Abstract
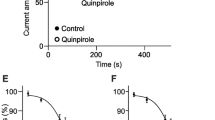
The expression of H1 receptor has been reported in amacrine cells of mouse and rat retinae. However, we assumed that other types of histamine receptors also function in amacrine cells. In order to confirm that histamine modulates the membrane potential in mouse amacrine cells, we measured voltage-gated currents using whole-cell configuration. Under voltage-clamp conditions, the amplitude of voltage-gated outward currents was enhanced by the application of 100 µM histamine in 65% of amacrine cells. Histamine also increased the amplitudes of voltage-gated inward currents in 72% of amacrine cells. When antagonists of the histamine H1, H2, or H3 receptors were applied to histamine-sensitive amacrine cells, all three types of these inhibitors reduced the effect of histamine. Moreover, we classified recorded cells into seven types based on their morphological characteristics. Two of the seven types, diffuse multistratified cells and AII amacrine cells, responded significantly to histamine. These results indicate that histamine affected the membrane potential via three types of histamine receptors. Furthermore, there were differences in the responses to histamine among types of amacrine cells. Histamine may be one of the important neurotransmitters and/or neuromodulators in the visual processing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown RE, Stevens DR, Haas HL (2001) The physiology of brain histamine. Prog Neurobiol 63(6):637–672
Clapham DE, Neer EJ (1993) New roles for G-protein beta gamma-dimers in transmembrane signalling. Nature 365(6445):403–406. doi:10.1038/365403a0
Dolphin AC (1998) Mechanisms of modulation of voltage-dependent calcium channels by G proteins. J Physiol 506(Pt 1):3–11
Eriksson KS, Peitsaro N, Karlstedt K, Kaslin J, Panula P (1998) Development of the histaminergic neurons and expression of histidine decarboxylase mRNA in the zebrafish brain in the absence of all peripheral histaminergic systems. Eur J Neurosci 10(12):3799–3812
Feigenspan A, Bormann J (1994) Facilitation of GABAergic signaling in the retina by receptors stimulating adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(23):10893–10897
Fioretti B, Catacuzzeno L, Tata AM, Franciolini F (2004) Histamine activates a background, arachidonic acid-sensitive K channel in embryonic chick dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 125(1):119–127. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.01.028
Frazao R, McMahon DG, Schunack W, Datta P, Heidelberger R, Marshak DW (2011) Histamine elevates free intracellular calcium in mouse retinal dopaminergic cells via H1-receptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(6):3083–3088. doi:10.1167/iovs.10-6160
Gastinger MJ, O’Brien JJ, Larsen NB, Marshak DW (1999) Histamine immunoreactive axons in the macaque retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40(2):487–495
Gastinger MJ, Yusupov RG, Glickman RD, Marshak DW (2004) The effects of histamine on rat and monkey retinal ganglion cells. Vis Neurosci 21(6):935–943. doi:10.1017/s0952523804216133
Gastinger MJ, Barber AJ, Vardi N, Marshak DW (2006a) Histamine receptors in mammalian retinas. J Comp Neurol 495(6):658–667. doi:10.1002/cne.20902
Gastinger MJ, Tian N, Horvath T, Marshak DW (2006b) Retinopetal axons in mammals: emphasis on histamine and serotonin. Curr Eye Res 31(7–8):655–667. doi:10.1080/02713680600776119
Greferath U, Kambourakis M, Barth C, Fletcher EL, Murphy M (2009) Characterization of histamine projections and their potential cellular targets in the mouse retina. Neuroscience 158(2):932–944. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.10.034
Haas H, Panula P (2003) The role of histamine and the tuberomammillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(2):121–130. doi:10.1038/nrn1034
Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O (2008) Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev 88(3):1183–1241. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2007
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 391(2):85–100
Imada H, Kokubo M, Ohkuma M, Kato T, Miyachi E (2010) Histamine and histamine receptor of ganglion cells in the gerbil retina. J Physiol Sci 60(S1):S136
Imada H, Sakai K, Ohkuma M, Miyachi E (2011) Histaminergic ganglion cells in the developing gerbil retina. J Physiol Sci 61(S1):S229
Kawai F, Kurahashi T, Kaneko A (1996) T-type Ca2+ channel lowers the threshold of spike generation in the newt olfactory receptor cell. J Gen Physiol 108(6):525–535
Kawai F, Kurahashi T, Kaneko A (1999) Adrenaline enhances odorant contrast by modulating signal encoding in olfactory receptor cells. Nat Neurosci 2(2):133–138. doi:10.1038/5686
Kawai F, Horiguchi M, Suzuki H, Miyachi E (2001) Na(+) action potentials in human photoreceptors. Neuron 30(2):451–458
Kolb H, Nelson R, Mariani A (1981) Amacrine cells, bipolar cells and ganglion cells of the cat retina: a Golgi study. Vision Res 21(7):1081–1114
Lin B, Masland RH (2006) Populations of wide-field amacrine cells in the mouse retina. J Comp Neurol 499(5):797–809. doi:10.1002/cne.21126
Luscher C, Slesinger PA (2010) Emerging roles for G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels in health and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(5):301–315. doi:10.1038/nrn2834
MacNeil MA, Masland RH (1998) Extreme diversity among amacrine cells: implications for function. Neuron 20(5):971–982
MacNeil MA, Heussy JK, Dacheux RF, Raviola E, Masland RH (1999) The shapes and numbers of amacrine cells: matching of photofilled with Golgi-stained cells in the rabbit retina and comparison with other mammalian species. J Comp Neurol 413(2):305–326
Maintz L, Novak N (2007) Histamine and histamine intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr 85(5):1185–1196
Masland RH (1988) Amacrine cells. Trends Neurosci 11(9):405–410
Matsumoto Y, Ogura T, Uemura H, Saito T, Masuda Y, Nakaya H (1999) Histamine H1-receptor-mediated modulation of the delayed rectifier K+ current in guinea-pig atrial cells: opposite effects on IKs and IKr. Br J Pharmacol 128(7):1545–1553. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702918
Ohkuma M, Kawai F, Horiguchi M, Miyachi E (2007) Patch-clamp recording of human retinal photoreceptors and bipolar cells. Photochem Photobiol 83(2):317–322. doi:10.1562/2006-06-15-ra-923
Reuveny E, Slesinger PA, Inglese J, Morales JM, Iniguez-Lluhi JA, Lefkowitz RJ, Bourne HR, Jan YN, Jan LY (1994) Activation of the cloned muscarinic potassium channel by G protein beta gamma subunits. Nature 370(6485):143–146. doi:10.1038/370143a0
Vila A, Satoh H, Rangel C, Mills SL, Hoshi H, O’Brien J, Marshak DR, Macleish PR, Marshak DW (2012) Histamine receptors of cones and horizontal cells in Old World monkey retinas. J Comp Neurol 520(3):528–543. doi:10.1002/cne.22731
Wässle H, Boycott BB (1991) Functional architecture of the mammalian retina. Physiol Rev 71(2):447–480
Wickman KD, Iniguez-Lluhl JA, Davenport PA, Taussig R, Krapivinsky GB, Linder ME, Gilman AG, Clapham DE (1994) Recombinant G-protein beta gamma-subunits activate the muscarinic-gated atrial potassium channel. Nature 368(6468):255–257. doi:10.1038/368255a0
Yu YC, Satoh H, Wu SM, Marshak DW (2009) Histamine enhances voltage-gated potassium currents of ON bipolar cells in macaque retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(2):959–965. doi:10.1167/iovs.08-2746
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan (SENRYAKU 1001034). We thank Dr. Fusao Kawai for advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KH, MO, and EM designed the study; KH performed experiments; KH and MO analyzed data; KH, MO, and EM interpreted results of experiments; KH prepared figures; KH and MO wrote the initial draft of the manuscript; KH, MO, and EM approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution. The article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horio, K., Ohkuma, M. & Miyachi, Ei. The Effect of Histamine on Inward and Outward Currents in Mouse Retinal Amacrine Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38, 757–767 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0542-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0542-9