Abstract
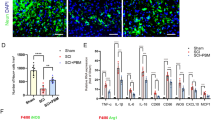
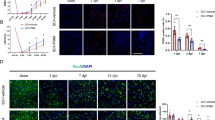
Spinal cord injury (SCI) stimulates reactive astrogliosis and the infiltration of macrophages, which interact with each other at the injured area. We previously found Photobiomodulation (PBM) significantly decreases the number of M1 macrophages at the injured area of SCI. But the exact nature of the astrocyte response following PBM and relationship with the macrophage have not been explored in detail. In this study, a BALB/c mice model with standardized bilateral spinal cord compression and a macrophage-astrocyte co-culture model were applied to study effects of PBM on astrocytes. Results showed that PBM inhibit the expression of the astrocyte markers glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and the secretion of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG) in the para-epicenter area, decrease the number of M1 macrophage in vivo. The in vitro experiments indicated M1 macrophages promote the cell viability of astrocytes and the expression of CSPG. However, PBM significantly inhibited the expression of GFAP, decreased activation of astrocyte, and downregulated the expression of CSPG by regulating M1 macrophages. These results demonstrate that PBM may regulate the interaction between macrophages and astrocytes after spinal cord injury, which inhibited the formation of glial scar.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartus K, James ND, Didangelos A, Bosch KD, Verhaagen J, Yanez-Munoz RJ, Rogers JH, Schneider BL, Muir EM, Bradbury EJ (2014) Large-scale chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan digestion with chondroitinase gene therapy leads to reduced pathology and modulates macrophage phenotype following spinal cord contusion injury. J Neurosci 34(14):4822–4836. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4369-13.2014
Basso DM, Fisher LC, Anderson AJ, Jakeman LB, McTigue DM, Popovich PG (2006) Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J Neurotrauma 23(5):635–659. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.23.635
Begum R, Powner MB, Hudson N, Hogg C, Jeffery G (2013) Treatment with 670 nm light up regulates cytochrome C oxidase expression and reduces inflammation in an age-related macular degeneration model. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57828. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057828
Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB (2002) Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 416(6881):636–640. https://doi.org/10.1038/416636a
Bungart BL, Dong L, Sobek D, Sun GY, Yao G, Lee JC (2014) Nanoparticle-emitted light attenuates amyloid-beta-induced superoxide and inflammation in astrocytes. Nanomedicine 10(1):15–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.10.007
Burda JE, Sofroniew MV (2014) Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron 81(2):229–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.034
Byrnes KR, Waynant RW, Ilev IK, Wu X, Barna L, Smith K, Heckert R, Gerst H, Anders JJ (2005) Light promotes regeneration and functional recovery and alters the immune response after spinal cord injury. Lasers Surg Med 36(3):171–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.20143
Carulli D, Laabs T, Geller HM, Fawcett JW (2005) Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans in neural development and regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15(1):116–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2005.01.014
David S, Kroner A (2011) Repertoire of microglial and macrophage responses after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(7):388–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3053
de Freitas LF, Hamblin MR (2016) Proposed mechanisms of photobiomodulation or low-level light therapy. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 22(3):348–364. https://doi.org/10.1109/jstqe.2016.2561201
Duarte KCN, Soares TT, Magri AMP, Garcia LA, Le Sueur-Maluf L, Renno ACM, Monteiro de Castro G (2018) Low-level laser therapy modulates demyelination in mice. J Photochem Photobiol, B 189:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.09.024
El Massri N, Weinrich TW, Kam JH, Jeffery G, Mitrofanis J (2018) Photobiomodulation reduces gliosis in the basal ganglia of aged mice. Neurobiol Aging 66:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.02.019
Falnikar A, Li K, Lepore AC (2015) Therapeutically targeting astrocytes with stem and progenitor cell transplantation following traumatic spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1619:91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.037
Fitch MT, Silver J (2008) CNS injury, glial scars, and inflammation: inhibitory extracellular matrices and regeneration failure. Exp Neurol 209(2):294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.05.014
Gensel JC, Zhang B (2015) Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1619:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.045
Gigo-Benato D, Geuna S, Rochkind S (2005) Phototherapy for enhancing peripheral nerve repair: a review of the literature. Muscle Nerve 31(6):694–701. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20305
Gu Y, Cheng X, Huang X, Yuan Y, Qin S, Tan Z, Wang D, Hu X, He C, Su Z (2019) Conditional ablation of reactive astrocytes to dissect their roles in spinal cord injury and repair. Brain Behav Immun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.04.016
Haan N, Zhu B, Wang J, Wei X, Song B (2015) Crosstalk between macrophages and astrocytes affects proliferation, reactive phenotype and inflammatory response, suggesting a role during reactive gliosis following spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflamm 12:109. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0327-3
Hara M, Kobayakawa K, Ohkawa Y, Kumamaru H, Yokota K, Saito T, Kijima K, Yoshizaki S, Harimaya K, Nakashima Y, Okada S (2017) Interaction of reactive astrocytes with type I collagen induces astrocytic scar formation through the integrin-N-cadherin pathway after spinal cord injury. Nat Med 23(7):818–828. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4354
Herrmann JE, Imura T, Song B, Qi J, Ao Y, Nguyen TK, Korsak RA, Takeda K, Akira S, Sofroniew MV (2008) STAT3 is a critical regulator of astrogliosis and scar formation after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 28(28):7231–7243. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1709-08.2008
Hu D, Zhu S, Potas JR (2016) Red LED photobiomodulation reduces pain hypersensitivity and improves sensorimotor function following mild T10 hemicontusion spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflamm 13(1):200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0679-3
Jain NB, Ayers GD, Peterson EN, Harris MB, Morse L, O’Connor KC, Garshick E (2015) Traumatic spinal cord injury in the United States, 1993–2012. JAMA 313(22):2236–2243. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.6250
Karimi-Abdolrezaee S, Billakanti R (2012) Reactive astrogliosis after spinal cord injury-beneficial and detrimental effects. Mol Neurobiol 46(2):251–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8287-4
LeComte MD, Shimada IS, Sherwin C, Spees JL (2015) Notch1-STAT3-ETBR signaling axis controls reactive astrocyte proliferation after brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(28):8726–8731. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1501029112
Lee HI, Lee SW, Kim NG, Park KJ, Choi BT, Shin YI, Shin HK (2017) Low-level light emitting diode therapy promotes long-term functional recovery after experimental stroke in mice. J Biophotonics 10(12):1761–1771. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201700038
Mayo L, Trauger SA, Blain M, Nadeau M, Patel B, Alvarez JI, Mascanfroni ID, Yeste A, Kivisakk P, Kallas K, Ellezam B, Bakshi R, Prat A, Antel JP, Weiner HL, Quintana FJ (2014) Regulation of astrocyte activation by glycolipids drives chronic CNS inflammation. Nat Med 20(10):1147–1156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3681
McKillop WM, Dragan M, Schedl A, Brown A (2013) Conditional Sox9 ablation reduces chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan levels and improves motor function following spinal cord injury. Glia 61(2):164–177. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22424
Nguyen DH, Cho N, Satkunendrarajah K, Austin JW, Wang J, Fehlings MG (2012) Immunoglobulin G (IgG) attenuates neuroinflammation and improves neurobehavioral recovery after cervical spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflamm 9:224. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-224
Novak ML, Koh TJ (2013) Macrophage phenotypes during tissue repair. J Leukoc Biol 93(6):875–881. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1012512
Okada S, Hara M, Kobayakawa K, Matsumoto Y, Nakashima Y (2018) Astrocyte reactivity and astrogliosis after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Res 126:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.10.004
Orr MB, Gensel JC (2018) Spinal cord injury scarring and inflammation: therapies targeting glial and inflammatory responses. Neurotherapeutics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-018-0631-6
Oudega M (2013) Inflammatory response after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 250:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.09.013
Renault-Mihara F, Mukaino M, Shinozaki M, Kumamaru H, Kawase S, Baudoux M, Ishibashi T, Kawabata S, Nishiyama Y, Sugai K, Yasutake K, Okada S, Nakamura M, Okano H (2017) Regulation of RhoA by STAT3 coordinates glial scar formation. J Cell Biol 216(8):2533–2550. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201610102
Silver J, Miller JH (2004) Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(2):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1326
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV (2010) Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):7–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0619-8
Song JW, Li K, Liang ZW, Dai C, Shen XF, Gong YZ, Wang S, Hu XY, Wang Z (2017) Low-level laser facilitates alternatively activated macrophage/microglia polarization and promotes functional recovery after crush spinal cord injury in rats. Sci Rep 7(1):620. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00553-6
Tang X, Davies JE, Davies SJ (2003) Changes in distribution, cell associations, and protein expression levels of NG2, neurocan, phosphacan, brevican, versican V2, and tenascin-C during acute to chronic maturation of spinal cord scar tissue. J Neurosci Res 71(3):427–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10523
Yang X, Askarova S, Sheng W, Chen JK, Sun AY, Sun GY, Yao G, Lee JC (2010) Low energy laser light (632.8 nm) suppresses amyloid-beta peptide-induced oxidative and inflammatory responses in astrocytes. Neuroscience 171(3):859–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.025
Yuan J, Liu W, Zhu H, Chen Y, Zhang X, Li L, Chu W, Wen Z, Feng H, Lin J (2017) Curcumin inhibits glial scar formation by suppressing astrocyte-induced inflammation and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res 1655:90–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.11.002
Authors Contributions
ZW and XYH designed and supervised experiments; JKS, JWZ, KL,TD, XYH and ZW wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data; JKS, JWZ, KL, QZ, ZWL and LQ developed the PBM-Macrophage irradiation model and performed the molecular biology experiment; JKS, JWZ, KL, QZ, JWS, JXZ performed the immunofluorescence staining.
Funding
This study was funded by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81572151, 81070996, 81101352) and Science and Technology Department of Shaanxi Province (Grant Nos. 2016SF-143, 2017SF-021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jiakai Sun, Jiawei Zhang, Kun Li, Qiao Zheng, Jiwei Song, Zhuowen Liang, Tan Ding, Lin Qiao, Jianxin Zhang, Xueyu Hu, Zhe Wang declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Ethical Approval
All animal care and experimental programs were conducted according to standard All applicable international and national ethical guidelines (National Institutes of Health Guide to the use of Laboratory Animals) and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Fourth Military Medical University. All efforts were made to minimize the number of mice used and their suffering.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Zhang, J., Li, K. et al. Photobiomodulation Therapy Inhibit the Activation and Secretory of Astrocytes by Altering Macrophage Polarization. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40, 141–152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00728-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00728-x