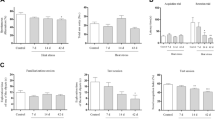
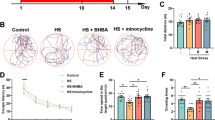
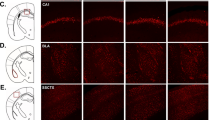
Abstract
Heat stress is known to result in neuroinflammation, neuronal damage, and disabilities in learning and memory in animals and humans. It has previously been reported that cognitive impairment caused by neuroinflammation may at least in part be mediated by defective hippocampal neurogenesis, and defective neurogenesis has been linked to aberrantly activated microglial cells. Moreover, the release of cytokines within the brain has been shown to contribute to the disruption of cognitive functions in several conditions following neuroinflammation. In this review, we summarize evolving evidence for the current understanding of inflammation-induced deficits in hippocampal neurogenesis, and the resulting behavioral impairments after heat stress. Furthermore, we provide valuable insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation-induced deficits in hippocampal neurogenesis, particularly relating to cognitive dysfunction following heat stress. Lastly, we aim to identify potential mechanisms through which neuroinflammation induces cognitive dysfunction, and elucidate how neuroinflammation contributes to defective hippocampal neurogenesis. This review may therefore help to better understand the relationship between hippocampal neurogenesis and heat stress.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- BrdU:
-
Neurons and bromodeoxyuridine
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- DCX:
-
Doublecortin
- DG:
-
Dentate gyrus
- GCL:
-
Granule cell layer
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GPX:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSAI-B4:
-
Griffonia simplicifolia lectin
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSSG:
-
Glutathione disulfide
- Iba-1:
-
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- IFNγ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-1R1:
-
Type 1 IL-1 receptor
- iNOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- LTD:
-
Long-term depression
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- MDA:
-
Oxidative stress marker
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- NeuN:
-
Neuronal nuclei
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NPC:
-
Neural progenitor cell
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SGZ:
-
Subgranular zone
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- TLR-2:
-
Toll-like receptor 2
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- TNF-R1:
-
TNF-α type 1 receptor
- tPA:
-
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
- TrkB:
-
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B
References
Aarum J, Sandberg K, Haeberlein SL, Persson MA (2003) Migration and differentiation of neural precursor cells can be directed by microglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(26):15983–15988. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2237050100
Albukrek D, Bakon M, Moran DS, Faibel M, Epstein Y (1997) Heat-stroke-induced cerebellar atrophy: clinical course. CT MRI Find Neuroradiol 39(3):195–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340050392
Anacker C, Hen R (2017) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive flexibility—linking memory and mood. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(6):335–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.45
Arevalo MA, Azcoitia I, Garcia-Segura LMJNRN (2015) The neuroprotective actions of oestradiol and oestrogen receptors. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3856
Baptista P, Andrade JP (2018) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation and possible functional and clinical correlates. Front Neuroanat 12:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00044
Bernabucci U, Lacetera N, Baumgard LH, Rhoads RP, Ronchi B, Nardone A (2010) Metabolic and hormonal acclimation to heat stress in domesticated ruminants. Animal 4(7):1167–1183. https://doi.org/10.1017/s175173111000090x
Bharati J, Dangi SS, Mishra SR, Chouhan VS, Verma V, Shankar O, Bharti MK, Paul A, Mahato DK, Rajesh G, Singh G, Maurya VP, Bag S, Kumar P, Sarkar M (2017) Expression analysis of Toll like receptors and interleukins in Tharparkar cattle during acclimation to heat stress exposure. J Therm Biol 65:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2017.02.002
Bin-Jumah M, Abd El-Hack ME, Abdelnour SA, Hendy YA, Ghanem HA, Alsafy SA, Khafaga AF, Noreldin AE, Shaheen H, Samak D, Momenah MA, Allam AA, AlKahtane AA, Alkahtani S, Abdel-Daim MM, Aleya L (2020) Potential use of chromium to combat thermal stress in animals: a review. Sci Tot Environ 707:135996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135996
Bohmanova J, Misztal I, Cole JB (2007) Temperature-humidity indices as indicators of milk production losses due to heat stress. J Dairy Sci 90(4):1947–1956. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2006-513
Bond AM, Ming GL, Song H (2015) Adult Mammalian neural stem cells and neurogenesis: five decades later. Cell Stem Cell 17(4):385–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.003
Bongioanni P, Del Carratore R, Corbianco S, Diana A, Cavallini G, Masciandaro SM, Dini M, Buizza R (2021) Climate change and neurodegenerative diseases. Environ Res 201:111511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111511
Boonruksa P, Maturachon T, Kongtip P, Woskie S (2020) Heat stress, physiological response, and heat-related symptoms among thai sugarcane workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176363
Bouchama A, Knochel JP (2002) Heat stroke. N Engl J Med 346(25):1978–1988. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra011089
Brown PL, Kiyatkin EA (2004) Brain hyperthermia induced by MDMA (ecstasy): modulation by environmental conditions. Eur J Neurosci 20(1):51–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03453.x
Bruce-Keller AJ (1999) Microglial-neuronal interactions in synaptic damage and recovery. J Neurosci Res 58(1):191–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4547(19991001)58:1%3c191::aid-jnr17%3e3.0.co;2-e
Chang CK, Chang CP, Liu SY, Lin MT (2007) Oxidative stress and ischemic injuries in heat stroke. Prog Brain Res 162:525–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6123(06)62025-6
Chen J, Li CR, Yang H, Liu J, Zhang T, Jiao SS, Wang YJ, Xu ZQ (2016) proBDNF attenuates hippocampal neurogenesis and induces learning and memory deficits in aged mice. Neurotox Res 29(1):47–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-015-9568-2
Cheng K, Yan E, Song Z, Li S, Zhang H, Zhang L, Wang C, Wang T (2019) Protective effect of resveratrol against hepatic damage induced by heat stress in a rat model is associated with the regulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. J Therm Biol 82:70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2019.03.012
Cian C, Barraud PA, Melin B, Raphel C (2001) Effects of fluid ingestion on cognitive function after heat stress or exercise-induced dehydration. Int J Psychophysiol 42(3):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8760(01)00142-8
Circu ML, Aw TY (2010) Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 48(6):749–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.12.022
Clelland CD, Choi M, Romberg C, Clemenson GD Jr, Fragniere A, Tyers P, Jessberger S, Saksida LM, Barker RA, Gage FH, Bussey TJ (2009) A functional role for adult hippocampal neurogenesis in spatial pattern separation. Science (New York, NY) 325(5937):210–213. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1173215
Cohen S, Janicki-Deverts D, Doyle WJ, Miller GE, Frank E, Rabin BS, Turner RB (2012) Chronic stress, glucocorticoid receptor resistance, inflammation, and disease risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(16):5995–5999. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118355109
Colonna M, Butovsky O (2017) Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol 35:441–468. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052358
Dahl GE, Tao S, Laporta J (2020) Heat stress impacts immune status in cows across the life cycle. Front Vet Sci 7:116. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.00116
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):339–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2822
Dikmen S, Hansen PJ (2009) Is the temperature-humidity index the best indicator of heat stress in lactating dairy cows in a subtropical environment? J Dairy Sci 92(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2008-1370
Ding Q, Vaynman S, Akhavan M, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2006) Insulin-like growth factor I interfaces with brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated synaptic plasticity to modulate aspects of exercise-induced cognitive function. Neuroscience 140(3):823–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.084
Edwards MJ, Wanner RA, Mulley RCJN, Neurobiology A (2010) Growth and development of the brain in normal and heat-retarded guinea-pigs. Neuropath Appl Neurobiol 2(6):439–450
Ekdahl CT, Claasen JH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2003) Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(23):13632–13637. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2234031100
Ekdahl CT, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2009) Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: the dual role of microglia. Neuroscience 158(3):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.052
Eskes C, Honegger P, Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Monnet-Tschudi F (2002) Microglial reaction induced by noncytotoxic methylmercury treatment leads to neuroprotection via interactions with astrocytes and IL-6 release. Glia 37(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.10019
Frielingsdorf H, Simpson DR, Thal LJ, Pizzo DP (2007) Nerve growth factor promotes survival of new neurons in the adult hippocampus. Neurobiol Dis 26(1):47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2006.11.015
Garaschuk O, Verkhratsky A (2019) Physiology of microglia. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 2034:27–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9658-2_3
Garcia R (2002) Stress, synaptic plasticity, and psychopathology. Rev Neurosci 13(3):195–208. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro.2002.13.3.195
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140(6):918–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.016
Grassivaro F, Menon R, Acquaviva M, Ottoboni L, Ruffini F, Bergamaschi A, Muzio L, Farina C, Martino G (2020) Convergence between microglia and peripheral macrophages phenotype during development and neuroinflammation. J Neurosci 40(4):784–795. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1523-19.2019
Green HF, Treacy E, Keohane AK, Sullivan AM, O’Keeffe GW, Nolan YM (2012) A role for interleukin-1beta in determining the lineage fate of embryonic rat hippocampal neural precursor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 49(3):311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2012.01.001
Groves JO, Leslie I, Huang GJ, McHugh SB, Taylor A, Mott R, Munafo M, Bannerman DM, Flint J (2013) Ablating adult neurogenesis in the rat has no effect on spatial processing: evidence from a novel pharmacogenetic model. PLoS Genet 9(9):e1003718. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003718
Gu ZT, Wang H, Li L, Liu YS, Deng XB, Huo SF, Yuan FF, Liu ZF, Tong HS, Su L (2014) Heat stress induces apoptosis through transcription-independent p53-mediated mitochondrial pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cell. Sci Rep 4:4469. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04469
Hagiwara S, Iwasaka H, Shingu C, Matsumoto S, Uchida T, Nishida T, Mizunaga S, Saikawa T, Noguchi T (2011) Danaparoid sodium attenuates the effects of heat stress. J Surg Res 171(2):762–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2010.05.008
Hancock PA, Vasmatzidis I (2003) Effects of heat stress on cognitive performance: the current state of knowledge. Int J Hypertherm 19(3):355–372. https://doi.org/10.1080/0265673021000054630
Hanisch UK, Kettenmann H (2007) Microglia: active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1387–1394. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1997
Hansen DV, Hanson JE, Sheng M (2018) Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J Cell Biol 217(2):459–472. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201709069
Harikai N, Tomogane K, Miyamoto M, Shimada K, Onodera S, Tashiro S (2003) Dynamic responses to acute heat stress between 34 degrees C and 38.5 degrees C, and characteristics of heat stress response in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 26(5):701–708. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.26.701
Hashioka S, Wu Z, Klegeris A (2020) Glia-driven neuroinflammation and systemic inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x18666201111104509
Hein AM, Stasko MR, Matousek SB, Scott-McKean JJ, Maier SF, Olschowka JA, Costa AC, O’Banion MK (2010) Sustained hippocampal IL-1beta overexpression impairs contextual and spatial memory in transgenic mice. Brain Behav Immun 24(2):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.002
Herbut P, Angrecka S, Walczak J (2018) Environmental parameters to assessing of heat stress in dairy cattle-a review. Int J Biometeorol 62(12):2089–2097. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-018-1629-9
Hofer S, Grandgirard D, Burri D, Frohlich TK, Leib SL (2011) Bacterial meningitis impairs hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70(10):890–899. https://doi.org/10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182303f31
Horton RM, Mankin JS, Lesk C, Coffel E, Raymond C (2016) A review of recent advances in research on extreme heat events. Curr Clim Change Rep 2(4):242–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-016-0042-x
Hossain ME, Matsuzaki K, Katakura M, Sugimoto N, Mamun AA, Islam R, Hashimoto M, Shido O (2017) Direct exposure to mild heat promotes proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 12(12):e0190356. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190356
Imayoshi I, Sakamoto M, Ohtsuka T, Takao K, Miyakawa T, Yamaguchi M, Mori K, Ikeda T, Itohara S, Kageyama R (2008) Roles of continuous neurogenesis in the structural and functional integrity of the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci 11(10):1153–1161. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2185
Iosif RE, Ekdahl CT, Ahlenius H, Pronk CJ, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Jacobsen SE, Lindvall O (2006) Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is a negative regulator of progenitor proliferation in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci 26(38):9703–9712. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2723-06.2006
Ju XH, Xu HJ, Yong YH, An LL, Jiao PR, Liao M (2014) Heat stress upregulation of Toll-like receptors 2/4 and acute inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) of Bama miniature pigs: an in vivo and in vitro study. Animal 8(9):1462–1468. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1751731114001268
Kehoe P, Bronzino JD (1999) Neonatal stress alters LTP in freely moving male and female adult rats. Hippocampus 9(6):651–658. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1063(1999)9:6%3c651::Aid-hipo6%3e3.0.Co;2-p
Kendler KS, Thornton LM, Gardner CO (2001) Genetic risk, number of previous depressive episodes, and stressful life events in predicting onset of major depression. Am J Psychiatry 158(4):582–586. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.158.4.582
Keohane A, Ryan S, Maloney E, Sullivan AM, Nolan YM (2010) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha impairs neuronal differentiation but not proliferation of hippocampal neural precursor cells: role of Hes1. Mol Cell Neurosci 43(1):127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2009.10.003
Khan VR, Brown IR (2002) The effect of hyperthermia on the induction of cell death in brain, testis, and thymus of the adult and developing rat. Cell Stress Chaperones 7(1):73–90. https://doi.org/10.1379/1466-1268(2002)007%3c0073:teohot%3e2.0.co;2
Kim HG, Kim TM, Park G, Lee TH, Oh MS (2013) Repeated heat exposure impairs nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 36(10):1556–1561. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b13-00268
Kisliouk T, Cramer T, Meiri N (2014) Heat stress attenuates new cell generation in the hypothalamus: a role for miR-138. Neuroscience 277:624–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.07.047
Klein B, Mrowetz H, Thalhamer J, Scheiblhofer S, Weiss R, Aigner L (2016) Allergy enhances neurogenesis and modulates microglial activation in the hippocampus. Front Cell Neurosci 10:169. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2016.00169
Koo JW, Duman RS (2008) IL-1beta is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(2):751–756. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0708092105
Koyama Y, Mukuda T, Hamasaki S, Nakane H, Kaidoh T (2018) Short-term heat exposure promotes hippocampal neurogenesis via activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in adult rats. Neuroscience 385:121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.045
Kranjac D, McLinden KA, Deodati LE, Papini MR, Chumley MJ, Boehm GW (2012) Peripheral bacterial endotoxin administration triggers both memory consolidation and reconsolidation deficits in mice. Brain Behav Immun 26(1):109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.08.005
Kuzumaki N, Ikegami D, Imai S, Narita M, Tamura R, Yajima M, Suzuki A, Miyashita K, Niikura K, Takeshima H, Ando T, Ushijima T, Suzuki T, Narita M (2010) Enhanced IL-1beta production in response to the activation of hippocampal glial cells impairs neurogenesis in aged mice. Synapse (New York, NY) 64(9):721–728. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20800
Lazarov O, Hollands C (2016) Hippocampal neurogenesis: learning to remember. Prog Neurobiol 138–140:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.12.006
Lazutkin A, Podgorny O, Enikolopov G (2019) Modes of division and differentiation of neural stem cells. Behav Brain Res 374:112118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112118
Lee W, Moon M, Kim HG, Lee TH, Oh MS (2015) Heat stress-induced memory impairment is associated with neuroinflammation in mice. J Neuroinflamm 12:102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0324-6
Leyk D, Hoitz J, Becker C, Glitz KJ, Nestler K, Piekarski C (2019) Health risks and interventions in exertional heat stress. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int 116(31–32):537–544. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2019.0537
Li L, Tan H, Gu Z, Liu Z, Geng Y, Liu Y, Tong H, Tang Y, Qiu J, Su L (2014) Heat stress induces apoptosis through a Ca(2)(+)-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 9(12):e111083. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111083
Lin H, Decuypere E, Buyse J (2006) Acute heat stress induces oxidative stress in broiler chickens. Comp Biochem Physiol A: Mol Integr Physiol 144(1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.01.032
Linnerbauer M, Wheeler MA, Quintana FJ (2020) Astrocyte crosstalk in CNS inflammation. Neuron 108(4):608–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.08.012
Liu F, Cottrell JJ, Furness JB, Rivera LR, Kelly FW, Wijesiriwardana U, Pustovit RV, Fothergill LJ, Bravo DM, Celi P, Leury BJ, Gabler NK, Dunshea FR (2016) Selenium and vitamin E together improve intestinal epithelial barrier function and alleviate oxidative stress in heat-stressed pigs. Exp Physiol 101(7):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1113/ep085746
Liu Y, Yu J, Shi YC, Zhang Y, Lin S (2019) The role of inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity-related cognitive impairment. Life Sci 233:116707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116707
McAnulty SR, McAnulty L, Pascoe DD, Gropper SS, Keith RE, Morrow JD, Gladden LB (2005) Hyperthermia increases exercise-induced oxidative stress. Int J Sports Med 26(3):188–192. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-820990
McMorris T, Swain J, Smith M, Corbett J, Delves S, Sale C, Harris RC, Potter J (2006) Heat stress, plasma concentrations of adrenaline, noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and cortisol, mood state and cognitive performance. Int J Psychophysiol 61(2):204–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2005.10.002
McPherson CA, Aoyama M, Harry GJ (2011) Interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 regulation of neural progenitor cell proliferation with hippocampal injury: differential regulatory pathways in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the adolescent and mature mouse brain. Brain Behav Immun 25(5):850–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2010.09.003
Mendes MS, Majewska AK (2021) An overview of microglia ontogeny and maturation in the homeostatic and pathological brain. Eur J Neurosci 53(11):3525–3547. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.15225
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science (new York, NY) 302(5651):1760–1765. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1088417
Moon M, Huh E, Lee W, Song EJ, Hwang DS, Lee TH, Oh MS (2017) Coptidis rhizoma prevents heat stress-induced brain damage and cognitive impairment in mice. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101057
Morris RG, Anderson E, Lynch GS, Baudry M (1986) Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature 319(6056):774–776. https://doi.org/10.1038/319774a0
Nayak D, Roth TL, McGavern DB (2014) Microglia development and function. Annu Rev Immunol 32:367–402. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120240
Pajares M, Ana IR, Manda G, Boscá L, Cuadrado A (2020) Inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071687
Parkhurst CN, Yang G, Ninan I, Savas JN, Yates JR 3rd, Lafaille JJ, Hempstead BL, Littman DR, Gan WB (2013) Microglia promote learning-dependent synapse formation through brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Cell 155(7):1596–1609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.030
Pearce SC, Mani V, Boddicker RL, Johnson JS, Weber TE, Ross JW, Rhoads RP, Baumgard LH, Gabler NK (2013) Heat stress reduces intestinal barrier integrity and favors intestinal glucose transport in growing pigs. PLoS ONE 8(8):e70215. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070215
Perry VH, Newman TA, Cunningham C (2003) The impact of systemic infection on the progression of neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(2):103–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1032
Pickering M, O’Connor JJ (2007) Pro-inflammatory cytokines and their effects in the dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:339–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6123(07)63020-9
Pucciariello C, Banti V, Perata P (2012) ROS signaling as common element in low oxygen and heat stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 59:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.02.016
Quinteiro-Filho WM, Rodrigues MV, Ribeiro A, Ferraz-de-Paula V, Pinheiro ML, Sa LR, Ferreira AJ, Palermo-Neto J (2012) Acute heat stress impairs performance parameters and induces mild intestinal enteritis in broiler chickens: role of acute hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation. J Anim Sci 90(6):1986–1994. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2011-3949
Ramon M, Diaz C, Perez-Guzman MD, Carabano MJ (2016) Effect of exposure to adverse climatic conditions on production in Manchega dairy sheep. J Dairy Sci 99(7):5764–5779. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-10909
Ratnayake U, Quinn TA, Castillo-Melendez M, Dickinson H, Walker DW (2012) Behaviour and hippocampus-specific changes in spiny mouse neonates after treatment of the mother with the viral-mimetic Poly I: C at mid-pregnancy. Brain Behav Immun 26(8):1288–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.08.011
Riazi K, Galic MA, Kentner AC, Reid AY, Sharkey KA, Pittman QJ (2015) Microglia-dependent alteration of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus during peripheral inflammation. J Neurosci 35(12):4942–4952. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4485-14.2015
Ruiz R, Roque A, Pineda E, Licona-Limon P, Jose Valdez-Alarcon J, Lajud N (2018) Early life stress accelerates age-induced effects on neurogenesis, depression, and metabolic risk. Psychoneuroendocrinology 96:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.07.012
Saxe MD, Battaglia F, Wang JW, Malleret G, David DJ, Monckton JE, Garcia AD, Sofroniew MV, Kandel ER, Santarelli L, Hen R, Drew MR (2006) Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(46):17501–17506. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607207103
Seguin JA, Brennan J, Mangano E, Hayley S (2009) Proinflammatory cytokines differentially influence adult hippocampal cell proliferation depending upon the route and chronicity of administration. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 5:5–14
Siew JJ, Chen HM, Chen HY, Chen HL, Chen CM, Soong BW, Wu YR, Chang CP, Chan YC, Lin CH, Liu FT, Chern Y (2019) Galectin-3 is required for the microglia-mediated brain inflammation in a model of Huntington’s disease. Nat Commun 10(1):3473. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11441-0
Sinha RK (2007) An approach to estimate EEG power spectrum as an index of heat stress using backpropagation artificial neural network. Med Eng Phys 29(1):120–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2006.01.011
Skibba JL, Powers RH, Stadnicka A, Cullinane DW, Almagro UA, Kalbfleisch JH (1991) Oxidative stress as a precursor to the irreversible hepatocellular injury caused by hyperthermia. Int J Hypertherm 7(5):749–761. https://doi.org/10.3109/02656739109056444
Smith MS, Upfold JB, Edwards MJ, Shiota K, Cawdell-Smith J (1992) The induction of neural tube defects by maternal hyperthermia: a comparison of the guinea-pig and human. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18(1):71–80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.1992.tb00765.x
Song Z, Cheng K, Zhang L, Wang T (2017) Dietary supplementation of enzymatically treated Artemisia annua could alleviate the intestinal inflammatory response in heat-stressed broilers. J Therm Biol 69:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtherbio.2017.07.015
Spalding KL, Bergmann O, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Huttner HB, Boström E, Westerlund I, Vial C, Buchholz BA, Possnert G, Mash DC, Druid H, Frisén J (2013) Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell 153(6):1219–1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.002
Sparkman NL, Kohman RA, Scott VJ, Boehm GW (2005) Bacterial endotoxin-induced behavioral alterations in two variations of the Morris water maze. Physiol Behav 86(1–2):244–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.07.016
Starkie RL, Hargreaves M, Rolland J, Febbraio MA (2005) Heat stress, cytokines, and the immune response to exercise. Brain Behav Immun 19(5):404–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2005.03.005
Suzuki K, Tominaga T, Ruhee RT, Ma S (2020) Characterization and modulation of systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise in relation to oxidative stress. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050401
Tan GY, Yang L, Fu YQ, Feng JH, Zhang MH (2010) Effects of different acute high ambient temperatures on function of hepatic mitochondrial respiration, antioxidative enzymes, and oxidative injury in broiler chickens. Poult Sci 89(1):115–122. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2009-00318
Vallieres L, Campbell IL, Gage FH, Sawchenko PE (2002) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in adult transgenic mice with chronic astrocytic production of interleukin-6. J Neurosci 22(2):486–492. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-02-00486.2002
Varasteh S, Braber S, Akbari P, Garssen J, Fink-Gremmels J (2015) Differences in susceptibility to heat stress along the chicken intestine and the protective effects of galacto-oligosaccharides. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0138975. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138975
Vasek MJ, Garber C, Dorsey D, Durrant DM, Bollman B, Soung A, Yu J, Perez-Torres C, Frouin A, Wilton DK, Funk K, DeMasters BK, Jiang X, Bowen JR, Mennerick S, Robinson JK, Garbow JR, Tyler KL, Suthar MS, Schmidt RE, Stevens B, Klein RS (2016) A complement-microglial axis drives synapse loss during virus-induced memory impairment. Nature 534(7608):538–543. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18283
Wang Y, Yang C, Elsheikh NAH, Li C, Yang F, Wang G, Li L (2019) HO-1 reduces heat stress-induced apoptosis in bovine granulosa cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Aging 11(15):5535–5547. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102136
White MG, Emery M, Nonner D, Barrett JN (2003) Caspase activation contributes to delayed death of heat-stressed striatal neurons. J Neurochem 87(4):958–968. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02077.x
White MG, Luca LE, Nonner D, Saleh O, Hu B, Barrett EF, Barrett JN (2007) Cellular mechanisms of neuronal damage from hyperthermia. Prog Brain Res 162:347–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6123(06)62017-7
Wolf SA, Boddeke HW, Kettenmann H (2017) Microglia in physiology and disease. Annu Rev Physiol 79:619–643. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034406
Wu MD, Hein AM, Moravan MJ, Shaftel SS, Olschowka JA, O’Banion MK (2012) Adult murine hippocampal neurogenesis is inhibited by sustained IL-1beta and not rescued by voluntary running. Brain Behav Immun 26(2):292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.09.012
Wu Y, Dissing-Olesen L, MacVicar BA, Stevens B (2015) Microglia: dynamic mediators of synapse development and plasticity. Trends Immunol 36(10):605–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2015.08.008
Xiao C, Mileva-Seitz V, Seroude L, Robertson RM (2007) Targeting HSP70 to motoneurons protects locomotor activity from hyperthermia in Drosophila. Dev Neurobiol 67(4):438–455. https://doi.org/10.1002/dneu.20344
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu K, Kokubu Y, Nishijima M, Takeda S, Ogura H, Kawabata K (2019) Effect of heat stress on blood-brain barrier integrity in iPS cell-derived microvascular endothelial cell models. PLoS ONE 14(9):e0222113. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222113
Yang YL, Lin MT (1999) Heat shock protein expression protects against cerebral ischemia and monoamine overload in rat heatstroke. Am J Physiol 276(6):H1961-1967. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1999.276.6.H1961
Yi G, Li L, Luo M, He X, Zou Z, Gu Z, Su L (2017) Heat stress induces intestinal injury through lysosome- and mitochondria-dependent pathway in vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget 8(25):40741–40755. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16580
Yun SH, Moon YS, Sohn SH, Jang IS (2012) Effects of cyclic heat stress or vitamin C supplementation during cyclic heat stress on HSP70, inflammatory cytokines, and the antioxidant defense system in Sprague Dawley rats. Exp Anim 61(5):543–553. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.61.543
Zhan Y, Paolicelli RC, Sforazzini F, Weinhard L, Bolasco G, Pagani F, Vyssotski AL, Bifone A, Gozzi A, Ragozzino D, Gross CT (2014) Deficient neuron-microglia signaling results in impaired functional brain connectivity and social behavior. Nat Neurosci 17(3):400–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3641
Zhang H, Petit GH, Gaughwin PM, Hansen C, Ranganathan S, Zuo X, Smith R, Roybon L, Brundin P, Mobley WC, Li JY (2013) NGF rescues hippocampal cholinergic neuronal markers, restores neurogenesis, and improves the spatial working memory in a mouse model of Huntington’s Disease. J Huntington’s Dis 2(1):69–82. https://doi.org/10.3233/jhd-120026
Zhang J, Malik A, Choi HB, Ko RW, Dissing-Olesen L, MacVicar BA (2014) Microglial CR3 activation triggers long-term synaptic depression in the hippocampus via NADPH oxidase. Neuron 82(1):195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.043
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Technological Innovation Guidance Project of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020QFY10-04), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFE0127000), and General Project of Basic Research of Shaanxi Province (No. 2020JM-603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. Review design: XZ and XC; writing—original draft preparation: XZ, JH, and YW; revised the figure and table: JH and YW; writing—review and editing: XZ, SZ, and XC.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Huang, J., Wu, Y. et al. Effect of Heat Stress on Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Insights into the Cellular and Molecular Basis of Neuroinflammation-Induced Deficits. Cell Mol Neurobiol 43, 1–13 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01165-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01165-5