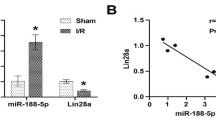Abstract
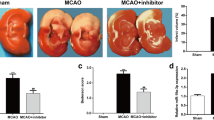
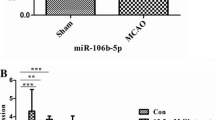
MiR-499a-5p was significantly downregulated in degenerative tissues and correlated with apoptosis. Nonetheless, the biological function of miR-499a-5p in acute ischemic stroke has been still unclear. In this study, we found that the plasma levels of miR-499a-5p were significantly downregulated in 64 ischemic stroke patients and negatively correlated with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score. Then, we constructed cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats after middle cerebral artery occlusion and subsequent reperfusion and oxygen–glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R)-treated SH-SY5Y cell model. Transfection with miR-499a-5p mimic was accomplished by intracerebroventricular injection in the in vivo I/R injury model. We further found that miR-499a-5p overexpression decreased infarct volumes and cell apoptosis in the in vivo I/R stroke model using TTC and TUNEL staining. PDCD4 was a direct target of miR-499a-5p by luciferase report assay and Western blotting. Knockdown of PDCD4 reduced the infarct damage and cortical neuron apoptosis caused by I/R injury. MiR-499a-5p exerted neuroprotective roles mainly through inhibiting PDCD4-mediated apoptosis by CCK-8 assay, LDH release assay, and flow cytometry analysis. These findings suggest that miR-499a-5p might represent a novel target that regulates brain injury by inhibiting PDCD4-mediating apoptosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data in this study are available in this published article.
Abbreviations
- I/R:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion
- OGD/R:
-
Oxygen–glucose deprivation and reoxygenation
- 3′-UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated region
- PDCD4:
-
Programmed cell death 4
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- TTC:
-
2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride
- TUNEL:
-
TdT-mediated dUTP Nick-end labeling
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- RT-qPCR:
-
Reverse transcription quantitative PCR
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5
Begum G, Yuan H, Kahle KT, Li L, Wang S, Shi Y, Shmukler BE, Yang SS, Lin SH, Alper SL, Sun D (2015) Inhibition of WNK3 kinase signaling reduces brain damage and accelerates neurological recovery after stroke. Stroke 46(7):1956–1965. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.008939
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling FN, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Gillespie C, Isasi CR, Jimenez MC, Jordan LC, Judd SE, Lackland D, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth L, Liu S, Longenecker CT, Lutsey PL, Mackey JS, Matchar DB, Matsushita K, Mussolino ME, Nasir K, O’Flaherty M, Palaniappan LP, Pandey A, Pandey DK, Reeves MJ, Ritchey MD, Rodriguez CJ, Roth GA, Rosamond WD, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Voeks JH, Willey JZ, Wilkins JT, Wu JH, Alger HM, Wong SS, Muntner P, American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee (2018) Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 137(12):e67–e492. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558
Chen H, Zhu H, Yang J, Zhu Y, Mei J, Shen H, Liang K, Zhang X (2019) Role of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4)-mediated Akt signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cell injury caused by lower-extremity ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Med Sci Monit 25:4811–4818. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.914035
Cheng Y, Liu X, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J, Zhang C (2009) MicroRNA-21 protects against the H(2)O(2)-induced injury on cardiac myocytes via its target gene PDCD4. J Mol Cell Cardiol 47(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.01.008
Chomova M, Zitnanova I (2016) Look into brain energy crisis and membrane pathophysiology in ischemia and reperfusion. Stress 19(4):341–348
Di Y, Lei Y, Yu F, Changfeng F, Song W, Xuming M (2014) MicroRNAs expression and function in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. J Mol Neurosci 53(2):242–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0293-8
Gu X, Dong M, Liu Z, Yang J, Shi Y (2020) MiR-499a-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and enhances radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells via targeting eIF4E. Onco Targets Ther 13:2913–2924. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s241631
He G, Xu W, Tong L, Li S, Su S, Tan X, Li C (2016) Gadd45b prevents autophagy and apoptosis against rat cerebral neuron oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury. Apoptosis 21(4):390–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1213-x
He S, Li Z, Yu Y, Zeng Q, Cheng Y, Ji W, Xia W, Lu S (2019) Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation, migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp Cell Res 379(2):203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.03.035
Hu Y, Deng H, Xu S, Zhang J (2015) MicroRNAs regulate mitochondrial function in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Mol Sci 16(10):24895–24917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024895
Jia Z, Lian W, Shi H, Cao C, Han S, Wang K, Li M, Zhang X (2017) Ischemic postconditioning protects against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via the HIF-1α/miR-21 axis. Sci Rep 7(1):16190. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16366-6
Liu J, Huang L, Su P, Song T, Zhang W, Fan J, Liu Y (2018a) MicroRNA-499a-5p inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting protein phosphatase 1D through protein kinase B/glycogen synthase kinase 3β signaling. Oncol Lett 15(4):4113–4120. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7814
Liu Y, Eaton ED, Wills TE, McCann SK, Antonic A, Howells DW (2018b) Human ischaemic cascade studies using SH-SY5Y cells: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Stroke Res 9(6):564–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-018-0620-4
Liu K, Ma L, Zhou F, Yang Y, Hu HB, Wang L, Zhong L (2019) Identification of microRNAs related to myocardial ischemic reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol 234(7):11380–11390. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27795
Lopez-Neblina F, Toledo AH, Toledo-Pereyra LH (2005) Molecular biology of apoptosis in ischemia and reperfusion. J Invest Surg 18(6):335–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941930500328862
Luengo-Fernandez R, Gray AM, Bull L, Welch S, Cuthbertson F, Rothwell PM, Oxford Vascular S (2013) Quality of life after TIA and stroke: ten-year results of the Oxford Vascular Study. Neurology 81(18):1588–1595. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182a9f45f
Machado NG, Alves MG, Carvalho RA, Oliveira PJ (2009) Mitochondrial involvement in cardiac apoptosis during ischemia and reperfusion: can we close the box? Cardiovasc Toxicol 9(4):211–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-009-9055-1
Matsuhashi S, Manirujjaman M, Hamajima H, Ozaki I (2019) Control mechanisms of the tumor suppressor PDCD4: expression and functions. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092304
Neshati V, Mollazadeh S, Fazly Bazzaz BS, de Vries AAF, Mojarrad M, Naderi-Meshkin H, Neshati Z, Mirahmadi M, Kerachian MA (2018) MicroRNA-499a-5p promotes differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to cardiomyocytes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186(1):245–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2734-2
Rao G, Zhang W, Song S (2019) MicroRNA-217 inhibition relieves cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting SIRT1. Mol Med Rep 20(2):1221–1229
Soejima H, Miyoshi O, Yoshinaga H, Masaki Z, Ozaki I, Kajiwara S, Niikawa N, Matsuhashi S, Mukai T (1999) Assignment of the programmed cell death 4 gene (PDCD4) to human chromosome band 10q24 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 87(1–2):113–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000015408
Special report from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Classification of cerebrovascular diseases III (1990). Stroke 21(4):637–676. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.21.4.637
Sun JC, Zheng B, Sun RX, Meng YK, Wang SM, Yang HS, Chen Y, Shi JG, Guo YF (2019) MiR-499a-5p suppresses apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells and degradation of their extracellular matrix by targeting SOX4. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108652
Tobin MK, Bonds JA, Minshall RD, Pelligrino DA, Testai FD, Lazarov O (2014) Neurogenesis and inflammation after ischemic stroke: what is known and where we go from here. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 34(10):1573–1584. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.130
Yang G, Liu Z, Wang L, Chen X, Wang X, Dong Q, Zhang D, Yang Z, Zhou Q, Sun J, Xue L, Wang X, Gao M, Li L, Yi R, Ilgiz G, Ai J, Zhao S (2018) MicroRNA-195 protection against focal cerebral ischemia by targeting CX3CR1. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.5.JNS173061
Yang Z, Li C, Fan XY, Liu LJ (2020) Circular RNA circ_0079593 promotes glioma development through regulating KPNA2 expression by sponging miR-499a-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(3):1288–1301. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202001_20186
Yin KJ, Deng Z, Huang H, Hamblin M, Xie C, Zhang J, Chen YE (2010) miR-497 regulates neuronal death in mouse brain after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 38(1):17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.12.021
Zhang Q, Zhang K, Zhang C, Ge H, Yin Y, Feng H, Hu R (2017) MicroRNAs as big regulators of neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation, differentiation and migration: a potential treatment for stroke. Curr Pharm Des 23(15):2252–2257
Zhao L, Wang B, Zhang W, Sun L (2020) Effect of miR-499a-5p on damage of cardiomyocyte induced by hypoxia-reoxygenation via downregulating CD38 protein. J Cell Biochem 121(2):996–1004. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29334
Zheng Y, Zhao P, Lian Y, Li S, Chen Y, Li L (2020) MiR-340-5p alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury via PI3K/Akt activation by targeting PDCD4. Neurochem Int 134:104650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104650
Zhong G, Long H, Ma S, Shunhan Y, Li J, Yao J (2019) miRNA-335-5p relieves chondrocyte inflammation by activating autophagy in osteoarthritis. Life Sci 226:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.071
Zong Z, Song Y, Xue Y, Ruan X, Liu X, Yang C, Zheng J, Cao S, Li Z, Liu Y (2019) Knockdown of LncRNA SCAMP1 suppressed malignant biological behaviours of glioma cells via modulating miR-499a-5p/LMX1A/NLRC5 pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23(8):5048–5062. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14362
Zuo X, Lu J, Manaenko A, Qi X, Tang J, Mei Q, Xia Y, Hu Q (2019) MicroRNA-132 attenuates cerebral injury by protecting blood–brain–barrier in MCAO mice. Exp Neurol 316:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.03.017
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
The use of the human blood samples for research purposes was approved by the Ethics Committee of the 1st Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University (Approval number: ZU349-2; 2017.8.16).
Consent to Participate
All participants signed the written informed consent, which is in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10571_2021_1085_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure 1S Selected four top targets of miR-499a-5p. (A) The potential interaction between miR-499a-5p and putative binding sites in the 3′UTR of four top targets (MRPS35, ARGLU1, PFN2, and HNRNPC). (B) Western blot analysis was used to determine the protein levels of four top targets (MRPS35, ARGLU1, PFN2, and HNRNPC) in SH-SY5Y cells transfected with miR-499a-5p mimic or miR-NC, and then was exposed (TIF 10201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, W., Ge, H., Chen, B. et al. Upregulation of miR-499a-5p Decreases Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Targeting PDCD4. Cell Mol Neurobiol 42, 2157–2170 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01085-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-021-01085-4