Abstract
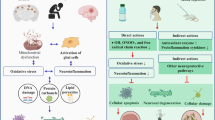
The brain is the most sensitive organ to hypoxia in the human body. Hypoxia in the brain will lead to damage to local brain tissue. When the blood supply of ischemic brain tissue is restored, the damage will worsen, that is, cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a gaseous signal molecule and a novel endogenous neuroregulator. Indeed, different concentrations of H2S have different effects on neurons. Low concentration of H2S can play an important protective role in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury by inducing anti-oxidative stress injury, inhibition of inflammatory response, inhibition of cell apoptosis, reduction of cerebrovascular endothelial cell injury, regulation of autophagy, and other ways, which provides a new idea for clinical diagnosis and treatment of related diseases. This review aims to report the recent research progress on the dual effect of H2S on brain tissue during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrabi SS, Parvez S, Tabassum H (2020) Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: mechanisms and targets. Protoplasma 257(2):335–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-019-01439-2
Carbone F, Bonaventura A, Montecucco F (2019) Neutrophil-related oxidants drive heart and brain remodeling after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Physiol 10:1587. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01587
Chen F, Liu Z, Peng W, Gao Z, Ouyang H, Yan T, Ding S, Cai Z, Zhao B, Mao L, Cao Z (2018) Activation of EphA4 induced by EphrinA1 exacerbates disruption of the blood-brain barrier following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 16(3):2651–2658. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6460
Chen Y, Zhang F, Yin J, Wu S, Zhou X (2020) Protective mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide in myocardial ischemia. J Cell Physiol 235(12):9059–9070. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29761
Cheng YC, Sheen JM, Hu WL, Hung YC (2017) Polyphenols and oxidative stress in atherosclerosis-related ischemic heart disease and stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8526438. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8526438
Coletti R, de Lima JBM, Vechiato FMV, de Oliveira FL, Debarba LK, Almeida-Pereira G, Elias LLK, Antunes-Rodrigues J (2019) Nitric oxide acutely modulates hypothalamic and neurohypophyseal carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulphide production to control vasopressin, oxytocin and atrial natriuretic peptide release in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 31(2):e12686. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12686
Cui Y, Duan X, Li H, Dang B, Yin J, Wang Y, Gao A, Yu Z, Chen G (2016) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Mol Neurobiol 53(6):3646–3657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9304-1
Damba T, Zhang M, Buist-Homan M, van Goor H, Faber KN, Moshage H (2019) Hydrogen sulfide stimulates activation of hepatic stellate cells through increased cellular bio-energetics. Nitric Oxide 92:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2019.08.004
Datzmann T, Hoffmann A, McCook O, Merz T, Wachter U, Preuss J, Vettorazzi S, Calzia E, Groger M, Kohn F, Schmid A, Denoix N, Radermacher P, Wepler M (2020) Effects of sodium thiosulfate (Na2S2O3) during resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock in swine with preexisting atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Res 151:104536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104536
Duan HZ, Wu CW, Shen SL, Zhang JY, Li L (2020) Neuroprotective effects of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats by calcium channel mediating hydrogen sulfide. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00940-0
Geng Y, Li E, Mu Q, Zhang Y, Wei X, Li H, Cheng L, Zhang B (2015) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation decreases early blood-brain barrier permeability and brain edema induced by cardiac arrest and resuscitation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(3):494–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.223
Gheibi S, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M, Kalalian-Moghaddam H, Vakili A, Asadi Y, Mehrjerdi FZ, Gheibi A (2014) Hydrogen sulfide protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci 54(2):264–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0284-9
Gojon G (2020) On H2S prodrugs. Antioxid Redox Signal 33(14):999–1002. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2020.8078
Guo P, Jin Z, Wu H, Li X, Ke J, Zhang Z, Zhao Q (2019) Effects of irisin on the dysfunction of blood-brain barrier in rats after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Behav 9(10):e01425. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.1425
Huang L, Chen C, Zhang X, Li X, Chen Z, Yang C, Liang X, Zhu G, Xu Z (2018) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via mediating autophagy and inflammation. J Mol Neurosci 64(1):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-1006-x
Jang H, Oh MY, Kim YJ, Choi IY, Yang HS, Ryu WS, Lee SH, Yoon BW (2014) Hydrogen sulfide treatment induces angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 92(11):1520–1528. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23427
Ji K, Xue L, Cheng J, Bai Y (2016) Preconditioning of H2S inhalation protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by induction of HSP70 through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Brain Res Bull 121:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.12.007
Jiang B, Tang G, Cao K, Wu L, Wang R (2010) Molecular mechanism for H(2)S-induced activation of K(ATP) channels. Antioxid Redox Signal 12(10):1167–1178. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2894
Jiang Z, Li C, Manuel ML, Yuan S, Kevil CG, McCarter KD, Lu W, Sun H (2015) Role of hydrogen sulfide in early blood-brain barrier disruption following transient focal cerebral ischemia. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117982
Jiang H, Xiao J, Kang B, Zhu X, Xin N, Wang Z (2016) PI3K/SGK1/GSK3beta signaling pathway is involved in inhibition of autophagy in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation by hydrogen sulfide. Exp Cell Res 345(2):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.07.005
Jiang WW, Huang BS, Han Y, Deng LH, Wu LX (2017) Sodium hydrosulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing overactivated autophagy in rats. FEBS Open Bio 7(11):1686–1695. https://doi.org/10.1002/2211-5463.12301
King AL, Lefer DJ (2011) Cytoprotective actions of hydrogen sulfide in ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Physiol 96(9):840–846. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2011.059725
Kozlowski S, Takeshita T, Boehncke WH, Takahashi H, Boyd LF, Germain RN, Berzofsky JA, Margulies DH (1991) Excess beta 2 microglobulin promoting functional peptide association with purified soluble class I MHC molecules. Nature 349(6304):74–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/349074a0
Kumar M, Sandhir R (2018) Hydrogen sulfide in physiological and pathological mechanisms in brain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 17(9):654–670. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527317666180605072018
Landry AP, Ballou DP, Banerjee R (2017) H2S oxidation by nanodisc-embedded human sulfide quinone oxidoreductase. J Biol Chem 292(28):11641–11649. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.788547
Lee M, McGeer E, Kodela R, Kashfi K, McGeer PL (2013) NOSH-aspirin (NBS-1120), a novel nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide releasing hybrid, attenuates neuroinflammation induced by microglial and astrocytic activation: a new candidate for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Glia 61(10):1724–1734. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22553
Li L, Jiang HK, Li YP, Guo YP (2015) Hydrogen sulfide protects spinal cord and induces autophagy via miR-30c in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Biomed Sci 22:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-015-0135-1
Li YL, Wu PF, Chen JG, Wang S, Han QQ, Li D, Wang W, Guan XL, Li D, Long LH, Huang JG, Wang F (2017) Activity-dependent sulfhydration signal controls N-methyl-D-aspartate subtype glutamate receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity via increasing d-serine availability. Antioxid Redox Signal 27(7):398–414. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2016.6936
Li H, Zhu L, Feng J, Hu X, Li C, Zhang B (2018) Hydrogen sulfide decreases blood-brain barrier damage via regulating protein kinase C and tight junction after cardiac arrest in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(3):994–1006. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490166
Libiad M, Yadav PK, Vitvitsky V, Martinov M, Banerjee R (2014) Organization of the human mitochondrial hydrogen sulfide oxidation pathway. J Biol Chem 289(45):30901–30910. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.602664
Liu H, Wang Y, Xiao Y, Hua Z, Cheng J, Jia J (2016) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates tissue plasminogen activator-induced cerebral hemorrhage following experimental stroke. Transl Stroke Res 7(3):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0459-5
Liu Z, Wang X, Li L, Wei G, Zhao M (2020) Hydrogen sulfide protects against paraquat-induced acute liver injury in rats by regulating oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, and inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:6325378. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6325378
Lo Faro ML, Fox B, Whatmore JL, Winyard PG, Whiteman M (2014) Hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide interactions in inflammation. Nitric Oxide 41:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2014.05.014
Lobov GI, Sokolova IB, Gorshkova OP, Shvetsova ME, Dvoretskii DP (2020) Contribution of hydrogen sulfide to dilation of rat cerebral arteries after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Bull Exp Biol Med 168(5):597–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04759-z
Luo J, Mills K, le Cessie S, Noordam R, van Heemst D (2020) Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress: what to do next? Ageing Res Rev 57:100982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2019.100982
Lv B, Jiang XM, Wang DW, Chen J, Han DF, Liu XL (2020) Protective effects and mechanisms of action of ulinastatin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Pharm Des 26(27):3332–3340. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200303114955
Lv B, Chen S, Tang C, Jin H, Du J, Huang Y (2021) Hydrogen sulfide and vascular regulation: an update. J Adv Res 27:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.05.007
Mansour SG, Puthumana J, Reese PP, Hall IE, Doshi MD, Weng FL, Schroppel B, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Bimali M, Parikh CR (2017) Associations between deceased-donor urine MCP-1 and kidney transplant outcomes. Kidney Int Rep 2(4):749–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2017.03.007
Marutani E, Yamada M, Ida T, Tokuda K, Ikeda K, Kai S, Shirozu K, Hayashida K, Kosugi S, Hanaoka K, Kaneki M, Akaike T, Ichinose F (2015) Thiosulfate mediates cytoprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide against neuronal ischemia. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.115.002125
Minamishima S, Bougaki M, Sips PY, Yu JD, Minamishima YA, Elrod JW, Lefer DJ, Bloch KD, Ichinose F (2009) Hydrogen sulfide improves survival after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation via a nitric oxide synthase 3-dependent mechanism in mice. Circulation 120(10):888–896. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.833491
Moldogazieva NT, Mokhosoev IM, Mel’nikova TI, Porozov YB, Terentiev AA (2019) Oxidative stress and advanced lipoxidation and glycation end products (ALEs and AGEs) in aging and age-related diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:3085756. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3085756
Narne P, Pandey V, Phanithi PB (2019) Role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in ischemic stroke and the emergent epigenetic underpinnings. Mol Neurobiol 56(3):1749–1769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1141-6
Olmez I, Ozyurt H (2012) Reactive oxygen species and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Neurochem Int 60(2):208–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2011.11.009
Pan H, Xie X, Chen D, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Yang G (2014) Protective and biogenesis effects of sodium hydrosulfide on brain mitochondria after cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Eur J Pharmacol 741:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.037
Panthi S, Chung HJ, Jung J, Jeong NY (2016) Physiological importance of hydrogen sulfide: emerging potent neuroprotector and neuromodulator. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:9049782. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9049782
Pushpakumar S, Kundu S, Sen U (2014) Endothelial dysfunction: the link between homocysteine and hydrogen sulfide. Curr Med Chem 21(32):3662–3672. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666140706142335
Qin H, Gu LZ, Gao L, Guo J (2013) Protective effect of H2S pretreatment on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and its mechanisms in rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 35(3):249–253. https://doi.org/10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2013.03.002
Ravindran S, Kurian GA (2019) Eventual analysis of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat brain: a paradigm of a shift in stress and its influence on cognitive functions. Cell Stress Chaperones 24(3):581–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-019-00990-4
Ren C, Du A, Li D, Sui J, Mayhan WG, Zhao H (2010) Dynamic change of hydrogen sulfide during global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion and its effect in rats. Brain Res 1345:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.017
Sarkar S, Chakraborty D, Bhowmik A, Ghosh MK (2019) Cerebral ischemic stroke: cellular fate and therapeutic opportunities. Front Biosci (landmark Ed) 24:435–450
Shan H, Qiu J, Chang P, Chu Y, Gao C, Wang H, Chen G, Luo C, Wang T, Chen X, Zhang M, Tao L (2019) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide offers neuroprotection on intracerebral hemorrhage injury through modulating endogenous H2S metabolism in mice. Front Cell Neurosci 13:349. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00349
Shao JL, Wan XH, Chen Y, Bi C, Chen HM, Zhong Y, Heng XH, Qian JQ (2011) H2S protects hippocampal neurons from anoxia-reoxygenation through cAMP-mediated PI3K/Akt/p70S6K cell-survival signaling pathways. J Mol Neurosci 43(3):453–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-010-9464-4
Shi Y, Qiu X, Dai M, Zhang X, Jin G (2019) Hyperoside attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and inhibiting apoptosis in rats. Transplant Proc 51(6):2051–2059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.04.066
Shibuya N, Koike S, Tanaka M, Ishigami-Yuasa M, Kimura Y, Ogasawara Y, Fukui K, Nagahara N, Kimura H (2013) A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells. Nat Commun 4:1366. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2371
Shui M, Liu X, Zhu Y, Wang Y (2016) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94(11):1187–1192. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0100
Souza LK, Araujo TS, Sousa NA, Sousa FB, Nogueira KM, Nicolau LA, Medeiros JV (2017) Evidence that d-cysteine protects mice from gastric damage via hydrogen sulfide produced by d-amino acid oxidase. Nitric Oxide 64:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2017.01.010
Stamatovic SM, Shakui P, Keep RF, Moore BB, Kunkel SL, Van Rooijen N, Andjelkovic AV (2005) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25(5):593–606. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600055
Sun Y, Zhu Y, Zhong X, Chen X, Wang J, Ying G (2018) Crosstalk between autophagy and cerebral ischemia. Front Neurosci 12:1022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.01022
Tan BH, Wong PT, Bian JS (2010) Hydrogen sulfide: a novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system. Neurochem Int 56(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.08.008
Tang G, Yang G, Jiang B, Ju Y, Wu L, Wang R (2013) H(2)S is an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(14):1634–1646. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4805
Tao L, Yu Q, Zhao P, Yang Q, Wang B, Yang Y, Kuai J, Ding Q (2019) Preconditioning with hydrogen sulfide ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in a mouse model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Chem Biol Interact 310:108738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108738
Tay AS, Hu LF, Lu M, Wong PT, Bian JS (2010) Hydrogen sulfide protects neurons against hypoxic injury via stimulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channel/protein kinase C/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/heat shock protein 90 pathway. Neuroscience 167(2):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.006
Tyagi N, Moshal KS, Sen U, Vacek TP, Kumar M, Hughes WM Jr, Kundu S, Tyagi SC (2009) H2S protects against methionine-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 11(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2073
Wang K, Ahmad S, Cai M, Rennie J, Fujisawa T, Crispi F, Baily J, Miller MR, Cudmore M, Hadoke PW, Wang R, Gratacos E, Buhimschi IA, Buhimschi CS, Ahmed A (2013) Dysregulation of hydrogen sulfide producing enzyme cystathionine gamma-lyase contributes to maternal hypertension and placental abnormalities in preeclampsia. Circulation 127(25):2514–2522. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001631
Wang M, Tang W, Zhu YZ (2017) An update on AMPK in hydrogen sulfide pharmacology. Front Pharmacol 8:810. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00810
Wang P, Shao BZ, Deng Z, Chen S, Yue Z, Miao CY (2018) Autophagy in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:98–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.01.001
Wang X, Xia P, Huang X (2019) A dansyl-appended N-heterocycle for Cu(2+) and S(2-) recognition via a displacement mode. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 210:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.11.017
Wang B, Huang C, Chen L, Xu D, Zheng G, Zhou Y, Wang X, Zhang X (2020) The emerging roles of the gaseous signaling molecules NO, H2S, and CO in the regulation of stem cells. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6(2):798–812. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01681
Wen JY, Wang M, Li YN, Jiang HH, Sun XJ, Chen ZW (2018) Vascular protection of hydrogen sulfide on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Front Neurol 9:779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00779
Whiteman M, Li L, Rose P, Tan CH, Parkinson DB, Moore PK (2010) The effect of hydrogen sulfide donors on lipopolysaccharide-induced formation of inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Antioxid Redox Signal 12(10):1147–1154. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2009.2899
Wu D, Zhong P, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Li J, Liu Z, Ji A, Li Y (2020a) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting autophagy via reactive oxygen species/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:585860. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.585860
Wu L, Xiong X, Wu X, Ye Y, Jian Z, Zhi Z, Gu L (2020b) Targeting oxidative stress and inflammation to prevent ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Mol Neurosci 13:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2020.00028
Xie L, Feng H, Li S, Meng G, Liu S, Tang X, Ma Y, Han Y, Xiao Y, Gu Y, Shao Y, Park CM, Xian M, Huang Y, Ferro A, Wang R, Moore PK, Wang H, Ji Y (2016) SIRT3 mediates the antioxidant effect of hydrogen sulfide in endothelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 24(6):329–343. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6331
Xie L, Yu S, Yang K, Li C, Liang Y (2017) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits autophagic neuronal cell death by reducing oxidative stress in spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8640284. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8640284
Xie W, Zhou P, Sun Y, Meng X, Dai Z, Sun G, Sun X (2018) Protective effects and target network analysis of ginsenoside Rg1 in cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury: a comprehensive overview of experimental studies. Cells 7(12):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7120270
Xin L, Junhua W, Long L, Jun Y, Yang X (2017) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects SH-SY5Y cells from OGD/rinduced injury. Curr Mol Med 17(8):563–567. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524018666180222121643
Xu S, Liu Z, Liu P (2014) Targeting hydrogen sulfide as a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol 172(2):313–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.068
Yang Y, Cai Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Xu Z (2018) Exosomes secreted by adipose-derived stem cells contribute to angiogenesis of brain microvascular endothelial cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro through microRNA-181b/TRPM7 axis. J Mol Neurosci 65(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1071-9
Yin J, Tu C, Zhao J, Ou D, Chen G, Liu Y, Xiao X (2013) Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in rats. Brain Res 1491:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.10.046
Yuan R, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhen F, Li X, Lai Q, Hu P, Wang X, Zhu Y, Fan H, Yao R (2019) Metformin reduces neuronal damage and promotes neuroblast proliferation and differentiation in a cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rat model. NeuroReport 30(3):232–240. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001190
Zhang D, Wang X, Tian X, Zhang L, Yang G, Tao Y, Liang C, Li K, Yu X, Tang X, Tang C, Zhou J, Kong W, Du J, Huang Y, Jin H (2018) The increased endogenous sulfur dioxide acts as a compensatory mechanism for the downregulated endogenous hydrogen sulfide pathway in the endothelial cell inflammation. Front Immunol 9:882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00882
Zhang J, Shan H, Tao L, Zhang M (2020) Biological effects of hydrogen sulfide and its protective role in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Mol Neurosci 70(12):2020–2030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-020-01608-6
Zhao M, Zhu P, Fujino M, Zhuang J, Guo H, Sheikh I, Zhao L, Li XK (2016) Oxidative stress in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Int J Mol Sci 17(12):2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122078
Zhao Y, Wei X, Song J, Zhang M, Huang T, Qin J (2019) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist rosiglitazone protects blood-brain barrier integrity following diffuse axonal injury by decreasing the levels of inflammatory mediators through a caveolin-1-dependent pathway. Inflammation 42(3):841–856. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0940-2
Zheng F, Han J, Lu H, Cui C, Yang J, Cui Q, Cai J, Zhou Y, Tang C, Xu G, Geng B (2018) Cystathionine beta synthase-hydrogen sulfide system in paraventricular nucleus reduced high fatty diet induced obesity and insulin resistance by brain-adipose axis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1864(10):3281–3291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.07.014
Zhong H, Song R, Pang Q, Liu Y, Zhuang J, Chen Y, Hu J, Hu J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang J (2018) Propofol inhibits parthanatos via ROS-ER-calcium-mitochondria signal pathway in vivo and vitro. Cell Death Dis 9(10):932. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0996-9
Zhou X, Cao Y, Ao G, Hu L, Liu H, Wu J, Wang X, Jin M, Zheng S, Zhen X, Alkayed NJ, Jia J, Cheng J (2014) CaMKKbeta-dependent activation of AMP-activated protein kinase is critical to suppressive effects of hydrogen sulfide on neuroinflammation. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(12):1741–1758. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5587
Zhu Y, Shui M, Liu X, Hu W, Wang Y (2017) Increased autophagic degradation contributes to the neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Metab Brain Dis 32(5):1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0014-4
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFA0108700, 2017YFA0105602), NSFC Projects of International Cooperation and Exchanges (81720108004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81974019), The Research Team Project of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (2017A030312007), The key program of Guangzhou science research plan (201904020047), The Special Projects of Dengfeng Program of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (DFJH201812, KJ012019119 KJ012020630, KJ012019423), Natural Science Foundation of China (82001301), and the start-up Foundation of Guangdong Province (2018A030310113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: DG, MM, SA, MIN; investigation: DG, MM, SA, MIN; original draft preparation: MM, SA, MIN; review and editing: DG, MM, SA, MIN, GL PZ; and funding acquisition MIN, GL, PZ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, G., Muqadas, M., Adlat, S. et al. Protective Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 15–25 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01166-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01166-4