Abstract
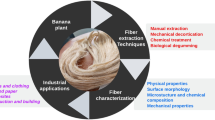
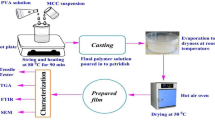
Cow dung possesses potential agricultural and energy value but is often regarded as waste and underutilized in most cases. This wastage of resources not only poses a challenge to agricultural sustainability but also limits economic development in rural areas. Cow dung contains natural cellulose components like cellulose and lignin that are derived and used to prepare fiber materials. This paper explores a potential value-added application of agricultural waste, i.e., cow dung fibers to reinforce the alkali-activated slag composites (AASC), which are fabricated based on an industrial by-product slag. The raw and alkali treated cow dung fibers were characterized using scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM–EDS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermo-gravimetric analysis (TGA) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The porosity, density, water absorption, strength and drying shrinkage of AASC were tested and used to evaluate the effect of alkali treated fibers on the properties of AASC. The results showed that subjecting cow dung fibers to alkali treatment improved their surface roughness and thermal stability. The addition of cow dung fibers led to an augmentation in the splitting tensile strength of AASC, primarily due to the bridging action of these fibers. In particular, the 28-day splitting tensile strength of AASC containing 1 wt% of untreated cow dung fibers increased by 17.1% over the reference sample, and this increase was more pronounced in the alkali treated fiber sample. Moreover, the alkali treatment effectively reduced the effects of loss of compressive strength and increased drying shrinkage caused by fiber incorporation. The findings of this paper are helpful to solve the management problems of cow dung waste, reduce the environmental burden and realize the value utilization of resources.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alomayri T, Shaikh FUA, Low IM (2013) Characterisation of cotton fibre-reinforced geopolymer composites. Compos Part B Eng 50:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.01.013
Andiç-Çakir Ö, Sarikanat M, Tüfekçi HB, Demirci C, Erdoğan ÜH (2014) Physical and mechanical properties of randomly oriented coir fiber-cementitious composites. Compos Part B Eng 61:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.01.029
Bahja B, Elouafi A, Tizliouine A, Omari LH (2021) Morphological and structural analysis of treated sisal fibers and their im-pact on mechanical properties in cementitious composites. J Build Eng 34:102025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.102025
Boopathi L, Sampath PS, Mylsamy K (2012) Investigation of physical, chemical and mechanical properties of raw and alkali treated Borassus fruit fiber. Compos Part B Eng 43:3044–3052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.05.002
Borchani KE, Carrot C, Jaziri M (2015) Untreated and alkali treated fibers from Alfa stem: effect of alkali treatment on structural, morphological and thermal features. Cellul 22(3):1577–1589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0583-5
do Amaral LM, de Souza Rodrigues C, Poggiali FSJ (2022) Hornification on vegetable fibers to improve fiber-cement composites: A critical review. J Build Eng 48:103947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103947
Elzeadani M, Bompa DV, Elghazouli AY (2022) One part alkali activated materials: a state-of-the-art review. J Build Eng 57:104871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104871
Guo B, Nakama S, Tian Q, Pahlevi ND, Hu Z, Sasaki K (2019) Suppression processes of anionic pollutants released from fly ash by various Ca additives. J Hazard Mater 371:474–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.036
Huang Y, Tan J, Xuan X, Liu L, Xie M, Liu H, Zheng G (2021) Study on untreated and alkali treated rice straw reinforced geopolymer composites. Mater Chem Phys 262:124304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.124304
Huang Y, Tan J, Xuan X, Wei S, Liu L, Yu S, Zheng G (2022) Durability of plant fiber reinforced alkali activated composites. Constr Build Mater 314:125501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125501
Jiang D, An P, Cui S, Sun S, Zhang J, Tuo T (2020) Effect of modification methods of wheat straw fibers on water absorbency and mechanical properties of wheat straw fiber cement-based composites. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5031025
Jiang D, Shi C, Zhang Z (2022) Recent progress in understanding setting and hardening of alkali-activated slag (AAS) materials. Cem Concr Compos 134:104795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2022.104795
Le Troëdec M, Sedan D, Peyratout C, Bonnet JP, Smith A, Guinebretiere R, Krausz P (2008) Influence of various chemical treatments on the composition and structure of hemp fibres. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 39(3):514–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2007.12.001
Li K, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Li Y, Lu L, Niu D (2022) Effect of pretreated cow dung fiber on mechanical and shrinkage properties of cementitious composites. J Clean Prod 348:131374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131374
Li Q, Ibrahim L, Zhou W, Zhang M, Yuan Z (2021) Treatment methods for plant fibers for use as reinforcement in cement-based materials. Cellul 28:5257–5268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03903-w
Joffre T, Segerholm K, Persson C, Bardage SL, Hendriks CLL, Isaksson P (2017) Characterization of interfacial stress transfer ability in acetylation-treated wood fibre composites using X-ray microtomography. Ind Crops Prod 95:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.10.009
Juenger MCG, Winnefeld F, Provis JL, Ideker JH (2011) Advances in alternative cementitious binders. Cem Concr Res 41:1232–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.11.012
Ma Y, Wu S, Zhuang J, Tong J, Qi H (2019) Tribological and physio-mechanical characterization of cow dung fibers reinforced friction composites: an effective utilization of cow dung waste. Tribol Int 131:200–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.10.026
Mendes BC, Pedroti LG, Vieira CMF, Marvila M, Azevedo AR, de Carvalho JMF, Ribeiro JCL (2021) Application of eco-friendly alternative activators in alkali-activated materials: a review. J Build Eng 35:102010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.102010
Poletanovic B, Dragas J, Ignjatovic I, Komljenovic M, Merta I (2020) Physical and mechanical properties of hemp fibre reinforced alkali-activated fly ash and fly ash/slag mortars. Constr Build Mater 259:119677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119677
Reddy TRK, Rao TS, Suvarna RP (2013) Studies on thermal characteristics of cow dung powder filled glass-polyester hybrid composites. Compos Part B Eng 56:670–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.059
Santana HA, Júnior NSA, Ribeiro DV, Cilla MS, Dias CM (2021) Vegetable fibers behavior in geopolymers and alka-li-activated cement based matrices: A review. J Build Eng 44:103291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103291
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Sepe R, Bollino F, Boccarusso L, Caputo F (2018) Influence of chemical treatments on mechanical properties of hemp fiber reinforced composites. Compos Part B Eng 133:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.09.030
Sfez S, De Meester S, Dewulf J (2017) Co-digestion of rice straw and cow dung to supply cooking fuel and fertilizers in rural India: Impact on human health, resource flows and climate change. Sci Total Environ 609:1600–1615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.150
Shang X, Yang J, Song Q, Wang L (2020) Efficacy of modified rice straw fibre on properties of cementitious composites. J Clean Prod 276:124184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124184
Si R, Zhan Y, Zang Y, Sun Y, Huang Y (2023) Effect of basalt fiber on fracture properties and drying shrinkage of alkali-activated slag with different silicate modulus. J Mater Res Technol 25:552–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.05.211
Sun Y, de Lima LM, Rossi L, Jiao D, Li Z, Ye G, De Schutter G (2023) Interpretation of the early stiffening process in alkali-activated slag pastes. Cem Concr Res 167:107118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2023.107118
Suwan T, Maichin P, Fan M, Jitsangiam P, Tangchirapat W, Chindaprasirt P (2022) Influence of alkalinity on self-treatment process of natural fiber and properties of its geopolymeric composites. Constr Build Mater 316:125817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125817
Tang Z, Yang X, Jiang H, Cong X, Tian W, Lu S (2023) Biomodification of bond performance of coconut fiber in cement mortar to enhance damping behavior. J Mater Civil Eng 35:04023351. https://doi.org/10.1061/jmcee7.mteng-15933
Toledo Filho RD, Ghavami K, Sanjuán MA, England GL (2005) Free, restrained and drying shrinkage of cement mortar composites reinforced with vegetable fibres. Cem Concr Compos 27:537–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2004.09.005
Tong Y, Zhao S, Ma J, Wang L, Zhang Y, Gao Y, Xie Y (2014) Improving cracking and drying shrinkage properties of cement mortar by adding chemically treated luffa fibres. Constr Build Mater 71:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.08.077
Van Nguyen C, Mangat PS (2020) Properties of rice straw reinforced alkali activated cementitious composites. Constr Build Mater 261:120536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120536
Vinod A, Gowda TGY, Vijay R, Sanjay MR, Gupta MK, Jamil M, Siengchin S (2021) Novel Muntingia Calabura bark fiber reinforced green-epoxy composite: a sustainable and green material for cleaner production. J Clean Prod 294:126337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126337
Wei J, Meyer C (2015) Degradation mechanisms of natural fiber in the matrix of cement composites. Cem Concr Res 73:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2015.02.019
Wongsa A, Kunthawatwong R, Naenudon S, Sata V, Chindaprasirt P (2020) Natural fiber reinforced high calcium fly ash geopolymer mortar. Constr Build Mater 241:118143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118143
Yang X, Li L, Zhao W, Tian Y, Zheng R, Deng S, Mu Y (2023) The influence of potassium hydroxide concentration and temperature on pulp characteristics and cow dung-based paper performance. J Nat Fibers 20:2164546. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2022.2164546
Yurt Ü (2020) An experimental study on fracture energy of alkali activated slag composites incorporated different fibers. J Build Eng 32:101519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101519
Yusefi M, Khalid M, Yasin FM, Abdullah LC, Ketabchi MR, Walvekar R (2018) Performance of cow dung reinforced bio-degradable poly (Lactic Acid) biocomposites for structural applications. J Polym Environ 26:474–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-0963-z
Zhang B, Zhu H, Cheng Y, Huseien GF, Shah KW (2022) Shrinkage mechanisms and shrinkage-mitigating strategies of alkali-activated slag composites: a critical review. Constr Build Mater 318:125993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125993
Zhang J, Shi C, Zhang Z, Ou Z (2017) Durability of alkali-activated materials in aggressive environments: a review on recent studies. Constr Build Mater 152:598–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.07.027
Zhou B, Wang L, Ma G, Zhao X, Zhao X (2020) Preparation and properties of bio-geopolymer composites with waste cotton stalk materials. J Clean Prod 245:118842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118842
Zhou X, Zeng Y, Chen P, Jiao Z, Zheng W (2021) Mechanical properties of basalt and polypropylene fibre-reinforced alkali-activated slag concrete. Const Build Mater 269:121284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121284
Zhang L, Sun X (2017) Using cow dung and spent coffee grounds to enhance the two-stage co-composting of green waste. Bioresour Technol 245:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.147
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Fujian Ocean and Fishery Bureau (FJHJF-L-2022-19), Fuzhou Science and Technology Bureau (2021-P-031), Natural Science Foundation of China (51978171) and Minjiang Scholar program of Fujian province, China (GXRC-19045).
Funding
This work was financially supported by Fujian Ocean and Fishery Bureau (FJHJF-L-2022–19), Fuzhou Science and Technology Bureau (2021-P-031), Natural Science Foundation of China (51978171) and Minjiang Scholar program of Fujian province, China (GXRC-19045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing- review & editing, Funding acquisition, Z.Y.; Investigation, Testing, Data analysis, Writing-original draft, K.Li.; and X.Yan., Investigation, Validation, Supervision, W.Wu.; Validation, Supervision, B.B.; and G.C.M. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The authors confirm that there were no ethical issues in preparing this manuscript.
Consent for publication
All the authors listed have approved the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Li, K., Yan, X. et al. Characterization and value-added applications of natural cellulose fibers derived from cow dung in cementitious composites. Cellulose (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05942-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05942-5