopamine depletion in rat model of parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1328:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.02.031
Kiferle L, Orsucci D, Mancuso M, Lo Gerfo A, Petrozzi L, Siciliano G, Ceravolo R, Bonuccelli U (2013) Twinkle mutation in an Italian family with external progressive ophthalmoplegia and parkinsonism: a case report and an update on the state of art. Neurosci Lett 556:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2013.09.034
Kim YY, Um JH, Yoon JH, Kim H, Lee DY, Lee YJ, Jee HJ, Kim YM, Jang JS, Jang YG (2019) Assessment of mitophagy in mt-Keima drosophila revealed an essential role of the PINK1-Parkin pathway in mitophagy induction in vivo. FASEB J 33(9):9742–9751
Klivenyi P, Calingasan NY, Starkov A, Stavrovskaya IG, Kristal BS, Yang L, Wieringa B, Beal MF (2004) Neuroprotective mechanisms of creatine occur in the absence of mitochondrial creatine kinase. Neurobiol Dis 15(3):610–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2003.12.014
Klivenyi P, Siwek D, Gardian G, Yang L, Starkov A, Cleren C, Ferrante RJ, Kowall NW, Abeliovich A, Beal MF (2006) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein are resistant to mitochondrial toxins. Neurobiol Dis 21(3):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2005.08.018
Kogelnik AM, Lott MT, Brown MD, Navathe SB, Wallace DC (1996) MITOMAP: a human mitochondrial genome database. Nucleic Acids Res 24(1):177–179. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.1.177
Kraytsberg Y, Kudryavtseva E, McKee AC, Geula C, Kowall NW, Khrapko K (2006) Mitochondrial DNA deletions are abundant and cause functional impairment in aged human substantia nigra neurons. Nat Genet 38(5):518–520. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1778
Krebiehl G, Ruckerbauer S, Burbulla LF, Kieper N, Maurer B, Waak J, Wolburg H, Gizatullina Z, Gellerich FN, Woitalla D, Riess O, Kahle PJ, Proikas-Cezanne T, Krüger R (2010) Reduced basal autophagy and impaired mitochondrial dynamics due to loss of Parkinson’s disease-associated protein DJ-1. PLoS ONE 5(2):e9367. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009367
Kumar N, Leonzino M, Hancock-Cerutti W, Horenkamp FA, Li P, Lees JA, Wheeler H, Reinisch KM, De Camilli P (2018) VPS13A and VPS13C are lipid transport proteins differentially localized at ER contact sites. J Cell Biol 217(10):3625–3639
Kuroda Y, Mitsui T, Kunishige M, Shono M, Akaike M, Azuma H, Matsumoto T (2006) Parkin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis in proliferating cells. Hum Mol Genet 15(6):883–895. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl006
Kwon SH, Lee SR, Park YJ, Ra M, Lee Y, Pang C, Kim KH (2019) Suppression of 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by hyperoside via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in dopaminergic neurons. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235832
Lai J-H, Chen K-Y, Wu JC-C, Olson L, Brené S, Huang C-Z, Chen Y-H, Kang S-J, Ma K-H, Hoffer BJ (2019) Voluntary exercise delays progressive deterioration of markers of metabolism and behavior in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1720:146301
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219(4587):979–980
Lashuel HA, Overk CR, Oueslati A, Masliah E (2013) The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(1):38–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3406
Lee JJ, Sanchez-Martinez A, Martinez Zarate A, Benincá C, Mayor U, Clague MJ, Whitworth AJ (2018) Basal mitophagy is widespread in drosophila but minimally affected by loss of Pink1 or parkin. J Cell Biol 217(5):1613–1622. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201801044
Lees AJ, Tolosa E, Olanow CW (2015) Four pioneers of L-dopa treatment: Arvid Carlsson, Oleh Hornykiewicz, George Cotzias, and Melvin Yahr. Mov Disord 30(1):19–36
Lesage S, Drouet V, Majounie E, Deramecourt V, Jacoupy M, Nicolas A, Cormier-Dequaire F, Hassoun SM, Pujol C, Ciura S (2016) Loss of VPS13C function in autosomal-recessive parkinsonism causes mitochondrial dysfunction and increases PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Am J Human Genet 98(3):500–513
Li X, Tan YC, Poulose S, Olanow CW, Huang XY, Yue Z (2007) Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2)/PARK8 possesses GTPase activity that is altered in familial Parkinson’s disease R1441C/G mutants. J Neurochem 103(1):238–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04743.x
Li L, Nadanaciva S, Berger Z, Shen W, Paumier K, Schwartz J, Mou K, Loos P, Milici AJ, Dunlop J, Hirst WD (2013) Human A53T α-synuclein causes reversible deficits in mitochondrial function and dynamics in primary mouse cortical neurons. PLoS ONE 8(12):e85815. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085815
Li Z, Wang P, Yu Z, Cong Y, Sun H, Zhang J, Zhang J, Sun C, Zhang Y, Ju X (2015) The effect of creatine and coenzyme q10 combination therapy on mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Eur Neurol 73(3–4):205–211. https://doi.org/10.1159/000377676
Li YI, Wong G, Humphrey J, Raj T (2019) Prioritizing Parkinson’s disease genes using population-scale transcriptomic data. Nat Commun 10(1):1–10
Lin MT, Cantuti-Castelvetri I, Zheng K, Jackson KE, Tan YB, Arzberger T, Lees AJ, Betensky RA, Beal MF, Simon DK (2012) Somatic mitochondrial DNA mutations in early Parkinson and incidental Lewy body disease. Ann Neurol 71(6):850–854. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23568
Lin K-J, Lin K-L, Chen S-D, Liou C-W, Chuang Y-C, Lin H-Y, Lin T-K (2019) The overcrowded crossroads: mitochondria, alpha-synuclein, and the endo-lysosomal system interaction in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(21):5312
Liu G, Zhang C, Yin J, Li X, Cheng F, Li Y, Yang H, Uéda K, Chan P, Yu S (2009) alpha-Synuclein is differentially expressed in mitochondria from different rat brain regions and dose-dependently down-regulates complex I activity. Neurosci Lett 454(3):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.02.056
Liu Q, Zhu D, Jiang P, Tang X, Lang Q, Yu Q, Zhang S, Che Y, Feng X (2019) Resveratrol synergizes with low doses of L-DOPA to improve MPTP-induced Parkinson disease in mice. Behav Brain Res 367:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.03.043
Liu YT, Huang X, Nguyen D, Shammas MK, Wu BP, Dombi E, Springer DA, Poulton J, Sekine S, Narendra DP (2020) Loss of CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 activates OMA1 peptidase to disrupt mitochondrial cristae phenocopying patient mutations. Hum Mol Genet 29(9):1547–1567. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddaa077
Longley MJ, Prasad R, Srivastava DK, Wilson SH, Copeland WC (1998) Identification of 5’-deoxyribose phosphate lyase activity in human DNA polymerase gamma and its role in mitochondrial base excision repair in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(21):12244–12248. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.21.12244
Lu KT, Ko MC, Chen BY, Huang JC, Hsieh CW, Lee MC, Chiou RY, Wung BS, Peng CH, Yang YL (2008) Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on MPTP-induced neuron loss mediated by free radical scavenging. J Agric Food Chem 56(16):6910–6913. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8007212
Ludtmann MHR, Abramov AY (2018) Mitochondrial calcium imbalance in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 663:86–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.044
Luoma P, Melberg A, Rinne JO, Kaukonen JA, Nupponen NN, Chalmers RM, Oldfors A, Rautakorpi I, Peltonen L, Majamaa K, Somer H, Suomalainen A (2004) Parkinsonism, premature menopause, and mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma mutations: clinical and molecular genetic study. Lancet (london, England) 364(9437):875–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(04)16983-3
Luoma P, Eerola J, Ahola S, Hakonen A, Hellström O, Kivistö KT, Tienari PJ, Suomalainen A (2007) Mitochondrial DNA polymerase gamma variants in idiopathic sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 69(11):1152–1159
Luth ES, Stavrovskaya IG, Bartels T, Kristal BS, Selkoe DJ (2014) Soluble, prefibrillar α-synuclein oligomers promote complex I-dependent, Ca2+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. J Biol Chem 289(31):21490–21507. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.545749
MacLeod DA, Rhinn H, Kuwahara T, Zolin A, Di Paolo G, McCabe BD, Marder KS, Honig LS, Clark LN, Small SA (2013) RAB7L1 interacts with LRRK2 to modify intraneuronal protein sorting and Parkinson’s disease risk. Neuron 77(3):425–439
Maita C, Maita H, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H (2013) Monomer DJ-1 and its N-terminal sequence are necessary for mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 mutants. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54087. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054087
Malek N, Swallow D, Grosset KA, Anichtchik O, Spillantini M, Grosset DG (2014) Alpha-synuclein in peripheral tissues and body fluids as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease—a systematic review. Acta Neurol Scand 130(2):59–72. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12247
Malpartida AB, Williamson M, Narendra DP, Wade-Martins R, Ryan BJ (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy in parkinson’s disease: from mechanism to therapy. Trends Biochem Sci 46(4):329–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2020.11.007
Mann V, Cooper J, Krige D, Daniel S, Schapira A, Marsden C (1992) Brain, skeletal muscle and platelet homogenate mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 115(2):333–342
Marder KS, Tang MX, Mejia-Santana H, Rosado L, Louis ED, Comella CL, Colcher A, Siderowf AD, Jennings D, Nance MA (2010) Predictors of parkin mutations in early-onset parkinson disease: the consortium on risk for early-onset parkinson disease study. Arch Neurol 67(6):731–738
Matsuda N, Kitami T, Suzuki T, Mizuno Y, Hattori N, Tanaka K (2006) Diverse effects of pathogenic mutations of Parkin that catalyze multiple monoubiquitylation in vitro. J Biol Chem 281(6):3204–3209. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M510393200
Matsumine H, Saito M, Shimoda-Matsubayashi S, Tanaka H, Ishikawa A, Nakagawa-Hattori Y, Yokochi M, Kobayashi T, Igarashi S, Takano H (1997) Localization of a gene for an autosomal recessive form of juvenile Parkinsonism to chromosome 6q25. 2–27. Am J Human Genet 60(3):588
Mautone N, Zwergel C, Mai A, Rotili D (2020) Sirtuin modulators: where are we now? a review of patents from 2015 to 2019. Expert Opin Ther Pat 30(6):389–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2020.1749264
Melrose H, Lincoln S, Tyndall G, Dickson D, Farrer M (2006) Anatomical localization of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 in mouse brain. Neuroscience 139(3):791–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.017
Meng H, Yamashita C, Shiba-Fukushima K, Inoshita T, Funayama M, Sato S, Hatta T, Natsume T, Umitsu M, Takagi J, Imai Y, Hattori N (2017) Loss of Parkinson’s disease-associated protein CHCHD2 affects mitochondrial crista structure and destabilizes cytochrome c. Nat Commun 8:15500. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15500
Mezzaroba L, Alfieri DF, Colado Simão AN, Vissoci Reiche EM (2019) The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotoxicology 74:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2019.07.007
Miguel R, Gago MF, Martins J, Barros P, Vale J, Rosas MJ (2014) POLG1-related levodopa-responsive parkinsonism. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 126:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.08.020
Minakawa EN, Yamakado H, Tanaka A, Uemura K, Takeda S, Takahashi R (2013) Chicken DT40 cell line lacking DJ-1, the gene responsible for familial Parkinson’s disease, displays mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurosci Res 77(4):228–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2013.09.006
Monzio Compagnoni G, Di Fonzo A, Corti S, Comi GP, Bresolin N, Masliah E (2020) The role of mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases: the lesson from Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 57(7):2959–2980
Moors TE, Hoozemans JJ, Ingrassia A, Beccari T, Parnetti L, Chartier-Harlin MC, van de Berg WD (2017) Therapeutic potential of autophagy-enhancing agents in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-017-0154-3
Morais VA, Haddad D, Craessaerts K, De Bock P-J, Swerts J, Vilain S, Aerts L, Overbergh L, Grünewald A, Seibler P (2014) PINK1 loss-of-function mutations affect mitochondrial complex I activity via NdufA10 ubiquinone uncoupling. Science 344(6180):203–207
Mortiboys H, Aasly J, Bandmann O (2013) Ursocholanic acid rescues mitochondrial function in common forms of familial Parkinson’s disease. Brain 136(Pt 10):3038–3050. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt224
Mukai R, Kawabata K, Otsuka S, Ishisaka A, Kawai Y, Ji ZS, Tsuboi H, Terao J (2012) Effect of quercetin and its glucuronide metabolite upon 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage in Neuro-2a cells. Free Radical Res 46(8):1019–1028. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2012.673720
Müller-Rischart AK, Pilsl A, Beaudette P, Patra M, Hadian K, Funke M, Peis R, Deinlein A, Schweimer C, Kuhn P-H (2013) The E3 ligase parkin maintains mitochondrial integrity by increasing linear ubiquitination of NEMO. Mol Cell 49(5):908–921
Muñoz Y, Carrasco CM, Campos JD, Aguirre P, Núñez MT (2016) Parkinson’s disease: the mitochondria-iron link. Parkinson’s Dis 2016:7049108. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7049108
Narendra D, Tanaka A, Suen D-F, Youle RJ (2008) Parkin is recruited selectively to impaired mitochondria and promotes their autophagy. J Cell Biol 183(5):795–803
Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen D-F, Gautier CA, Shen J, Cookson MR, Youle RJ (2010) PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol 8(1)
Nass S, Nass MM (1963) Intramitochondrial fibers with DNA characteristics. II. enzymatic and other hydrolytic treatments. J Cell Biol 19(3):613–629. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.19.3.613
Negida A, Menshawy A, El Ashal G, Elfouly Y, Hani Y, Hegazy Y, El Ghonimy S, Fouda S, Rashad Y (2016) Coenzyme Q10 for patients with parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CNS Neurol Disord 15(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527314666150821103306
Nieto M, Gil-Bea FJ, Dalfó E, Cuadrado M, Cabodevilla F, Sánchez B, Catena S, Sesma T, Ribé E, Ferrer I, Ramírez MJ, Gómez-Isla T (2006) Increased sensitivity to MPTP in human alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 27(6):848–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.04.010
Nuamnaichati N, Mangmool S, Chattipakorn N, Parichatikanond W (2020) Stimulation of GLP-1 receptor inhibits methylglyoxal-induced mitochondrial dysfunctions in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts: potential role of Epac/PI3K/Akt pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:805. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00805
Obeso J, Stamelou M, Goetz C, Poewe W, Lang A, Weintraub D, Burn D, Halliday GM, Bezard E, Przedborski S (2017) Past, present, and future of Parkinson’s disease: a special essay on the 200th anniversary of the Shaking Palsy. Mov Disord 32(9):1264–1310
Okatsu K, Oka T, Iguchi M, Imamura K, Kosako H, Tani N, Kimura M, Go E, Koyano F, Funayama M (2012) PINK1 autophosphorylation upon membrane potential dissipation is essential for parkin recruitment to damaged mitochondria. Nat Commun 3(1):1–10
Okatsu K, Sato Y, Yamano K, Matsuda N, Negishi L, Takahashi A, Yamagata A, Goto-Ito S, Mishima M, Ito Y (2018) Structural insights into ubiquitin phosphorylation by PINK1. Sci Rep 8(1):1–10
Orr AL, Rutaganira FU, de Roulet D, Huang EJ, Hertz NT, Shokat KM, Nakamura K (2017) Long-term oral kinetin does not protect against α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration in rodent models of parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 109:106–116
Ouzren N, Delcambre S, Ghelfi J, Seibler P, Farrer MJ, König IR, Aasly JO, Trinh J, Klein C, Grünewald A (2019) Mitochondrial DNA deletions discriminate affected from unaffected LRRK2 mutation carriers. Ann Neurol 86(2):324–326. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25510
Paisán-Ruíz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simón J, van der Brug M, López de Munain A, Aparicio S, Gil AM, Khan N, Johnson J, Martinez JR, Nicholl D, Martí Carrera I, Pena AS, de Silva R, Lees A, Martí-Massó JF, Pérez-Tur J, Wood NW, Singleton AB (2004) Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked parkinson’s disease. Neuron 44(4):595–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.023
Palle S, Neerati P (2018) Improved neuroprotective effect of resveratrol nanoparticles as evinced by abrogation of rotenone-induced behavioral deficits and oxidative and mitochondrial dysfunctions in rat model of parkinson’s disease. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 391(4):445–453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1474-8
Parihar MS, Parihar A, Fujita M, Hashimoto M, Ghafourifar P (2008) Mitochondrial association of alpha-synuclein causes oxidative stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(7–8):1272–1284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7589-1
Park J, Lee SB, Lee S, Kim Y, Song S, Kim S, Bae E, Kim J, Shong M, Kim JM, Chung J (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction in drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature 441(7097):1157–1161. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04788
Park J-S, Davis RL, Sue CM (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: new mechanistic insights and therapeutic perspectives. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 18(5):1–11
Parker WD Jr, Parks JK (2005) Mitochondrial ND5 mutations in idiopathic parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326(3):667–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.093
Patel RV, Mistry BM, Shinde SK, Syed R, Singh V, Shin HS (2018) Therapeutic potential of quercetin as a cardiovascular agent. Eur J Med Chem 155:889–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.053
Pereira SS, Monteiro MP, Costa MM, Ferreira J, Alves MG, Oliveira PF, Jarak I, Pignatelli D (2019) MAPK/ERK pathway inhibition is a promising treatment target for adrenocortical tumors. J Cell Biochem 120(1):894–906. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27451
Pickett SJ, Deen D, Pyle A, Santibanez-Koref M, Hudson G (2022) Interactions between nuclear and mitochondrial SNPs and parkinson’s disease risk. Mitochondrion 63:85–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2022.02.002
Pickrell AM, Youle RJ (2015) The roles of PINK1, parkin, and mitochondrial fidelity in parkinson’s disease. Neuron 85(2):257–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.007
Pickrell AM, Huang CH, Kennedy SR, Ordureau A, Sideris DP, Hoekstra JG, Harper JW, Youle RJ (2015) Endogenous parkin preserves dopaminergic substantia nigral neurons following mitochondrial DNA mutagenic stress. Neuron 87(2):371–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.06.034
Plun-Favreau H, Klupsch K, Moisoi N, Gandhi S, Kjaer S, Frith D, Harvey K, Deas E, Harvey RJ, McDonald N (2007) The mitochondrial protease HtrA2 is regulated by parkinson’s disease-associated kinase PINK1. Nat Cell Biol 9(11):1243–1252
Podlesniy P, Puigròs M, Serra N, Fernández-Santiago R, Ezquerra M, Tolosa E, Trullas R (2019) Accumulation of mitochondrial 7S DNA in idiopathic and LRRK2 associated parkinson’s disease. EBioMedicine 48:554–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.09.015
Poenisch M, Burger N, Staeheli P, Bauer G, Schneider U (2009) Protein X of borna disease virus inhibits apoptosis and promotes viral persistence in the central nervous systems of newborn-infected rats. J Virol 83(9):4297–4307. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.02321-08
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(51):2045–2047
Prasuhn J, Davis RL, Kumar KR (2021) Targeting mitochondrial impairment in parkinson’s disease: challenges and opportunities. Front Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.615461
Pridgeon JW, Olzmann JA, Chin L-S, Li L (2007) PINK1 protects against oxidative stress by phosphorylating mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1. PLoS Biol 5(7):e172
Pyle A, Brennan R, Kurzawa-Akanbi M, Yarnall A, Thouin A, Mollenhauer B, Burn D, Chinnery PF, Hudson G (2015) Reduced cerebrospinal fluid mitochondrial DNA is a biomarker for early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 78(6):1000–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24515
Pyle A, Anugrha H, Kurzawa-Akanbi M, Yarnall A, Burn D, Hudson G (2016) Reduced mitochondrial DNA copy number is a biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 38:216 e217-216 e210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.033
Ramonet D, Daher JP, Lin BM, Stafa K, Kim J, Banerjee R, Westerlund M, Pletnikova O, Glauser L, Yang L, Liu Y, Swing DA, Beal MF, Troncoso JC, McCaffery JM, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Galter D, Thomas B, Lee MK, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Moore DJ (2011) Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18568. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018568
Rappold PM, Cui M, Grima JC, Fan RZ, de Mesy-Bentley KL, Chen L, Zhuang X, Bowers WJ, Tieu K (2014) Drp1 inhibition attenuates neurotoxicity and dopamine release deficits in vivo. Nat Commun 5:5244. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6244
Remes AM, Hinttala R, Kärppä M, Soini H, Takalo R, Uusimaa J, Majamaa K (2008) Parkinsonism associated with the homozygous W748S mutation in the POLG1 gene. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14(8):652–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.01.009
Ren Q, Ma M, Yang J, Nonaka R, Yamaguchi A, Ishikawa K-i, Kobayashi K, Murayama S, Hwang SH, Saiki S (2018) Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115(25):E5815–E5823
Richter G, Sonnenschein A, Grünewald T, Reichmann H, Janetzky B (2002) Novel mitochondrial DNA mutations in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 109(5):721–729
Rizek P, Kumar N, Jog MS (2016) An update on the diagnosis and treatment of Parkinson disease. CMAJ 188(16):1157–1165
Rojas JC, Simola N, Kermath BA, Kane JR, Schallert T, Gonzalez-Lima F (2009) Striatal neuroprotection with methylene blue. Neuroscience 163(3):877–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.012
Rosa AI, Fonseca I, Nunes MJ, Moreira S, Rodrigues E, Carvalho AN, Rodrigues CMP, Gama MJ, Castro-Caldas M (2017) Novel insights into the antioxidant role of tauroursodeoxycholic acid in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863(9):2171–2181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.06.004
Rothfuss O, Fischer H, Hasegawa T, Maisel M, Leitner P, Miesel F, Sharma M, Bornemann A, Berg D, Gasser T, Patenge N (2009) Parkin protects mitochondrial genome integrity and supports mitochondrial DNA repair. Hum Mol Genet 18(20):3832–3850. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp327
Saarni SI, Härkänen T, Sintonen H, Suvisaari J, Koskinen S, Aromaa A, Lönnqvist J (2006) The impact of 29 chronic conditions on health-related quality of life: a general population survey in Finland using 15D and EQ-5D. Qual Life Res 15(8):1403–1414
Saha S, Guillily MD, Ferree A, Lanceta J, Chan D, Ghosh J, Hsu CH, Segal L, Raghavan K, Matsumoto K, Hisamoto N, Kuwahara T, Iwatsubo T, Moore L, Goldstein L, Cookson M, Wolozin B (2009) LRRK2 modulates vulnerability to mitochondrial dysfunction in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 29(29):9210–9218. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2281-09.2009
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307(5712):1098–1101. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1106148
Sarraf SA, Raman M, Guarani-Pereira V, Sowa ME, Huttlin EL, Gygi SP, Harper JW (2013) Landscape of the PARKIN-dependent ubiquitylome in response to mitochondrial depolarization. Nature 496(7445):372–376
Schapira AH (2008) Mitochondria in the aetiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 7(1):97–109
Schapira A, Cooper J, Dexter D, Clark J, Jenner P, Marsden C (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 54(3):823–827
Scorziello A, Borzacchiello D, Sisalli MJ, Di Martino R, Morelli M, Feliciello A (2020) Mitochondrial homeostasis and signaling in Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 12:100
Shahmoradian SH, Lewis AJ, Genoud C, Hench J, Moors TE, Navarro PP, Castaño-Díez D, Schweighauser G, Graff-Meyer A, Goldie KN, Sütterlin R, Huisman E, Ingrassia A, Gier Y, Rozemuller AJM, Wang J, Paepe A, Erny J, Staempfli A, Hoernschemeyer J, Großerüschkamp F, Niedieker D, El-Mashtoly SF, Quadri M, Van IWFJ, Bonifati V, Gerwert K, Bohrmann B, Frank S, Britschgi M, Stahlberg H, Van de Berg WDJ, Lauer ME (2019) Lewy pathology in Parkinson’s disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat Neurosci 22(7):1099–1109. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0423-2
Shanmughapriya S, Langford D, Natarajaseenivasan K (2020) Inter and intracellular mitochondrial trafficking in health and disease. Ageing Res Rev 62:101128
Shavali S, Brown-Borg HM, Ebadi M, Porter J (2008) Mitochondrial localization of alpha-synuclein protein in alpha-synuclein overexpressing cells. Neurosci Lett 439(2):125–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.005
Shi X, Zhao M, Fu C, Fu A (2017) Intravenous administration of mitochondria for treating experimental Parkinson’s disease. Mitochondrion 34:91–100
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo SI, Yoshikawa M, Kitada T, Matsumine H, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Yamamura Y, Shimizu N (1999) Immunohistochemical and subcellular localization of Parkin protein: absence of protein in autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism patients. Ann Neurol 45(5):668–672
Shults CW, Oakes D, Kieburtz K, Beal MF, Haas R, Plumb S, Juncos JL, Nutt J, Shoulson I, Carter J, Kompoliti K, Perlmutter JS, Reich S, Stern M, Watts RL, Kurlan R, Molho E, Harrison M, Lew M (2002) Effects of coenzyme Q10 in early Parkinson disease: evidence of slowing of the functional decline. Arch Neurol 59(10):1541–1550. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.59.10.1541
Sim CH, Lio DS, Mok SS, Masters CL, Hill AF, Culvenor JG, Cheng HC (2006) C-terminal truncation and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations down-regulate the protein serine/threonine kinase activity of PTEN-induced kinase-1. Hum Mol Genet 15(21):3251–3262. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl398
Simon DK, Mayeux R, Marder K, Kowall NW, Beal MF, Johns DR (2000) Mitochondrial DNA mutations in complex I and tRNA genes in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 54(3):703–709. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.54.3.703
Smith ES, Clark ME, Hardy GA, Kraan DJ, Biondo E, Gonzalez-Lima F, Cormack LK, Monfils M, Lee HJ (2017) Daily consumption of methylene blue reduces attentional deficits and dopamine reduction in a 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 359:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.07.001
Snow BJ, Rolfe FL, Lockhart MM, Frampton CM, O’Sullivan JD, Fung V, Smith RA, Murphy MP, Taylor KM (2010) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ as a disease-modifying therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Dis 25(11):1670–1674. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23148
Song LK, Ma KL, Yuan YH, Mu Z, Song XY, Niu F, Han N, Chen NH (2015) Targeted Overexpression of α-Synuclein by rAAV2/1 Vectors Induces Progressive Nigrostriatal Degeneration and Increases Vulnerability to MPTP in Mouse. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0131281. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131281
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388(6645):839–840. https://doi.org/10.1038/42166
Steger M, Tonelli F, Ito G, Davies P, Trost M, Vetter M, Wachter S, Lorentzen E, Duddy G, Wilson S, Baptista MA, Fiske BK, Fell MJ, Morrow JA, Reith AD, Alessi DR, Mann M (2016) Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12813
Subramaniam SR, Vergnes L, Franich NR, Reue K, Chesselet MF (2014) Region specific mitochondrial impairment in mice with widespread overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Neurobiol Dis 70:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2014.06.017
Swatek KN, Komander D (2016) Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res 26(4):399–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2016.39
Synofzik M, Asmus F, Reimold M, Schöls L, Berg D (2010) Sustained dopaminergic response of parkinsonism and depression in POLG-associated parkinsonism. Mov Dis 25(2):243–245. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22865
Szelechowski M, Bétourné A, Monnet Y, Ferré CA, Thouard A, Foret C, Peyrin JM, Hunot S, Gonzalez-Dunia D (2014) A viral peptide that targets mitochondria protects against neuronal degeneration in models of parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun 5:5181. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6181
Taanman JW, Schapira AH (2005) Analysis of the trinucleotide CAG repeat from the DNA polymerase gamma gene (POLG) in patients with parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 376(1):56–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.023
Tang BL (2017) Sirtuins as modifiers of parkinson’s disease pathology. J Neurosci Res 95(4):930–942. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23806
Tang F-L, Liu W, Hu J-X, Erion JR, Ye J, Mei L, Xiong W-C (2015) VPS35 deficiency or mutation causes dopaminergic neuronal loss by impairing mitochondrial fusion and function. Cell Rep 12(10):1631–1643
Tapias V, Hu X, Luk KC, Sanders LH, Lee VM, Greenamyre JT (2017) Synthetic alpha-synuclein fibrils cause mitochondrial impairment and selective dopamine neurodegeneration in part via iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(15):2851–2874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2541-x
Tarohda T, Ishida Y, Kawai K, Yamamoto M, Amano R (2005) Regional distributions of manganese, iron, copper, and zinc in the brains of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced parkinsonian rats. Anal Bioanal Chem 383(2):224–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3423-x
Tiangyou W, Hudson G, Ghezzi D, Ferrari G, Zeviani M, Burn D, Chinnery P (2006) POLG1 in idiopathic parkinson disease. Neurology 67(9):1698–1700
Tomiyama H, Mizuta I, Li Y, Funayama M, Yoshino H, Li L, Murata M, Yamamoto M, Kubo S-i, Mizuno Y (2008) LRRK2 P755L variant in sporadic parkinson’s disease. J Hum Genet 53(11):1012–1015
Trinh J, Zeldenrust FM, Huang J, Kasten M, Schaake S, Petkovic S, Madoev H, Grünewald A, Almuammar S, König IR (2018) Genotype-phenotype relations for the Parkinson’s disease genes SNCA, LRRK2, VPS35: MDSGene systematic review. Mov Disord 33(12):1857–1870
Trinh D, Israwi AR, Arathoon LR, Gleave JA, Nash JE (2021) The multi-faceted role of mitochondria in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 156(6):715–752
Tzeng IS (2022) Role of mitochondria DNA A10398G polymorphism on development of Parkinson’s disease: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. J Clin Lab Anal 36(3):e24274. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24274
Tzoulis C, Tran GT, Schwarzlmüller T, Specht K, Haugarvoll K, Balafkan N, Lilleng PK, Miletic H, Biermann M, Bindoff LA (2013) Severe nigrostriatal degeneration without clinical parkinsonism in patients with polymerase gamma mutations. Brain 136(Pt 8):2393–2404. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt103
Uhrbrand A, Stenager E, Pedersen MS, Dalgas U (2015) Parkinson’s disease and intensive exercise therapy—a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Neurol Sci 353(1–2):9–19
Valente EM, Bentivoglio AR, Dixon PH, Ferraris A, Ialongo T, Frontali M, Albanese A, Wood NW (2001) Localization of a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, PARK6, on human chromosome 1p35-p36. Am J Human Genet 68(4):895–900
Valente EM, Abou Sleiman PM, Caputo V, Muqit MM, Harvey K, Gispert S, Ali Z, Del Turco D, Bentivoglio AR, Healy DG (2004) Hereditary early-onset parkinson’s disease caused by mutations. Science 304(5674):1158–1160
van der Merwe C, van Dyk HC, Engelbrecht L, van der Westhuizen FH, Kinnear C, Loos B, Bardien S (2017) Curcumin rescues a PINK1 Knock Down SH-SY5Y cellular model of parkinson’s disease from mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. Mol Neurobiol 54(4):2752–2762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9843-0
Van Goethem G, Dermaut B, Löfgren A, Martin JJ, Van Broeckhoven C (2001) Mutation of POLG is associated with progressive external ophthalmoplegia characterized by mtDNA deletions. Nat Genet 28(3):211–212. https://doi.org/10.1038/90034
Vandenberghe W, Van Laere K, Debruyne F, Van Broeckhoven C, Van Goethem G (2009) Neurodegenerative parkinsonism and progressive external ophthalmoplegia with a twinkle mutation. Mov Disord 24(2):308–309. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22198
Vives-Bauza C, Andreu AL, Manfredi G, Beal MF, Janetzky B, Gruenewald TH, Lin MT (2002) Sequence analysis of the entire mitochondrial genome in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290(5):1593–1601. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2002.6388
Wang X, Yan MH, Fujioka H, Liu J, Wilson-Delfosse A, Chen SG, Perry G, Casadesus G, Zhu X (2012) LRRK2 regulates mitochondrial dynamics and function through direct interaction with DLP1. Hum Mol Genet 21(9):1931–1944. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/dds003
Wang W, Wang X, Fujioka H, Hoppel C, Whone AL, Caldwell MA, Cullen PJ, Liu J, Zhu X (2016) Parkinson’s disease–associated mutant VPS35 causes mitochondrial dysfunction by recycling DLP1 complexes. Nat Med 22(1):54–63
Wang H, Dong X, Liu Z, Zhu S, Liu H, Fan W, Hu Y, Hu T, Yu Y, Li Y, Liu T, Xie C, Gao Q, Li G, Zhang J, Ding Z, Sun J (2018) Resveratrol suppresses rotenone-induced neurotoxicity through activation of SIRT1/Akt1 signaling pathway. Anat Rec (hoboken, NJ: 2007) 301(6):1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23781
Wang Y, He J, Liao M, Hu M, Li W, Ouyang H, Wang X, Ye T, Zhang Y, Ouyang L (2019) An overview of sirtuins as potential therapeutic target: Structure, function and modulators. Eur J Med Chem 161:48–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.10.028
Wang WW, Han R, He HJ, Li J, Chen SY, Gu Y, Xie C (2021) Administration of quercetin improves mitochondria quality control and protects the neurons in 6-OHDA-lesioned Parkinson’s disease models. Aging 13(8):11738–11751. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202868
Wenzel DM, Lissounov A, Brzovic PS, Klevit RE (2011) UBCH7 reactivity profile reveals parkin and HHARI to be RING/HECT hybrids. Nature 474(7349):105–108
Winkler-Stuck K, Kirches E, Mawrin C, Dietzmann K, Lins H, Wallesch C-W, Kunz W, Wiedemann F (2005) Re-evaluation of the dysfunction of mitochondrial respiratory chain in skeletal muscle of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 112(4):499–518
Winklhofer KF (2014) Parkin and mitochondrial quality control: toward assembling the puzzle. Trends Cell Biol 24(6):332–341
Wu Y, Li X, Zhu JX, Xie W, Le W, Fan Z, Jankovic J, Pan T (2011) Resveratrol-activated AMPK/SIRT1/autophagy in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosignals 19(3):163–174. https://doi.org/10.1159/000328516
Xi Y, Feng D, Tao K, Wang R, Shi Y, Qin H, Murphy MP, Yang Q, Zhao G (2018) MitoQ protects dopaminergic neurons in a 6-OHDA induced PD model by enhancing Mfn2-dependent mitochondrial fusion via activation of PGC-1α. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta Mol Basis Dis 1894(9 Pt B):2859–2870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.05.018
Xia X, Bai Y, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xu R, Gao X, Li X, He J (2017) Effects of 10 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in disorders of consciousness. Front Neurol 8:182
Xu D, Shan B, Sun H, Xiao J, Zhu K, Xie X, Li X, Liang W, Lu X, Qian L (2016) USP14 regulates autophagy by suppressing K63 ubiquitination of Beclin 1. Genes Dev 30(15):1718–1730
Yan A, Liu Z, Song L, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wu N, Lin J, Liu Y, Liu Z (2018) Idebenone alleviates neuroinflammation and modulates microglial polarization in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells and MPTP-induced parkinson’s disease mice. Front Cell Neurosci 12:529. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00529
Yang X, Zhang Y, Xu H, Luo X, Yu J, Liu J, Chang RC (2016) Neuroprotection of Coenzyme Q10 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr Top Med Chem 16(8):858–866. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026615666150827095252
Ylönen S, Ylikotila P, Siitonen A, Finnilä S, Autere J, Majamaa K (2013) Variations of mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 260(12):3144–3149
Yoon JH, Mo JS, Kim MY, Ann EJ, Ahn JS, Jo EH, Lee HJ, Lee YC, Seol W, Yarmoluk SM, Gasser T, Kahle PJ, Liu GH, Belmonte JCI, Park HS (2017) LRRK2 functions as a scaffolding kinase of ASK1-mediated neuronal cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864(12):2356–2368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.09.001
Yoshino H, Nakagawa-Hattori Y, Kondo T, Mizuno Y (1992) Mitochondrial complex I and II activities of lymphocytes and platelets in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Parkinson’s Dis Dementia Sect 4(1):27–34
Zhou K, Yang HY, Tang PY, Liu W, Luo YJ, Lv B, Yin J, Jiang T, Chen J, Cai WH, Fan J (2018) Mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 protects cortical neurons from excitotoxicity: a mechanistic pathway. Neural Regen Res 13(9):1552–1560. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.235299
Zhu ZG, Sun MX, Zhang WL, Wang WW, Jin YM, Xie CL (2017) The efficacy and safety of coenzyme Q10 in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neurol Sci 38(2):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2757-9
Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, Lincoln S, Kachergus J, Hulihan M, Uitti RJ, Calne DB, Stoessl AJ, Pfeiffer RF, Patenge N, Carbajal IC, Vieregge P, Asmus F, Müller-Myhsok B, Dickson DW, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Wszolek ZK, Gasser T (2004) Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron 44(4):601–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2004.11.005
Zsurka G, Peeva V, Kotlyar A, Kunz WS (2018) Is there still any role for oxidative stress in mitochondrial DNA-dependent aging? Genes. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040175
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors would like to appreciate Dr. Khoshnam for suggesting the topic of this article. All authors contributed to the study conception and design, drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and approval of the final version. MA: designed and contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. MJ: contributed to preparing the figure and writing the manuscript. YF: revised the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This is a review article. There is not ethical approval applicable.
Informed Consent
This is a review article. There is not consent to publish applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abrishamdar, M., Jalali, M.S. & Farbood, Y. Targeting Mitochondria as a Therapeutic Approach for Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 1499–1518 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01265-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-022-01265-w